文章目录
- shell定义和功能
- myshell.c
- GetCwd()
- GetUsrName()
- GetHostName()
- MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
- GetUserCommand()
- SplitCommand()
- Die()
- ExecuteCommand()
- GetHome()
- Cd()
- CheckBuildin()
- CheckRedir()
- myshell.c完整代码
- makefile
- 测试
- 函数和进程之间的相似性
Shell是一个功能强大的工具,它既是用户与Linux/Unix系统之间交互的桥梁,也是一种命令语言和程序设计语言。
shell定义和功能
定义:
Shell是一个用C语言编写的程序,它是用户使用Linux/Unix系统的接口。Shell提供了一个界面,通过这个界面,用户可以访问操作系统内核的服务。
功能:
作为命令语言,Shell能够交互式地解释和执行用户输入的命令。
作为程序设计语言,Shell提供了变量定义、赋值、条件判断、循环控制等高级编程功能,用户可以利用这些功能编写Shell脚本来自动化完成复杂的任务。
用下图的时间轴来表示事件的发生次序。其中时间从左向右。shell由标识为sh的方块代表,它随着时间的流逝从左向右移动。shell从用户读入字符串"ls"。shell建立一个新的进程,然后在那个进程中运行ls程序并等待那个进程结束。

然后shell读取新的一行输入,建立一个新的进程,在这个进程中运行程序 并等待这个进程结束。所以要写一个shell,需要循环以下过程:
- 获取命令行
- 解析命令行
- 建立一个子进程(fork)
- 替换子进程(execvp)
- 父进程等待子进程退出(wait)
下面我们来实现一个简易的shell
myshell.c
GetCwd()
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if(cwd==NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
功能:获取当前工作目录的路径。
实现:首先尝试从环境变量PWD中获取当前工作目录的路径。如果PWD不存在,则返回字符串"None"。
GetUsrName()
const char* GetUsrName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
功能:获取当前用户的用户名。
实现:从环境变量USER中获取当前用户的用户名。如果USER不存在,则返回字符串"None"。
GetHostName()
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* name = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
功能:获取当前主机的名称。
实现:从环境变量HOSTNAME中获取当前主机的名称。如果HOSTNAME不存在,则返回字符串"None"。
MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
const char* name = GetUsrName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
SkipPath(cwd);
const char* ManageSign = "->";
const char* CommonSign = ">";
printf("[%s@%s %s]%s ",name,hostname,cwd[1]=='\0'?"/":cwd+1,
!strcmp("root",name)?ManageSign:CommonSign);
fflush(stdout);
}
功能:构建并打印命令行提示符。
实现:结合用户名、主机名和当前工作目录,构建一个命令行提示符,并打印到标准输出。如果用户名是root,则使用特殊的提示符->,否则使用>。
GetUserCommand()
int GetUserCommand()
{
char* s = fgets(command,sizeof(command),stdin);
if(s == NULL) return -1;
int n = strlen(command);
command[n - 1]='\0';
return n - 1;
}
功能:从标准输入读取用户输入的命令。
实现:使用fgets从标准输入读取一行文本到command数组中,并去除换行符。如果读取失败,则返回-1。
SplitCommand()
void SplitCommand()
{
int index = 0;
gArgv[index++] = strtok(command,SEP);
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL,SEP));
}
功能:将用户输入的命令字符串分割成参数数组。
实现:使用strtok函数以空格为分隔符,将command字符串分割成多个参数,并存储在gArgv数组中。
Die()
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
功能:终止程序。
实现:调用exit(1)来终止程序,并返回错误码1。
ExecuteCommand()
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0) Die();
if(id == 0)
{
if(filename != NULL)
{
if(redir_type == In_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_RDONLY);
dup2(fd,0);
}
else if(redir_type == Out_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else if(redir_type == App_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else {}
}
execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
if(lastcode != 0)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode);
}
}
}
}
功能:执行用户输入的命令。
实现:首先使用fork创建一个子进程。在子进程中,根据filename和redir_type处理重定向,然后使用execvp执行命令。如果命令执行失败,则execvp会返回-1,并设置errno,此时子进程通过exit(errno)退出。在父进程中,使用waitpid等待子进程结束,并获取子进程的退出状态。
GetHome()
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
if(home== NULL) return "/";
return home;
}
功能:获取用户的主目录路径。
实现:从环境变量HOME中获取用户的主目录路径。如果HOME不存在,则返回根目录"/"。
Cd()
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();
chdir(path);
char temp[SIZE*2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
size_t temp_len = strlen(temp);
if (temp_len > (sizeof(cwd) - 5)) { // 5 for "PWD=" and the null terminator
temp_len = sizeof(cwd) - 5;
temp[temp_len] = '\0'; // 确保 temp 是以 null 终止的
}
snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);
putenv(cwd);
}
功能:改变当前工作目录。
实现:如果gArgv[1](即命令的第二个参数)存在,则尝试将其作为新路径改变当前工作目录。如果gArgv[1]为空,则尝试将HOME环境变量的值作为新路径。成功改变目录后,更新cwd环境变量以反映新的工作目录。
CheckBuildin()
bool CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
if(strcmp("cd",gArgv[0]) == 0)
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
else if(!strcmp("echo",gArgv[0])&&!strcmp(gArgv[1],"$?"))
{
yes=1;
printf("%d",lastcode);
lastcode=0;
}
return yes;
}
功能:检查命令是否为内建命令,并执行之。
实现:如果命令是cd或echo $?,则执行相应的内建命令。cd命令通过调用Cd函数实现,echo $?命令则打印上一个命令的退出状态。
CheckRedir()
void CheckRedir()
{
int pos = 0;
int n = strlen(command);
while(pos < n)
{
if(command[pos]=='>')
{
if(command[pos+1]=='>')
{
redir_type = App_Redir;
command[pos++]='\0';
pos++;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = Out_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
}
else if(command[pos]=='<')
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = In_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else pos++;
}
}
功能:检查并处理命令中的重定向。
实现:遍历命令字符串,查找重定向符号(>或<),并根据符号的类型(输入重定向、输出重定向、追加重定向)设置redir_type和filename变量。
myshell.c完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define NUM 1000
#define SIZE 64
#define SkipPath(p) do{ p+=strlen(p)-1; while(*p!='/') p--; }while(0)
#define SkipSpace(cmd, pos) do {\
while(1)\
{\
if(isspace(cmd[pos]))\
pos++;\
else break;\
}\
}while(0)
#define None_Redir 0
#define In_Redir 1
#define Out_Redir 2
#define App_Redir 3
char cwd[SIZE*2];
char* gArgv[NUM];
char command[NUM];
char* filename = NULL;
const char* SEP =" ";
int redir_type = 0;
int lastcode = 0;
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if(cwd==NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
const char* GetUsrName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* name = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if(name==NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
const char* name = GetUsrName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
SkipPath(cwd);
const char* ManageSign = "->";
const char* CommonSign = ">";
printf("[%s@%s %s]%s ",name,hostname,cwd[1]=='\0'?"/":cwd+1,
!strcmp("root",name)?ManageSign:CommonSign);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand()
{
char* s = fgets(command,sizeof(command),stdin);
if(s == NULL) return -1;
int n = strlen(command);
command[n - 1]='\0';
return n - 1;
}
void SplitCommand()
{
int index = 0;
gArgv[index++] = strtok(command,SEP);
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL,SEP));
}
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0) Die();
if(id == 0)
{
if(filename != NULL)
{
if(redir_type == In_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_RDONLY);
dup2(fd,0);
}
else if(redir_type == Out_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else if(redir_type == App_Redir)
{
int fd = open(filename,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
dup2(fd,1);
}
else {}
}
execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
if(lastcode != 0)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode);
}
}
}
}
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
if(home== NULL) return "/";
return home;
}
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if(path == NULL) path = GetHome();
chdir(path);
char temp[SIZE*2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
size_t temp_len = strlen(temp);
if (temp_len > (sizeof(cwd) - 5)) { // 5 for "PWD=" and the null terminator
temp_len = sizeof(cwd) - 5;
temp[temp_len] = '\0'; // 确保 temp 是以 null 终止的
}
snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",temp);
putenv(cwd);
}
bool CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
if(strcmp("cd",gArgv[0]) == 0)
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
else if(!strcmp("echo",gArgv[0])&&!strcmp(gArgv[1],"$?"))
{
yes=1;
printf("%d",lastcode);
lastcode=0;
}
return yes;
}
void CheckRedir()
{
int pos = 0;
int n = strlen(command);
while(pos < n)
{
if(command[pos]=='>')
{
if(command[pos+1]=='>')
{
redir_type = App_Redir;
command[pos++]='\0';
pos++;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = Out_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
}
else if(command[pos]=='<')
{
command[pos++]='\0';
redir_type = In_Redir;
SkipSpace(command,pos);
filename = command + pos;
}
else pos++;
}
}
int main()
{
while(1)
{
//命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//获取用户字符串
int n = GetUserCommand();
if(n<=0) continue;
//检查重定向
CheckRedir();
//切割字符
SplitCommand();
//内建命令
n = CheckBuildin();
if(n) continue;
//执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
filename = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
makefile
mytest:myshell.c
gcc -o $@ $^
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f mytest
测试


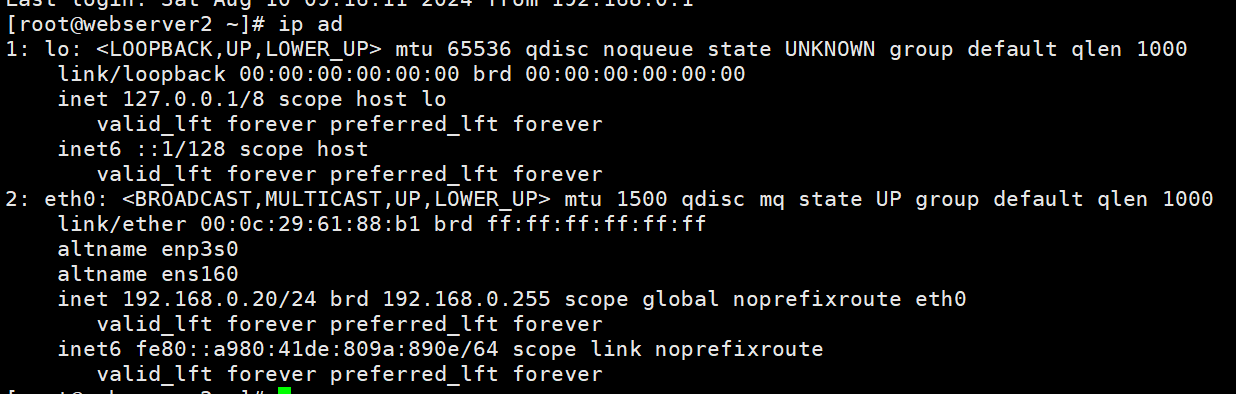
make后出现了目标程序mytest*
运行一下

mytest运行后自主shell出现了,测试一下功能

ctrl c推出自主shell

函数和进程之间的相似性
exec/exit就像call/return
一个C程序有很多函数组成。一个函数可以调用另外一个函数,同时传递给它一些参数。被调用的函数执行一定的
操作,然后返回一个值。每个函数都有他的局部变量,不同的函数通过call/return系统进行通信。
这种通过参数和返回值在拥有私有数据的函数间通信的模式是结构化程序设计的基础。Linux鼓励将这种应用于程
序之内的模式扩展到程序之间。如下图:

一个C程序可以fork/exec另一个程序,并传给它一些参数。这个被调用的程序执行一定的操作,然后通过exit(n)来返回值。调用它的进程可以通过wait(&ret)来获取exit的返回值。






![[米联客-XILINX-H3_CZ08_7100] FPGA程序设计基础实验连载-26浅谈XILINX FIFO的基本使用](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3c582fd8da444ddba8e798b26e0859b8.png)