- 操作系统:ubuntu22.04
- OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9
- IDE:Visual Studio Code
- 编程语言:C++11
算法描述
计算一组数组的直方图。
函数 cv::calcHist 计算一个或多个数组的直方图。用于递增直方图bin的元组的元素是从相同位置的相应输入数组中获取的。下面的示例展示了如何为彩色图像计算一个2D色调-饱和度直方图。
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat src, hsv;
if( argc != 2 || !(src=imread(argv[1], IMREAD_COLOR)).data )
return -1;
cvtColor(src, hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
// Quantize the hue to 30 levels
// and the saturation to 32 levels
int hbins = 30, sbins = 32;
int histSize[] = {hbins, sbins};
// hue varies from 0 to 179, see cvtColor
float hranges[] = { 0, 180 };
// saturation varies from 0 (black-gray-white) to
// 255 (pure spectrum color)
float sranges[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { hranges, sranges };
MatND hist;
// we compute the histogram from the 0-th and 1-st channels
int channels[] = {0, 1};
calcHist( &hsv, 1, channels, Mat(), // do not use mask
hist, 2, histSize, ranges,
true, // the histogram is uniform
false );
double maxVal=0;
minMaxLoc(hist, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0);
int scale = 10;
Mat histImg = Mat::zeros(sbins*scale, hbins*10, CV_8UC3);
for( int h = 0; h < hbins; h++ )
for( int s = 0; s < sbins; s++ )
{
float binVal = hist.at<float>(h, s);
int intensity = cvRound(binVal*255/maxVal);
rectangle( histImg, Point(h*scale, s*scale),
Point( (h+1)*scale - 1, (s+1)*scale - 1),
Scalar::all(intensity),
-1 );
}
namedWindow( "Source", 1 );
imshow( "Source", src );
namedWindow( "H-S Histogram", 1 );
imshow( "H-S Histogram", histImg );
waitKey();
}
函数原型1
void cv::calcHist
(
const Mat * images,
int nimages,
const int * channels,
InputArray mask,
OutputArray hist,
int dims,
const int * histSize,
const float ** ranges,
bool uniform = true,
bool accumulate = false
)
参数1
- 参数 images 源数组。它们都应该具有相同的深度(CV_8U, CV_16U 或 CV_32F),并且具有相同的尺寸。每一个都可以有任意数量的通道。
- 参数nimages 源图像的数量。
- 参数channels 用于计算直方图的各维通道列表。第一个数组的通道编号从 0 到 images[0].channels()-1,第二个数组的通道编号从 images[0].channels() 到 images[0].channels() + images[1].channels()-1,依此类推。
- 参数mask O可选掩码。如果矩阵不为空,它必须是一个与 images[i] 同尺寸的8位数组。非零的掩码元素标记了计入直方图的数组元素。
- 参数hist 输出直方图,它是一个稠密或稀疏的多维数组。
- 参数dims 直方图的维数,必须是正数且不大于 CV_MAX_DIMS(在当前 OpenCV 版本中等于 32)。
- 参数histSize 直方图每个维度的大小数组。
- 参数ranges 每个维度直方图bin边界的数组。当直方图是均匀的(uniform=true)时,对于每个维度 i,只需指定第0个直方图bin的下(包含)边界 L0 和最后一个直方图bin histSize[i]-1 的上(不包含)边界 UhistSize[i]−1。也就是说,在均匀直方图的情况下,ranges[i] 是一个包含2个元素的数组。当直方图不是均匀的(uniform=false)时,ranges[i] 包含 histSize[i]+1 个元素:L0, U0=L1, U1=L2, …, UhistSize[i]−2=LhistSize[i]−1, UhistSize[i]−1。不在 L0 和 UhistSize[i]−1 之间的数组元素不会被计入直方图。
- 参数uniform 指示直方图是否是均匀的标志(参见上面的描述)。
- 参数accumulate 累积标志。如果设置,那么在分配直方图开始时不将其清空。此功能使您能够从几组数组中计算单个直方图,或随时间更新直方图。
函数原型2
这是一个重载的成员函数,为了方便而提供。它与上述函数的不同之处仅在于它接受的参数。
这个变体使用 SparseMat 作为输出。
void cv::calcHist
(
const Mat * images,
int nimages,
const int * channels,
InputArray mask,
SparseMat & hist,
int dims,
const int * histSize,
const float ** ranges,
bool uniform = true,
bool accumulate = false
)
函数原型3
这是一个重载的成员函数,为了方便而提供。它与上述函数的不同之处仅在于它接受的参数。
这个变体只支持均匀直方图。
ranges 参数要么是一个空向量,要么是一个展平的向量,包含 histSize.size() * 2 个元素(即 histSize.size() 个元素对)。每对元素的第一个和第二个元素分别指定下界和上界。
void cv::calcHist
(
InputArrayOfArrays images,
const std::vector< int > & channels,
InputArray mask,
OutputArray hist,
const std::vector< int > & histSize,
const std::vector< float > & ranges,
bool accumulate = false
)
代码示例
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
int main()
{
// 加载图像
cv::Mat image = cv::imread( "/media/dingxin/data/study/OpenCV/sources/images/qiu.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR );
if ( image.empty() )
{
std::cerr << "Error: Image not found or unable to read." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 将图像从BGR转换到HSV颜色空间
cv::Mat hsv;
cvtColor( image, hsv, cv::COLOR_BGR2HSV );
// 定义直方图参数
int hue_bins = 180; // 色调范围是从0到179
int sat_bins = 256; // 饱和度范围是从0到255
int histSize[] = { hue_bins, sat_bins };
// H和S的范围
float hue_range[] = { 0, 180 };
float sat_range[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { hue_range, sat_range };
// 指定我们要计算直方图的两个通道(Hue和Saturation)
int channels[] = { 0, 1 };
// 创建一个空的直方图
cv::Mat hist;
calcHist( &hsv, 1, channels, cv::Mat(), // 图像,图像数量,通道,掩码
hist, 2, histSize, ranges, true, false ); // 2D直方图,直方图尺寸,范围
// 对直方图进行归一化,使其值在 0 到 255 之间
cv::normalize( hist, hist, 0, 255, cv::NORM_MINMAX, -1, cv::Mat() );
int hist_w = 512;
int hist_h = 400;
int bin_w = cvRound( ( double )hist_w / hue_bins );
cv::Mat histImage( hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar( 0, 0, 0 ) );
for ( int h = 0; h < hue_bins; h++ )
for ( int s = 0; s < sat_bins; s++ )
{
double binVal = hist.at< float >( h, s ); // 获取直方图值
int val = cvRound( binVal ); // 四舍五入
cv::rectangle( histImage, cv::Point( h * bin_w, hist_h ), cv::Point( ( h + 1 ) * bin_w, hist_h - val ), cv::Scalar( 255, 0, 0 ), -1 );
}
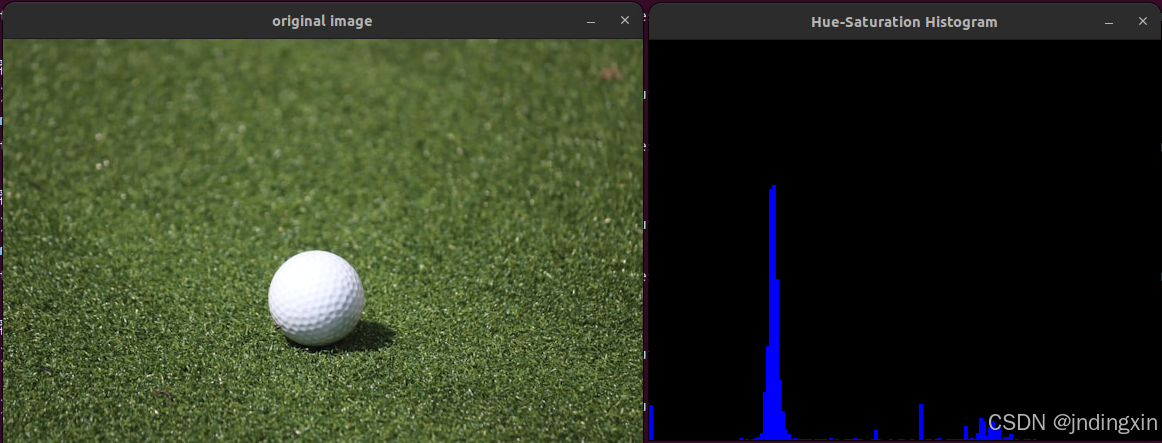
cv::imshow( "original image", image );
cv::imshow( "Hue-Saturation Histogram", histImage );
cv::waitKey( 0 );
return 0;
}
运行结果