定义数据库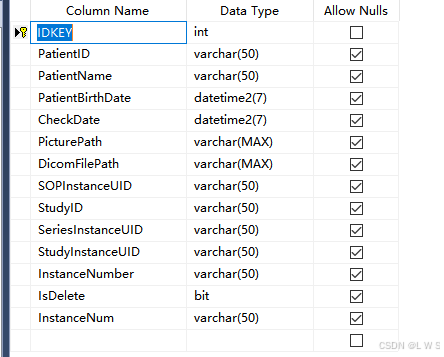
数据库名称:T_dicomPatientMsg
注意5大约束条件:
1.主键约束:primary key IDKEY设置为主键,主键设置自增长
2.唯一性约束:unique
3.默认约束:default 所有值都要设置默认值,除了主键
4.检查约束:check
5.外键约束:foreign key
定义实体
public class DicomPatientMsg
{
[Key]
public int IDKEY { get; set; } //设为主键,注意实体名称需要与数据库实体名称一致
public string PatientID { get; set; }
public string PatientName { get; set; }
public DateTime PatientBirthDate { get; set; }
public DateTime CheckDate { get; set; }
public string PicturePath { get; set; }
public string DicomFilePath { get; set; }
public string SOPInstanceUID { get; set; }
public string StudyID { get; set; }
public string StudyInstanceUID { get; set; }
public string SeriesInstanceUID { get; set; }
public string InstanceNum { get; set; }
public bool IsDelete { get; set; }
}SQL帮助类
连接池实现并发连接
public class SqlHelper
{
private readonly AppDbContext _context;
//构造函数注入DB_context
public SqlHelper(AppDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// 增加实体
public async Task AddAsync<T>(T entity) where T : class
{
await _context.Set<T>().AddAsync(entity);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
// 获取所有实体
public async Task<List<T>> GetAllAsync<T>() where T : class
{
return await _context.Set<T>().ToListAsync();
}
// 根据ID获取实体
public async Task<T> GetByIdAsync<T>(int id) where T : class
{
return await _context.Set<T>().FindAsync(id);
}
// 更新实体
public async Task UpdateAsync<T>(T entity) where T : class
{
_context.Set<T>().Update(entity);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
// 删除实体
public async Task DeleteAsync<T>(T entity, bool isDelete = false) where T : class
{
if (isDelete)
{
_context.Set<T>().Remove(entity);
}
else
{
var property = entity.GetType().GetProperty("IsDeleted");
if (property != null && property.PropertyType == typeof(bool))
{
property.SetValue(entity, true);
_context.Set<T>().Update(entity);
}
else
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Error");
}
}
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
} public async Task AddAsync<T>(T entity) where T : class
{
await _context.Set<T>().AddAsync(entity);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}//增加实体
public 表面方法是公开的,所有其他类都可以调用
async 表方法内可能包含异步操作,允许方法在内部使用"await"
await 在异步操作中使用,会暂停当前方法的执行(阻塞当前线程),直到方法执行完成后,才会继续执行下面的代码,暂停期间,控制权会返回给调用方(如UI线程)
Task 当一个 方法的返回类型是Task时,表面这个方法是异步的,但它不返回任何值(即它是'void'的异步版本,同理int的异步版本为Task<int>)。通过Task,调用者可以选择是否等待这个方法完成
AddAsync<T>(T entity) T是泛型类型的参数,它使得这个方法可以处理任意类型的实体对象。T由调用者传入的entity类型所决定。如果不使用泛型,只处理某一实体类型如User,也可以写成AddUserAsync(User entity)
where T : class 约束条件,限制了T必须是一个类
private readonly AppDbContext _context;
//构造函数注入DB_context
public SqlHelper(AppDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}这里为什么要用构造函数去注入DbContext
DbContext通常代表数据库的会话(增删改查等),每个DbContext实例都代表与数据库的一次交互。
配置AppDbContext
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
// 定义数据库表
public DbSet<DicomPatientMsg> T_dicomPatientMsg { get;set;}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<DicomPatientMsg>().HasQueryFilter(e => !e.IsDelete); //过滤已软删除的记录
}
}在appsettings.json配置数据库连接字符串
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Database=Colposcope;User Id=sa;Password=123;TrustServerCertificate=True;"
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
//TrustServerCertificate=true 禁用SSL验证
注册DbContext 服务
// 从配置文件读取字符串
var connectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
// 添加DbContext服务
builder.Services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>((options) => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));
//添加SqlHelper,DicomFunc 和控制器类到 DI 容器
builder.Services.AddScoped<SqlHelper>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<DicomFunc>();使用数据库
private readonly static SqlHelper sqlHelper = SqlHelper.Instance;
DicomPatientMsg msg = new DicomPatientMsg()
{
DicomFilePath = patientMsg.DicomFilePath,
PatientID = patientMsg.PatientID,
PatientName = patientMsg.PatientName,
CheckDate = checkDate,
PicturePath = patientMsg.PicturePath,
SOPInstanceUID = dataset.GetString(DicomTag.SOPInstanceUID),
StudyID = dataset.GetString(DicomTag.StudyID),
StudyInstanceUID = dataset.GetString(DicomTag.StudyInstanceUID),
SeriesInstanceUID = dataset.GetString(DicomTag.SeriesInstanceUID),
InstanceNum = dataset.GetString(DicomTag.InstanceNumber),
};
//存储到sql
await sqlHelper.AddAsync(msg);下面理清一下这个数据库的使用流程:
1. 依赖链
DicomController 依赖 DicomFunc,而 DicomFunc 依赖 SqlHelper,SqlHelper 又依赖 AppDbContext。
DicomController依赖DicomFuncDicomFunc依赖SqlHelperSqlHelper依赖AppDbContext
2. 服务注册
AppDbContext的注册:使用AddDbContext<AppDbContext>将数据库上下文注册到 DI 容器中。这允许SqlHelper构造函数接收AppDbContext实例。SqlHelper的注册:我们使用AddScoped<SqlHelper>()注册SqlHelper,让DicomFunc可以注入它。DicomFunc的注册:我们注册DicomFunc,确保DicomController能够接收它。
3. 依赖注入的执行
当一个请求到达DicomController时,ASP.NET Core的依赖注入容器会
-
实例化
控制器依赖于DicomController:DicomFunc,容器会尝试实例化DicomFunc。 -
实例化
DicomFunc:DicomFunc的构造函数依赖于SqlHelper,容器会进一步尝试实例化SqlHelper。 -
实例化
SqlHelper:SqlHelper的构造函数依赖于AppDbContext。AppDbContext是通过AddDbContext方法注册到容器中的,它会被自动提供给SqlHelper。 -
实例化
容器会从依赖注入容器中提取并实例化AppDbContext:AppDbContext,这可能涉及数据库连接的初始化等操作。 -
完成实例化:
- 最终,
AppDbContext实例被注入到SqlHelper中。 SqlHelper实例被注入到DicomFunc中。DicomFunc实例被注入到DicomController中。
- 最终,