0 python知识
0.1 os库常见用法
os 库提供了许多用于操作操作系统功能的函数。常见用法包括:
- 文件和目录操作:
os.listdir(path):列出指定路径下的所有文件和目录。os.mkdir(path):创建新目录。os.remove(path):删除文件。os.rmdir(path):删除空目录。os.rename(src, dst):重命名文件或目录。
- 路径操作:
os.path.join(path, *paths):连接路径。os.path.exists(path):检查路径是否存在。os.path.isfile(path):检查路径是否为文件。os.path.isdir(path):检查路径是否为目录。
- 环境变量:
os.getenv(key, default=None):获取环境变量的值。os.environ:访问和修改环境变量。
- 进程管理:
os.system(command):在子终端中执行命令。os.getpid():获取当前进程的ID。os.getppid():获取父进程的ID。
0.2 call
在 Python 中,魔术方法 <font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font> 的作用是使得一个对象可以像函数一样被调用。当你实现了 <font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font> 方法后,Python 会在你使用 <font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">()</font> 操作符调用对象时自动触发这个方法。下面是详细的解释:
魔术方法 <font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>
- 定义
**<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>**方法:当你在一个类中定义了<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法时,这个类的实例就可以被调用。也就是说,如果<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法被定义了,那么你可以用圆括号<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">()</font>来调用这个对象,并且这个调用会触发<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法。 - 调用对象:
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj()</font>这样的语法实际上是调用了<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj.__call__()</font>。这就是为什么在之前的示例中,调用<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj(1, 2, 3, key='value')</font>会触发<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法。
示例解释
以下是一个更详细的示例:
pythonCopy Codeclass CallableClass:
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print("被调用了!")
print("参数:", args)
print("关键字参数:", kwargs)
# 创建类的实例
obj = CallableClass()
# 调用实例,就像调用函数一样
obj(1, 2, 3, key='value')
在这个示例中:
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">CallableClass</font>类定义了一个<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法。- 当你创建
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">CallableClass</font>的实例<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj</font>时,<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj</font>实际上是一个可调用的对象。 - 当你写
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj(1, 2, 3, key='value')</font>时,Python 解释器会将其视为<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">obj.__call__(1, 2, 3, key='value')</font>,因此<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法会被自动调用。
使用场景
使用 <font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font> 方法可以让你的对象表现得像函数一样,这在一些场景中非常有用,例如:
- 工厂函数:可以用来创建复杂对象或进行一些初始化操作。
- 策略模式:你可以使用
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>方法来封装一些可变的算法或策略。 - 装饰器:在创建自定义装饰器时,你可以使用
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font>来实现。
总之,<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">__call__</font> 方法的存在使得类的实例可以像函数一样被调用,并且它会在这种调用操作发生时被自动触发。
1 Anaconda
1.1 存储位置修改
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_69317550/article/details/135134588
1.2 安装pytorch
pytorch为环境的库名
conda create -n pytorch python=3.6
1.2.1 激活pytorch
conda activate pytorch
1.3 在1.2的环境中安装Jupyter
conda install nb_conda
或者 conda install jupyter notebook
启动:jupyter notebook
1.4 系统环境变量配置
E:\Anaconda
E:\Anaconda\Scripts\
E:\Anaconda\Library\bin
E:\Anaconda\Library\mingw-w64\bin
1.5 安装opencv
https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/opencv-contrib-python/注意要根据自己电脑和python版本进行选择,举个例子,cp35表示python3.5版本,下图中前两个是linux版本,后两个分别是Windows32和Windows64版本的

然后在控制台输入
pip install opencv_contrib_python-3.4.7.28-cp35-cp35m-win32.whl #具体文件名根据自己下载的修改
如果出现ERROR: Could not install packages due to an OSError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'E:\桌面\pytorchLearn\opencv_contrib_python-3.2.0.7-cp36-cp36m-w_amd64.whl’问题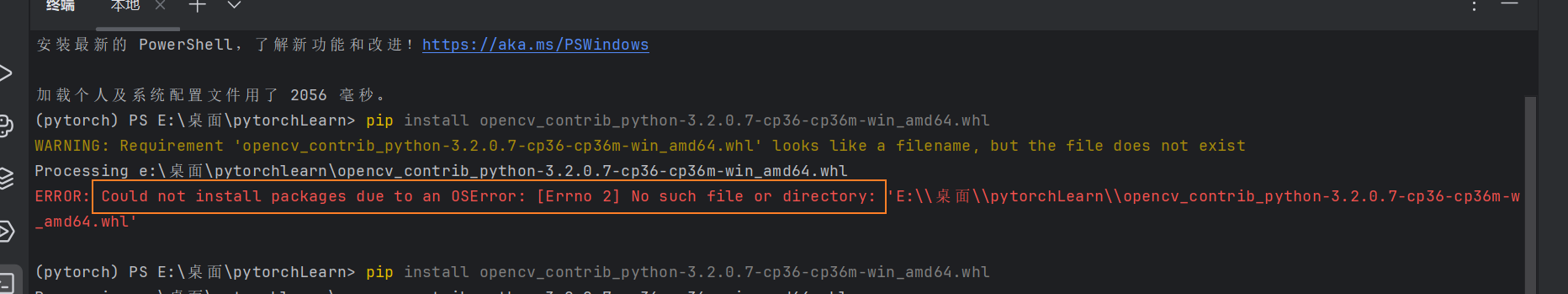
解决:把该文件放到对应的文件夹下
再次输入安装命令
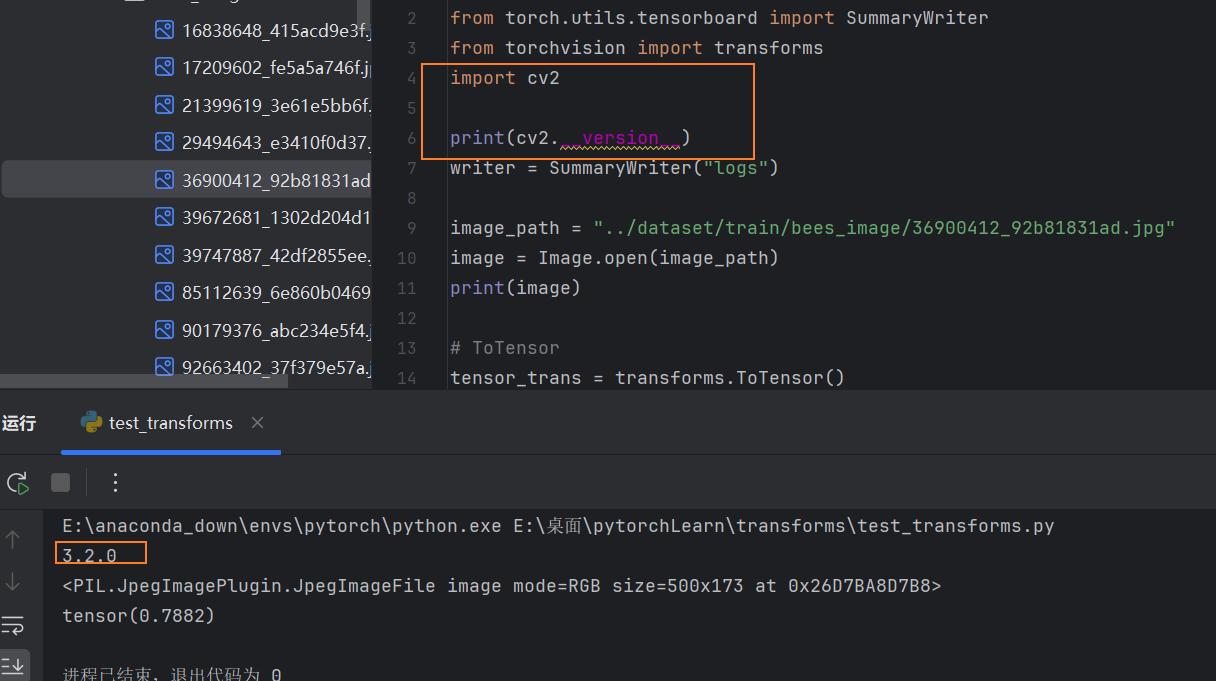
可以用相关命令,只不过pycharm没有提示
2 pytorch
2.1 安装查看gpu对应的cuda
https://blog.csdn.net/zeng001201/article/details/118437337
在电脑桌面右键NVIDIA控制面板,点击帮助->系统信息->组件
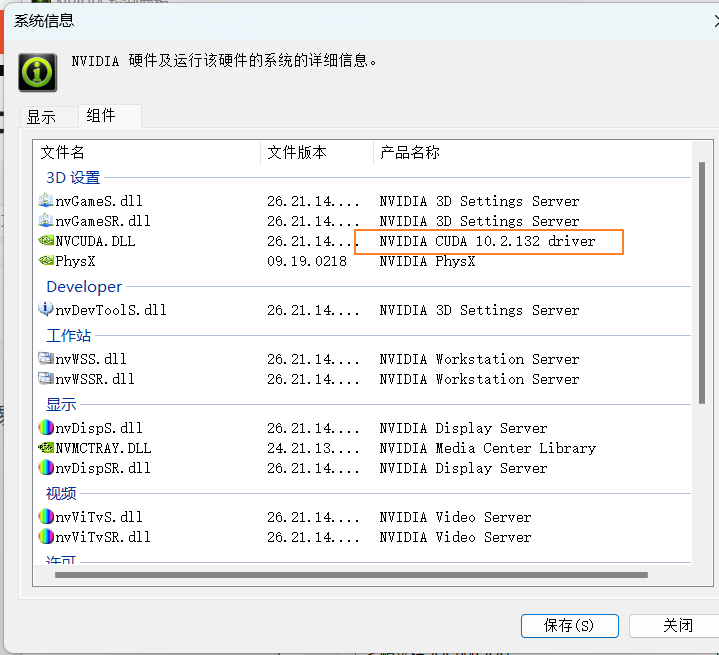
gtx 1060安装的pytorch 版本 cuda 10.2
python 3.6
conda install pytorch1.7.0 torchvision0.8.0 torchaudio==0.7.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
conda install pytorch==1.7.0 torchvision==0.8.0 torchaudio==0.7.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
conda install pytorch==1.9.0 torchvision==0.10.0 torchaudio==0.9.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
检验pytorch安装成功且可以使用gpu
python
import torch
torch.cuda.is_available()
(1)输入python 可以进入
(2)输入import torch 不报错
(3)torch.cuda.is_available()返回true
2.2 PyCharm创建、cmd及未知问题
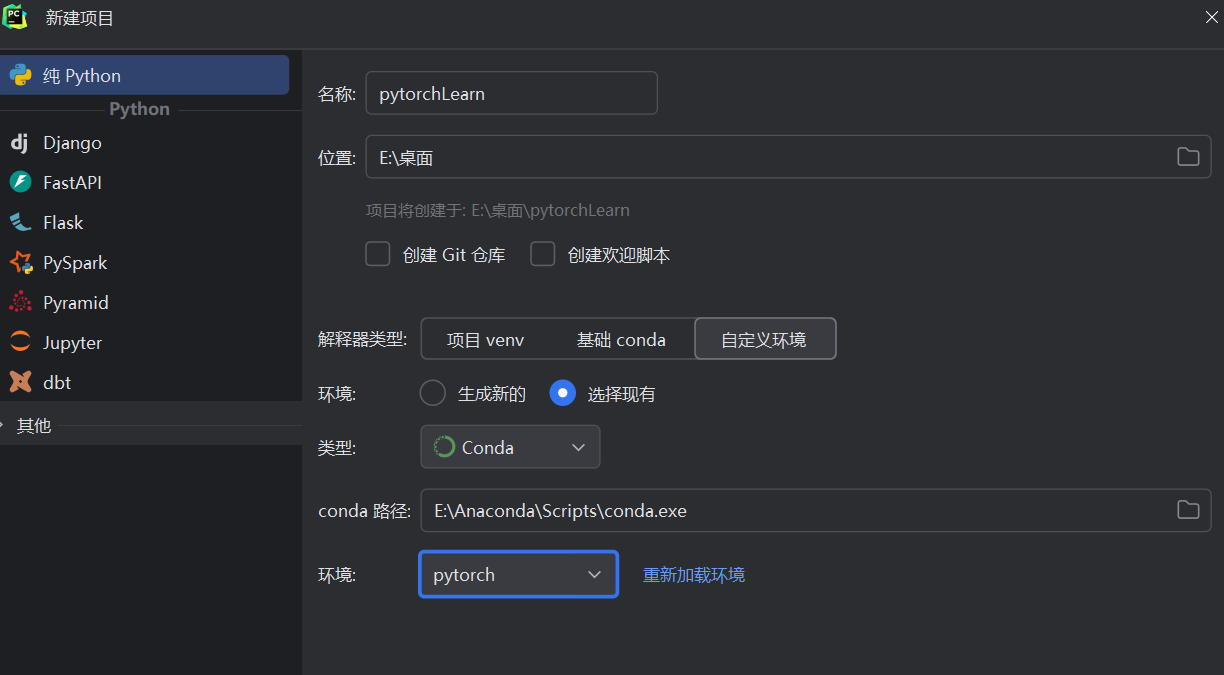
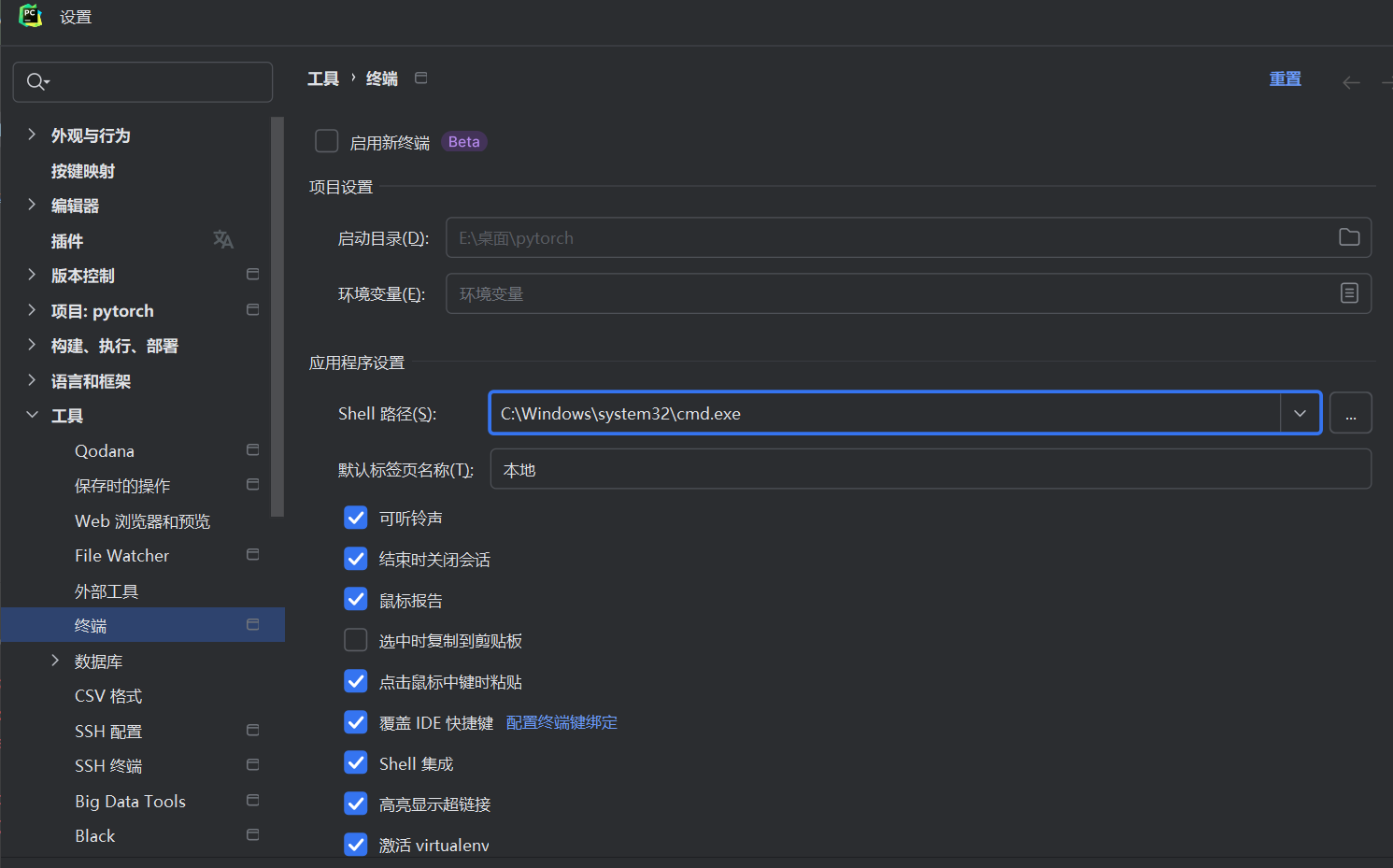
如果出现numpy的错误,先pip uninstall numpy,在install回来
2.3 蚂蚁蜜蜂分类数据集
蚂蚁蜜蜂分类数据集和下载连接https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/hymenoptera_data.zip
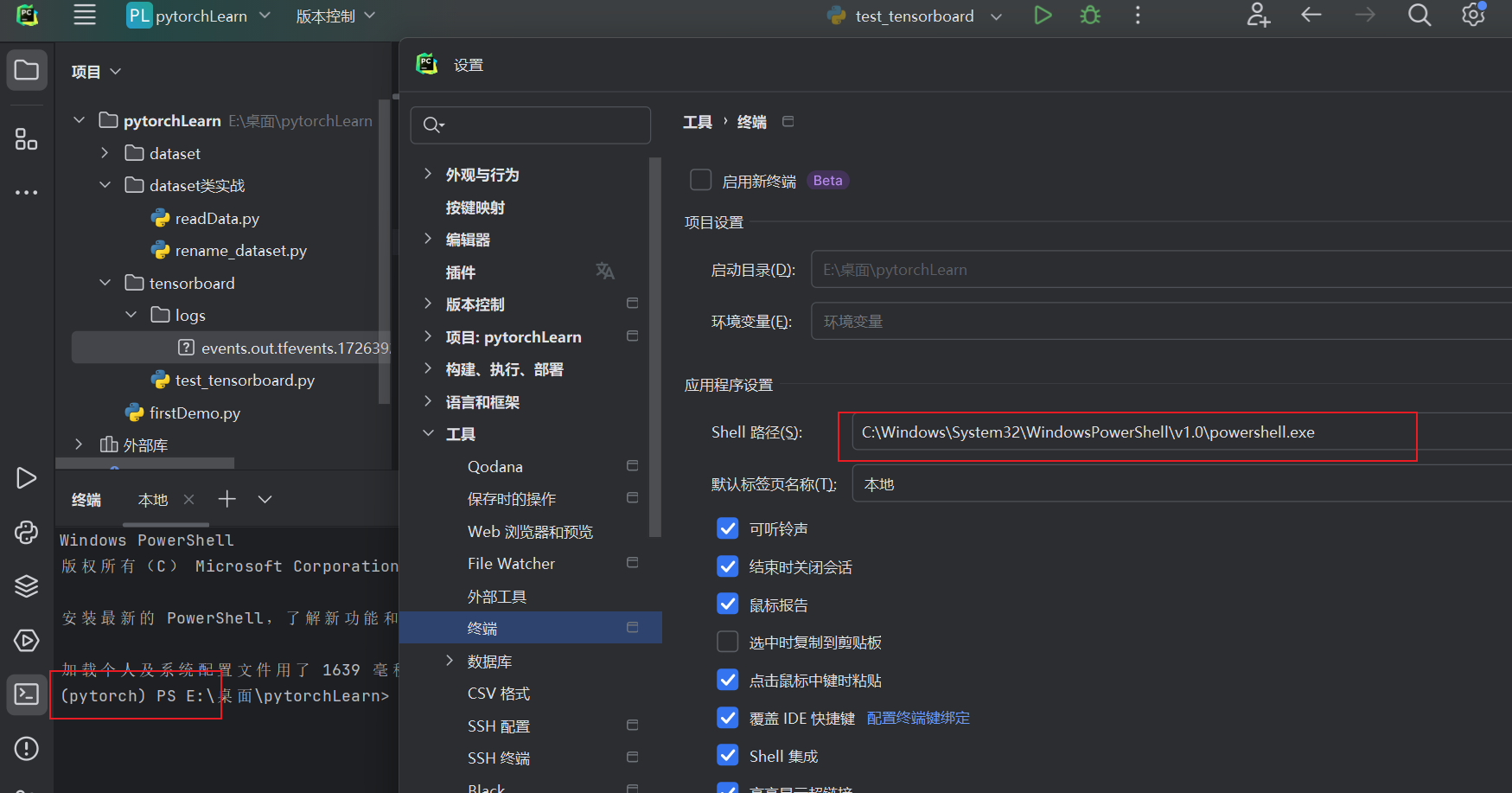
2.4 Pycharm 终端设置为pytorch环境
2.6 Dataset类实战
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from PIL import Image
import os
# help(Dataset)
class MyData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir, img_dir, label_dir):
self.root_dir = root_dir
self.img_dir = img_dir
self.label_dir = label_dir
self.image_path = os.listdir(os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.img_dir))
self.label_path = os.listdir(os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir))
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image_name = self.image_path[idx]
label_name = self.label_path[idx]
image = Image.open(os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.img_dir, image_name))
with open(os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir, label_name), 'r') as f:
label = f.readline()
return image, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_path)
root_dir = "../dataset/train"
img_dir = "ants_image"
label_dir = "ants_label"
ants_dataset = MyData(root_dir, img_dir, label_dir)
img_dir = "bees_image"
label_dir = "bees_label"
bees_dataset = MyData(root_dir, img_dir, label_dir)
train_dataset = ants_dataset + bees_dataset
# 测试
image, label = bees_dataset[1]
print(image)
print(label)
image.show()
2.7 TensorBoard的使用
2.7.1 打开logs文件夹并指定端口
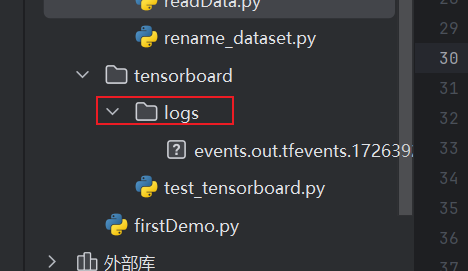
tensorboard --logdir="tensorboard\logs" --port=6007
2.7.2 图像乱的解决方式–清楚所有logs,重新运行并执行2.7.1
2.8 Transforms的使用
2.8.1 ToTensor() 转化为Tensor形式
2.8.2 Normalize() 图像归化/标准化
它会将图像的每个像素值减去给定的均值,并除以给定的标准差
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">transforms.Normalize([1, 2, 3], [3, 2, 1])</font> 的作用是:
- 均值:每个通道的均值是
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">[1, 2, 3]</font>。 - 标准差:每个通道的标准差是
<font style="color:rgb(36, 41, 47);background-color:rgb(244, 246, 248);">[3, 2, 1]</font>。 - 图像一般RGB 三通道