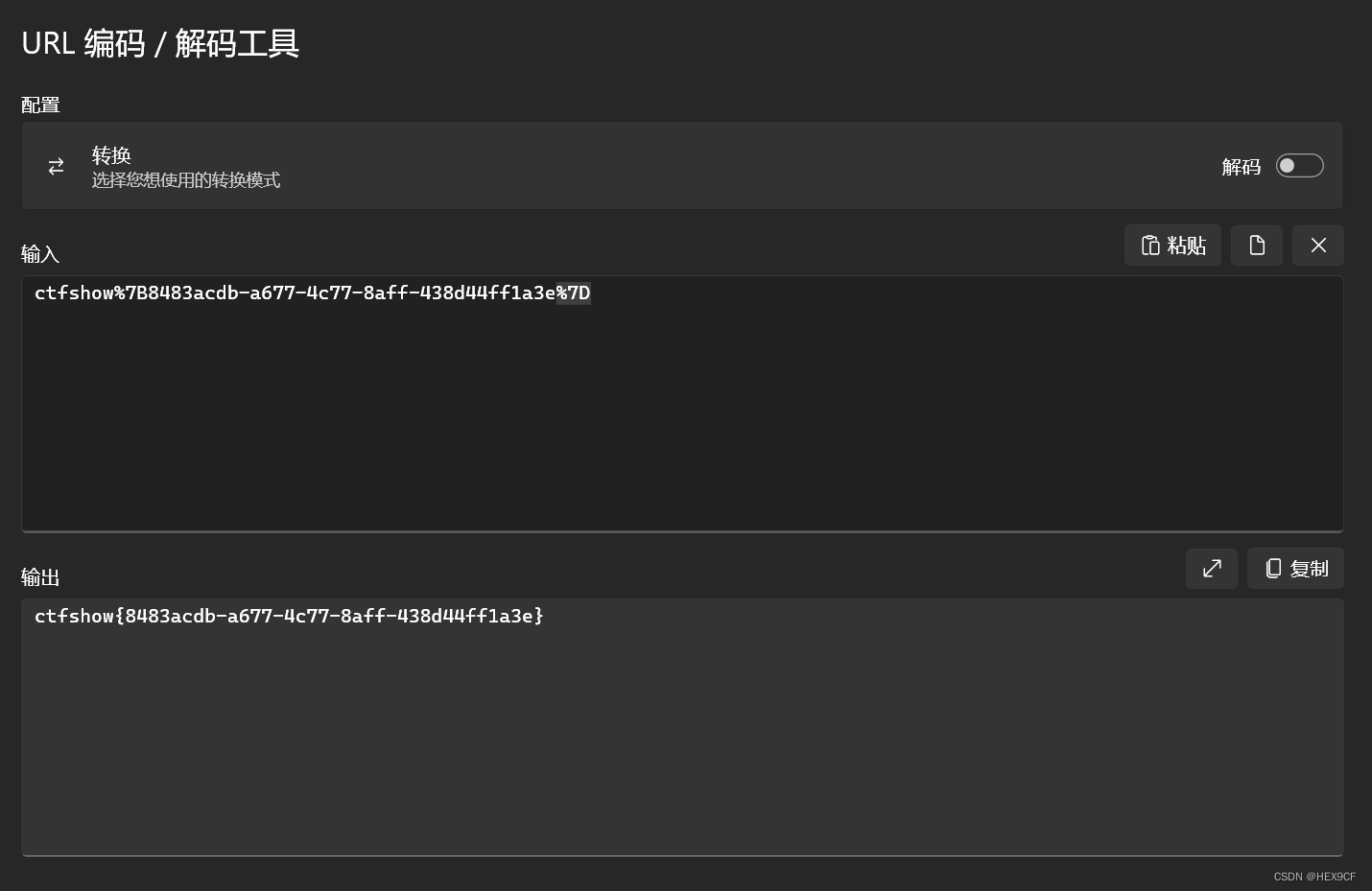
### 思路
1. **建图**:将订单视为图的节点,已知关系视为图的边,构建无向图。
2. **连通分量**:使用深度优先搜索(DFS)或广度优先搜索(BFS)找到图中的所有连通分量。
3. **排序**:对每个连通分量中的订单编号进行排序。
4. **输出**:按最小订单编号的顺序输出每个连通分量。
### 伪代码
1. 读取输入的订单数量n和关系数量m。
2. 构建图的邻接表表示。
3. 使用DFS/BFS找到所有连通分量。
4. 对每个连通分量中的订单编号进行排序。
5. 按最小订单编号的顺序输出每个连通分量。
### C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void dfs(int node, vector<vector<int>>& graph, vector<bool>& visited, vector<int>& component) {
visited[node] = true;
component.push_back(node);
for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
dfs(neighbor, graph, visited, component);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> graph(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
graph[a].push_back(b);
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
vector<bool> visited(n + 1, false);
vector<vector<int>> components;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!visited[i]) {
vector<int> component;
dfs(i, graph, visited, component);
sort(component.begin(), component.end());
components.push_back(component);
}
}
sort(components.begin(), components.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
});
cout << components.size() << endl;
for (const auto& component : components) {
for (int order : component) {
cout << order << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}