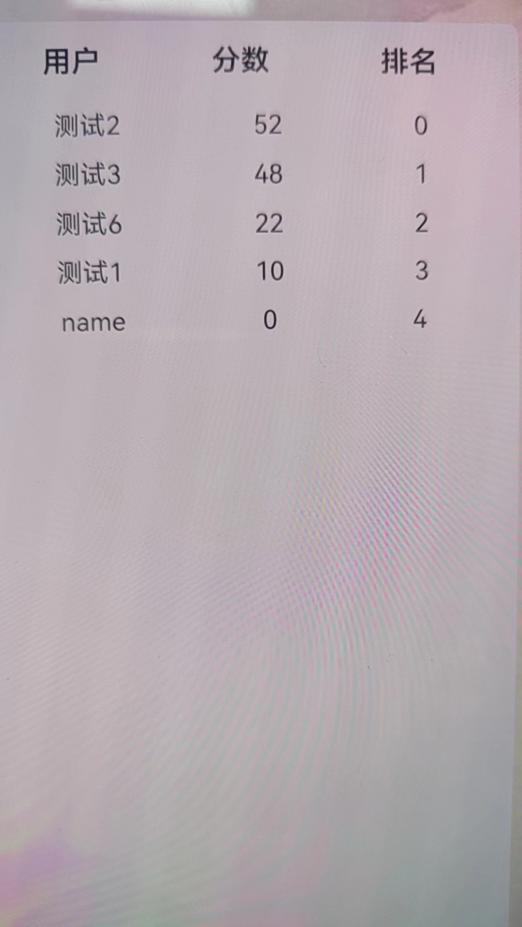
模型定义
import torch
from torch import nn
__all__ = ['UNet', 'NestedUNet']
class VGGBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, middle_channels, out_channels):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, middle_channels, 3, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(middle_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(middle_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, input_channels=3, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
nb_filter = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512]
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)#scale_factor:放大的倍数 插值
self.conv0_0 = VGGBlock(input_channels, nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.conv1_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv2_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1], nb_filter[2], nb_filter[2])
self.conv3_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[2], nb_filter[3], nb_filter[3])
self.conv4_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[3], nb_filter[4], nb_filter[4])
self.conv3_1 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[3]+nb_filter[4], nb_filter[3], nb_filter[3])
self.conv2_2 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[2]+nb_filter[3], nb_filter[2], nb_filter[2])
self.conv1_3 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1]+nb_filter[2], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv0_4 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0]+nb_filter[1], nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.final = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, input):
x0_0 = self.conv0_0(input)
x1_0 = self.conv1_0(self.pool(x0_0))
x2_0 = self.conv2_0(self.pool(x1_0))
x3_0 = self.conv3_0(self.pool(x2_0))
x4_0 = self.conv4_0(self.pool(x3_0))
x3_1 = self.conv3_1(torch.cat([x3_0, self.up(x4_0)], 1))
x2_2 = self.conv2_2(torch.cat([x2_0, self.up(x3_1)], 1))
x1_3 = self.conv1_3(torch.cat([x1_0, self.up(x2_2)], 1))
x0_4 = self.conv0_4(torch.cat([x0_0, self.up(x1_3)], 1))
output = self.final(x0_4)
return output
class NestedUNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, input_channels=3, deep_supervision=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
nb_filter = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512]
self.deep_supervision = deep_supervision
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
self.conv0_0 = VGGBlock(input_channels, nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.conv1_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv2_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1], nb_filter[2], nb_filter[2])
self.conv3_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[2], nb_filter[3], nb_filter[3])
self.conv4_0 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[3], nb_filter[4], nb_filter[4])
self.conv0_1 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0]+nb_filter[1], nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.conv1_1 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1]+nb_filter[2], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv2_1 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[2]+nb_filter[3], nb_filter[2], nb_filter[2])
self.conv3_1 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[3]+nb_filter[4], nb_filter[3], nb_filter[3])
self.conv0_2 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0]*2+nb_filter[1], nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.conv1_2 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1]*2+nb_filter[2], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv2_2 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[2]*2+nb_filter[3], nb_filter[2], nb_filter[2])
self.conv0_3 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0]*3+nb_filter[1], nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
self.conv1_3 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[1]*3+nb_filter[2], nb_filter[1], nb_filter[1])
self.conv0_4 = VGGBlock(nb_filter[0]*4+nb_filter[1], nb_filter[0], nb_filter[0])
if self.deep_supervision:
self.final1 = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.final2 = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.final3 = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
self.final4 = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
else:
self.final = nn.Conv2d(nb_filter[0], num_classes, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, input):
# print('input:',input.shape)
x0_0 = self.conv0_0(input)
# print('x0_0:',x0_0.shape)
x1_0 = self.conv1_0(self.pool(x0_0))
# print('x1_0:',x1_0.shape)
x0_1 = self.conv0_1(torch.cat([x0_0, self.up(x1_0)], 1))
# print('x0_1:',x0_1.shape)
x2_0 = self.conv2_0(self.pool(x1_0))
# print('x2_0:',x2_0.shape)
x1_1 = self.conv1_1(torch.cat([x1_0, self.up(x2_0)], 1))
# print('x1_1:',x1_1.shape)
x0_2 = self.conv0_2(torch.cat([x0_0, x0_1, self.up(x1_1)], 1))
# print('x0_2:',x0_2.shape)
x3_0 = self.conv3_0(self.pool(x2_0))
# print('x3_0:',x3_0.shape)
x2_1 = self.conv2_1(torch.cat([x2_0, self.up(x3_0)], 1))
# print('x2_1:',x2_1.shape)
x1_2 = self.conv1_2(torch.cat([x1_0, x1_1, self.up(x2_1)], 1))
# print('x1_2:',x1_2.shape)
x0_3 = self.conv0_3(torch.cat([x0_0, x0_1, x0_2, self.up(x1_2)], 1))
# print('x0_3:',x0_3.shape)
x4_0 = self.conv4_0(self.pool(x3_0))
# print('x4_0:',x4_0.shape)
x3_1 = self.conv3_1(torch.cat([x3_0, self.up(x4_0)], 1))
# print('x3_1:',x3_1.shape)
x2_2 = self.conv2_2(torch.cat([x2_0, x2_1, self.up(x3_1)], 1))
# print('x2_2:',x2_2.shape)
x1_3 = self.conv1_3(torch.cat([x1_0, x1_1, x1_2, self.up(x2_2)], 1))
# print('x1_3:',x1_3.shape)
x0_4 = self.conv0_4(torch.cat([x0_0, x0_1, x0_2, x0_3, self.up(x1_3)], 1))
# print('x0_4:',x0_4.shape)
if self.deep_supervision:
output1 = self.final1(x0_1)
output2 = self.final2(x0_2)
output3 = self.final3(x0_3)
output4 = self.final4(x0_4)
return [output1, output2, output3, output4]
else:
output = self.final(x0_4)
return output
损失函数
BCEDiceLoss:
- 这个损失函数结合了二元交叉熵损失(Binary Cross Entropy, BCE)和 Dice Loss。
- BCE 于衡量模型输出和真实标签之间的二值化像素级别匹配情况。
- Dice Loss 用于量模型输出和真实标签之间的相似度,但这里采用了一种稍微不同的计算方式,即将 Dice Loss 作为 1 减去 Dice 相似度的平均值,这样得到的损失越小,说明相似度越高。
LovaszHingeLoss:
- 这个损失函数采用的是 Lovasz-Hinge Loss,它是一种用于处理不平衡数据集的损失函数,尤其适用于像素级别的分类任务。
- Lovasz-Hinge Loss 能够更好地处理类别不平衡和边界情况,相比于交叉熵损失,在处理不平衡数据时更加稳定。
LovaszHingeLoss相关介绍
测试用例:
lovasz_losses.py 相关内容
"""
Lovasz-Softmax and Jaccard hinge loss in PyTorch
Maxim Berman 2018 ESAT-PSI KU Leuven (MIT License)
"""
from __future__ import print_function, division
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
try:
from itertools import ifilterfalse
except ImportError: # py3k
from itertools import filterfalse as ifilterfalse
def lovasz_grad(gt_sorted):
"""
Computes gradient of the Lovasz extension w.r.t sorted errors
See Alg. 1 in paper
"""
p = len(gt_sorted)
gts = gt_sorted.sum()
intersection = gts - gt_sorted.float().cumsum(0)
union = gts + (1 - gt_sorted).float().cumsum(0)
jaccard = 1. - intersection / union
if p > 1: # cover 1-pixel case
jaccard[1:p] = jaccard[1:p] - jaccard[0:-1]
return jaccard
def iou_binary(preds, labels, EMPTY=1., ignore=None, per_image=True):
"""
IoU for foreground class
binary: 1 foreground, 0 background
"""
if not per_image:
preds, labels = (preds,), (labels,)
ious = []
for pred, label in zip(preds, labels):
intersection = ((label == 1) & (pred == 1)).sum()
union = ((label == 1) | ((pred == 1) & (label != ignore))).sum()
if not union:
iou = EMPTY
else:
iou = float(intersection) / float(union)
ious.append(iou)
iou = mean(ious) # mean accross images if per_image
return 100 * iou
def iou(preds, labels, C, EMPTY=1., ignore=None, per_image=False):
"""
Array of IoU for each (non ignored) class
"""
if not per_image:
preds, labels = (preds,), (labels,)
ious = []
for pred, label in zip(preds, labels):
iou = []
for i in range(C):
if i != ignore: # The ignored label is sometimes among predicted classes (ENet - CityScapes)
intersection = ((label == i) & (pred == i)).sum()
union = ((label == i) | ((pred == i) & (label != ignore))).sum()
if not union:
iou.append(EMPTY)
else:
iou.append(float(intersection) / float(union))
ious.append(iou)
ious = [mean(iou) for iou in zip(*ious)] # mean accross images if per_image
return 100 * np.array(ious)
# --------------------------- BINARY LOSSES ---------------------------
def lovasz_hinge(logits, labels, per_image=True, ignore=None):
"""
Binary Lovasz hinge loss
logits: [B, H, W] Variable, logits at each pixel (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, binary ground truth masks (0 or 1)
per_image: compute the loss per image instead of per batch
ignore: void class id
"""
if per_image:
loss = mean(lovasz_hinge_flat(*flatten_binary_scores(log.unsqueeze(0), lab.unsqueeze(0), ignore))
for log, lab in zip(logits, labels))
else:
loss = lovasz_hinge_flat(*flatten_binary_scores(logits, labels, ignore))
return loss
def lovasz_hinge_flat(logits, labels):
"""
Binary Lovasz hinge loss
logits: [P] Variable, logits at each prediction (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [P] Tensor, binary ground truth labels (0 or 1)
ignore: label to ignore
"""
if len(labels) == 0:
# only void pixels, the gradients should be 0
return logits.sum() * 0.
signs = 2. * labels.float() - 1.
errors = (1. - logits * Variable(signs))
errors_sorted, perm = torch.sort(errors, dim=0, descending=True)
perm = perm.data
gt_sorted = labels[perm]
grad = lovasz_grad(gt_sorted)
loss = torch.dot(F.relu(errors_sorted), Variable(grad))
return loss
def flatten_binary_scores(scores, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Flattens predictions in the batch (binary case)
Remove labels equal to 'ignore'
"""
scores = scores.view(-1)
labels = labels.view(-1)
if ignore is None:
return scores, labels
valid = (labels != ignore)
vscores = scores[valid]
vlabels = labels[valid]
return vscores, vlabels
class StableBCELoss(torch.nn.modules.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(StableBCELoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, input, target):
neg_abs = - input.abs()
loss = input.clamp(min=0) - input * target + (1 + neg_abs.exp()).log()
return loss.mean()
def binary_xloss(logits, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Binary Cross entropy loss
logits: [B, H, W] Variable, logits at each pixel (between -\infty and +\infty)
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, binary ground truth masks (0 or 1)
ignore: void class id
"""
logits, labels = flatten_binary_scores(logits, labels, ignore)
loss = StableBCELoss()(logits, Variable(labels.float()))
return loss
# --------------------------- MULTICLASS LOSSES ---------------------------
def lovasz_softmax(probas, labels, classes='present', per_image=False, ignore=None):
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [B, C, H, W] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1).
Interpreted as binary (sigmoid) output with outputs of size [B, H, W].
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
classes: 'all' for all, 'present' for classes present in labels, or a list of classes to average.
per_image: compute the loss per image instead of per batch
ignore: void class labels
"""
if per_image:
loss = mean(lovasz_softmax_flat(*flatten_probas(prob.unsqueeze(0), lab.unsqueeze(0), ignore), classes=classes)
for prob, lab in zip(probas, labels))
else:
loss = lovasz_softmax_flat(*flatten_probas(probas, labels, ignore), classes=classes)
return loss
def lovasz_softmax_flat(probas, labels, classes='present'):
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [P, C] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1)
labels: [P] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
classes: 'all' for all, 'present' for classes present in labels, or a list of classes to average.
"""
if probas.numel() == 0:
# only void pixels, the gradients should be 0
return probas * 0.
C = probas.size(1)
losses = []
class_to_sum = list(range(C)) if classes in ['all', 'present'] else classes
for c in class_to_sum:
fg = (labels == c).float() # foreground for class c
if (classes == 'present' and fg.sum() == 0):
continue
if C == 1:
if len(classes) > 1:
raise ValueError('Sigmoid output possible only with 1 class')
class_pred = probas[:, 0]
else:
class_pred = probas[:, c]
errors = (Variable(fg) - class_pred).abs()
errors_sorted, perm = torch.sort(errors, 0, descending=True)
perm = perm.data
fg_sorted = fg[perm]
losses.append(torch.dot(errors_sorted, Variable(lovasz_grad(fg_sorted))))
return mean(losses)
def flatten_probas(probas, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Flattens predictions in the batch
"""
if probas.dim() == 3:
# assumes output of a sigmoid layer
B, H, W = probas.size()
probas = probas.view(B, 1, H, W)
B, C, H, W = probas.size()
probas = probas.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(-1, C) # B * H * W, C = P, C
labels = labels.view(-1)
if ignore is None:
return probas, labels
valid = (labels != ignore)
vprobas = probas[valid.nonzero().squeeze()]
vlabels = labels[valid]
return vprobas, vlabels
def xloss(logits, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Cross entropy loss
"""
return F.cross_entropy(logits, Variable(labels), ignore_index=255)
# --------------------------- HELPER FUNCTIONS ---------------------------
def isnan(x):
return x != x
def mean(l, ignore_nan=False, empty=0):
"""
nanmean compatible with generators.
"""
l = iter(l)
if ignore_nan:
l = ifilterfalse(isnan, l)
try:
n = 1
acc = next(l)
except StopIteration:
if empty == 'raise':
raise ValueError('Empty mean')
return empty
for n, v in enumerate(l, 2):
acc += v
if n == 1:
return acc
return acc / n
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from lovasz_losses import lovasz_hinge
# __all__ = ['BCEDiceLoss', 'LovaszHingeLoss']
class BCEDiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, input, target):
bce = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, target)
smooth = 1e-5
input = torch.sigmoid(input)
num = target.size(0)
input = input.view(num, -1)
target = target.view(num, -1)
intersection = (input * target)
dice = (2. * intersection.sum(1) + smooth) / (input.sum(1) + target.sum(1) + smooth)
dice = 1 - dice.sum() / num
return 0.5 * bce + dice
class LovaszHingeLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, input, target):
input = input.squeeze(1)
target = target.squeeze(1)
loss = lovasz_hinge(input, target, per_image=True)
return loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
import torch
# 假设模型输出和真实标签都是二值化的图像,大小为(1, H, W)
output = torch.tensor([[[0.3, 0.7], [0.8, 0.6]]]) # 模型输出
# output = output.round().long()
target = torch.tensor([[[0, 1], [1, 0]]],dtype=torch.float) # 真实标签
bce_dice_loss = BCEDiceLoss()
bce_dice = bce_dice_loss(output, target)
lovasz_hinge_loss = LovaszHingeLoss()
lovasz_hinge = lovasz_hinge_loss(output, target)
print("BCE Dice Loss:", bce_dice)
print("Lovasz Hinge Loss:", lovasz_hinge)
原理解释和数学公式:
BCEDiceLoss 原理:
- BCE Dice Loss 结合了二元交叉熵损失和 Dice Loss。其数学表达式如下:
B C E _ D i c e _ L o s s = 0.5 × B C E + ( 1 − D i c e ) BCE\_Dice\_Loss = 0.5 \times BCE + (1 - Dice) BCE_Dice_Loss=0.5×BCE+(1−Dice)
其中, B C E BCE BCE 表示二元交叉熵损失, D i c e Dice Dice 表示 Dice 相似度。这个损失函数的目标是最小化二元交叉熵损失和最大化 Dice 相似度,以达到更好的模型训练效果。
LovaszHingeLoss 原理:
- Lovasz-Hinge Loss 是一种非平衡数据集上的损失函数,用于像素级别的分类任务。其数学表达式如下:
L o v a s z _ H i n g e _ L o s s = lovasz_hinge ( i n p u t , t a r g e t ) Lovasz\_Hinge\_Loss = \text{lovasz\_hinge}(input, target) Lovasz_Hinge_Loss=lovasz_hinge(input,target)
这里的 lovasz_hinge \text{lovasz\_hinge} lovasz_hinge 是一个函数,用于计算 Lovasz-Hinge Loss。
训练

评估函数
metrics.py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def iou_score(output, target):
smooth = 1e-5
if torch.is_tensor(output):
output = torch.sigmoid(output).data.cpu().numpy()
if torch.is_tensor(target):
target = target.data.cpu().numpy()
output_ = output > 0.5
target_ = target > 0.5
intersection = (output_ & target_).sum()
union = (output_ | target_).sum()
return (intersection + smooth) / (union + smooth)
def dice_coef(output, target):
smooth = 1e-5
output = torch.sigmoid(output).view(-1).data.cpu().numpy()
target = target.view(-1).data.cpu().numpy()
intersection = (output * target).sum()
return (2. * intersection + smooth) / \
(output.sum() + target.sum() + smooth)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import numpy as np
import torch
# 假设模型输出和真实标签都是二值化的图像,大小为(1, H, W)
output = torch.tensor([[[0.3, 0.7], [0.8, 0.6]]]) # 模型输出
target = torch.tensor([[[0, 1], [1, 0]]]) # 真实标签
iou = iou_score(output, target)
dice = dice_coef(output, target)
print("IoU Score:", iou)
print("Dice Coefficient:", dice)

IoU(Intersection over Union)评分函数原理
IoU 是一种常用的图像分割评价指标,它衡量了模型输出与真实标签之间的重程度。其数学公式如下:
I o U = T P T P + F P + F N IoU = \frac{{TP}}{{TP + FP + FN}} IoU=TP+FP+FNTP
其中, T P TP TP 表示真正例(模型正确预测为正样本的数量), F P FP FP 表示假正例(模型错误预测为正样本的数量), F N FN FN 表示假负例(模型错误预测为负样本的数量)。
Dice Coefficient评分函数原理
Dice Coefficient 也是一种常用的图像分割评价指标,衡量模型输出和真实标签之间的相似度。其数学公式如下:
D i c e = 2 × T P 2 × T P + F P + F N Dice = \frac{{2 \times TP}}{{2 \times TP + FP + FN}} Dice=2×TP+FP+FN2×TP
其中, T P TP TP 表示真正例, F P FP FP 表示假正例, F N FN FN 表示假负例,与 IoU 公式中的定义相同。
这两个评分函数都以模型的真正例为分子,而分母则是真正例、假正例和假负例的总和,以此来衡量模型预测结果与真实标签的相似程度。公式中的平滑因子用于避免分母为零的情况,增加了数值稳定性。