======关注点一点,友谊深一点=====
🌲 静态资源访问
在我们开发web应用的时候,需要引入大量的js、css、图片等静态资源。
默认配置
SpringBoot 默认提供的静态资源目录位置需要置于classpath下,目录名需要符合如下规则:
- /static
- /public
- /resources
- /META-INF/resources
举例:我们可以在 src/main/resources/ ⽬录下创建 static ,在该位置放置⼀个图⽚⽂件。启动
程序后,尝试访问 http://localhost:8080/D.jpg 。如能显示图⽚,配置成功。
提示:有的时候复制图片到idea之后,无法更新图片到项目中,这个时候访问不到图片,此时可以rebuild project 重构一下项目,再启动服务即可看到图片。
渲染Web⻚⾯
在之前的示例中,我们都是通过@RestController来处理请求,所以返回的内容为json对象。那么如果需要渲染html⻚⾯的时候,要如何实现呢?
🌲 模板引擎
SpringBoot实际上不推荐使用JSP,而使用HTML去实现动态页面。在动态HTML实现上Spring Boot依然可以完美胜任,并且提供了多种模板引擎的默认配置⽀持,所以在推荐的模板引擎下,我们可以很快的上⼿开发动态⽹站。
SpringBoot提供了默认配置的模板引擎主要有以下⼏种:
- Thymeleaf
- FreeMarker
- Velocity
- Groovy
- Mustache
SpringBoot建议使⽤这些模板引擎,避免使⽤JSP,若⼀定要使⽤JSP将⽆法实现SpringBoot的多 种特性,
当你使⽤上述模板引擎中的任何⼀个,它们默认的模板配置路径为:src/main/resources/templates 。当然也可以修改这个路径,具体如何修改,可在后续各模板引擎的配置属性中查询并修改。
🌲 Thymeleaf模板引擎
🌾 Thymeleaf 简介
Thymeleaf是⼀个XML/XHTML/HTML5模板引擎,可⽤于Web与⾮Web环境中的应⽤开发。它是⼀个开源的Java库,基于Apache License 2.0许可,由Daniel Fernández创建,该作者还是Java加密库Jasypt的作者。
Thymeleaf提供了⼀个⽤于整合SpringMVC的可选模块,在应⽤开发中,你可以使⽤Thymeleaf来完全代替JSP或其他模板引擎,如Velocity、FreeMarker等。Thymeleaf的主要⽬标在于提供⼀种可被浏览 器正确显示的、格式良好的模板创建⽅式,因此也可以⽤作静态建模。你可以使⽤它创建经过验证的 XML与HTML模板。相对于编写逻辑或代码,开发者只需将标签属性添加到模板中即可。接下来,这些标签属性就会在DOM(⽂档对象模型)上执⾏预先制定好的逻辑。
示例模板:
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th th:text="#{msgs.headers.name}">Name</td>
<th th:text="#{msgs.headers.price}">Price</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="prod : ${allProducts}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Oranges</td>
<td th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(prod.price,1,2)}">0.99</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>可以看到Thymeleaf主要以属性的⽅式加⼊到html标签中,浏览器在解析html时,当检查到没有的属性时候会忽略,所以Thymeleaf的模板可以通过浏览器直接打开展现,这样⾮常有利于前后端的分离。
在SpringBoot中使⽤Thymeleaf,只需要引⼊下⾯依赖,并在默认的模板路径src/main/resources/templates 下编写模板⽂件即可完成。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>在完成配置之后,举⼀个简单的例⼦,在快速⼊⻔⼯程的基础上,举⼀个简单的示例来通过Thymeleaf 渲染⼀个⻚⾯。
- 首先在resources/templates目录中新建一个index.html,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 th:text="${msg}"></h2>
</body>
</html>注意:在使用Thymeleaf需要先声明语法规则,具体代码如下:
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">- 然后添加Controller控制器方法,代码如下:
package com.moxuan.boot_07_thymeleaf.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class ThymeleafController {
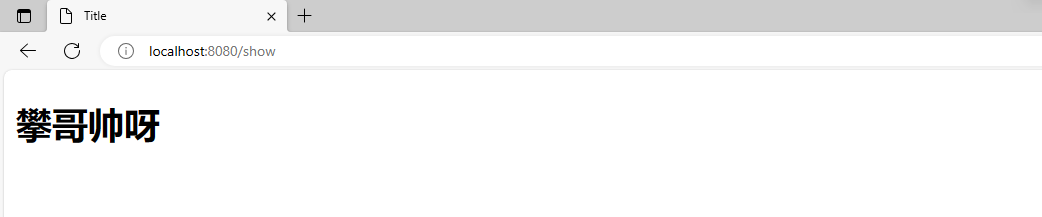
@RequestMapping("/show")
public String showMsg(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","攀哥帅呀");
return "index";
}
}
- 打开浏览器,发送请求进行测试:
🌾 Thymeleaf的默认参数配置
如有需要修改默认配置的时候,只需复制下⾯要修改的属性到 application.properties 中,并修改
成需要的值,如修改模板⽂件的扩展名,修改默认的模板路径等。
# Enable template caching.
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true
# Check that the templates location exists.
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true
# Content-Type value.
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
# Enable MVC Thymeleaf view resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true
# Template encoding.
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
# Comma-separated list of view names that should be excluded from resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names=
# Template mode to be applied to templates. See also StandardTemplateModeHandlers.
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
# Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
# Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html 🌾 Thymeleaf 的特点
Thymeleaf 模板引擎具有以下特点:
- 动静结合:Thymeleaf 既可以直接使用浏览器打开,查看页面的静态效果,也可以通过 Web 应用程序进行访问,查看动态页面效果。
- 开箱即用:Thymeleaf 提供了 Spring 标准方言以及一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
- 多方言支持:它提供了 Thymeleaf 标准和 Spring 标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现 JSTL、 OGNL 表达式;必要时,开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
- 与 SpringBoot 完美整合:SpringBoot 为 Thymeleaf 提供了的默认配置,并且还为 Thymeleaf 设置了视图解析器,因此 Thymeleaf 可以与 Spring Boot 完美整合。
🌾 Thymeleaf 语法规则
在使用 Thymeleaf 之前,首先要在页面的 html 标签中声明名称空间,示例代码如下。
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">在 html 标签中声明此名称空间,可避免编辑器出现 html 验证错误,但这一步并非必须进行的,即使我们不声明该命名空间,也不影响 Thymeleaf 的使用。
Thymeleaf 模板引擎支持多种表达式:
| 表达式名字 | 语法 | 用途 |
| 变量取值 | ${...} | 获取请求域、session域、application域,对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{...} | 获取上下文对象值,简化自定义对象属性的访问 |
| 消息 | #{...} | 获取国际化等值(根据地区语言环境,获取各个国家地区语言文字) |
| 链接 | @{...} | 生成链接(对静态页面连接赋予动态项目名支持) |
| 片段表达式 | ~{...} | jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
🍁 变量
Thymeleaf通过${}来获取model中的变量,注意这不是el表达式,而是ognl表达式,但是语法非常像。
- 新建User类,代码如下:
package com.moxuan.boot_07_thymeleaf.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
String name;
int age;
User friend;// 对象类型属性
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}- 控制器中将User数据封装到model中:
@RequestMapping("/show2")
public String show2(Model model){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(21);
user.setName("Jack Chen");
user.setFriend(new User("李小龙", 30));
model.addAttribute("user", user);
return "index";
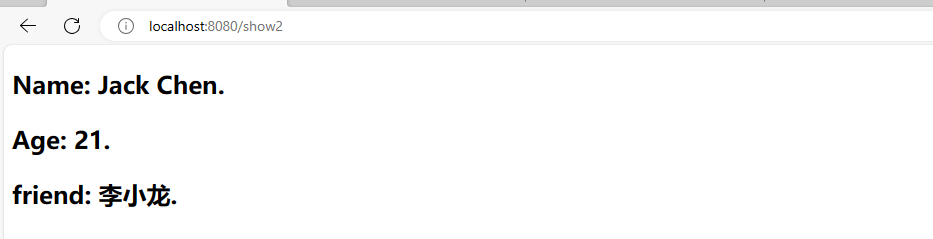
}- 在index.html中获取数据
<h2>
<p>Name: <span th:text="${user.name}"></span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="${user.age}"></span>.</p>
<p>friend: <span th:text="${user.friend.name}"></span>.</p>
</h2>- 运行效果
当实体类属性数量比较多的时候,频繁的写user.就会非常麻烦。因此,Thymeleaf提供了自定义变量来解决,修改上面index.html代码如下:
<h2 th:object="${user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{name}">Jack</span>.</p>
<p>Age: <span th:text="*{age}">21</span>.</p>
<p>friend: <span th:text="*{friend.name}">Rose</span>.</p>
</h2>- 首先在 h2上 用 th:object="${user}"获取user的值,并且保存
- 然后,在h2内部的任意元素上,可以通过 *{属性名}的方式,来获取user中的属性,这样就省去了大量的user.前缀了
🍁 方法
Thymeleaf支持方法调用,例如:
<h2 th:object="${user}">
<p>FirstName: <span th:text="*{name.split(' ')[0]}">Jack</span>.</p>
<p>LastName: <span th:text="*{name.split(' ')[1]}">Li</span>.</p>
</h2>这里我们调用了name(是一个字符串)的split方法。
🍁 字面值
有的时候,我们需要在指令中填写基本类型如:字符串、数值、布尔等,并不希望被Thymeleaf解析为变量,这个时候称为字面值。
早期版本需要使用一对'单引号引用的内容就是字符串字面值了:
<p>
你正在观看 <span th:text="'攀帅讲解的'">Thymeleaf</span> 的字符串常量值.
</p>目前的版本可以直接写
<p>
你正在观看 <span th:text="憨批讲解的">Thymeleaf</span> 的字符串常量值.
</p>数字字面量
<p>今年是 <span th:text="2023">1900</span>.</p>
<p>两年后将会是 <span th:text="2023+ 2">1902</span>.</p>布尔字面量
<div th:if="true">
你是"处"
</div>🍁 字符串拼接
我们经常会用到普通字符串与表达式拼接的情况:
<span th:text="'欢迎您:' + ${user.name} + '!'"></span>字符串字面值拼接需要用'',拼接起来非常麻烦,Thymeleaf对此进行了简化,使用一对|即可:
<span th:text="|欢迎您:${user.name}|"></span>与上面是完全等效的,这样就省去了字符串字面值的书写。
🌾 运算符
需要注意:${}内部的是通过OGNL表达式引擎解析的,外部的才是通过Thymeleaf的引擎解析,因此运算符尽量放在${}外进行。
🍁算术运算符
支持的算术运算符:+ - * / %
<span th:text="${user.age}"></span>
<span th:text="${user.age}%2 == 0"></span>🍁 条件运算符
三元运算
<span th:text="${user.sex} ? '男':'女'"></span>三元运算符的三个部分:conditon ? then : else
- condition:条件
- then:条件成立的结果
- else:不成立的结果
其中的每一个部分都可以是Thymeleaf中的任意表达式。
有的时候,我们取一个值可能为空,这个时候需要做非空判断,可以使用 表达式 ?: 默认值简写:
<span th:text="${user.name} ?: '二狗'"></span>🌾Thymeleaf 内置对象
Thymeleaf中提供了一些内置对象,并且在这些对象中提供了一些方法,方便我们来调用。获取这些对象,需要使用#对象名来引用。
🍁 环境相关对象
| 对象 | 作用 |
| #ctx | 获取Thymeleaf自己的Context对象 |
| #request | 如果是web程序,可以获取HttpServletRequest对象 |
| #response | 如果是web程序,可以获取HttpServletReponse对象 |
| #session | 如果是web程序,可以获取HttpSession对象 |
| #servletContext | 如果是web程序,可以获取HttpServletContext对象 |
🍁全局对象
| 对象 | 作用 |
| #dates | 处理java.util.date的工具对象 |
| #calendars | 处理java.util.calendar的工具对象 |
| #numbers | 用来对数字格式化的方法 |
| #strings | 用来处理字符串的方法 |
| #bools | 用来判断布尔值的方法 |
| #arrays | 用来护理数组的方法 |
| #lists | 用来处理List集合的方法 |
| #sets | 用来处理set集合的方法 |
| #maps | 用来处理map集合的方法 |
我们在Controller中添加日期类型对象
@RequestMapping("/show3")
public String show3(Model model){
model.addAttribute("today", new Date());
return "date";
}新建date.html,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
今天是: <span th:text="${#dates.format(today,'yyyy-MM-dd')}">2018-04-25</span>
</p>
</body>
</html>🌾 循环遍历
循环也是非常频繁使用的需求,我们可以使用th:each指令来完成
🍁 遍历list集合
- 在控制器中准备数据
@RequestMapping("/show4")
public String show4(Model model){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("周润发",65));
users.add(new User("梁朝伟",63));
users.add(new User("刘德华",61));
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("users",users);
return "foreach";
}- 添加foreach.html ,代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>
用户列表
</h2>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" height="500px">
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user:${users}">
<td th:text="${user.name}">攀哥</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">18</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>- 在迭代的同时,我们也可以获取迭代的状态对象:
<h2>
用户列表
</h2>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" height="500px">
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
<td>序号</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user,stat:${users}">
<td th:text="${stat.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}">攀哥</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">18</td>
</tr>
</table>stat对象包含以下属性:
- index,从0开始的角标
- count,元素的个数,从1开始
- size,总元素个数
- current,当前遍历到的元素
- even/odd,返回是否为奇偶,boolean值
- first/last,返回是否为第一或最后,boolean值
🍁 遍历map集合
- 在控制器中准备数据:
@RequestMapping("/show4")
public String show4(Model model){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("周润发",65));
users.add(new User("梁朝伟",63));
users.add(new User("刘德华",61));
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("users",users);
Map<String,User> maps = new HashMap<>();
maps.put("fg",new User("周润发",65));
maps.put("wg",new User("梁朝伟",63));
maps.put("hg",new User("刘德华",61));
model.addAttribute("maps",maps);
return "foreach";
}- 在foreach.html中添加遍历map集合的代码
<p th:each="userMap,stat:${maps}">
<span th:text="${stat.count}"></span>
<!--getKey() 获取键 -->
<span th:text="${userMap.getKey()}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.name}"></span>
<span th:text="${userMap.value.age}"></span>
</p>🌾 逻辑判断
🍁 if判断
Thymeleaf中使用th:if 或者 th:unless ,两者的意思恰好相反。
- 修改控制器中的数据
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("周润发",65));
users.add(new User("梁朝伟",63));
users.add(new User("彭于晏",48));
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("users",users);- 修改foreach.html中的表格代码添加”状态“列
<h2>
用户列表
</h2>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" height="500px">
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
<td>序号</td>
<td>状态</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user,stat:${users}">
<td th:text="${stat.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}">攀哥</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">18</td>
<td th:if="${user.age} > 60"> 老baby</td>
<td th:unless="${user.age} > 60"> 魅力王</td>
</tr>
</table>🍁 分支switch
这里要使用两个指令:th:switch 和 th:case
需要注意的是,一旦有一个th:case成立,其它的则不再判断。与java中的switch是一样的。
另外th:case="*"表示默认,放最后。
<h2>
用户列表
</h2>
<table border="1" width="50%" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0" height="500px">
<tr>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
<td>序号</td>
<td>状态</td>
<td>角色</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="user,stat:${users}" >
<td th:text="${stat.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.name}">攀哥</td>
<td th:text="${user.age}">18</td>
<td th:if="${user.age} > 60"> 老baby</td>
<td th:unless="${user.age} > 60"> 魅力王</td>
<td th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="admin" style="background:red" th:text="超级管理员"></p>
<p th:case="user" style="background:green" th:text="普通用户"></p>
<p th:case="manager" style="background:blue" th:text="部门经理"></p>
<p th:case="*" style="background:yellow" th:text="啥也不是"></p>
</td>
</tr>
</table>修改控制器层数据源:
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User("周润发",65,"admin"));
users.add(new User("梁朝伟",63,"manager"));
users.add(new User("彭于晏",48,"user"));
users.add(new User("宋喆",20));
System.out.println(users);
model.addAttribute("users",users);更多学习资料:小破(B)站: 墨轩大楼















![[240929] 12 款最佳免费开源隐写工具 | Llama 3.2: 开源、可定制模型,革新边缘人工智能和视觉体验](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cb736925c2a2433f98c6d9928399479f.png#pic_center)
