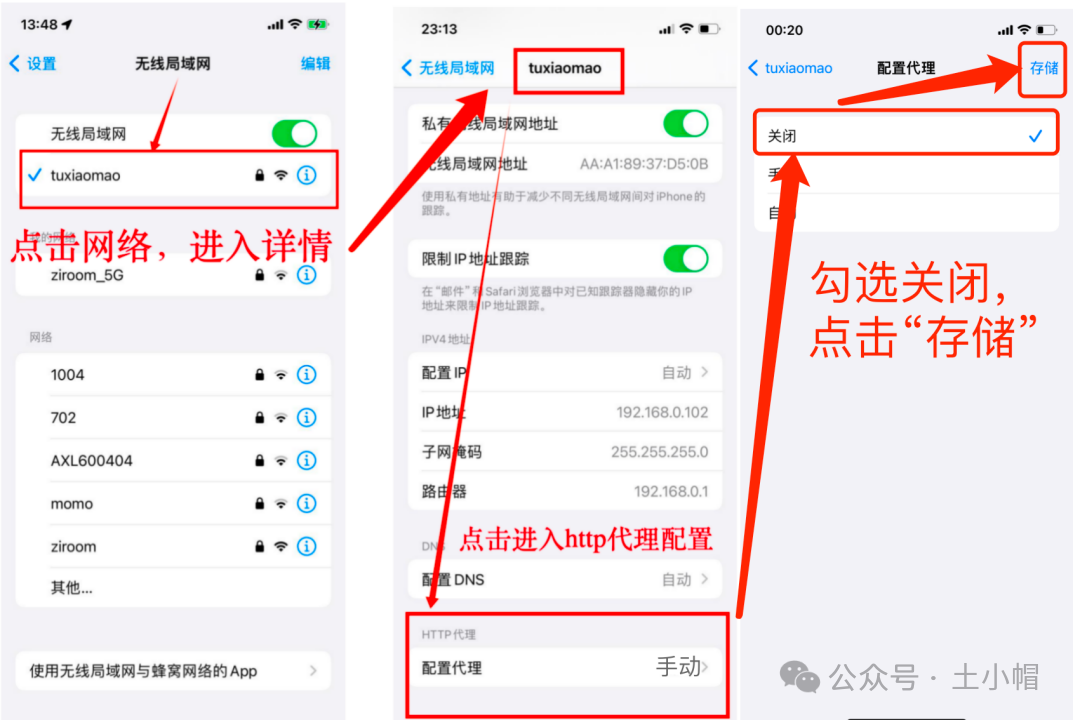
什么是OpenFeign?
OpenFeign 是一个声明式的 HTTP 客户端,旨在简化微服务架构中不同服务之间的 HTTP 调用。它通过集成 Ribbon 实现了客户端负载均衡,并且能够与 Eureka、Consul 等服务发现组件无缝对接。使用 OpenFeign,开发者只需定义接口并使用注解来配置 HTTP 请求,从而避免了编写大量的模板代码。
cloud官网介绍Feign:Spring Cloud OpenFeign
OpenFeign源码:GitHub - OpenFeign/feign: Feign makes writing java http clients easier
Feign 的实现
Feign 在 Ribbon + RestTemplate 的基础上进行了进一步封装,帮助开发者定义和实现依赖服务的接口。通过 Feign,开发者只需创建一个接口并使用注解进行配置,即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用 Spring Cloud Ribbon 时自动封装服务调用客户端的开发工作。
Feign 和 OpenFeign 的区别
| 特性 | Feign | OpenFeign |
|---|---|---|
| 依赖 | <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId> </dependency> | <dependency> |
| 作用 | 轻量级 RESTful HTTP 服务客户端,内置 Ribbon 用于客户端负载均衡,调用服务注册中心的服务。 | 在 Feign 的基础上支持 SpringMVC 的注解(如 @RequestMapping),通过动态代理生成实现类,实现负载均衡并调用其他服务。 |
OpenFeign 的优点
-
声明式调用:通过注解定义 HTTP 请求,代码更加简洁和易读。
-
集成 Ribbon:支持客户端负载均衡,确保请求在多个服务实例之间均匀分布。
-
支持服务发现:与 Eureka、Consul 等服务发现组件无缝集成,自动发现和调用服务。
-
支持熔断:与 Hystrix、Sentinel 等熔断器集成,提升系统的稳定性和容错能力。
-
可扩展性:支持自定义拦截器、编码器和解码器,便于根据需求进行扩展和定制化。
基本用法
父项目的 pom.xml 文件定义了所有子模块共享的依赖和插件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.9</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging> <!-- 这里设置为pom -->
<name>demo</name>
<description>demo</description>
<url/>
<licenses>
<license/>
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer/>
</developers>
<scm>
<connection/>
<developerConnection/>
<tag/>
<url/>
</scm>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2023.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba.cloud/spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2023.0.1.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.cloud/spring-cloud-starter-openfeign -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<!-- 定义子模块 -->
<modules>
<module>service1</module>
<module>service2</module>
<module>common</module>
</modules>
</project>
子项目 common
common 是一个简单的 Spring Boot 服务,提供一个 REST API。
ServiceBController.java
package com.example.common.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ServiceBController {
@GetMapping("/api/resource")
public String getResource() {
return "来自服务c的问候!";
}
}子项目 service-a
service1 使用 OpenFeign 调用 service-b 的服务。
Service1Application.java
在启动类,加上 @EnableFeignClients 注解。
package cloud.service1;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
public class Service1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Service1Application.class, args);
}
}
ServiceBClient.java
package cloud.service1.client;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "service-b", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface ServiceBClient {
@GetMapping("/api/resource")
String getResource();
}ServiceAController.java
package cloud.service1.controller;
import cloud.service1.client.ServiceBClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ServiceAController {
private final ServiceBClient serviceBClient;
public ServiceAController(ServiceBClient serviceBClient) {
this.serviceBClient = serviceBClient;
}
@GetMapping("/api/resource")
public String getResource() {
return serviceBClient.getResource();
}
}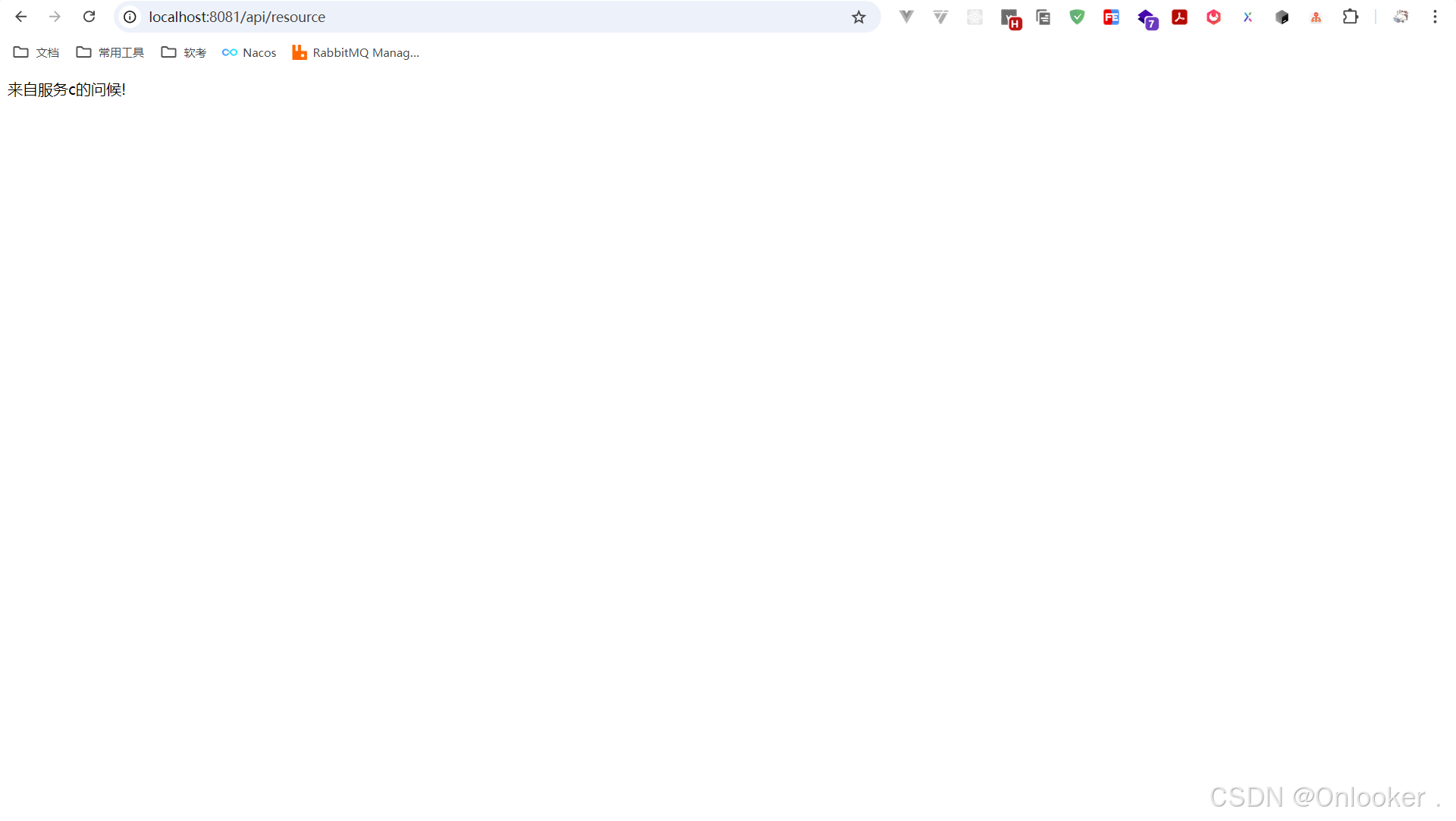
如图所示,证明已经访问成功了。
@FeignClient 标签的常用属性
@FeignClient 注解是 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中用于声明一个 Feign 客户端的核心注解。它提供了丰富的属性来配置 Feign 客户端的行为,以满足不同场景下的微服务调用需求。
1、name
- 类型: String
- 描述: 指定 Feign 客户端调用的服务名称。这是一个必填属性,通常是注册在服务发现(如 Nacos)中的服务名。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user")
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}2、url
- 类型: String
- 描述: 指定服务的 URL,通常用于调试或服务未注册到服务发现时。url 属性会覆盖 name 属性。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}3、configuration
- 类型: Class<?>[]
- 描述: 指定自定义配置类,配置类可以用来定制 Feign 客户端的行为,如请求拦截器、编码器和解码器等。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}配置类示例:
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor requestInterceptor() {
return template -> template.header("Custom-Header", "CustomHeaderValue");
}
}4、fallback
- 类型: Class<?>
- 描述: 指定服务降级的实现类。当 Feign 客户端调用失败时,会调用 fallback 指定的类中的方法。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", fallback = UserClientFallback.class)
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}5、fallbackFactory
- 类型: Class<?>
- 描述: 指定服务降级的工厂类,该工厂类可以提供更多的上下文信息,例如异常信息。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", fallbackFactory = UserClientFallbackFactory.class)
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}6、path
- 类型: String
- 描述: 指定服务的统一前缀路径,在定义 Feign 接口的方法时可以省略该路径。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", path = "/api/users")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}7、decode404
- 类型: boolean
- 描述: 指定是否将 HTTP 404 响应解码为 Feign 客户端的 fallback,默认值为 false。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", decode404 = true)
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}8、primary
- 类型: boolean
- 描述: 指定该 Feign 客户端是否为主要的 @Primary Bean,这对某些场景下的自动装配很有用,默认值为 true。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", primary = false)
public interface UserClient {
// ...
}9、contextId
- 类型: String
- 描述: 用于在多 Feign 客户端实例中区分不同的上下文 ID。特别适用于多个 Feign 客户端指向同一服务时的配置。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", contextId = "userClient1")
public interface UserClient1 {
// ...
}
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", contextId = "userClient2")
public interface UserClient2 {
// ...
}添加请求头信息
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,可以通过多种方式添加请求头信息。以下是三种常见的方法:
1. 在方法参数上添加请求头信息
可以在 Feign 客户端接口的方法参数上使用 @RequestHeader 注解来添加请求头信息。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/api/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id, @RequestHeader("Custom-Header") String customHeader);
}2. 使用 Feign 配置类定义请求拦截器
如果需要在所有请求中添加相同的请求头,可以通过定义一个 Feign 请求拦截器来实现。
定义 Feign 配置类:
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor requestInterceptor() {
return requestTemplate -> {
requestTemplate.header("Custom-Header", "CustomHeaderValue");
requestTemplate.header("Another-Header", "AnotherHeaderValue");
};
}
}在 Feign 客户端中使用配置类:
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/api/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}3. 动态添加请求头信息
如果需要根据某些条件动态添加请求头信息,可以在拦截器中编写逻辑。
定义 Feign 配置类:
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor requestInterceptor() {
return requestTemplate -> {
// 动态添加请求头信息
String customHeaderValue = getCustomHeaderValue();
requestTemplate.header("Custom-Header", customHeaderValue);
};
}
private String getCustomHeaderValue() {
// 根据某些条件动态生成请求头值
return "DynamicHeaderValue";
}
}在 Feign 客户端中使用配置类:
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/api/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}超时控制
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,超时控制是非常重要的,特别是在微服务架构中,确保服务之间的调用不会因为超时而导致整个系统的不稳定。OpenFeign 提供了两种超时参数:connectTimeout 和 readTimeout,分别用于控制连接超时和读取超时。
第一步:提供方接口,制造超时场景
首先,我们需要在提供方接口中制造一个超时场景,以便在消费方调用时能够触发超时。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟超时场景
Thread.sleep(5000); // 休眠 5 秒
return new User(id, "John Doe");
}
}第二步:消费方接口调用
在消费方接口中调用提供方接口,并配置超时参数。
@FeignClient(name = "demo-user", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface UserClient {
@GetMapping("/api/users/{id}")
User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}第三步:超时处理
我们可以在默认客户端和命名客户端上配置超时。OpenFeign 使用两个超时参数:
- connectTimeout:防止因服务器处理时间过长而阻塞调用者。
- readTimeout:从连接建立时开始应用,当返回响应的时间过长时就会被触发。
配置超时参数
可以通过配置文件(如 application.yml 或 application.properties)来设置超时参数。
示例:application.yml
feign:
client:
config:
default:
connectTimeout: 2000 # 连接超时时间,单位为毫秒
readTimeout: 3000 # 读取超时时间,单位为毫秒示例:application.properties
feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=2000
feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=3000手动创建 Feign Client
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,通常使用 @FeignClient 注解来声明一个 Feign 客户端。然而,有时可能需要手动创建 Feign 客户端,例如在某些特殊场景下,或者需要更细粒度的控制。
示例代码
定义 Feign 接口
首先,定义一个标准的 Feign 接口。
public interface FooClient {
@GetMapping("/api/foo")
String getFoo();
}手动创建 Feign 客户端
使用 Feign Builder API 手动创建两个 Feign 客户端实例,并为每个客户端配置不同的请求拦截器。
import feign.Feign;
import feign.auth.BasicAuthRequestInterceptor;
import feign.Client;
import feign.Contract;
import feign.Encoder;
import feign.Decoder;
import feign.micrometer.MicrometerObservationCapability;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClientsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
// 导入 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供的默认配置
@Import(FeignClientsConfiguration.class)
@RestController
public class FooController {
// 定义两个 Feign 客户端实例
private FooClient fooClient;
private FooClient adminClient;
// 自动注入 Feign 所需的组件
@Autowired
public FooController(Client client, Encoder encoder, Decoder decoder, Contract contract, MicrometerObservationCapability micrometerObservationCapability) {
// 创建第一个 Feign 客户端实例,配置用户认证
this.fooClient = Feign.builder()
.client(client) // 设置客户端
.encoder(encoder) // 设置编码器
.decoder(decoder) // 设置解码器
.contract(contract) // 设置契约(注解解析器)
.addCapability(micrometerObservationCapability) // 添加 Micrometer 观测能力
.requestInterceptor(new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("user", "user")) // 设置请求拦截器,使用用户认证
.target(FooClient.class, "https://PROD-SVC"); // 指定目标服务 URL
// 创建第二个 Feign 客户端实例,配置管理员认证
this.adminClient = Feign.builder()
.client(client) // 设置客户端
.encoder(encoder) // 设置编码器
.decoder(decoder) // 设置解码器
.contract(contract) // 设置契约(注解解析器)
.addCapability(micrometerObservationCapability) // 添加 Micrometer 观测能力
.requestInterceptor(new BasicAuthRequestInterceptor("admin", "admin")) // 设置请求拦截器,使用管理员认证
.target(FooClient.class, "https://PROD-SVC"); // 指定目标服务 URL
}
// 示例方法,使用 fooClient 和 adminClient
public void exampleMethod() {
String fooResponse = fooClient.getFoo(); // 调用用户认证的 Feign 客户端
String adminResponse = adminClient.getFoo(); // 调用管理员认证的 Feign 客户端
System.out.println("Foo Response: " + fooResponse);
System.out.println("Admin Response: " + adminResponse);
}
}Feign Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 的支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供了对 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 的支持,使得在 Feign 客户端中可以轻松集成熔断器(Circuit Breaker)功能。通过配置,可以全局启用或禁用 CircuitBreaker 支持,并且可以自定义 CircuitBreaker 的名称模式。
启用 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 支持
如果 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 在 classpath 上,并且 spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.enabled=true,Feign 将用 CircuitBreaker 来包装所有方法。
示例配置
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
circuitbreaker:
enabled: true禁用特定客户端的 CircuitBreaker 支持
为了在每个客户端的基础上禁用 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 的支持,可以创建一个具有 "prototype" scope 的 Feign.Builder。
import feign.Feign;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public Feign.Builder feignBuilder() {
return Feign.builder();
}
}CircuitBreaker 名称模式
CircuitBreaker 的名称遵循这种模式 <feignClientClassName>#<calledMethod>(<parameterTypes>)。例如,当调用一个带有 FooClient 接口的 @FeignClient,并且被调用的接口方法 bar 没有参数,那么 CircuitBreaker 的名称将是 FooClient#bar()。
自定义 CircuitBreaker 名称模式
从 2020.0.2 开始,CircuitBreaker 名称模式已经从 <feignClientName>_<calledMethod> 改变。使用 2020.0.4 中引入的 CircuitBreakerNameResolver,可以保留旧的命名模式。
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.CircuitBreakerNameResolver;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public CircuitBreakerNameResolver circuitBreakerNameResolver() {
return (String feignClientName, Target<?> target, Method method) -> feignClientName + "_" + method.getName();
}
}启用 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker Group
要启用 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker group,请将spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.group.enabled 属性设置为 true(默认为 false)。
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
circuitbreaker:
group:
enabled: true使用配置属性配置 CircuitBreaker
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,可以通过配置属性来配置 CircuitBreaker。
定义 Feign 客户端
首先,定义一个 Feign 客户端接口。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
// 使用 @FeignClient 注解定义 Feign 客户端
@FeignClient(url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient {
// 定义一个 GET 请求方法
@GetMapping("/demo")
String getDemo();
}配置 CircuitBreaker
通过配置属性来配置 CircuitBreaker。
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
circuitbreaker:
enabled: true # 启用 CircuitBreaker
alphanumeric-ids:
enabled: true # 启用字母数字 ID
resilience4j:
circuitbreaker:
instances:
DemoClientgetDemo: # CircuitBreaker 实例名称
minimumNumberOfCalls: 69 # 最小调用次数
timelimiter:
instances:
DemoClientgetDemo: # 时间限制器实例名称
timeoutDuration: 10s # 超时时间如果你想切换回 Spring Cloud 2022.0.0 之前使用的 CircuitBreaker 名称模式,可以将 spring.cloud.openfeign.circuitbreaker.alphanumeric-ids.enabled 设置为 false。
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
circuitbreaker:
enabled: true
alphanumeric-ids:
enabled: false # 禁用字母数字 ID,使用旧的命名模式Feign Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker Fallback
Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker 支持 fallback 的概念:一个默认的代码路径,在 circuit 打开或出现错误时执行。要为一个给定的 @FeignClient 启用 fallback,可以将 fallback 属性设置为实现 fallback 的类名。我们还需要将我们的实现声明为一个 Spring Bean。
定义 Feign 客户端
定义一个 Feign 客户端接口,并使用 @FeignClient 注解,设置 fallback 属性。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@FeignClient(name = "test", url = "http://localhost:${server.port}/", fallback = Fallback.class)
protected interface TestClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello getHello();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hellonotfound")
String getException();
}定义 Fallback 类
定义一个 Fallback 类,实现 Feign 客户端接口,并在熔断器打开或出现错误时提供降级响应。
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.NoFallbackAvailableException;
@Component
static class Fallback implements TestClient {
@Override
public Hello getHello() {
throw new NoFallbackAvailableException("Boom!", new RuntimeException());
}
@Override
public String getException() {
return "Fixed response";
}
}使用 FallbackFactory 访问触发原因
如果需要访问使 fallback 触发的原因,可以使用 @FeignClient 里面的 fallbackFactory 属性。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.FallbackFactory;
@FeignClient(name = "test", url = "http://localhost:${server.port}/", fallbackFactory = TestClientFallbackFactory.class)
protected interface TestClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
Hello getHello();
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hellonotfound")
String getException();
}
@Component
static class TestClientFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<TestClient> {
@Override
public TestClient create(Throwable cause) {
return new TestClient() {
@Override
public Hello getHello() {
System.out.println("Fallback cause: " + cause);
throw new NoFallbackAvailableException("Boom!", cause);
}
@Override
public String getException() {
System.out.println("Fallback cause: " + cause);
return "Fixed response";
}
};
}
}Feign 和 @Primary
当使用 Feign 与 Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker fallback 时,ApplicationContext 中可能存在多个相同类型的 Bean。这将导致 @Autowired 不起作用,因为没有确切的一个 Bean,或一个被标记为 @Primary 的 Bean。为了解决这个问题,Spring Cloud OpenFeign 将所有 Feign 实例标记为 @Primary,因此 Spring Framework 将知道要注入哪个 Bean。在某些情况下,这可能是不可取的。要关闭这种行为,将 @FeignClient 的 primary 属性设置为 false。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@FeignClient(name = "test", url = "http://localhost:${server.port}/", primary = false)
public interface TestClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "/hello")
String getHello();
}Feign 继承的支持
Feign 支持接口继承,这意味着你可以定义一个通用的接口,然后在多个 Feign 客户端中继承和重用这个接口。通过接口继承,可以减少代码重复,提高代码的可维护性和可读性。
定义通用接口
首先,定义一个通用的接口,包含一些通用的方法。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
public interface CommonApi {
@GetMapping("/common/{id}")
String getCommon(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}定义 Feign 客户端接口
定义一个 Feign 客户端接口,继承通用接口,并添加一些特定于该客户端的方法。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@FeignClient(name = "demo-service", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient extends CommonApi {
@GetMapping("/demo/{id}")
String getDemo(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}使用 Feign 客户端
在需要使用 Feign 客户端的地方,注入并调用接口方法。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private DemoClient demoClient;
@GetMapping("/demo/{id}")
public String getDemo(@PathVariable Long id) {
return demoClient.getDemo(id);
}
@GetMapping("/common/{id}")
public String getCommon(@PathVariable Long id) {
return demoClient.getCommon(id);
}
}Feign request/response 压缩
在微服务架构中,网络传输的数据量可能会非常大,尤其是在处理大量数据或频繁调用远程服务时。为了减少网络传输的开销,可以对 Feign 的请求和响应进行压缩。Feign 支持通过配置启用 Gzip 压缩,从而减少数据传输的大小,提高性能。
在配置文件中启用 Feign 的请求和响应压缩。
application.yml
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
compression:
request:
enabled: true # 启用请求压缩
mime-types: text/xml,application/xml,application/json # 指定压缩的 MIME 类型
min-request-size: 2048 # 指定最小请求大小(字节)
response:
enabled: true # 启用响应压缩application.properties
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.enabled=true
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.mime-types=text/xml,application/xml,application/json
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.request.min-request-size=2048
spring.cloud.openfeign.compression.response.enabled=trueFeign 日志
每个创建的 Feign 客户端都会创建一个 logger。默认情况下,logger 的名字是用于创建 Feign 客户端的接口的全类名称。Feign 的日志只响应 DEBUG 级别。
配置 Feign 日志
1、配置日志级别
在 application.yml 或 application.properties 中配置 Feign 客户端的日志级别。
application.yml
logging:
level:
project.user.UserClient: DEBUGapplication.properties
logging.level.project.user.UserClient=DEBUG配置 Logger.Level
可以为每个客户端配置 Logger.Level 对象,告诉 Feign 要记录多少内容。选择是:
- NONE: 没日志(默认)。
- BASIC: 只记录请求方法和 URL 以及响应状态代码和执行时间。
- HEADERS: 记录基本信息以及请求和响应头。
- FULL: 记录请求和响应的 header、正文和元数据。
import feign.Logger;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel() {
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}Micrometer 的支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供了对 Micrometer 的支持,使得 Feign 客户端的调用可以被 Micrometer 观察到。通过启用 Micrometer 支持,可以收集 Feign 客户端的调用指标,并将其集成到 Micrometer 的监控系统中。
配置 Micrometer 支持
在配置文件中启用 Micrometer 支持。
application.yml
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
micrometer:
enabled: true # 启用 Micrometer 支持application.properties
spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=true禁用 Micrometer 支持
可以通过以下两种方式禁用 Micrometer 支持:
- 从 classpath 中排除 feign-micrometer。
- 将 spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled 设置为 false。
application.yml
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
micrometer:
enabled: false # 禁用 Micrometer 支持application.properties
spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=false自定义 MicrometerObservationCapability
可以通过注册你自己的 MicrometerObservationCapability Bean 来自定义 Micrometer 支持。
import io.micrometer.observation.ObservationRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.MicrometerObservationCapability;
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public MicrometerObservationCapability micrometerObservationCapability(ObservationRegistry registry) {
return new MicrometerObservationCapability(registry);
}
}使用 MicrometerCapability
仍然可以在 Feign 中使用 MicrometerCapability(仅支持指标),你需要禁用 Micrometer 支持(spring.cloud.openfeign.micrometer.enabled=false)并创建一个 MicrometerCapability Bean。
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.MicrometerCapability;
@Configuration
public class FooConfiguration {
@Bean
public MicrometerCapability micrometerCapability(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
return new MicrometerCapability(meterRegistry);
}
}Feign 缓存
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供了对 Spring 缓存的支持,使得 Feign 客户端可以识别其接口上的 @Cache* 注解。通过启用缓存支持,可以减少对远程服务的调用次数,提高性能。
启用 Feign 缓存
在 Spring Boot 应用的主类上启用缓存。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients
@EnableCaching
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}定义一个 Feign 客户端接口,并使用 @Cacheable 注解。
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@FeignClient(name = "demo-service", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient {
@GetMapping("/demo/{filterParam}")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "demo-cache", key = "#keyParam")
String demoEndpoint(String keyParam, @PathVariable String filterParam);
}禁用 Feign 缓存
可以通过属性 spring.cloud.openfeign.cache.enabled=false 来禁用 Feign 缓存功能。
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
cache:
enabled: false # 禁用 Feign 缓存Feign @QueryMap 的支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供了一个等价的 @SpringQueryMap 注解,用于将 POJO 或 Map 参数注解为查询参数 map。通过使用 @SpringQueryMap 注解,可以更方便地将复杂对象转换为查询参数,而不需要手动拼接查询字符串。
1. 定义 POJO 类
首先,定义一个 POJO 类,用于表示查询参数。
public class QueryParams {
private String param1;
private String param2;
// Getters and Setters
}2. 定义 Feign 客户端接口
定义一个 Feign 客户端接口,并使用 @SpringQueryMap 注解将 POJO 或 Map 参数注解为查询参数 map。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.SpringQueryMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@FeignClient(name = "demo-service", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient {
@GetMapping("/demo")
String getDemo(@SpringQueryMap QueryParams queryParams);
}3. 使用 Feign 客户端
在需要使用 Feign 客户端的地方,注入并调用接口方法。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@Autowired
private DemoClient demoClient;
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String getDemo() {
QueryParams queryParams = new QueryParams();
queryParams.setParam1("value1");
queryParams.setParam2("value2");
return demoClient.getDemo(queryParams);
}
}HATEOAS 的支持
Spring 提供了一些 API 来创建遵循 HATEOAS 原则的 REST 表示,如 Spring Hateoas 和 Spring Data REST。如果你的项目使用了 org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-hateoas 或 org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-rest starter,Feign HATEOAS 支持会被默认启用。
当HATEOAS支持被启用时,Feign 客户端被允许序列化和反序列化 HATEOAS 表示模型: EntityModel、 CollectionModel 和 PagedModel.。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.hateoas.CollectionModel;
import org.springframework.hateoas.EntityModel;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
@FeignClient(name = "demo-service", url = "http://localhost:8080")
public interface DemoClient {
@GetMapping("/demo/{id}")
EntityModel<Demo> getDemo(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@GetMapping("/demos")
CollectionModel<EntityModel<Demo>> getAllDemos();
}OAuth2 的支持
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 提供了对 OAuth2 的支持,使得 Feign 客户端可以自动获取并附加 OAuth2 访问令牌到请求头中。通过启用 OAuth2 支持,可以简化与 OAuth2 保护的资源的交互。
在配置文件中启用 OAuth2 支持,并指定 OAuth2 客户端的注册 ID。
spring:
cloud:
openfeign:
oauth2:
enabled: true # 启用 OAuth2 支持
clientRegistrationId: my-client-registration-id # 指定 OAuth2 客户端的注册 ID转换负载均衡的 HTTP 请求
在 Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中,你可以使用选定的 ServiceInstance 来转换负载均衡的 HTTP 请求。为了实现这一点,你需要实现和定义 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer,该接口允许你在请求发送到目标服务之前对其进行转换。
实现 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer
1. 实现 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer
首先,实现 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer 接口,并在 transformRequest 方法中定义请求转换逻辑。
import feign.Request;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
// 定义一个 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer Bean
@Bean
public LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer transformer() {
return new LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer() {
// 实现 transformRequest 方法,定义请求转换逻辑
@Override
public Request transformRequest(Request request, ServiceInstance instance) {
// 创建一个新的请求头 Map,并复制原始请求的请求头
Map<String, Collection<String>> headers = new HashMap<>(request.headers());
// 添加自定义请求头,包含服务 ID
headers.put("X-ServiceId", Collections.singletonList(instance.getServiceId()));
// 添加自定义请求头,包含实例 ID
headers.put("X-InstanceId", Collections.singletonList(instance.getInstanceId()));
// 创建并返回一个新的 Request 对象,包含转换后的请求头
return Request.create(request.httpMethod(), request.url(), headers, request.body(), request.charset(),
request.requestTemplate());
}
};
}
}2. 配置 Feign 客户端
在 Feign 客户端配置中,启用负载均衡并使用自定义的 LoadBalancerFeignRequestTransformer。
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
// 定义一个 Feign 客户端接口,启用负载均衡
@FeignClient(name = "demo-service")
public interface DemoClient {
// 定义一个 GET 请求方法
@GetMapping("/demo/{id}")
String getDemo(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}参考文章
常见的应用属性
Spring Cloud OpenFeign 中文文档