秋招面试专栏推荐 :深度学习算法工程师面试问题总结【百面算法工程师】——点击即可跳转
💡💡💡本专栏所有程序均经过测试,可成功执行💡💡💡
专栏目录 :《YOLOv8改进有效涨点》专栏介绍 & 专栏目录 | 目前已有100+篇内容,内含各种Head检测头、损失函数Loss、Backbone、Neck、NMS等创新点改进——点击即可跳转
结构重参数化技术能提升深度学习模型性能而不增加推理成本。卷积重参数化(OREPA)通过将复杂训练模块简化为单次卷积,显著降低了训练成本。本文将介绍将C2f和OREPA融合改进提升目标检测的性能。文章在介绍主要的原理后,将手把手教学如何进行模块的代码添加和修改,并将修改后的完整代码放在文章的最后,方便大家一键运行,小白也可轻松上手实践。以帮助您更好地学习深度学习目标检测YOLO系列的挑战。
专栏地址:YOLOv8改进——更新各种有效涨点方法——点击即可跳转
目录
1.原理
2. 将C2f_OREPA添加到yolov8网络中
2.1 C2f_OREPA代码实现
2.2 C2f_OREPA的神经网络模块代码解析
2.3 更改init.py文件
2.4 添加yaml文件
2.5 注册模块
2.6 执行程序
3. 完整代码分享
4. GFLOPs
5. 进阶
6. 总结
1.原理

论文地址:Online Convolutional Re-parameterization——点击即可跳转
官方代码:官方代码仓库——点击即可跳转
OREPA(Online Convolutional Re-parameterization)是一种旨在提高深度模型训练效率的结构化重参数化方法。它通过将复杂的训练时块压缩为单个卷积层,从而显著降低训练开销。 主要原理:
-
块线性化 (Block Linearization):
-
去除训练时块中的非线性归一化层,引入线性缩放层。
-
线性缩放层具有与归一化层相似的性质,即它们可以多样化不同分支的优化方向。
-
线性缩放层是线性的,可以在训练过程中合并到卷积层中。
-
-
块压缩 (Block Squeezing):
-
将线性块简化为单个卷积层。
-
通过合并中间特征图上的操作,将计算和内存开销从 O(H × W) 降低到 O(KH × KW)。
-
其中 (H, W) 和 (KH, KW) 分别是特征图和卷积核的空间形状。 优势:
-
-
降低训练成本: 通过减少中间计算层和缓冲特征图的存储,OREPA 显著降低了训练开销。
-
提高训练速度: OREPA 可以将训练速度提高 1.5 倍到 2.3 倍。
-
提高模型性能: OREPA-ResNet 和 OREPA-VGG 在 ImageNet 上优于之前的重参数化方法。
-
探索更复杂的重参数化拓扑: OREPA 的高效性使得探索更复杂和可能更强大的重参数化拓扑成为可能。 总结: OREPA 通过将复杂的训练时块压缩为单个卷积层,有效地降低了训练开销,同时保持了高精度。它为训练大规模神经网络和探索更强大的重参数化拓扑提供了一种经济高效的方法。
2. 将C2f_OREPA添加到yolov8网络中
2.1 C2f_OREPA代码实现
关键步骤一: 将下面代码粘贴到在/ultralytics/ultralytics/nn/modules/block.py中,并在该文件的__all__中添加“C2f_OREPA”
import math
import torch.nn.init as init
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
def transI_fusebn(kernel, bn):
gamma = bn.weight
std = (bn.running_var + bn.eps).sqrt()
return kernel * ((gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)), bn.bias - bn.running_mean * gamma / std
class SEAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512,reduction=16):
super().__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
def transVI_multiscale(kernel, target_kernel_size):
H_pixels_to_pad = (target_kernel_size - kernel.size(2)) // 2
W_pixels_to_pad = (target_kernel_size - kernel.size(3)) // 2
return F.pad(kernel, [W_pixels_to_pad, W_pixels_to_pad, H_pixels_to_pad, H_pixels_to_pad])
class OREPA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=None,
groups=1,
dilation=1,
act=True,
internal_channels_1x1_3x3=None,
deploy=False,
single_init=False,
weight_only=False,
init_hyper_para=1.0, init_hyper_gamma=1.0):
super(OREPA, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy
self.nonlinear = Conv.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
self.weight_only = weight_only
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.groups = groups
self.stride = stride
padding = autopad(kernel_size, padding, dilation)
self.padding = padding
self.dilation = dilation
if deploy:
self.orepa_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
else:
self.branch_counter = 0
self.weight_orepa_origin = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), kernel_size, kernel_size))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_origin, a=math.sqrt(0.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
self.weight_orepa_avg_conv = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1,
1))
self.weight_orepa_pfir_conv = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1,
1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_avg_conv, a=0.0)
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_pfir_conv, a=0.0)
self.register_buffer(
'weight_orepa_avg_avg',
torch.ones(kernel_size,
kernel_size).mul(1.0 / kernel_size / kernel_size))
self.branch_counter += 1
self.branch_counter += 1
self.weight_orepa_1x1 = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1,
1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_1x1, a=0.0)
self.branch_counter += 1
if internal_channels_1x1_3x3 is None:
internal_channels_1x1_3x3 = in_channels if groups <= 4 else 2 * in_channels
if internal_channels_1x1_3x3 == in_channels:
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1 = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros(in_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1, 1))
id_value = np.zeros(
(in_channels, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1, 1))
for i in range(in_channels):
id_value[i, i % int(in_channels / self.groups), 0, 0] = 1
id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(id_value).type_as(
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1)
self.register_buffer('id_tensor', id_tensor)
else:
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1 = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros(internal_channels_1x1_3x3,
int(in_channels / self.groups), 1, 1))
id_value = np.zeros(
(internal_channels_1x1_3x3, int(in_channels / self.groups), 1, 1))
for i in range(internal_channels_1x1_3x3):
id_value[i, i % int(in_channels / self.groups), 0, 0] = 1
id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(id_value).type_as(
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1)
self.register_buffer('id_tensor', id_tensor)
#init.kaiming_uniform_(
#self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1, a=math.sqrt(0.0))
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2 = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_channels,
int(internal_channels_1x1_3x3 / self.groups),
kernel_size, kernel_size))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2, a=math.sqrt(0.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
expand_ratio = 8
self.weight_orepa_gconv_dw = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(in_channels * expand_ratio, 1, kernel_size,
kernel_size))
self.weight_orepa_gconv_pw = nn.Parameter(
torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels * expand_ratio / self.groups), 1, 1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_gconv_dw, a=math.sqrt(0.0))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_orepa_gconv_pw, a=math.sqrt(0.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
self.vector = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.branch_counter, self.out_channels))
if weight_only is False:
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.out_channels)
self.fre_init()
init.constant_(self.vector[0, :], 0.25 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #origin
init.constant_(self.vector[1, :], 0.25 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #avg
init.constant_(self.vector[2, :], 0.0 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #prior
init.constant_(self.vector[3, :], 0.5 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #1x1_kxk
init.constant_(self.vector[4, :], 1.0 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #1x1
init.constant_(self.vector[5, :], 0.5 * math.sqrt(init_hyper_gamma)) #dws_conv
self.weight_orepa_1x1.data = self.weight_orepa_1x1.mul(init_hyper_para)
self.weight_orepa_origin.data = self.weight_orepa_origin.mul(init_hyper_para)
self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2.data = self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2.mul(init_hyper_para)
self.weight_orepa_avg_conv.data = self.weight_orepa_avg_conv.mul(init_hyper_para)
self.weight_orepa_pfir_conv.data = self.weight_orepa_pfir_conv.mul(init_hyper_para)
self.weight_orepa_gconv_dw.data = self.weight_orepa_gconv_dw.mul(math.sqrt(init_hyper_para))
self.weight_orepa_gconv_pw.data = self.weight_orepa_gconv_pw.mul(math.sqrt(init_hyper_para))
if single_init:
# Initialize the vector.weight of origin as 1 and others as 0. This is not the default setting.
self.single_init()
def fre_init(self):
prior_tensor = torch.Tensor(self.out_channels, self.kernel_size,
self.kernel_size)
half_fg = self.out_channels / 2
for i in range(self.out_channels):
for h in range(3):
for w in range(3):
if i < half_fg:
prior_tensor[i, h, w] = math.cos(math.pi * (h + 0.5) *
(i + 1) / 3)
else:
prior_tensor[i, h, w] = math.cos(math.pi * (w + 0.5) *
(i + 1 - half_fg) / 3)
self.register_buffer('weight_orepa_prior', prior_tensor)
def weight_gen(self):
weight_orepa_origin = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw',
self.weight_orepa_origin,
self.vector[0, :])
weight_orepa_avg = torch.einsum('oihw,hw->oihw', self.weight_orepa_avg_conv, self.weight_orepa_avg_avg)
weight_orepa_avg = torch.einsum(
'oihw,o->oihw',
torch.einsum('oi,hw->oihw', self.weight_orepa_avg_conv.squeeze(3).squeeze(2),
self.weight_orepa_avg_avg), self.vector[1, :])
weight_orepa_pfir = torch.einsum(
'oihw,o->oihw',
torch.einsum('oi,ohw->oihw', self.weight_orepa_pfir_conv.squeeze(3).squeeze(2),
self.weight_orepa_prior), self.vector[2, :])
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1 = None
if hasattr(self, 'weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1'):
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1 = (self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1 +
self.id_tensor).squeeze(3).squeeze(2)
elif hasattr(self, 'weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1'):
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1 = self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1.squeeze(3).squeeze(2)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2 = self.weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2
if self.groups > 1:
g = self.groups
t, ig = weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1.size()
o, tg, h, w = weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2.size()
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1 = weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1.view(
g, int(t / g), ig)
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2 = weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2.view(
g, int(o / g), tg, h, w)
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('gti,gothw->goihw',
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1,
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2).reshape(
o, ig, h, w)
else:
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('ti,othw->oihw',
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1,
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2)
weight_orepa_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', weight_orepa_1x1_kxk, self.vector[3, :])
weight_orepa_1x1 = 0
if hasattr(self, 'weight_orepa_1x1'):
weight_orepa_1x1 = transVI_multiscale(self.weight_orepa_1x1,
self.kernel_size)
weight_orepa_1x1 = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', weight_orepa_1x1,
self.vector[4, :])
weight_orepa_gconv = self.dwsc2full(self.weight_orepa_gconv_dw,
self.weight_orepa_gconv_pw,
self.in_channels, self.groups)
weight_orepa_gconv = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', weight_orepa_gconv,
self.vector[5, :])
weight = weight_orepa_origin + weight_orepa_avg + weight_orepa_1x1 + weight_orepa_1x1_kxk + weight_orepa_pfir + weight_orepa_gconv
return weight
def dwsc2full(self, weight_dw, weight_pw, groups, groups_conv=1):
t, ig, h, w = weight_dw.size()
o, _, _, _ = weight_pw.size()
tg = int(t / groups)
i = int(ig * groups)
ogc = int(o / groups_conv)
groups_gc = int(groups / groups_conv)
weight_dw = weight_dw.view(groups_conv, groups_gc, tg, ig, h, w)
weight_pw = weight_pw.squeeze().view(ogc, groups_conv, groups_gc, tg)
weight_dsc = torch.einsum('cgtihw,ocgt->cogihw', weight_dw, weight_pw)
return weight_dsc.reshape(o, int(i/groups_conv), h, w)
def forward(self, inputs=None):
if hasattr(self, 'orepa_reparam'):
return self.nonlinear(self.orepa_reparam(inputs))
weight = self.weight_gen()
if self.weight_only is True:
return weight
out = F.conv2d(
inputs,
weight,
bias=None,
stride=self.stride,
padding=self.padding,
dilation=self.dilation,
groups=self.groups)
return self.nonlinear(self.bn(out))
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
return transI_fusebn(self.weight_gen(), self.bn)
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'or1x1_reparam'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.orepa_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.kernel_size, stride=self.stride,
padding=self.padding, dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups, bias=True)
self.orepa_reparam.weight.data = kernel
self.orepa_reparam.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_origin')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_1x1')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv2')
if hasattr(self, 'weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1'):
self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_idconv1')
elif hasattr(self, 'weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1'):
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_1x1_kxk_conv1')
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_avg_avg')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_avg_conv')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_pfir_conv')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_prior')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_gconv_dw')
self.__delattr__('weight_orepa_gconv_pw')
self.__delattr__('bn')
self.__delattr__('vector')
def init_gamma(self, gamma_value):
init.constant_(self.vector, gamma_value)
def single_init(self):
self.init_gamma(0.0)
init.constant_(self.vector[0, :], 1.0)
class OREPA_LargeConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1,
stride=1, padding=None, groups=1, dilation=1, act=True, deploy=False):
super(OREPA_LargeConv, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size % 2 == 1 and kernel_size > 3
padding = autopad(kernel_size, padding, dilation)
self.stride = stride
self.padding = padding
self.layers = int((kernel_size - 1) / 2)
self.groups = groups
self.dilation = dilation
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
internal_channels = out_channels
self.nonlinear = Conv.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
if deploy:
self.or_large_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
else:
for i in range(self.layers):
if i == 0:
self.__setattr__('weight'+str(i), OREPA(in_channels, internal_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, groups=groups, weight_only=True))
elif i == self.layers - 1:
self.__setattr__('weight'+str(i), OREPA(internal_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=self.stride, padding=1, weight_only=True))
else:
self.__setattr__('weight'+str(i), OREPA(internal_channels, internal_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, weight_only=True))
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
#self.unfold = torch.nn.Unfold(kernel_size=3, dilation=1, padding=2, stride=1)
def weight_gen(self):
weight = getattr(self, 'weight'+str(0)).weight_gen().transpose(0, 1)
for i in range(self.layers - 1):
weight2 = getattr(self, 'weight'+str(i+1)).weight_gen()
weight = F.conv2d(weight, weight2, groups=self.groups, padding=2)
return weight.transpose(0, 1)
'''
weight = getattr(self, 'weight'+str(0))(inputs=None).transpose(0, 1)
for i in range(self.layers - 1):
weight = self.unfold(weight)
weight2 = getattr(self, 'weight'+str(i+1))(inputs=None)
weight = torch.einsum('akl,bk->abl', weight, weight2.view(weight2.size(0), -1))
k = i * 2 + 5
weight = weight.view(weight.size(0), weight.size(1), k, k)
return weight.transpose(0, 1)
'''
def forward(self, inputs):
if hasattr(self, 'or_large_reparam'):
return self.nonlinear(self.or_large_reparam(inputs))
weight = self.weight_gen()
out = F.conv2d(inputs, weight, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding, dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups)
return self.nonlinear(self.bn(out))
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
return transI_fusebn(self.weight_gen(), self.bn)
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'or_large_reparam'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.or_large_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.kernel_size, stride=self.stride,
padding=self.padding, dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups, bias=True)
self.or_large_reparam.weight.data = kernel
self.or_large_reparam.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
for i in range(self.layers):
self.__delattr__('weight'+str(i))
self.__delattr__('bn')
class ConvBN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, deploy=False, nonlinear=None):
super().__init__()
if nonlinear is None:
self.nonlinear = nn.Identity()
else:
self.nonlinear = nonlinear
if deploy:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
else:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
if hasattr(self, 'bn'):
return self.nonlinear(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
else:
return self.nonlinear(self.conv(x))
def switch_to_deploy(self):
kernel, bias = transI_fusebn(self.conv.weight, self.bn)
conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.conv.in_channels, out_channels=self.conv.out_channels, kernel_size=self.conv.kernel_size,
stride=self.conv.stride, padding=self.conv.padding, dilation=self.conv.dilation, groups=self.conv.groups, bias=True)
conv.weight.data = kernel
conv.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('conv')
self.__delattr__('bn')
self.conv = conv
class OREPA_3x3_RepVGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
stride=1, padding=None, groups=1, dilation=1, act=True,
internal_channels_1x1_3x3=None,
deploy=False):
super(OREPA_3x3_RepVGG, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy
self.nonlinear = Conv.default_act if act is True else act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity()
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.groups = groups
padding = autopad(kernel_size, padding, dilation)
assert padding == kernel_size // 2
self.stride = stride
self.padding = padding
self.dilation = dilation
self.branch_counter = 0
self.weight_rbr_origin = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels/self.groups), kernel_size, kernel_size))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_origin, a=math.sqrt(1.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
if groups < out_channels:
self.weight_rbr_avg_conv = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels/self.groups), 1, 1))
self.weight_rbr_pfir_conv = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(in_channels/self.groups), 1, 1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_avg_conv, a=1.0)
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_pfir_conv, a=1.0)
self.weight_rbr_avg_conv.data
self.weight_rbr_pfir_conv.data
self.register_buffer('weight_rbr_avg_avg', torch.ones(kernel_size, kernel_size).mul(1.0/kernel_size/kernel_size))
self.branch_counter += 1
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.branch_counter += 1
if internal_channels_1x1_3x3 is None:
internal_channels_1x1_3x3 = in_channels if groups < out_channels else 2 * in_channels # For mobilenet, it is better to have 2X internal channels
if internal_channels_1x1_3x3 == in_channels:
self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_idconv1 = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(in_channels, int(in_channels/self.groups), 1, 1))
id_value = np.zeros((in_channels, int(in_channels/self.groups), 1, 1))
for i in range(in_channels):
id_value[i, i % int(in_channels/self.groups), 0, 0] = 1
id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(id_value).type_as(self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_idconv1)
self.register_buffer('id_tensor', id_tensor)
else:
self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1 = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(internal_channels_1x1_3x3, int(in_channels/self.groups), 1, 1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1, a=math.sqrt(1.0))
self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2 = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, int(internal_channels_1x1_3x3/self.groups), kernel_size, kernel_size))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2, a=math.sqrt(1.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
expand_ratio = 8
self.weight_rbr_gconv_dw = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(in_channels*expand_ratio, 1, kernel_size, kernel_size))
self.weight_rbr_gconv_pw = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels, in_channels*expand_ratio, 1, 1))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_gconv_dw, a=math.sqrt(1.0))
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.weight_rbr_gconv_pw, a=math.sqrt(1.0))
self.branch_counter += 1
if out_channels == in_channels and stride == 1:
self.branch_counter += 1
self.vector = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.branch_counter, self.out_channels))
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.fre_init()
init.constant_(self.vector[0, :], 0.25) #origin
init.constant_(self.vector[1, :], 0.25) #avg
init.constant_(self.vector[2, :], 0.0) #prior
init.constant_(self.vector[3, :], 0.5) #1x1_kxk
init.constant_(self.vector[4, :], 0.5) #dws_conv
def fre_init(self):
prior_tensor = torch.Tensor(self.out_channels, self.kernel_size, self.kernel_size)
half_fg = self.out_channels/2
for i in range(self.out_channels):
for h in range(3):
for w in range(3):
if i < half_fg:
prior_tensor[i, h, w] = math.cos(math.pi*(h+0.5)*(i+1)/3)
else:
prior_tensor[i, h, w] = math.cos(math.pi*(w+0.5)*(i+1-half_fg)/3)
self.register_buffer('weight_rbr_prior', prior_tensor)
def weight_gen(self):
weight_rbr_origin = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', self.weight_rbr_origin, self.vector[0, :])
weight_rbr_avg = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', torch.einsum('oihw,hw->oihw', self.weight_rbr_avg_conv, self.weight_rbr_avg_avg), self.vector[1, :])
weight_rbr_pfir = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', torch.einsum('oihw,ohw->oihw', self.weight_rbr_pfir_conv, self.weight_rbr_prior), self.vector[2, :])
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1 = None
if hasattr(self, 'weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_idconv1'):
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1 = (self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_idconv1 + self.id_tensor).squeeze()
elif hasattr(self, 'weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1'):
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1 = self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1.squeeze()
else:
raise NotImplementedError
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2 = self.weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2
if self.groups > 1:
g = self.groups
t, ig = weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1.size()
o, tg, h, w = weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2.size()
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1 = weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1.view(g, int(t/g), ig)
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2 = weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2.view(g, int(o/g), tg, h, w)
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('gti,gothw->goihw', weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1, weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2).view(o, ig, h, w)
else:
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('ti,othw->oihw', weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv1, weight_rbr_1x1_kxk_conv2)
weight_rbr_1x1_kxk = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', weight_rbr_1x1_kxk, self.vector[3, :])
weight_rbr_gconv = self.dwsc2full(self.weight_rbr_gconv_dw, self.weight_rbr_gconv_pw, self.in_channels)
weight_rbr_gconv = torch.einsum('oihw,o->oihw', weight_rbr_gconv, self.vector[4, :])
weight = weight_rbr_origin + weight_rbr_avg + weight_rbr_1x1_kxk + weight_rbr_pfir + weight_rbr_gconv
return weight
def dwsc2full(self, weight_dw, weight_pw, groups):
t, ig, h, w = weight_dw.size()
o, _, _, _ = weight_pw.size()
tg = int(t/groups)
i = int(ig*groups)
weight_dw = weight_dw.view(groups, tg, ig, h, w)
weight_pw = weight_pw.squeeze().view(o, groups, tg)
weight_dsc = torch.einsum('gtihw,ogt->ogihw', weight_dw, weight_pw)
return weight_dsc.view(o, i, h, w)
def forward(self, inputs):
weight = self.weight_gen()
out = F.conv2d(inputs, weight, bias=None, stride=self.stride, padding=self.padding, dilation=self.dilation, groups=self.groups)
return self.nonlinear(self.bn(out))
class Bottleneck_OREPA(Bottleneck):
"""Standard bottleneck with OREPA."""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, k=(3, 3), e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, kernels, expand
super().__init__(c1, c2, shortcut, g, k, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
if k[0] == 1:
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_)
else:
self.cv1 = OREPA(c1, c_, k[0])
self.cv2 = OREPA(c_, c2, k[1], groups=g)
class C3_OREPA(C3):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck_OREPA(c_, c_, shortcut, g, k=(1, 3), e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
class C2f_OREPA(C2f):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(Bottleneck_OREPA(self.c, self.c, shortcut, g, k=(3, 3), e=1.0) for _ in range(n))
2.2 C2f_OREPA的神经网络模块代码解析
-
这段代码定义了两个类
Bottleneck_OREPA和C2f_OREPA,它们分别是现有类Bottleneck和C2f的扩展版本。这些类的主要作用是在标准的瓶颈架构中集成一个名为OREPA的模块。以下是对代码的详细解析:1.
Bottleneck_OREPA类这个类继承自
Bottleneck类,并通过引入OREPA模块来修改其行为。构造函数(
__init__方法)-
参数说明:
-
c1: 输入通道数。 -
c2: 输出通道数。 -
shortcut: 是否使用快捷连接(残差连接),布尔值。 -
g: 卷积操作中的组数。 -
k: 一个包含两个卷积核大小的元组。 -
e: 扩展系数,用于计算隐藏层通道数。
-
-
操作流程:
-
首先,通过
super()调用父类Bottleneck的构造函数。 -
接着,根据公式
c_ = int(c2 * e)计算隐藏层的通道数c_。 -
根据
k[0]的值,决定self.cv1是用标准卷积(Conv)还是OREPA模块来初始化。如果k[0] == 1,使用Conv,否则使用OREPA。 -
self.cv2总是使用OREPA模块进行初始化。
-
2.
C2f_OREPA类这个类继承自
C2f类,并通过使用Bottleneck_OREPA模块来替换标准的瓶颈模块,进一步修改其行为。构造函数(
__init__方法)-
参数说明:
-
c1: 输入通道数。 -
c2: 输出通道数。 -
n: 块中瓶颈模块的数量。 -
shortcut: 是否使用快捷连接,布尔值。 -
g: 卷积操作中的组数。 -
e: 扩展系数,用于计算隐藏层通道数。
-
-
操作流程:
-
首先,通过
super()调用父类C2f的构造函数。 -
然后,创建一个包含
n个Bottleneck_OREPA模块的列表,并将其赋值给self.m。每个Bottleneck_OREPA模块的输入和输出通道数都是相同的 (self.c),并且使用相同的参数 (shortcut,g,k,e) 进行初始化。
-
总结
-
Bottleneck_OREPA是Bottleneck类的扩展版本,它将标准的卷积操作替换或增强为OREPA模块。 -
C2f_OREPA是C2f类的扩展版本,使用Bottleneck_OREPA模块代替标准的瓶颈模块,从而集成OREPA模块以可能提升网络性能。
OREPA模块可能是一个自定义的卷积操作,用于提升网络的性能,尽管具体实现细节在这里没有提供。 -
2.3 更改init.py文件
关键步骤二:修改modules文件夹下的__init__.py文件,先导入函数

然后在下面的__all__中声明函数

2.4 添加yaml文件
关键步骤三:在/ultralytics/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8下面新建文件yolov8_C2f_OREPA.yaml文件,粘贴下面的内容
- OD【目标检测】
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f_OREPA, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f_OREPA, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)- Seg【语义分割】
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f_OREPA, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f_OREPA, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f_OREPA, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Segment, [nc, 32, 256]] # Segment(P3, P4, P5)温馨提示:因为本文只是对yolov8基础上添加模块,如果要对yolov8n/l/m/x进行添加则只需要指定对应的depth_multiple 和 width_multiple。不明白的同学可以看这篇文章: yolov8yaml文件解读——点击即可跳转
# YOLOv8n
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 1024 # max_channels
# YOLOv8s
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 1024 # max_channels
# YOLOv8l
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 512 # max_channels
# YOLOv8m
depth_multiple: 0.67 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.75 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 768 # max_channels
# YOLOv8x
depth_multiple: 1.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.25 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 512 # max_channels2.5 注册模块
关键步骤四:在task.py的parse_model函数中注册

2.6 执行程序
在train.py中,将model的参数路径设置为yolov8_C2f_OREPA.yaml的路径
建议大家写绝对路径,确保一定能找到
from ultralytics import YOLO
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from pathlib import Path
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
model = YOLO("ultralytics/cfg/v8/yolov8.yaml") # 你要选择的模型yaml文件地址
# Use the model
results = model.train(data=r"你的数据集的yaml文件地址",
epochs=100, batch=16, imgsz=640, workers=4, name=Path(model.cfg).stem) # 训练模型🚀运行程序,如果出现下面的内容则说明添加成功🚀
from n params module arguments
0 -1 1 464 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [3, 16, 3, 2]
1 -1 1 4672 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [16, 32, 3, 2]
2 -1 1 20608 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [32, 32, 1, True]
3 -1 1 18560 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [32, 64, 3, 2]
4 -1 2 145664 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [64, 64, 2, True]
5 -1 1 73984 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [64, 128, 3, 2]
6 -1 2 561664 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [128, 128, 2, True]
7 -1 1 295424 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [128, 256, 3, 2]
8 -1 1 1168384 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [256, 256, 1, True]
9 -1 1 164608 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.SPPF [256, 256, 5]
10 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
11 [-1, 6] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
12 -1 1 330240 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [384, 128, 1]
13 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
14 [-1, 4] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
15 -1 1 85248 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [192, 64, 1]
16 -1 1 36992 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [64, 64, 3, 2]
17 [-1, 12] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
18 -1 1 305664 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [192, 128, 1]
19 -1 1 147712 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [128, 128, 3, 2]
20 [-1, 9] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
21 -1 1 1201152 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f_OREPA [384, 256, 1]
22 [15, 18, 21] 1 897664 ultralytics.nn.modules.head.Detect [80, [64, 128, 256]]
YOLOv8_C2f_REPVGGOREPA summary: 205 layers, 5458704 parameters, 5458688 gradients, 6.5 GFLOPs
3. 完整代码分享
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tLFA6_X4X5ru7_N06uHg5g?pwd=areb提取码: areb
4. GFLOPs
关于GFLOPs的计算方式可以查看:百面算法工程师 | 卷积基础知识——Convolution
未改进的YOLOv8nGFLOPs
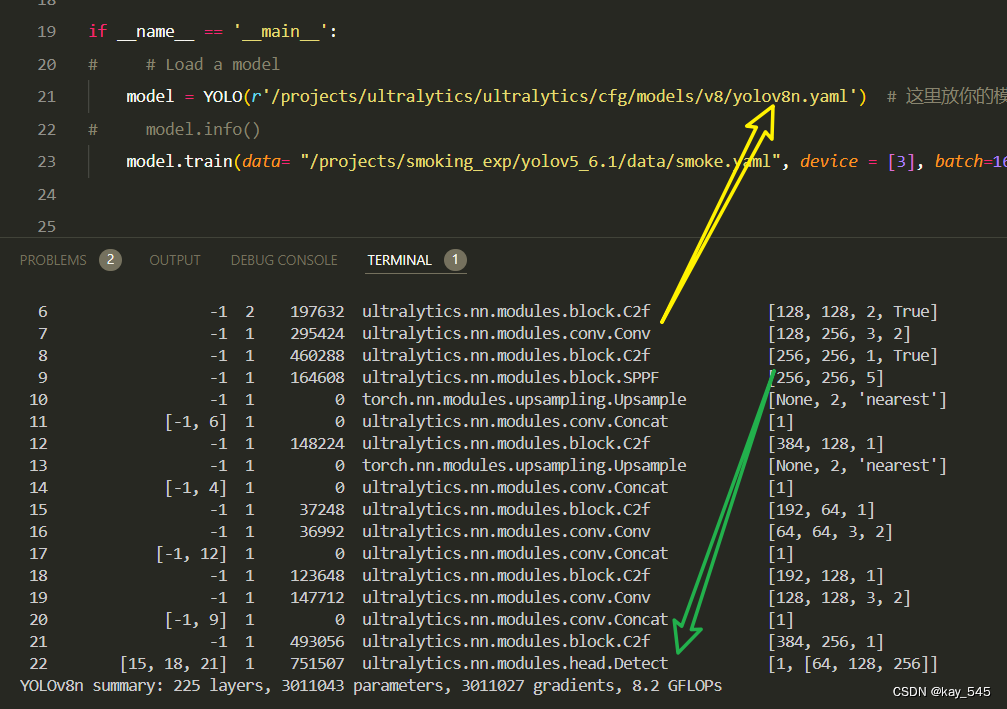
改进后的GFLOPs

5. 进阶
可以与其他的注意力机制或者损失函数等结合,进一步提升检测效果
6. 总结
OREPA(Online Convolutional Re-parameterization)通过将复杂的训练时块压缩为单个卷积层,显著降低了深度模型的训练开销。它首先去除训练时块中的非线性归一化层,并引入线性缩放层来代替。线性缩放层与归一化层具有相似的性质,即可以多样化不同分支的优化方向,从而提高模型性能。由于线性缩放层是线性的,可以在训练过程中合并到卷积层中,从而将复杂的线性块简化为单个卷积层。这样,OREPA 就可以将中间特征图上的计算和内存开销从 O(H × W) 降低到 O(KH × KW),其中 (H, W) 和 (KH, KW) 分别是特征图和卷积核的空间形状。OREPA 的主要优势在于降低了训练成本、提高了训练速度,并使探索更复杂和更强大的重参数化拓扑成为可能。