树莓派通过串口驱动HC-08蓝牙模块
文章目录
- 树莓派通过串口驱动HC-08蓝牙模块
- 一、HC-08蓝牙模块介绍
- 二、树莓派与蓝牙模块硬件连接
- 三、树莓派通过蓝牙控制设备
一、HC-08蓝牙模块介绍

蓝牙模块,是一种集成的蓝牙功能的PCB板,用于短距离无线通信,按照功能分为蓝牙数据模块和蓝牙语音模块,是集成蓝牙功能的芯片和基本电路的集合,用于无线网络通讯。
**HC-08蓝牙串口通信模块是新一代的基于 Bluetooth Specification V4.0 BLE蓝牙协议的数传模块**。**无线工作频段为 2.4GHz** ISM,调制方式是 GFSK。模块最大发射功率为 4dBm, 接收灵敏度-93dBm,空旷环境下和 iphone4s 可以实现 80 米超远距离通信。
产品带底板焊排针,引出6个引脚,可直接同单片机的串口进行连接,待匹配成功后,即可当成一堆串口穿透数据。
产品的参数:
1、引脚
EN(KEY)、VCC、GND、RXD、TXD、STATE共6个引脚,,STATE是蓝牙状态引出引脚,未连接时输出低电平。连接时输出高电平,EN相当于KEY引脚,可消除主机配对记忆。这两个引脚我们不必关注,按照要求连接好其余4个引脚即可。
2、电压说明
输入电压为3.2-6V,电源自带防止反接功能,但是反接不能工作;
3、状态指示
模块上有状态指示灯,配对前,主机未记录从机地址,每秒亮100ms;主机记录从机地址,每秒亮900ms;配对后,主机灯与从机灯都常亮。
4、接口电平
数据的输入输出接口RXD、TXD为3.2-6V TTL电平,可以同单片机直接连接。
5、通信距离
空旷环境下,通信距离可达80m;
6、通信格式
配对成功后,可以作为全双共串口使用,无需了解蓝牙协议,但只支持8位数据位,1位停止位,无校验位的通信格式,校验位可以更改。
7、默认值
波特率9600,蓝牙名HC-08。
二、树莓派与蓝牙模块硬件连接


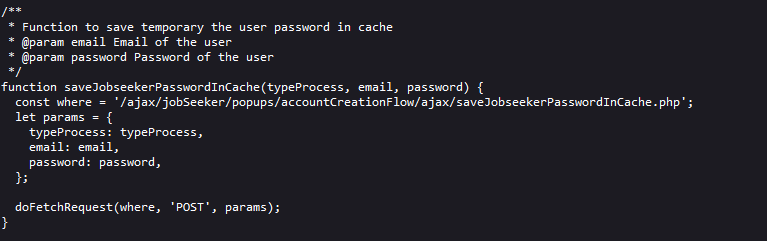
三、树莓派通过蓝牙控制设备
/* mySerialTool.h */
#ifndef __MYSERIALTOOL_H__
#define __MYSERIALTOOL_H__
/*
* @Author: <NAME> 打开指定的串口设备,并设置波特率
*
* @param device 串口设备名称,如"/dev/ttyUSB0"
* @param baud 波特率,如9600、115200等
* @return 成功返回文件描述符,失败返回-1
*/
int mySerialOpen(const char *device, const int baud);
/*
* @Author: 向指定的串口设备发送字符串
*
* @param fd 串口设备文件描述符
* @param str 要发送的字符串
* @return 无
*/
void mySerialSendString(const int fd, const char *str);
/*
* @Author: 从指定的串口设备读取字符串
*
* @param fd 串口设备文件描述符
* @param buffer 读取到的字符串存放的缓冲区
* @return 读取到的字符串的长度,失败返回-1
*/
int mySerialReadString(const int fd, char *buffer);
#endif
/* mySerialTool.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
/*打开指定的串口设备,并设置波特率*/
int mySerialOpen(const char *device, const int baud)
{
struct termios options; // 串口配置参数
speed_t myBaud; // 波特率
int status, fd; // 状态和文件描述符
//根据传入的波特率参数设置相应的波特率
switch(baud){
case 9600:
myBaud = B9600;
break;
case 115200:
myBaud = B115200;
break;
default:
printf("不支持的波特率!\n");
return -2;
}
//打开串口设备
if( (fd = open(device, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY)) == -1){
printf("无法打开串口设备\n");
return -1;
}
// 设置文件描述符的标志为读写模式
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_RDWR);
// 获取当前串口配置
tcgetattr(fd, &options);
// 设置串口为原始模式,无特殊处理
cfmakeraw(&options);
// 设置输入波特率
cfsetispeed(&options, myBaud);
// 设置输出波特率
cfsetospeed(&options, myBaud);
// 清除标志位并设置数据格式
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD);
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; // 无奇偶校验位
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; // 1个停止位
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; // 清除数据位
options.c_cflag |= CS8; // 设置为8位数据位
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG); // 非规范模式,不执行输入处理
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST; // 输出处理
// 设置读取时的超时和最小接收字符数
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 100; // 10秒超时
// 应用串口配置
tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &options);
// 使用ioctl设置串口的DTR和RTS信号
ioctl(fd, TIOCMGET, &status);
status |= TIOCM_DTR;
status |= TIOCM_RTS;
ioctl(fd, TIOCMSET, &status);
// 短暂延时
usleep(10000); // 10毫秒延时
return fd; // 返回文件描述符
}
/*向指定的串口设备发送字符串*/
void mySerialSendString(const int fd, const char *str)
{
int ret;
ret = write(fd, str, strlen(str)); // 发送字符串
if(ret == -1){
printf("串口发送失败!\n");
exit(-1); // 发送失败,退出程序
}
}
/*从指定的串口设备读取字符串*/
int mySerialReadString(const int fd, char *buffer)
{
int n_read;
n_read = read(fd, buffer, 32); // 读取串口数据
if(n_read == -1){
printf("串口读取失败!\n");
exit(-1); // 读取失败,退出程序
}
}
/* main.c */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include "mySerialTool.h"
#define LED1 26 //定义四个LED引脚
#define LED2 27
#define LED3 28
#define LED4 29
void LED_GPIO_Init()
{
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT); //设置四个LED引脚为输出模式
pinMode(LED2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED4, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED4, HIGH); //初始化四个LED为高电平
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
int n_read; //读取数据长度
char readBuf[32] = {'\0'}; //接收数据缓存
if(argc < 2){ //查看命令行参数是否存在
printf("Usage: %s /dev/ttyAMA0\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName, argv[1]); //拷贝设备名到deviceName
fd = mySerialOpen(deviceName, 9600); //打开串口
if(fd < 0){
printf("打开串口设备失败\n");
return -1;
}
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //初始化wiringPi
printf("初始化wiringPi失败\n");
return -1;
}
LED_GPIO_Init(); //初始化LED引脚
while(1){
n_read = mySerialReadString(fd, readBuf);
//printf("读到的数据为:%s\n", readBuf);
if(strstr(readBuf, "open1") != NULL){
printf("打开LED1\n");
digitalWrite(LED1, LOW);
mySerialSendString(fd, "open LED1 success\n");
}else if(strstr(readBuf, "open2") != NULL){
printf("打开LED2\n");
digitalWrite(LED2, LOW);
mySerialSendString(fd, "open LED2 success\n");
}else if(strstr(readBuf, "open3") != NULL){
printf("打开LED3\n");
digitalWrite(LED3, LOW);
mySerialSendString(fd, "open LED3 success\n");
}else if(strstr(readBuf, "open4") != NULL){
printf("打开LED4\n");
digitalWrite(LED4, LOW);
mySerialSendString(fd, "open LED4 success\n");
}else if(strstr(readBuf, "close") != NULL){
printf("关闭所有LED\n");
digitalWrite(LED1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LED4, HIGH);
mySerialSendString(fd, "close all LED success\n");
}
memset(readBuf, '\0', sizeof(readBuf));
}
return 0;
}












![[AHK]动态创建带ListBox的窗口,答选择题的界面](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f942af05b1e443548639df6fdec07516.png)