Title
题目
I 2U-Net: A dual-path U-Net with rich information interaction for medical image segmentation
I 2U-Net: 一种具有丰富信息交互的双路径U-Net用于医学图像分割
01
文献速递介绍
在计算机视觉领域,医学图像分割是主要的挑战之一,例如皮肤镜图像中的皮肤病变分割(Dai 等,2022),结肠镜图像中的息肉分割(Fan 等,2020),磁共振图像中的脑肿瘤分割(Wang 等,2021),以及腹部CT图像中的多器官分割(Cao 等,2021)。这些分割结果提供了关于解剖区域的有价值信息,便于进行详细分析,并极大地帮助医生描绘损伤、监测疾病进展和评估适当的治疗需求。随着对智能医学图像分析的需求不断增长,精确且稳健的分割方法变得愈发重要。
为了应对这一需求,许多具有编码器-解码器结构的深度学习方法被提出(Ramesh 等,2021)。这些方法通常使用编码器来提取图像特征,并使用解码器将提取的特征恢复到原始图像大小并输出最终的分割结果。作为编码器-解码器网络的代表,U-Net(Ronneberger 等,2015)在许多医学分割任务中证明了其有效性,这启发了系列高效U形分割网络的发展,如Attention U-Net(Oktay 等,2018)、Res-UNet(Xiao 等,2018)和DR-UNet(Li 等,2019)。
Abatract
摘要
Although the U-shape networks have achieved remarkable performances in many medical image segmentationtasks, they rarely model the sequential relationship of hierarchical layers. This weakness makes it difficultfor the current layer to effectively utilize the historical information of the previous layer, leading tounsatisfactory segmentation results for lesions with blurred boundaries and irregular shapes. To solve thisproblem, we propose a novel dual-path U-Net, dubbed I2U-Net. The newly proposed network encourageshistorical information re-usage and re-exploration through rich information interaction among the dual paths,allowing deep layers to learn more comprehensive features that contain both low-level detail description andhigh-level semantic abstraction. Specifically, we introduce a multi-functional information interaction module(MFII), which can model cross-path, cross-layer, and cross-path-and-layer information interactions via a unifieddesign, making the proposed I2U-Net behave similarly to an unfolded RNN and enjoying its advantage ofmodeling time sequence information. Besides, to further selectively and sensitively integrate the informationextracted by the encoder of the dual paths, we propose a holistic information fusion and augmentation module(HIFA), which can efficiently bridge the encoder and the decoder. Extensive experiments on four challengingtasks, including skin lesion, polyp, brain tumor, and abdominal multi-organ segmentation, consistently showthat the proposed I2U-Net has superior performance and generalization ability over other state-of-the-artmethods.
尽管U形网络在许多医学图像分割任务中取得了显著的表现,但它们很少对层次结构的顺序关系进行建模。这一弱点使得当前层难以有效利用前一层的历史信息,导致对于边界模糊和形状不规则的病变的分割结果不理想。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的双路径U-Net网络,称为I2U-Net。该新提出的网络通过双路径之间的丰富信息交互,鼓励历史信息的再利用和再探索,使得深层能够学习更全面的特征,这些特征既包含低级的细节描述,又包含高级的语义抽象。具体而言,我们引入了一个多功能信息交互模块(MFII),通过统一设计实现跨路径、跨层和跨路径与层的信息交互,使得所提出的I2U-Net表现得类似于展开的循环神经网络(RNN),并享有其在建模时间序列信息方面的优势。此外,为了进一步选择性和敏感地整合双路径编码器提取的信息,我们提出了一个整体信息融合和增强模块(HIFA),该模块能够高效地连接编码器和解码器。在皮肤病变、息肉、脑肿瘤和腹部多器官分割等四个具有挑战性的任务上进行的大量实验表明,所提出的I2U-Net在性能和泛化能力上均优于其他最先进的方法。
Method
方法
Chen et al. (2017) revealed that residual connection (He et al.,enables feature re-usage while dense connection (Huang et al.,encourages new feature exploration, which are both importantfor learning valuable representations. They also found that while residual and dense connections differ on the surface, both of them aremanifestations of a higher-order recurrent neural network (HORNN).Motivated by these, we propose a dual-path U-Net for medical imagesegmentation, dubbed I2U-Net. One path of I2U-Net is dedicated toimage feature information, while the other is to hidden state information with shared convolutional kernels along the depth. This structureallows I2U-Net to work similarly to an unfolded RNN (LeCun et al.,2015; Zhao et al., 2021) and enjoy its advantage of modeling time sequence information. It also allows I2U-Net to inherit the advantages ofresidual and dense connections, enabling convenient re-usage of historyfeatures and flexible exploration of new features with an acceptablecomputation cost.Fig. 2 exhibits an overview of the proposed I2U-Net. Unlike traditional U-Nets, the proposed I2U-Net is a dual-path U-shape network equipped with a multi-functional information interaction module(MFII) and a holistic information fusion and augmentation module(HIFA).
Chen 等人(2017)揭示,残差连接(He 等,2016)能够实现特征的再利用,而密集连接(Huang 等,2017)则鼓励新特征的探索,这两者对于学习有价值的表示都非常重要。他们还发现,虽然残差连接和密集连接在表面上有所不同,但它们都是高阶递归神经网络(HORNN)的一种体现。受到这些启发,我们提出了一种用于医学图像分割的双路径U-Net,称为I2U-Net。I2U-Net的一条路径专注于图像特征信息,而另一条路径则专注于隐藏状态信息,两者在深度上共享卷积核。该结构使得I2U-Net的工作方式类似于展开的RNN(LeCun 等,2015;Zhao 等,2021),并享有其在建模时间序列信息方面的优势。它还使得I2U-Net能够继承残差和密集连接的优点,在可接受的计算成本下实现历史特征的方便再利用和新特征的灵活探索。图2展示了所提出的I2U-Net的概览。与传统的U-Net不同,所提出的I2U-Net是一种双路径U形网络,配备了多功能信息交互模块(MFII)和整体信息融合与增强模块(HIFA)。
Conclusion
结论
This paper proposed a dual-path U-net (dubbed I2U-Net) with richinformation interaction for medical image segmentation, which workssimilarly to an unfolded RNN and enjoys the advantage of modeling thetime-sequential relationship between different network layers. Specifically, I2U-Net developed a multi-functional information interactionmodule (MFII) that enables the current layer to effectively re-use andre-explore the previous layers’ historical information, allowing deeplayers to learn more comprehensive features that contain both low-leveldetail description and high-level semantic abstraction. Moreover, I2UNet developed a holistic information fusion and augmentation module(HIFA) to sensitively augment the information extracted by the dualpath encoder. The proposed HIFA merges the advantage of local andglobal operation and can flexibly learn discriminative representationfrom a wider frequency range, bridging the encoder and the decodermore efficiently. Thanks to these creative designs, extensive experiments on four challenging tasks, including skin lesion, polyp, braintumor, and abdominal multi-organ segmentation, consistently provedthat the proposed I2U-Net has excellent segmentation performance andgeneralization ability.
这篇论文提出了一种用于医学图像分割的双路径U-Net(称为I2U-Net),该网络具有丰富的信息交互功能,工作方式类似于展开的RNN,具有建模不同网络层之间时间序列关系的优势。具体而言,I2U-Net开发了一个多功能信息交互模块(MFII),使当前层能够有效地再利用和再探索前一层的历史信息,使得深层能够学习到包含低级细节描述和高级语义抽象的更全面特征。此外,I2U-Net还开发了一个整体信息融合和增强模块(HIFA),该模块能够敏感地增强双路径编码器提取的信息。提出的HIFA模块结合了局部和全局操作的优点,能够灵活地从更广泛的频率范围中学习辨别性表示,更有效地连接编码器和解码器。得益于这些创新设计,在皮肤病变、息肉、脑肿瘤和腹部多器官分割等四个具有挑战性的任务上进行的大量实验一致证明,所提出的I2U-Net具有出色的分割性能和泛化能力。
Figure
图
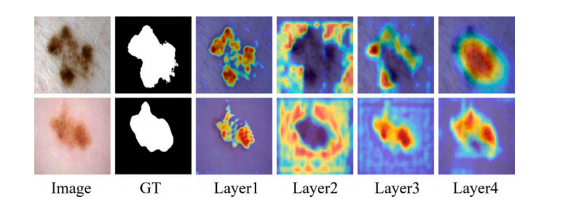
Fig. 1. Heat maps in four different layers of the U-Net.
图1. U-Net不同四层中的热图。
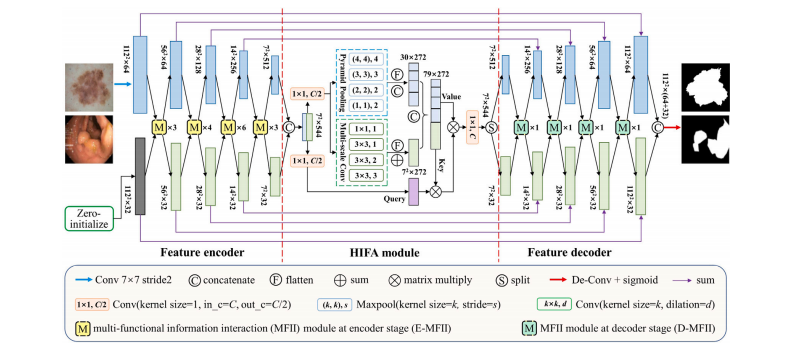
Fig. 2. Illustration of the proposed I2U-Net. I2U-Net is a dual-path U-Net with rich information interaction. One path uses medical images as input to extract image featureinformation like traditional U-Nets. In contrast, the other path uses zero-initialized learnable matrix as input to store the hidden state information with shared convolutional kernelsalong the depth. This structure allows I2U-Net to work similarly to an unfolded RNN and enjoy its advantages, including modeling the time-sequential relationship of hierarchicallayers and making the most of historical information.
图2. 所提出的I2U-Net示意图。I2U-Net 是一种具有丰富信息交互的双路径 U-Net。一条路径使用医学图像作为输入,类似于传统的 U-Net,用于提取图像特征信息。而另一条路径使用零初始化的可学习矩阵作为输入,用于在深度上共享卷积核的情况下存储隐藏状态信息。该结构使 I2U-Net 的工作方式类似于展开的 RNN,并享有其优势,包括建模层次结构的时间序列关系以及最大限度地利用历史信息。
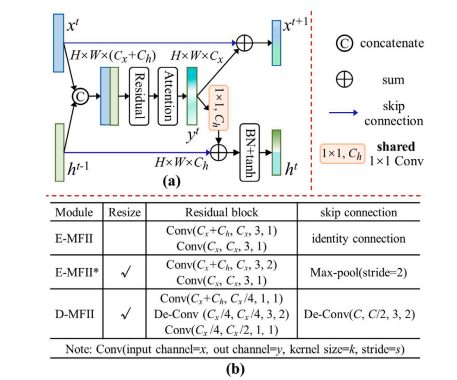
Fig. 3. Illustration of the proposed MFII module. MFII enables multi-faceted information interaction among the dual paths of I2U-Net. MFII has three differentrepresentations: E-MFII, E-MFII, and D-MFII. E-MFII and E-MFII are used in theencoder stage. Their difference is that E-MFII reduces the feature size by convolutionwith stride 2, while E-MFII keeps the size unchanged. D-MFII is used in the decoderstage, which increases the feature size by deconvolution.
图3. 所提出的MFII模块示意图。MFII模块实现了I2U-Net双路径之间的多方面信息交互。MFII具有三种不同的表示形式:E-MFII、E-MFII和D-MFII。E-MFII和E-MFII用于编码器阶段,它们的区别在于E-MFII*通过步长为2的卷积来减少特征尺寸,而E-MFII保持尺寸不变。D-MFII用于解码器阶段,通过反卷积增加特征尺寸。
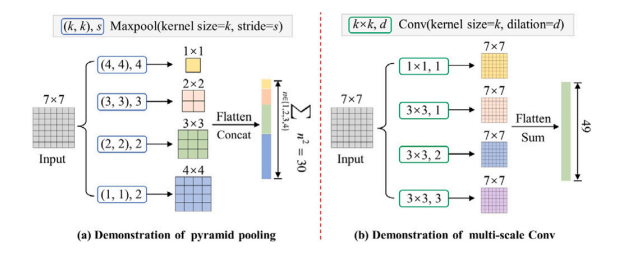
Fig. 4. Demonstration of the pyramid pooling and the multi-scale atrous convolutionin HIFA module.
图4. HIFA模块中金字塔池化和多尺度膨胀卷积的演示。

Fig. 5. Sample results of skin lesion segmentation on ISIC2018 (first three rows)and PH2 (last two rows). The colors white, green, and red represent the correctsegmentation, under-segmentation, and over-segmentation, respectively.
图5. 在ISIC2018(前三行)和PH2(最后两行)上的皮肤病变分割示例结果。白色、绿色和红色分别表示正确分割、欠分割和过分割。
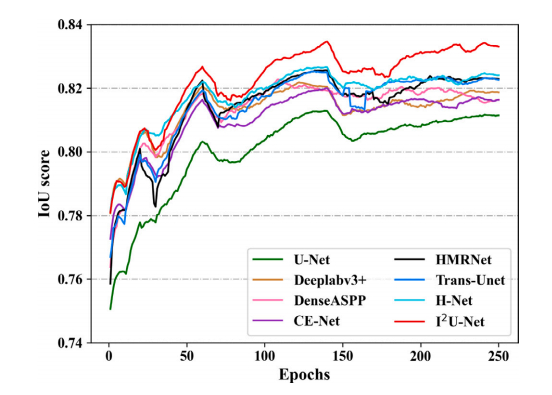
Fig. 6. Trend graph of IoU score in skin lesion segmentation task
图6. 皮肤病变分割任务中IoU评分的趋势图。
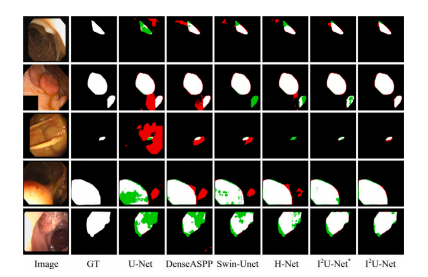
Fig. 7. Sample results of polyp segmentation on five public datasets. The colorswhite, green, and red represent the correct segmentation, under-segmentation, andover-segmentation, respectively.
图7. 在五个公共数据集上的息肉分割示例结果。白色、绿色和红色分别表示正确分割、欠分割和过分割。
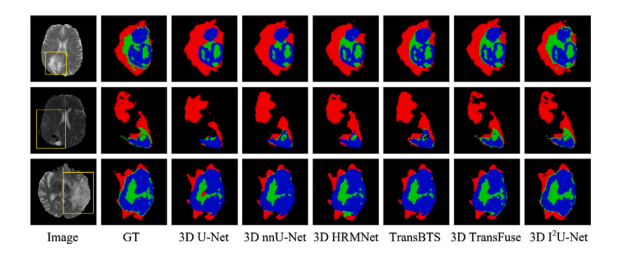
Fig. 8. Sample results of brain tumor segmentation. The union of red, blue, and greenregions represents the Whole Tumor(WT); the union of red and blue regions representsthe Tumor Core (TC); and the green region denotes the Enhancing Tumor (ET).
图8. 脑肿瘤分割的示例结果。红色、蓝色和绿色区域的联合代表整个肿瘤(WT);红色和蓝色区域的联合代表肿瘤核心(TC);绿色区域表示增强肿瘤(ET)。
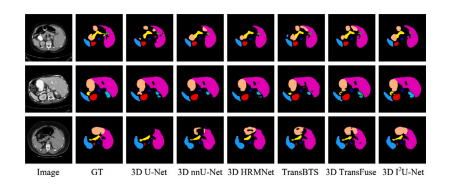
Fig. 9. Sample results of abdominal multi-organ segmentation.
图9. 腹部多器官分割的示例结果。
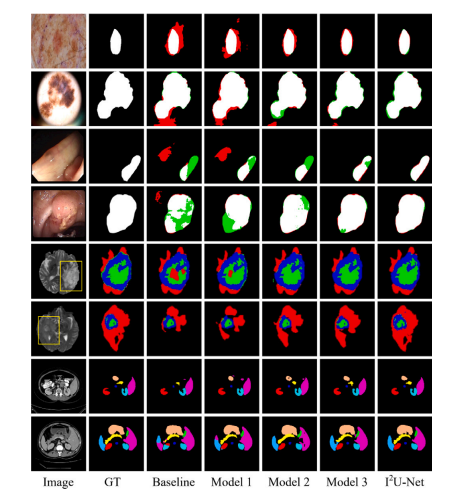
Fig. 10. Segmentation results of different models in our system.
图10. 我们系统中不同模型的分割结果。
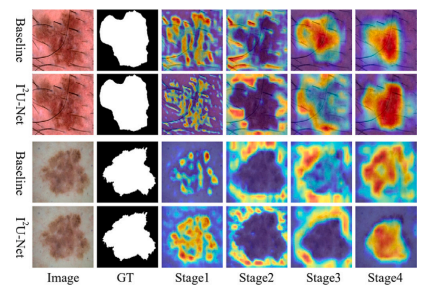
Fig. 11. Heat maps are obtained by the four encoder stages of the Baseline and ourI 2U-Net.
图11. 热图由基线模型和我们的 I2U-Net 的四个编码器阶段生成。
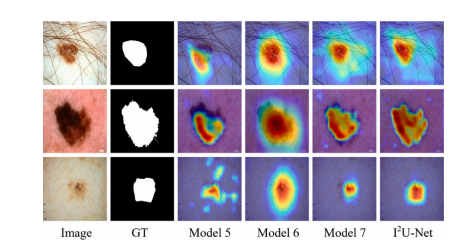
Fig. 12. Heat maps are obtained by different bridges in our system.
图12. 热图由我们系统中不同的桥接模块生成
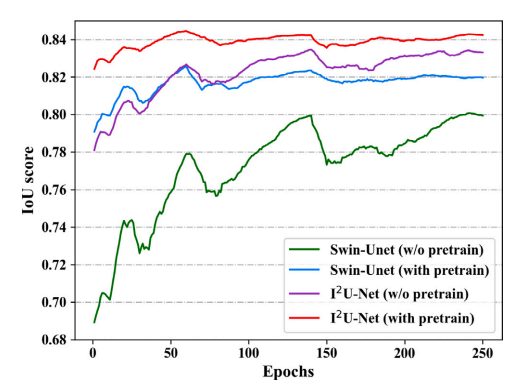
Fig. 13. Influence of pre-trained parameters on IoU score of skin disease segmentationtasks.
图13. 预训练参数对皮肤病分割任务中IoU评分的影响。
Table
表
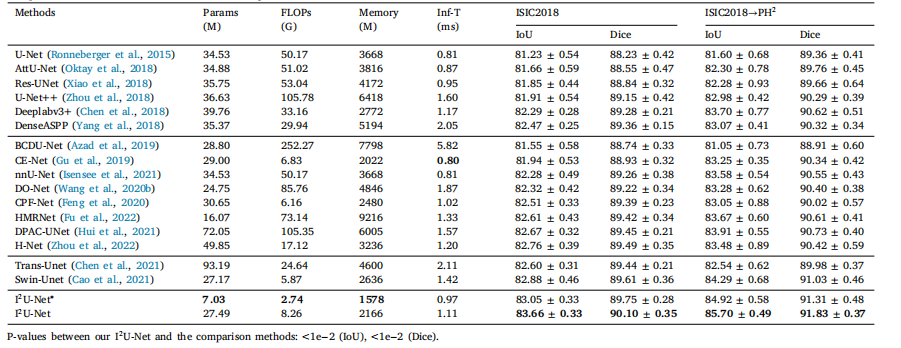
Table 1Compared with different methods for skin lesion segmentation. The best results are in bold.
表1 与不同方法在皮肤病变分割中的比较。最佳结果以粗体显示。
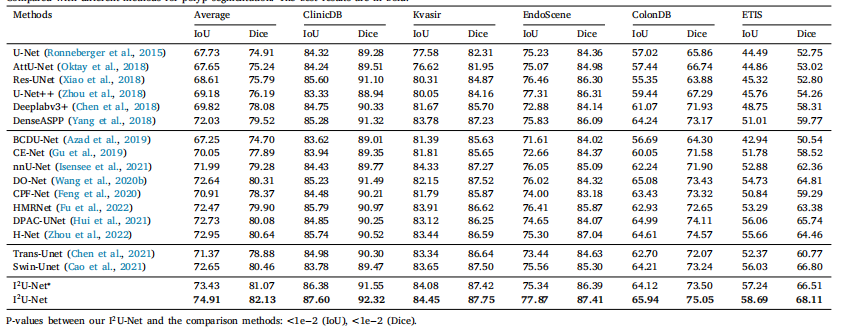
Table 2Compared with different methods for polyp segmentation. The best results are in bold.
表2 与不同方法在息肉分割中的比较。最佳结果以粗体显示。
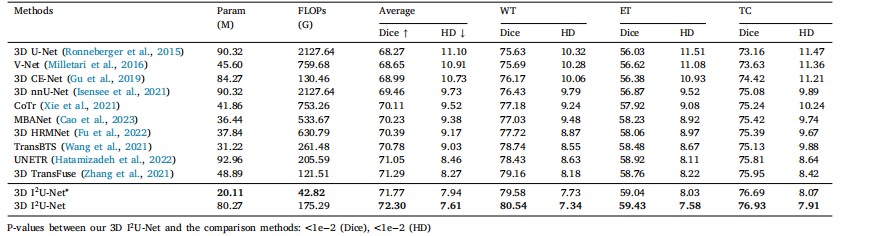
Table 3Compared with different methods for brain tumor segmentation. WT, ET and TC represent Whole Tumor, Enhancing Tumor and Tumor Core sub-regions, respectively. The bestresults are in bold.
表3 与不同方法在脑肿瘤分割中的比较。WT、ET 和 TC 分别代表整个肿瘤、增强肿瘤和肿瘤核心子区域。最佳结果以粗体显示。
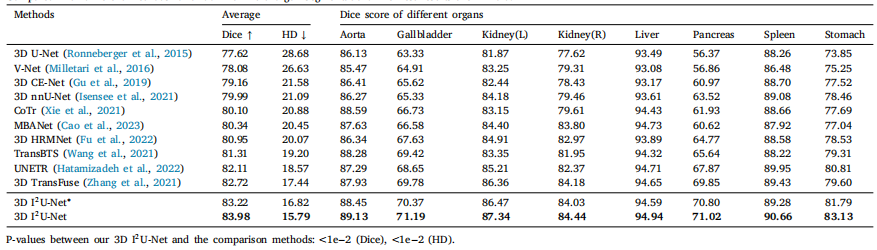
Table 4Compared with different methods for abdominal multi-organ segmentation. The best results are in bold
表4 与不同方法在腹部多器官分割中的比较。最佳结果以粗体显示。
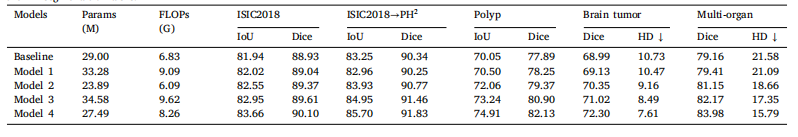
Table 5Segmentation performances of different models in our system. The proposed I2U-Net is Model 4. The number of parameter and FLOPs are calculated based onthe 2D segmentation tasks.
表5 我们系统中不同模型的分割性能。所提出的 I2U-Net 为模型 4。参数数量和 FLOPs 是基于 2D 分割任务计算的。
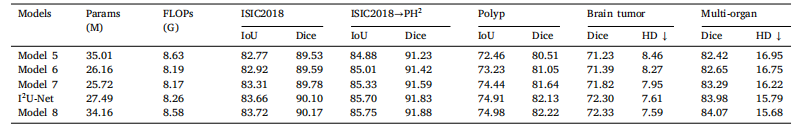
Table 6Segmentation performance of I2U-Net variants equipped with different bridges. The number of parameter and FLOPs are calculated based on the 2D segmentationtasks.
表6 配备不同桥接模块的 I2U-Net 变体的分割性能。参数数量和 FLOPs 是基于 2D 分割任务计算的。
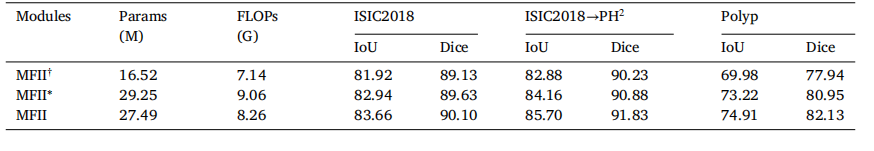
Table 7Segmentation performances of MFII and its two variants.
表7 MFII及其两个变体的分割性能
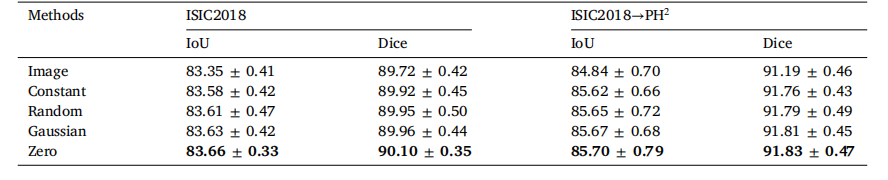
Table 8Segmentation performance of different hidden state initialization methods.
表8 不同隐藏状态初始化方法的分割性能。
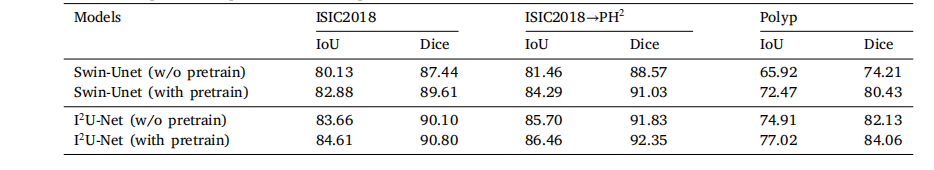
Table 9Influence of pre-trained parameters on the performance of different methods.
表9 预训练参数对不同方法性能的影响。