introsort是introspective sort采⽤了缩写,他的名字其实表达了他的实现思路,他的思路就是进行⾃我侦测和反省,快排递归深度太深(sgi stl中使⽤的是深度为2倍排序元素数量的对数值)那就说明在这种数据序列下,选key出现了问题,性能在快速退化,那么就不要再进⾏快排分割递归了,改换为堆排序进⾏排序。(这也是C++中,STL中的快排的实现原理)
我们可以通过以下代码知道递归深度(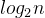 ):
):
int N = nums.size();
int logn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i *= 2)
{
logn++;
}也可以使用库中的log2()函数;
在官方库中,当深度超过时,2倍是一个比较合适的数;
在实现快排的过程,我们就可以在递归代码++递归的深度,这样,代码就可以知道现在递归到几层了:

代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 辅助函数,用于下沉堆中的一个节点
void siftDown(vector<int>& arr, int start, int end)
{
int parent = start;
while ((parent * 2 + 1) <= end)
{ // 有左子节点
int child = parent * 2 + 1; // 左子节点索引
int rightChild = (child + 1 <= end) ? child + 1 : child; // 右子节点索引,如果存在
// 选择较大的子节点作为比较对象
if (arr[rightChild] > arr[child])
{
child = rightChild;
}
// 如果父节点的值小于子节点的值,交换它们
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])
{
swap(arr[parent], arr[child]);
parent = child; // 更新父节点为当前子节点,继续下沉
}
else
{
break; // 父节点大于子节点,不需要下沉
}
}
}
// 构建堆
void buildHeap(vector<int>& arr)
{
for (int i = arr.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
siftDown(arr, i, arr.size() - 1);
}
}
// 堆排序
void heapSort(vector<int>& arr)
{
buildHeap(arr); // 构建堆
for (int i = arr.size() - 1; i > 0; --i)
{
swap(arr[0], arr[i]); // 交换堆顶元素和最后一个元素
siftDown(arr, 0, i - 1); // 重新下沉堆顶元素
}
}
// 插入排序函数,用于小区间排序
void insertionSort(std::vector<int>& arr, int left, int right)
{
for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; ++i)
{
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= left && arr[j] > key)
{
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
--j;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// 自省排序的快速排序部分
int Partition(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++;
swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
}
}
swap(arr[i + 1], arr[high]);
return i + 1;
}
// 自省排序
void IntroSort(vector<int>& arr, int low, int high, int depth = 0, int depthMAX = -1)
{
if (depthMAX == -1)
{
depthMAX = 2 * log2(arr.size());
}
if (low >= high) return;
// 插入排序对小数组更高效
// 小区间优化
if (high - low + 1 < 16)
{
insertionSort(arr, low, high);
}
else
{
// 快速排序的分区操作
int pi = Partition(arr, low, high);
// 递归排序左半部分和右半部分
IntroSort(arr, low, pi - 1, depth + 1, depthMAX);
IntroSort(arr, pi + 1, high, depth + 1, depthMAX);
}
// 增加递归深度判断,避免栈溢出
if (depth > depthMAX)
{
heapSort(arr);
}
}
// 打印数组
void PrintArray(const vector<int>& arr)
{
for (int num : arr)
{
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
srand(static_cast<unsigned int>(time(0))); // 初始化随机数种子
vector<int> arr = { 10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4 };
cout << "Original array: ";
PrintArray(arr);
// 计算最大递归深度
int depthMAX = log2(arr.size()) * 2;
IntroSort(arr, 0, arr.size() - 1, 0, depthMAX);
cout << "Sorted array: ";
PrintArray(arr);
return 0;
}