Title
题目
Deep unfolding network with spatial alignment for multi-modal MRI reconstruction
用于多模态MRI重建的具有空间对齐的深度展开网络
01
文献速递介绍
磁共振成像(MRI)因其无创性、高分辨率和显著的软组织对比度,已成为广泛使用的医学成像技术。然而,由于MR信号空间编码的重复采集和硬件限制,MR扫描相对较慢。这一耗时的过程可能会导致患者的不适,使其产生移动,从而在图像中引入运动伪影,进而可能对后续的疾病诊断产生负面影响。因此,加速MRI采集在临床实践中具有重要意义。为了加速MRI采集,一个可行的策略是减少收集的k空间数据量,然后通过欠采样数据重建全采样图像。
压缩感知MRI(CS-MRI)方法使得在采样率显著低于奈奎斯特采样定理所要求的情况下能够从欠采样数据中进行准确重建(Lustig等人,2007年)。这些方法旨在基于不同的先验(例如,结构化稀疏性(Lai等人,2016年;Yang等人,2015年)、非局部稀疏性(Qu等人,2014年;Eksioglu,2016年))设计一些手工定制的正则化项,并将其构建到算法优化中以约束解空间。尽管这些方法具有理论上的保证,但手工定制一个最优的正则化项仍然具有挑战性。另一种替代方法是基于深度学习的方法,这些方法由于其高准确性和速度,已在MRI重建领域引起了广泛关注(Wang等人,2016年;Sriram等人,2020年;Zhu等人,2018年)。通过学习鲁棒的特征表示,基于深度学习的方法在重建性能上取得了显著的成果。然而,大多数基于深度学习的方法是一个“黑箱”过程,缺乏临床实践中所需的可解释性。为了解决这一“黑箱”问题,提出了深度展开网络(Yang等人,2020a;Xin等人,2022年;Huang等人,2024年;Zhang等人,2022年;Jiang等人,2023b,a),它将成像模型和领域知识融入网络中。通过将优化算法的迭代展开为深度神经网络,这些网络使得学习过程具有可解释性。
尽管深度展开网络在MRI重建中具有潜力,但大多数方法主要集中于单一模态的信息利用。然而,在临床实践中,常常会获取不同对比度的MR图像,因为每种模态揭示了不同的组织和器官特征,而模态之间的互补信息有助于更准确的诊断。虽然不同模态的MR图像显示了不同的信号类型,但它们在空间上是对应的,并描绘了相同的解剖结构。研究(Xiang等人,2018年;Feng等人,2023年;Bian等人,2022年;Lei等人,2023年)表明,利用另一模态(参考模态)的信息可以改善一个模态(目标模态)的重建效果。但是,这些多模态MRI重建方法都基于图像完全对齐的假设,而在实际中这很少见。由于未充分挖掘不同模态之间的关联性,模态间错位可能会对重建性能产生负面影响。
Aastract
摘要
Multi-modal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers complementary diagnostic information, but somemodalities are limited by the long scanning time. To accelerate the whole acquisition process, MRI reconstruction of one modality from highly under-sampled k-space data with another fully-sampled reference modality isan efficient solution. However, the misalignment between modalities, which is common in clinic practice, cannegatively affect reconstruction quality. Existing deep learning-based methods that account for inter-modalitymisalignment perform better, but still share two main common limitations: (1) The spatial alignment task isnot adaptively integrated with the reconstruction process, resulting in insufficient complementarity betweenthe two tasks; (2) the entire framework has weak interpretability. In this paper, we construct a novel DeepUnfolding Network with Spatial Alignment, termed DUN-SA, to appropriately embed the spatial alignmenttask into the reconstruction process. Concretely, we derive a novel joint alignment-reconstruction model witha specially designed aligned cross-modal prior term. By relaxing the model into cross-modal spatial alignmentand multi-modal reconstruction tasks, we propose an effective algorithm to solve this model alternatively.Then, we unfold the iterative stages of the proposed algorithm and design corresponding network modulesto build DUN-SA with interpretability. Through end-to-end training, we effectively compensate for spatialmisalignment using only reconstruction loss, and utilize the progressively aligned reference modality to provideinter-modality prior to improve the reconstruction of the target modality. Comprehensive experiments onfour real datasets demonstrate that our method exhibits superior reconstruction performance compared tostate-of-the-art methods.
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)提供了互补的诊断信息,但某些模态由于扫描时间较长而受限。为了加速整个采集过程,通过使用另一种全采样的参考模态从高度欠采样的k空间数据中重建某一模态的MRI,是一种有效的解决方案。然而,在临床实践中,模态间的错位较为常见,这会对重建质量产生负面影响。现有的基于深度学习的方法虽然考虑了模态间的错位问题,表现更好,但仍存在两个主要局限:(1)空间对齐任务未能与重建过程自适应地集成,导致两个任务之间的互补性不足;(2)整个框架的可解释性较弱。
在本文中,我们构建了一种新颖的具有空间对齐的深度展开网络(Deep Unfolding Network with Spatial Alignment, DUN-SA),将空间对齐任务恰当地嵌入到重建过程中。具体而言,我们推导出一种新颖的联合对齐-重建模型,该模型带有专门设计的对齐跨模态先验项。通过将模型松弛为跨模态空间对齐和多模态重建任务,我们提出了一种有效的算法交替解决该模型。然后,我们展开所提出算法的迭代阶段,并设计相应的网络模块来构建具有可解释性的DUN-SA。通过端到端训练,我们仅使用重建损失就有效地补偿了空间错位,并利用逐步对齐的参考模态提供跨模态先验,以改善目标模态的重建。基于四个真实数据集的全面实验表明,我们的方法在重建性能上优于最先进的方法。
Method
方法
In Section 3, we propose a joint alignment-reconstruction model formulti-modal MRI reconstruction and design an optimization algorithmin Section 3.1. Then, we unfold the iterative stages of the proposedalgorithm with corresponding network modules and build DUN-SA inSection 3.2. Finally, we introduce the details of network parametersand network training in Section 3.3.
在第3节中,我们提出了一个用于多模态MRI重建的联合对齐-重建模型,并在第3.1节中设计了一个优化算法。然后,在第3.2节中,我们展开了所提算法的迭代阶段并设计了相应的网络模块,构建了DUN-SA。最后,在第3.3节中,我们介绍了网络参数和网络训练的细节。
Conclusion
结论
In this paper, we propose a novel joint alignment and reconstructionmodel for multi-modal MRI reconstruction. By developing an alignedcross-modal prior term, we integrate the spatial alignment task into thereconstruction process. We design an optimization algorithm for solvingit and then unfold each iterative stage into the corresponding networkmodule. As a result, we have constructed a deep unfolding networkwith interpretability, termed DUN-SA. Through end-to-end training, wefully leverage both intra-modality and inter-modality priors. Comprehensive experiments conducted on four real datasets have demonstratedthat the proposed DUN-SA outperforms current state-of-the-art methodsin both quantitative and qualitative assessments. Additionally, we haveverified that DUN-SA is relatively robust to misalignment, with minimalimpact on spatial alignment even as acceleration factors increase.
在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的多模态MRI重建的联合对齐与重建模型。通过引入对齐的跨模态先验项,我们将空间对齐任务集成到重建过程中。我们为此设计了一个优化算法,并将每个迭代阶段展开为相应的网络模块。因此,我们构建了一个具有可解释性的深度展开网络,称为DUN-SA。通过端到端训练,我们充分利用了模态内和模态间的先验信息。基于四个真实数据集进行的全面实验表明,所提出的DUN-SA在定量和定性评估中均优于当前最先进的方法。此外,我们验证了DUN-SA在面对错位时表现出较强的鲁棒性,即使加速因子增加,空间对齐的影响也最小。
Figure
图
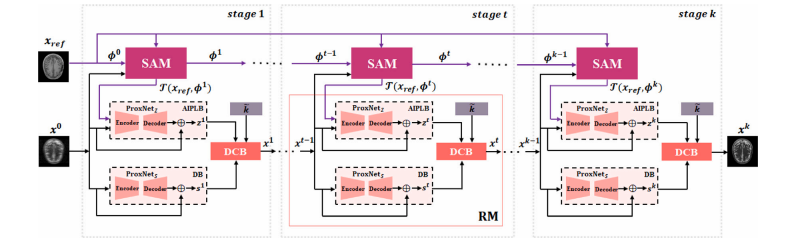
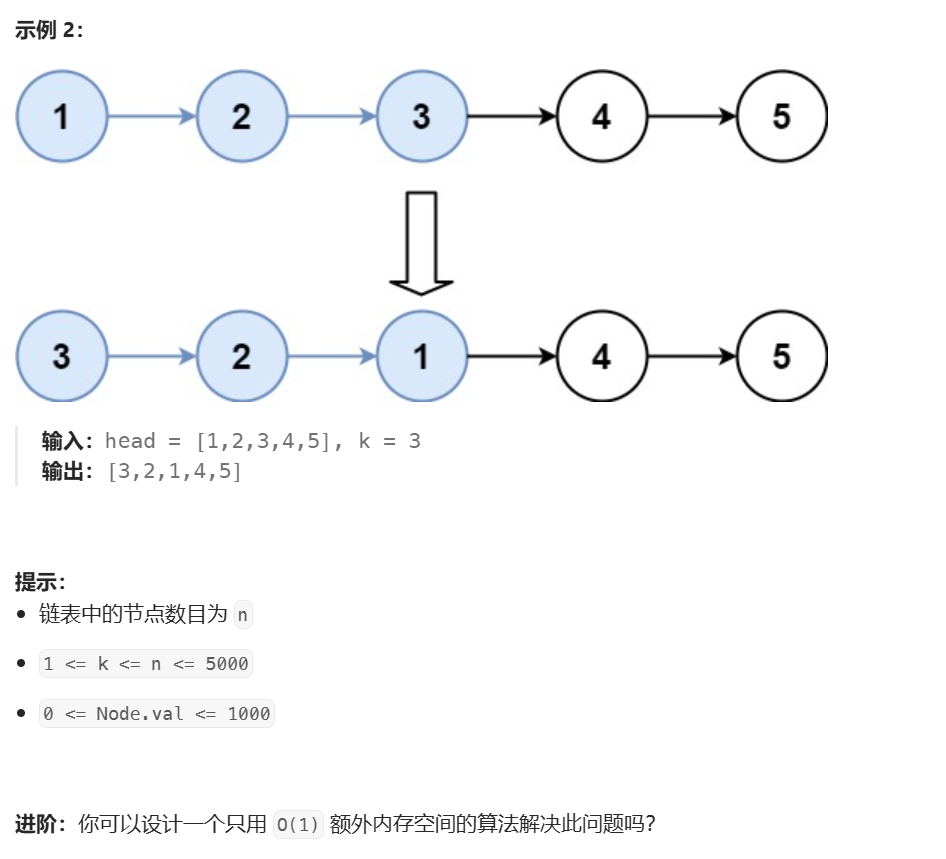
Fig. 1. The overall structure of the proposed Deep Unfolding Network with Spatial Alignment (DUN-SA) consists of SAM (Spatial Alignment Module) and RM (ReconstructionModule). The RM is composed of AIPLB (Aligned Inter-modality Prior Learning Block), DB (Denoising Block), and DCB (Data Consistency Block). SAM is used to solve spatialalignment task, while RM is for reconstruction task. Specifically, AIPLB is used to learn aligned inter-modality prior, DB is used to learn denoising prior, and DCB is used toenforce data consistency constraint.
图1. 所提出的具有空间对齐的深度展开网络(DUN-SA)的整体结构包括空间对齐模块(SAM)和重建模块(RM)。RM由对齐的跨模态先验学习块(AIPLB)、去噪块(DB)和数据一致性块(DCB)组成。SAM用于解决空间对齐任务,而RM用于重建任务。具体而言,AIPLB用于学习对齐的跨模态先验,DB用于学习去噪先验,DCB用于强制执行数据一致性约束。
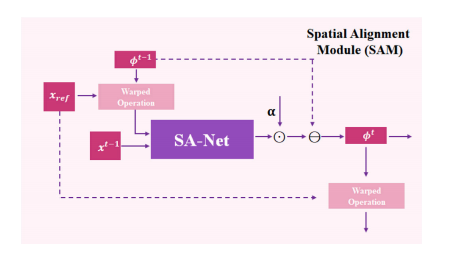
Fig. 2. Architecture of Spatial Alignment Module (SAM).
图2. 空间对齐模块(SAM)的结构图。
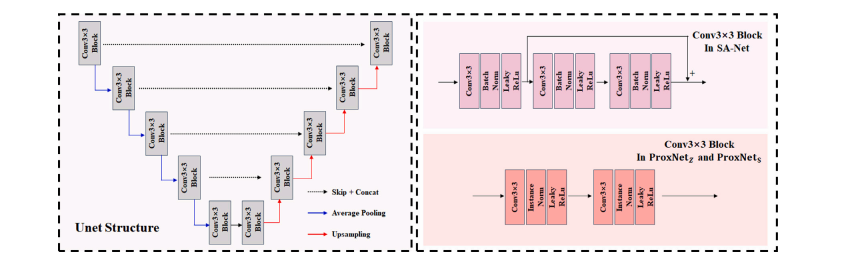
Fig. 3. Detailed configurations of SA-Net, ProxNet𝑍 and ProxNet𝑆 .
图3. SA-Net、ProxNet𝑍 和 ProxNet𝑆 的详细配置。
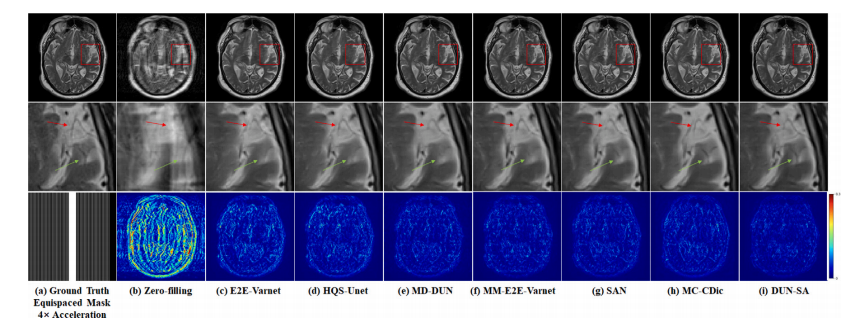
Fig. 4. Visual comparison with representative methods for 4× acceleration under 1D equispaced subsampling mask on fastMRI dataset. First row: Reconstructed images by different methods; second row: Zoomed-in region of interest; third row: Equispaced mask of 4× acceleration and error maps of different methods.
图4. 在fastMRI数据集上,使用1D等间隔欠采样掩模进行4×加速的代表性方法的视觉比较。第一行:不同方法重建的图像;第二行:感兴趣区域的放大图;第三行:4×加速的等间隔掩模及不同方法的误差图。
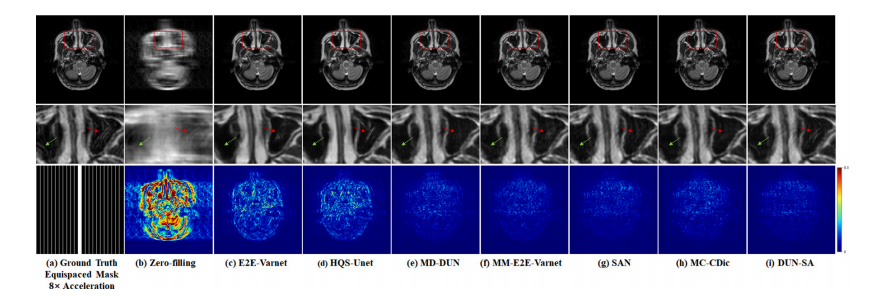
Fig. 5. Visual comparison with representative methods for 8× acceleration under 1D equispaced subsampling mask on the IXI dataset. First row: Reconstructed images by differentmethods; second row: Zoomed-in region of interest; third row: Equispaced mask of 8× acceleration and error maps of different methods.
图5. 在IXI数据集上,使用1D等间隔欠采样掩模进行8×加速的代表性方法的视觉比较。第一行:不同方法重建的图像;第二行:感兴趣区域的放大图;第三行:8×加速的等间隔掩模及不同方法的误差图。
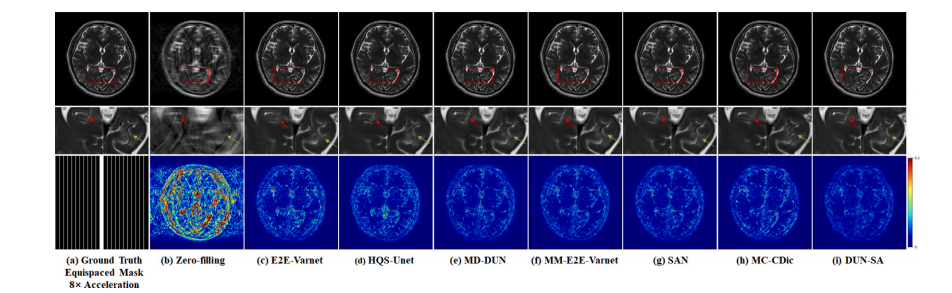
Fig. 6. Visual comparison with representative methods for 8× acceleration under 1D equispaced subsampling mask on the In-house dataset. First row: Reconstructed images bydifferent methods; second row: Zoomed-in region of interest; third row: Equispaced mask of 8× acceleration and error maps of different methods.
图6. 在自建数据集上,使用1D等间隔欠采样掩模进行8×加速的代表性方法的视觉比较。第一行:不同方法重建的图像;第二行:感兴趣区域的放大图;第三行:8×加速的等间隔掩模及不同方法的误差图。
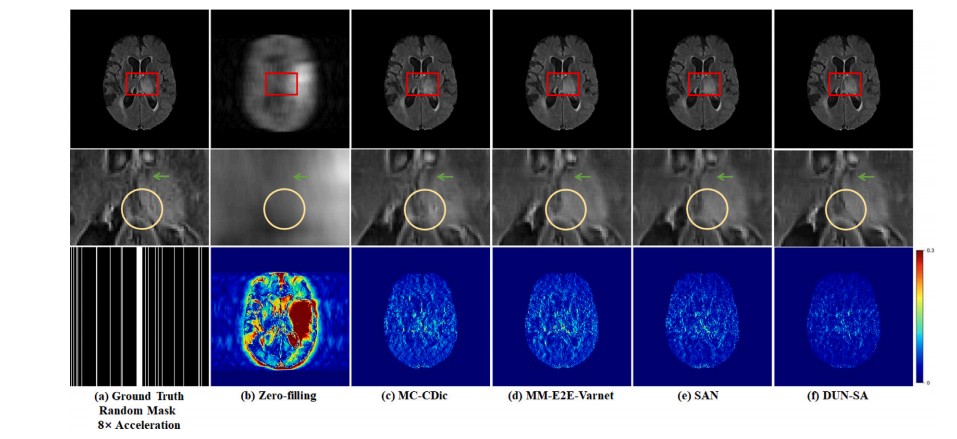
Fig. 7. Visual comparison with representative methods for 8× acceleration under 1D random subsampling mask on the BraTs 2018 dataset. First row: Reconstructed images by different methods; second row: Zoomed-in region of interest; third row: Random mask of 8× acceleration and error maps of different methods.
图7. 在BraTs 2018数据集上,使用1D随机欠采样掩模进行8×加速的代表性方法的视觉比较。第一行:不同方法重建的图像;第二行:感兴趣区域的放大图;第三行:8×加速的随机掩模及不同方法的误差图。
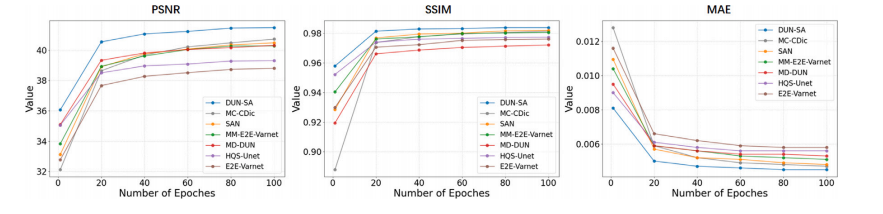
Fig. 8. Comparison on the learning trajectories of different models on the fastMRI dataset for 4× acceleration under equispaced mask.
图8. 不同模型在fastMRI数据集上使用等间隔掩模进行4×加速时学习轨迹的比较。
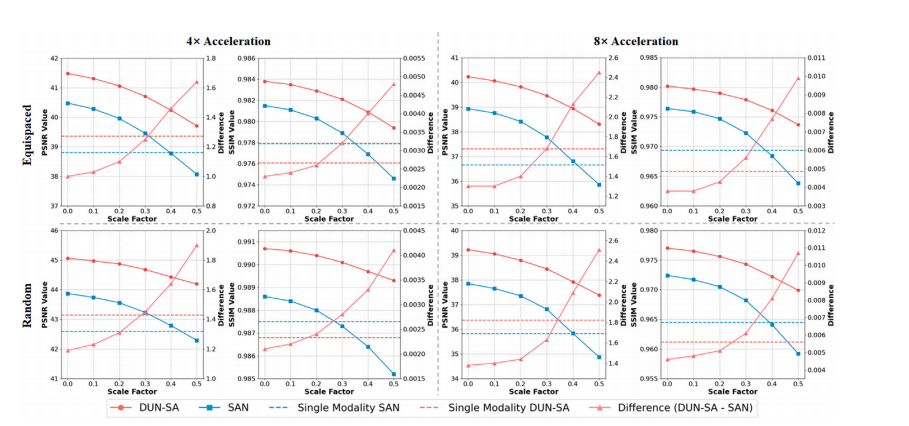
Fig. 9. Quantitative comparison of multi-modal MRI reconstruction on the fastMRI dataset with different scales of simulated spatial misalignment. Left y-axes are for reconstruction performances (‘‘DUN-SA’’, ‘‘SAN’’, ‘‘Single Modality SAN’’ and ‘‘Single Modality DUN-SA’’) while the right y-axes are for the ‘‘Difference’’ between ‘‘DUN-SA’’ and ‘‘SAN’’.
图9. 在fastMRI数据集上,针对不同尺度的模拟空间错位进行多模态MRI重建的定量比较。左侧y轴表示重建性能(“DUN-SA”、“SAN”、“单模态SAN”和“单模态DUN-SA”),右侧y轴表示“DUN-SA”和“SAN”之间的“差异”。
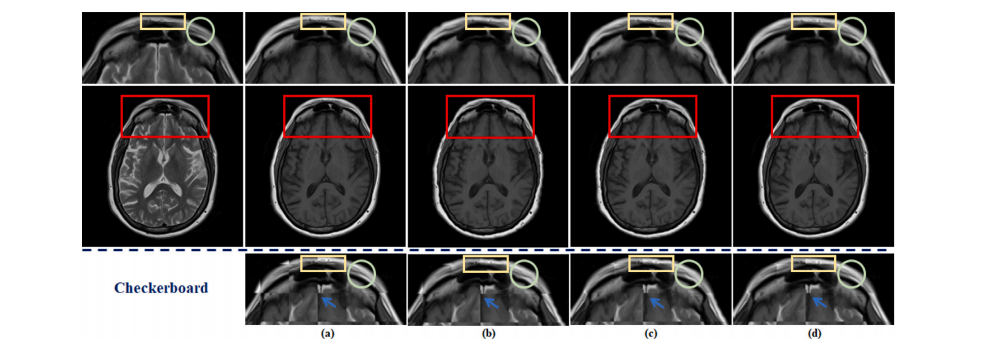
Fig. 10. The visualization of the effects of spatial alignment on the fastMRI dataset. (a) shows the original fully-sampled T1 image. (b) represents the results of aligning anunder-sampled T2 image with a fully-sampled T1 image by traditional method. (c) depicts the results of integrating traditional spatial alignment with reconstruction for jointoptimization. (d) displays the result of DUN-SA. Details are shown in the first row: zoomed-in view of aligned T1 images and third row: zoomed-in views of checkerboardvisualizations.
图10. 空间对齐对fastMRI数据集影响的可视化。(a) 显示了原始全采样的T1图像;(b) 代表使用传统方法将欠采样的T2图像与全采样的T1图像对齐的结果;(c) 描述了将传统空间对齐与重建结合进行联合优化的结果;(d) 显示了DUN-SA的结果。具体细节如下:第一行显示对齐后的T1图像的放大视图,第三行显示棋盘可视化的放大视图。
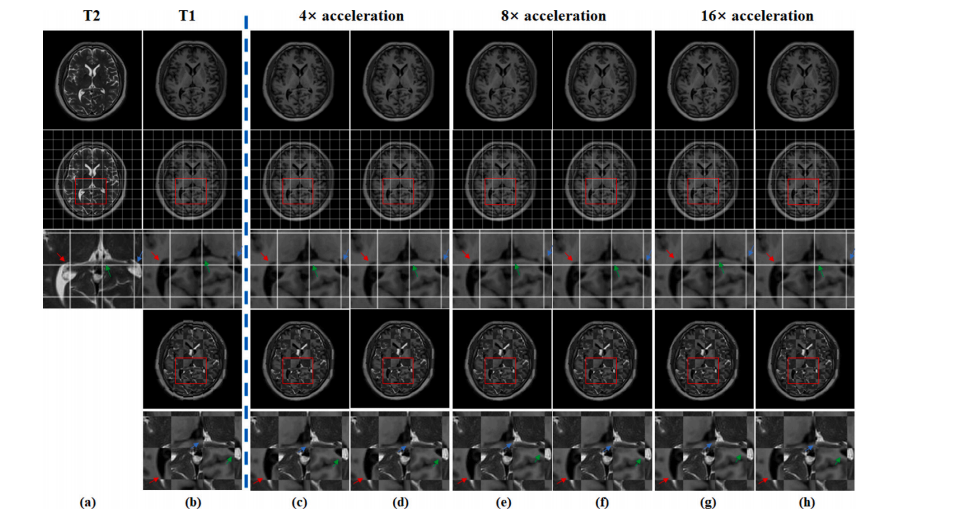
Fig. 11. The visualization of the effects of spatial alignment on the In-house dataset. (a), (b) represent fully-sampled T2-weighted image and fully-sampled T1-weighted image,respectively. (c), (e), and (g) depict T1-weighted images aligned using SAN under different acceleration factors, while (d), (f), and (h) display T1-weighted images aligned usingDUN-SA under different acceleration factors. In the second row, a grid is used to facilitate observation of the spatial position of each aforementioned image, with zoomed-inviews presented in the third row. In the fourth row, checkerboard visualizations are employed to demonstrate the misalignment between T2-weighted image and T1-weightedimage/aligned T1-weighted image, and the last row magnifies the corresponding areas to display the details more clearly.
图11. 空间对齐在自建数据集上的效果可视化。(a) 和 (b) 分别表示全采样的T2加权图像和全采样的T1加权图像;(c)、(e) 和 (g) 展示了在不同加速因子下使用SAN对齐的T1加权图像,而 (d)、(f) 和 (h) 显示了在不同加速因子下使用DUN-SA对齐的T1加权图像。第二行使用网格以便于观察上述每个图像的空间位置,第三行展示了放大的视图。第四行使用棋盘可视化展示了T2加权图像与T1加权图像/对齐的T1加权图像之间的错位,最后一行放大了相应区域以更清晰地显示细节。
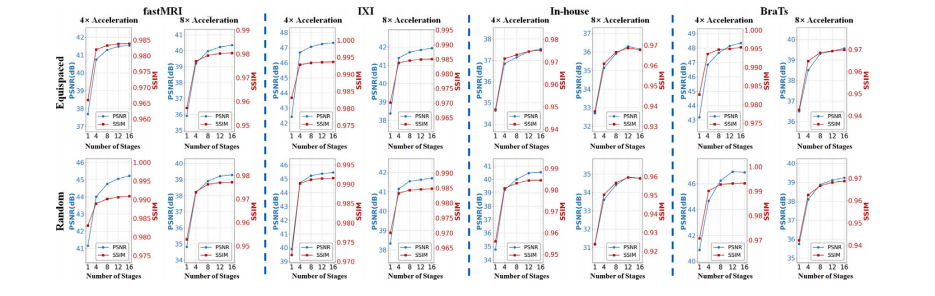
Fig. 12. The PSNR and SSIM curves on the fastMRI, IXI, In-house and BraTs datasets with different numbers of stages k
图12. fastMRI、IXI、自建数据集和BraTs数据集在不同阶段数 kkk 下的PSNR和SSIM曲线。
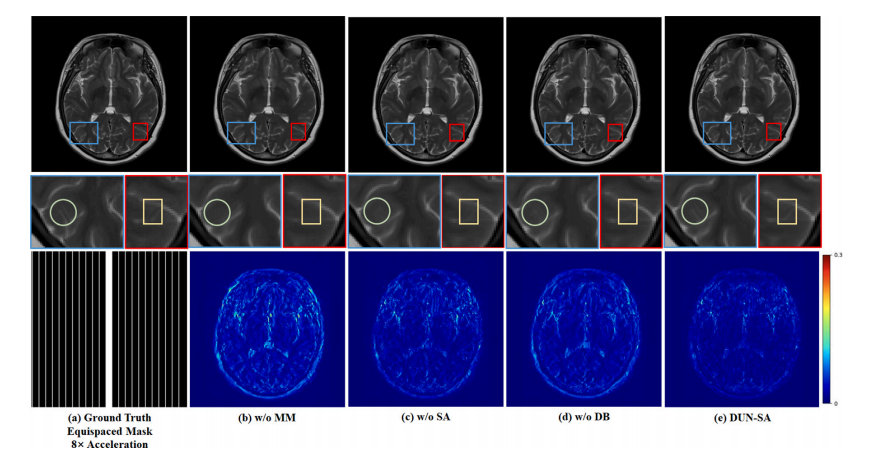
Fig. 13. Visual comparison with effect of each component for 8× acceleration under 1D equispaced subsampling mask on the fastMRI dataset. First row: Reconstructed images bydifferent methods; second row: Zoomed-in region of interest; third row: Equispaced mask of 8× acceleration and error maps of different methods.
图13. 不同组件在fastMRI数据集上使用1D等间隔欠采样掩模进行8×加速的视觉比较。第一行:不同方法重建的图像;第二行:感兴趣区域的放大图;第三行:8×加速的等间隔掩模及不同方法的误差图。
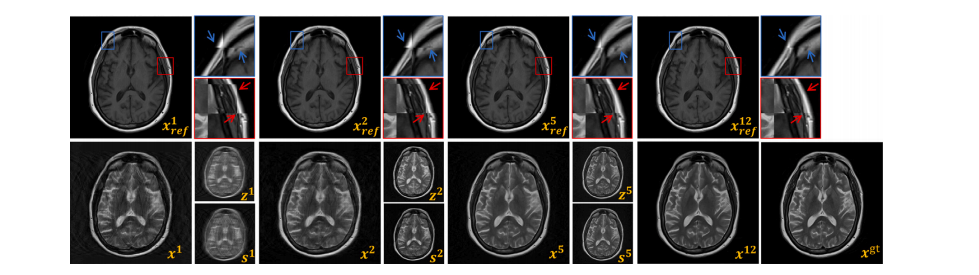
Fig. 14. Visualization of Intermediate Results at Stage t: ground truth 𝑥 𝑔𝑡, reconstructed image 𝑥 𝑡 , warped reference image (𝑥ref, 𝜙**𝑡 ) denoted as 𝑥 𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑓 , inter-modality prior 𝑧 𝑡 , andintra-modality prior 𝑠 𝑡 .
图14. 第 ttt 阶段的中间结果可视化:包括真实图像 𝑥 𝑔𝑡,重建图像 𝑥 𝑡,经过变换的参考图像 (𝑥ref, 𝜙**𝑡 ),表示为 𝑥 𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑓,跨模态先验 𝑧 𝑡,以及模态内先验 𝑠 𝑡。
Table
表
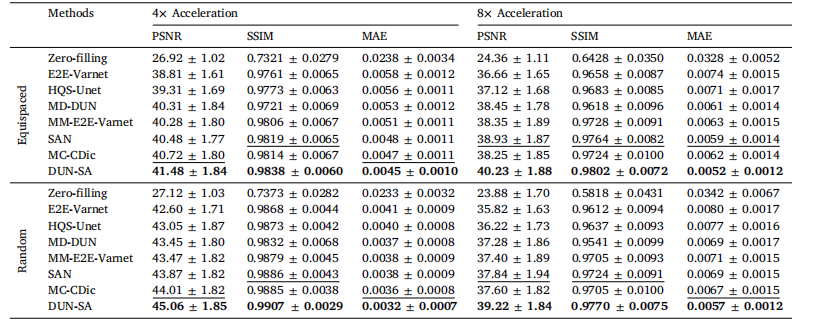
Table 1Quantitative evaluation of DUN-SA vs. other methods on the fastMRI dataset for 4× and 8× acceleration under equispaced and random 1Dsubsampling masks, where T1-weighted images are used as reference modality to assist the reconstruction of T2-weighted images. Best resultsare emphasized in bold, and the second best are emphasized with an underline.
表1 对比DUN-SA与其他方法在fastMRI数据集上进行4×和8×加速的定量评估,分别使用等间隔和随机一维欠采样掩模,其中T1加权图像作为参考模态辅助T2加权图像的重建。最佳结果以粗体强调,次优结果以下划线强调。
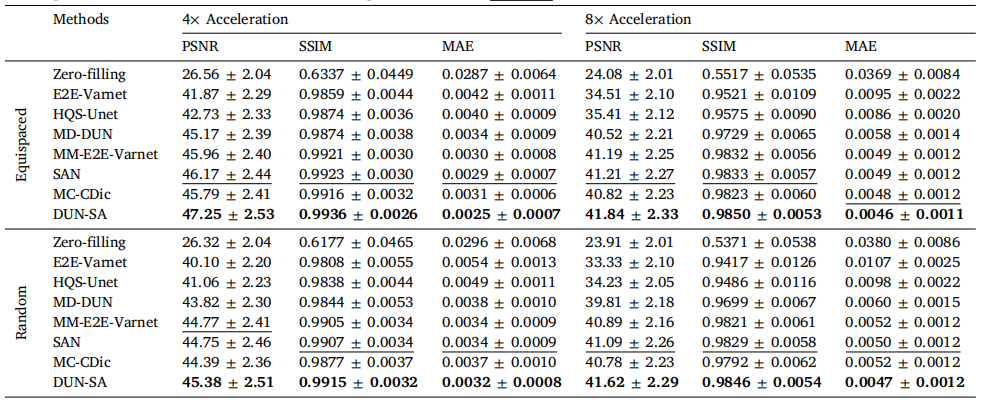
Table 2Quantitative evaluation of DUN-SA vs. other methods on the IXI dataset for 4× and 8× acceleration under equispaced and random 1Dsubsampling masks, where PD-weighted images are used as reference modality to assist the reconstruction of T2-weighted images. Best resultsare emphasized in bold, and the second best are emphasized with an underline.
表2 对比DUN-SA与其他方法在IXI数据集上进行4×和8×加速的定量评估,分别使用等间隔和随机一维欠采样掩模,其中PD加权图像作为参考模态辅助T2加权图像的重建。最佳结果以粗体强调,次优结果以下划线强调。
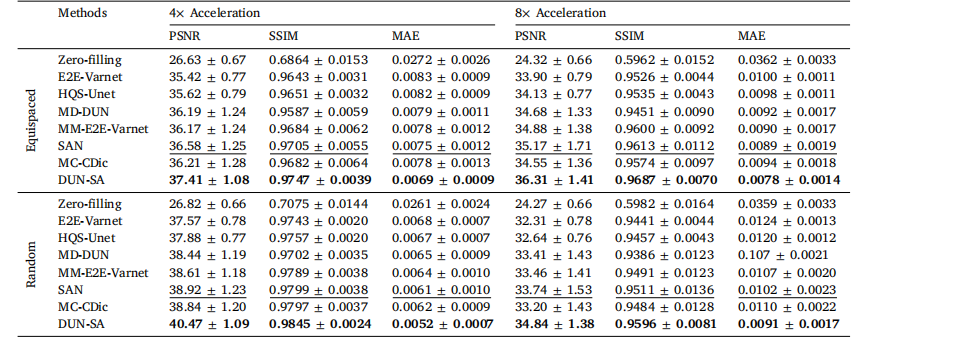
Table 3Quantitative evaluation of DUN-SA vs. other methods on the In-house dataset for 4× and 8× acceleration under equispaced and random 1Dsubsampling masks, where T1-weighted images are used as reference modality to assist the reconstruction of T2-weighted images. Best resultsare emphasized in bold, and the second best are emphasized with an underline.
表3 对比DUN-SA与其他方法在自建数据集上进行4×和8×加速的定量评估,分别使用等间隔和随机一维欠采样掩模,其中T1加权图像作为参考模态辅助T2加权图像的重建。最佳结果以粗体强调,次优结果以下划线强调。
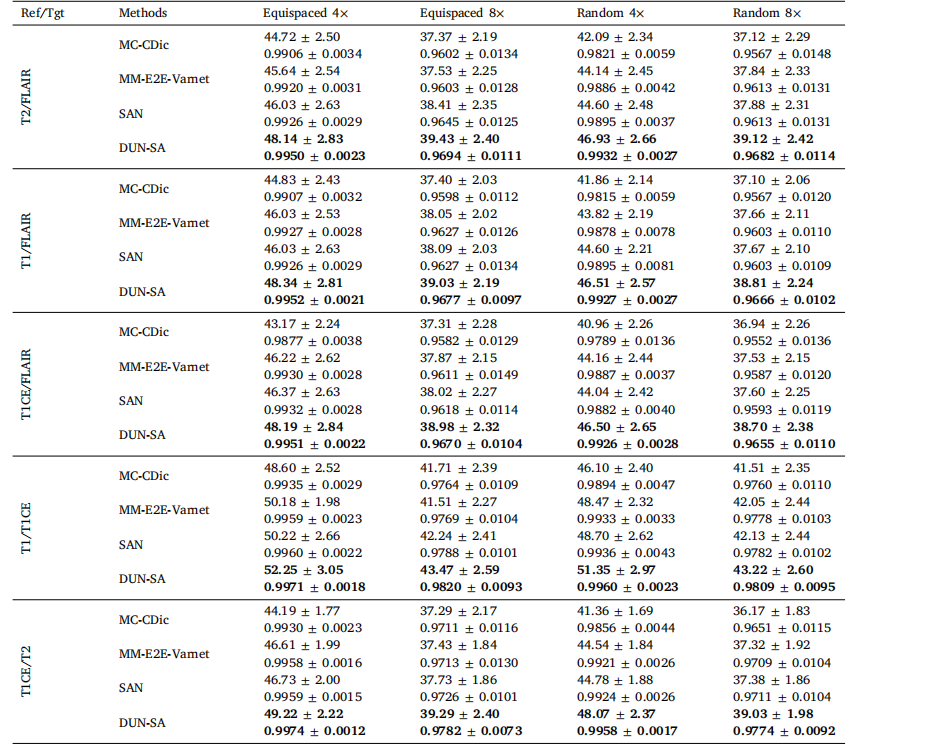
Table 4Quantitative evaluation of DUN-SA vs. other methods on the BraTs 2018 dataset for 4× and 8× acceleration under equispaced and random1D subsampling masks, where the Reference/Target modalities are T2/FLAIR; T1/FLAIR; T1CE/FLAIR; T1/T1CE; T1CE/T2. Best results areemphasized in bold.
表4对比DUN-SA与其他方法在BraTs 2018数据集上进行4×和8×加速的定量评估,分别使用等间隔和随机一维欠采样掩模,其中参考/目标模态为T2/FLAIR;T1/FLAIR;T1CE/FLAIR;T1/T1CE;T1CE/T2。最佳结果以粗体强调。
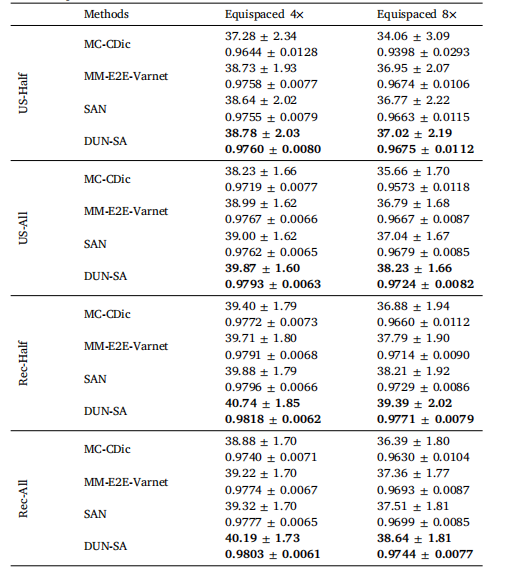
Table 5Evaluation of adaptation to scenarios with imperfect reference data. US-Half/RecHalf (US-All/Rec-all) indicates that half (all) reference modality data to beunder-sampled/reconstructed.
表5 评估在参考数据不完美场景下的适应性。US-Half/RecHalf(US-All/Rec-all)表示参考模态数据的一半(全部)被欠采样/重建。
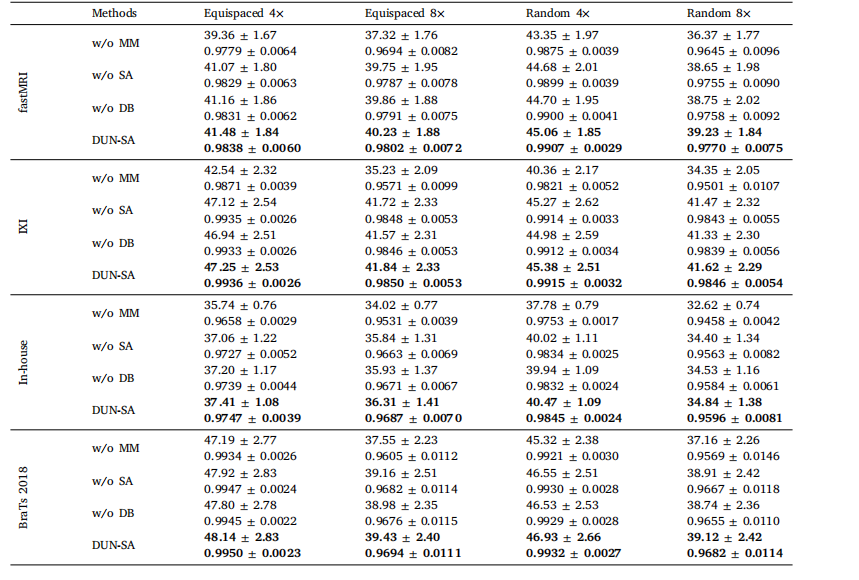
Table 6Effect of each component on the performance of DUN-SA on the fastMRI, IXI, In-house and BraTs datasets for 4× and 8× acceleration underequispaced and random subsampling masks, measured in PSNR and SSIM.
表6各组件对DUN-SA在fastMRI、IXI、自建数据集和BraTs数据集上进行4×和8×加速时的性能影响,分别在等间隔和随机欠采样掩模下,以PSNR和SSIM为测量指标。

Table 7Complexity analysis of representative models.
表7代表性模型的复杂性分析。