本节以一个“账本”为例,使用首选项的相关接口实现了对账单的增、删、改、查操作,并使用自动化测试框架arkxtest来对应用进行自动化测试。
为了演示该功能,创建一个名为“ArkTSPreferences”的应用。应用源码可以在文末《跟老卫学HarmonyOS开发》链接找到。
1. 操作Preferences
首先要获取一个Preferences来操作首选项。
在src/main/ets目录下创建名为“common”目录,用于存放常用的工具类。在该common目录创建工具类PreferencesUtil,代码如下:
// 导入preferences模块
import { preferences } from '@kit.ArkData';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
let context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
let options: preferences.Options = { name: 'myStore' };
export default class PreferencesUtil {
private dataPreferences: preferences.Preferences | null = null;
// 调用getPreferences方法读取指定首选项持久化文件,
// 将数据加载到Preferences实例,用于数据操作
async getPreferencesFromStorage() {
await preferences.getPreferences(context, options).then((data) => {
this.dataPreferences = data;
console.info(`Succeeded in getting preferences`);
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`Failed to get preferences, Cause:` + err);
});
}
}
复制为了对数据进行保存、查询、删除查操作,我们要封装对应接口。首选项接口提供的保存、查询、删除方法均有callback和Promise两种异步回调方式,本例子使用了Promise异步回调。代码如下:
// 将用户输入的数据,保存到缓存的Preference实例中
async putPreference(key: string, data: string) {
if (this.dataPreferences === null) {
await this.getPreferencesFromStorage();
} else {
await this.dataPreferences.put(key, data).then(() => {
console.info(`Succeeded in putting value`);
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`Failed to get preferences, Cause:` + err);
});
// 将Preference实例存储到首选项持久化文件中
await this.dataPreferences.flush();
}
}
// 使用Preferences的get方法读取数据
async getPreference(key: string) {
let result: string= '';
if (this.dataPreferences === null) {
await this.getPreferencesFromStorage();
} else {
await this.dataPreferences.get(key, '').then((data) => {
result = data.toString();
console.info(`Succeeded in getting value`);
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
console.error(`Failed to get preferences, Cause:` + err);
});
}
return result;
}
// 从内存中移除指定文件对应的Preferences单实例。
// 移除Preferences单实例时,应用不允许再使用该实例进行数据操作,否则会出现数据一致性问题。
async deletePreferences() {
preferences.deletePreferences(context, options, (err: BusinessError) => {
if (err) {
console.error(`Failed to delete preferences. Code:${err.code}, message:${err.message}`);
return;
}
this.dataPreferences = null;
console.info('Succeeded in deleting preferences.');
})
}
复制2. 账目信息的表示
在src/main/ets目录下创建名为“database”目录,并在该database目录下创建类AccountData,代码如下:
export default interface AccountData {
id: number;
accountType: number;
typeText: string;
amount: number;
}
复制AccountData各属性含义如下:
- id:主键。
- accountType:账目类型。0表示支出;1表示收入。
- typeText:账目的具体类别。
- amount:账目金额。
3. 设计界面
为了简化程序,突出核心逻辑,我们的界面设计的非常简单,只是一个Text组件和四个Button组件。四个Button组件用于触发增、删、改、查操作,而Text组件用于展示每次操作后的结果。修改Index代码如下:
// 导入PreferencesUtil
import PreferencesUtil from '../common/PreferencesUtil';
// 导入AccountData
import AccountData from '../database/AccountData';
const PREFERENCES_KEY = 'fruit';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World'
private preferencesUtil = new PreferencesUtil();
async aboutToAppear() {
// 初始化首选项
await this.preferencesUtil.getPreferencesFromStorage();
// 获取结果
this.preferencesUtil.getPreference(PREFERENCES_KEY).then(resultData => {
this.message = resultData;
});
}
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.id('text_result')
.fontSize(50)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
// 增加
Button(('增加'), { type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width(140)
.fontSize(40)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
// 保存数据
let newAccount: AccountData = { id: 1, accountType: 0, typeText: '苹果', amount: 0 };
this.preferencesUtil.putPreference(PREFERENCES_KEY, JSON.stringify(newAccount));
})
// 查询
Button(('查询'), { type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width(140)
.fontSize(40)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
// 获取结果
this.preferencesUtil.getPreference(PREFERENCES_KEY).then(resultData => {
this.message = resultData;
});
})
// 修改
Button(('修改'), { type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width(140)
.fontSize(40)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
// 修改数据
let newAccount: AccountData = { id: 1, accountType: 1, typeText: '栗子', amount: 1 };
this.preferencesUtil.putPreference(PREFERENCES_KEY, JSON.stringify(newAccount));
})
// 删除
Button(('删除'), { type: ButtonType.Capsule })
.width(140)
.fontSize(40)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 20 })
.onClick(() => {
this.preferencesUtil.deletePreferences();
})
}
.width('100%')
}
.height('100%')
}
}
复制上述代码,在aboutToAppear生命周期阶段,初始化了Preferences。点击“新增”会将预设好的数据“{ id: 1, accountType: 0, typeText: '苹果', amount: 0 }”写入到Preferences。点击“修改”会将预设好的“{ id: 1, accountType: 1, typeText: '栗子', amount: 1 }”的数据更新到Preferences。点击“删除”则会从内存中移除指定文件对应的Preferences单实例。
4. 运行
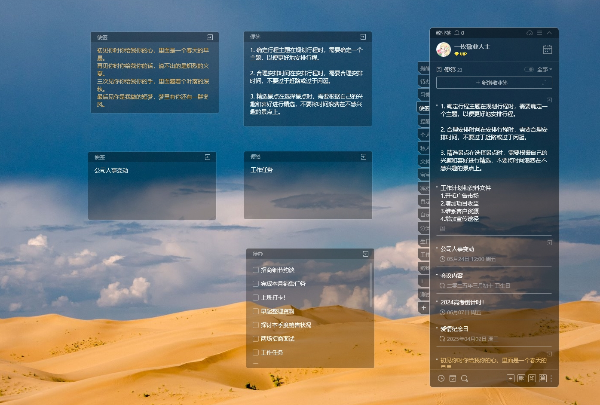
运行应用显示的界面效果如下图所示。

当用户点击“增加”后再点击“查询”时,界面如下图所示,证明数据已经成功写入Preferences。

当用户点击“修改”后再点击“查询”时,界面如下图所示,证明数据已经被修改并更新回Preferences。

当用户点击“删除”后再点击“查询”时,界面如下图所示,证明数据已经从Preferences删除。

5. 编写UI测试脚本
UI测试基于单元测试,UI测试脚本在单元测试脚本上增加了对UiTest接口,具体请参考API文档。
如下的示例代码是在上面的单元测试脚本基础上增量编写,实现的是在启动的应用页面上进行点击操作,然后检测当前页面变化是否为预期变化。
在“ohosTest/ets/test/”目录下,是专门用于存放具体测试代码的。在该目录下,已经存在了一个测试用例样板代码Ability.test.ets文件,基于该文件进行编写UI测试脚本。修改后,代码如下:
import { describe, it, expect } from '@ohos/hypium';
import { abilityDelegatorRegistry, Driver, ON } from '@kit.TestKit';
import { UIAbility, Want } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import AccountData from '../../../main/ets/database/AccountData';
const delegator: abilityDelegatorRegistry.AbilityDelegator = abilityDelegatorRegistry.getAbilityDelegator()
const bundleName = abilityDelegatorRegistry.getArguments().bundleName;
function sleep(time: number) {
return new Promise<void>((resolve: Function) => setTimeout(resolve, time));
}
export default function abilityTest() {
describe('ActsAbilityTest', () => {
// 编写UI测试脚本
it('testUi',0, async (done: Function) => {
console.info("uitest: testUi begin");
// 启动待测试的 ability
const want: Want = {
bundleName: bundleName,
abilityName: 'EntryAbility'
}
await delegator.startAbility(want);
await sleep(1000);
// 检查顶层显示的 ability
await delegator.getCurrentTopAbility().then((Ability: UIAbility)=>{
console.info("get top ability");
expect(Ability.context.abilityInfo.name).assertEqual('EntryAbility');
})
// UI 测试代码
// 初始化driver
let driver = Driver.create();
await driver.delayMs(1000);
// 查找'增加'按钮
let buttonAdd = await driver.findComponent(ON.text('增加'));
// 点击按钮
await buttonAdd.click();
await driver.delayMs(1000);
// 查找'查询'按钮
let buttonQuery = await driver.findComponent(ON.text('查询'));
// 点击按钮
await buttonQuery.click();
await driver.delayMs(1000);
// 查找 id 为'text_result'的 Text 组件
let text = await driver.findComponent(ON.id('text_result'));
// 检查文本内容
await text.getText().then(result => {
let newAccount: AccountData = { id: 1, accountType: 0, typeText: '苹果', amount: 0 };
expect(result).assertEqual(JSON.stringify(newAccount))
});
done();
})
})
}
复制上述代码主要做了以下几件事:
- 查找增加按钮,并进行点击;
- 查找查询按钮,并进行点击;
- 查找Text组件,断言该Text组件文本内容是否与期望的值一致。
6. 运行UI测试脚本
首先,启动模拟器或者真机。在模拟器或者真机上安装应用。
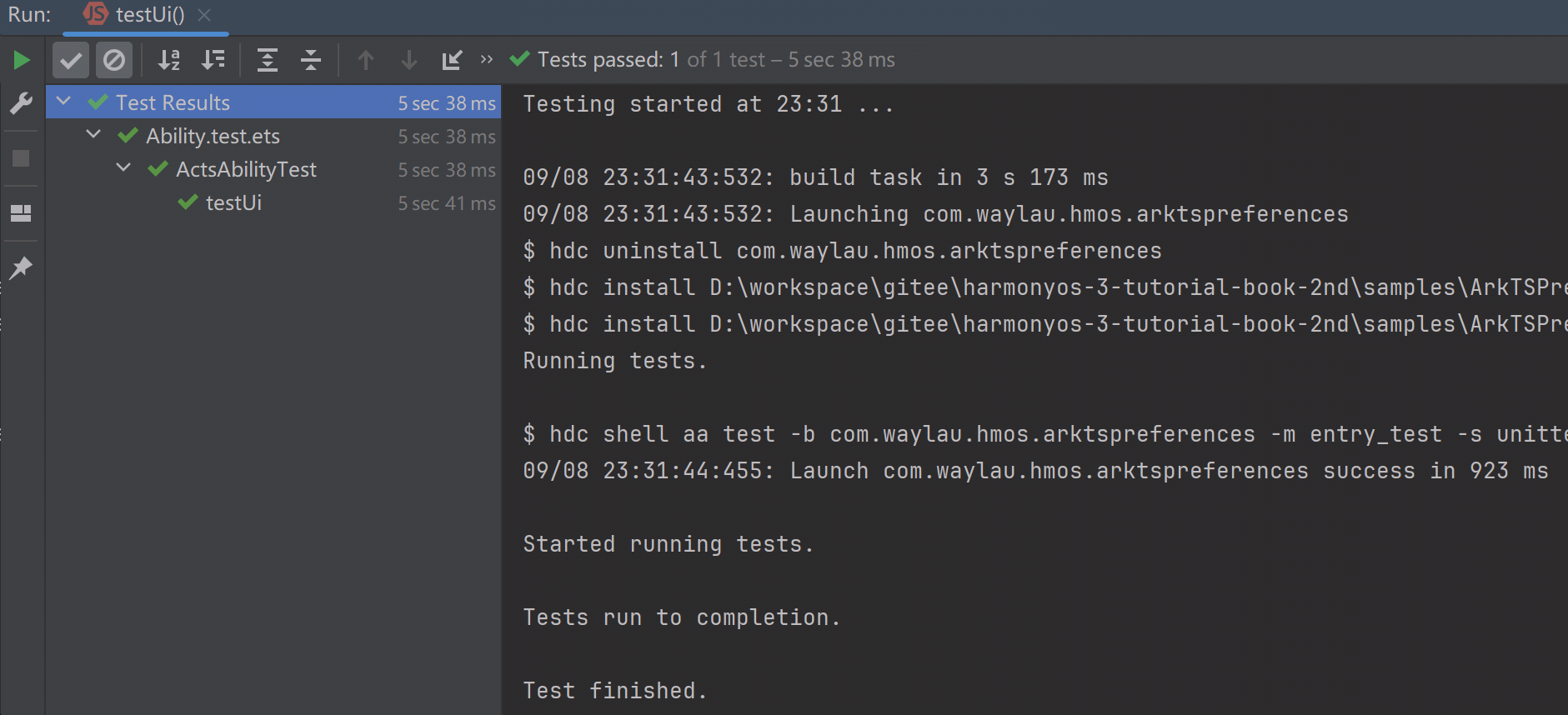
其次,点击如下图13-1所示的测试用例的左侧三角按钮,以运行测试脚本。
如果断言成功,则说明测试通过,可以看到如下绿色打勾的标识。
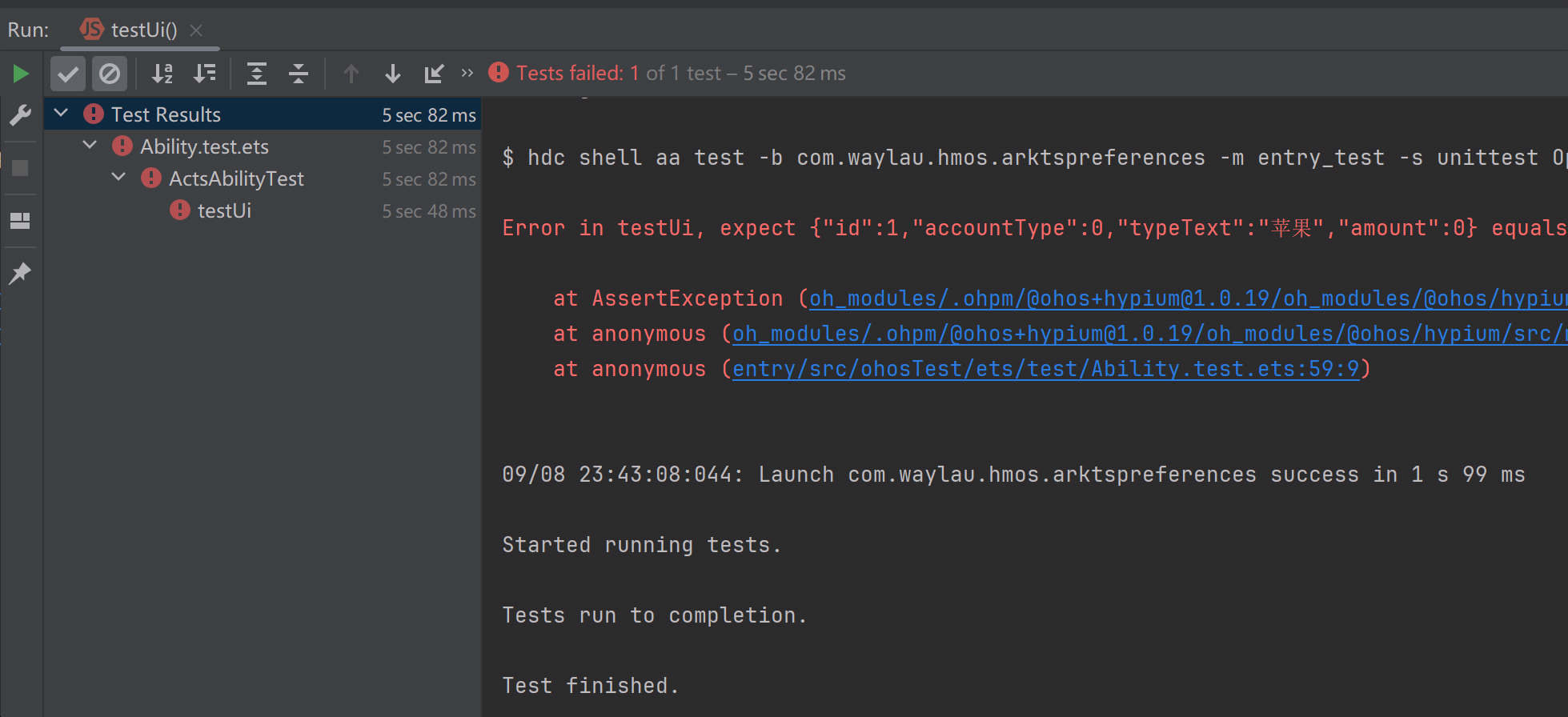
如果断言失败,则说明测试没有通过,可以看到如下红色告警标识,并会提示断言失败的原因。
7. 参考
- 《跟老卫学HarmonyOS开发》 开源免费教程,GitHub - waylau/harmonyos-tutorial: HarmonyOS Tutorial. 《跟老卫学HarmonyOS开发》
- 《鸿蒙HarmonyOS手机应用开发实战》(清华大学出版社)
- 《鸿蒙HarmonyOS应用开发从入门到精通战》(北京大学出版社)
- “鸿蒙系统实战短视频App 从0到1掌握HarmonyOS”(鸿蒙系统实战短视频App 从0到1掌握HarmonyOS_实战课程_慕课网)
- 《鸿蒙HarmonyOS应用开发入门》(清华大学出版社)
- “2024鸿蒙零基础快速实战-仿抖音App开发(ArkTS版)”(2024 鸿蒙零基础快速实战-仿抖音App开发( ArkTS版 )_实战课程_慕课网)