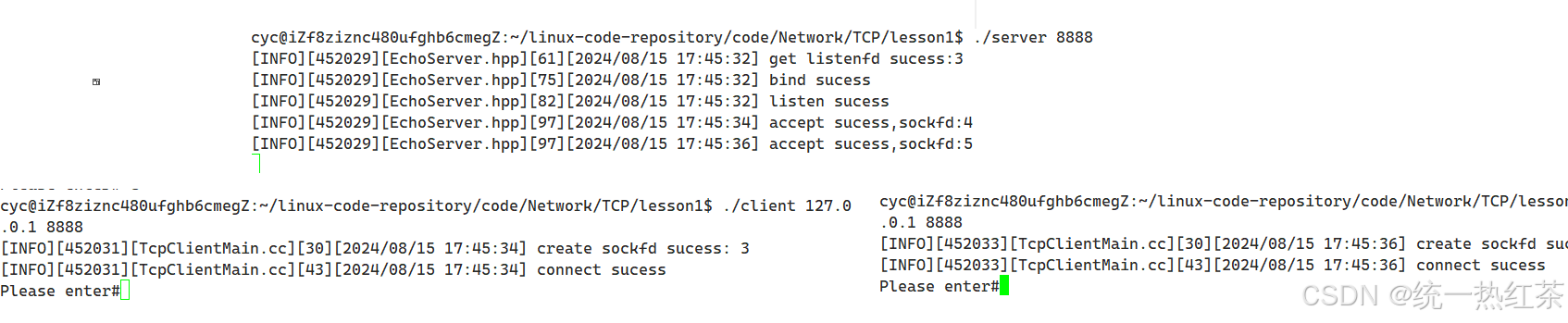
一.路由匹配模块介绍
路由匹配模块可以验证路由键(routing key)和绑定键(binding key)的合法性,并根据不同的交换机类型(如Direct、Fanout和Topic)进行消息的路由匹配。


二.Routine类的实现
设计思路
在消息队列系统中,消息路由是一个关键的功能。
交换机根据路由键将消息发送到与其匹配的队列,而不同类型的交换机有不同的路由规则。Routine类的设计目标是处理这些规则:
- 合法性校验:验证路由键和绑定键的字符规则是否符合预期。例如,routing_key只允许字母、数字、点和下划线,而binding_key还允许通配符(
*和#)。 - 路由匹配算法:根据交换机类型,确定routing_key和binding_key是否匹配,特别是在
Topic类型的交换机中,复杂的匹配规则需要使用动态规划来实现
代码细节分析
合法性校验:
routineKeyValid()方法用于验证路由键是否合法,允许的字符包括字母、数字、点和下划线。bindingKeyValid()方法则允许更多字符,包括通配符*和#,并对绑定键的格式进行了更严格的检查。例如,*和#必须独立作为单词出现,且#不能和其他通配符同时出现。
static bool routineKeyValid(const std::string &rkey)
{
// 包含的字符规则: 0-9,a-z,A-Z, . _
for (auto &ch : rkey)
{
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ||
ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ||
ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ||
ch == '.' || ch == '_')
continue;
else
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool bindingKeyValid(const std::string &bkey)
{
// 1. 包含的字符规则 0-9,a-z,A-Z, . _ * #
for (auto &ch : bkey)
{
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ||
ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ||
ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ||
ch == '.' || ch == '_' ||
ch == '*' || ch == '#')
continue;
else
return false;
}
// 2. 单词直接以.作为分隔符,#和* 必须独立作为单词出现
std::vector<std::string> words;
StrHelper::split(bkey, ".", words);
for (auto &word : words)
{
if (word.size() > 1 &&
(word.find('*') != std::string::npos ||
word.find('#') != std::string::npos))
return false;
}
// 3. #可以匹配0-n个单词,即#前后不能有*和#的通配符
for (int i = 1; i < words.size(); ++i)
{
if (words[i] == "#" && words[i - 1] == "#")
return false;
else if (words[i] == "#" && words[i - 1] == "*")
return false;
else if (words[i] == "*" && words[i - 1] == "#")
return false;
}
return true;
}路由匹配:
route()方法根据不同的交换机类型决定是否匹配成功:
DIRECT类型:路由键和绑定键必须完全相等。
FANOUT类型:无论路由键如何,都会匹配成功。
TOPIC类型:使用动态规划(DP)方法实现复杂的通配符匹配逻辑。
首先将路由键和绑定键按.分隔为多个单词,然后通过DP表逐步匹配各个单词。
如果绑定键包含#或*,则会根据通配符的规则处理。
动态规划的应用:
DP表的初始化确保了在开始时没有匹配任何字符时(dp[0][0])的正确性。如果绑定键的第一个字符是#,那么也允许匹配空路由键(dp[1][0])。
在填充DP表时,#可以匹配零个或多个单词,而*则只能匹配一个单词。这种设计有效地解决了通配符的匹配问题。

实现总结
Routine类处理了不同类型的消息路由需求,特别是在处理Topic类型的复杂路由规则时,使用了动态规划来高效地完成匹配。
三.全部代码
#pragma once
#include "../common_mq/helper.hpp"
#include "../common_mq/logger.hpp"
#include "../common_mq/msg.pb.h"
namespace mq
{
class Routine
{
public:
static bool routineKeyValid(const std::string &rkey)
{
// 包含的字符规则: 0-9,a-z,A-Z, . _
for (auto &ch : rkey)
{
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ||
ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ||
ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ||
ch == '.' || ch == '_')
continue;
else
return false;
}
return true;
}
static bool bindingKeyValid(const std::string &bkey)
{
// 1. 包含的字符规则 0-9,a-z,A-Z, . _ * #
for (auto &ch : bkey)
{
if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ||
ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z' ||
ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z' ||
ch == '.' || ch == '_' ||
ch == '*' || ch == '#')
continue;
else
return false;
}
// 2. 单词直接以.作为分隔符,#和* 必须独立作为单词出现
std::vector<std::string> words;
StrHelper::split(bkey, ".", words);
for (auto &word : words)
{
if (word.size() > 1 &&
(word.find('*') != std::string::npos ||
word.find('#') != std::string::npos))
return false;
}
// 3. #可以匹配0-n个单词,即#前后不能有*和#的通配符
for (int i = 1; i < words.size(); ++i)
{
if (words[i] == "#" && words[i - 1] == "#")
return false;
else if (words[i] == "#" && words[i - 1] == "*")
return false;
else if (words[i] == "*" && words[i - 1] == "#")
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 路由匹配是否成功
static bool route(msg::ExchangeType type, const std::string &rkey, const std::string &bkey)
{
if (type == msg::ExchangeType::DIRECT)
return rkey == bkey;
else if (type == msg::ExchangeType::FANOUT)
return true;
else//TOPIC
{
// 1.字符串分别以.为分隔符切分
std::vector<std::string> rkeys;
size_t routine_sz = StrHelper::split(rkey, ".", rkeys);
std::vector<std::string> bkeys;
size_t bind_sz = StrHelper::split(bkey, ".", bkeys);
// 2.创建dp表
std::vector<std::vector<bool>> dp(bind_sz+1,std::vector<bool>(routine_sz+1,false));
// 3.初始化dp表
// dp[0][0]=true
// binding_key起始字符为0时,dp[1][0]=true
dp[0][0]=true;
if(bind_sz>0 && bkeys[0] == "#")
dp[1][0] = true;
// 4.填充dp表
for(int i=1;i<=bind_sz;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=routine_sz;j++)
{
if(bkeys[i-1] == "#")
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] | dp[i][j-1] | dp[i-1][j];
else if(bkeys[i-1] == "*" || bkeys[i-1] == rkeys[j-1])
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}
}
// 5.返回最后一个元素
return dp[bind_sz][routine_sz];
}
}
};
};