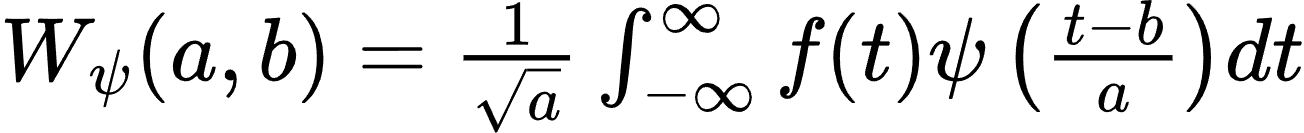1.说明
业界比较主流的数据血缘系统,目前还没能达到与调度系统耦合,最大难点在于代码解析。当某张表下游太多时(特别是维度表),展示也失去了意义,所以多用于排查某张应用表的上游从哪里开。使用方一般为对数仓表结构不太熟悉的业务/数据经理想要了解有哪些数据。
2.部署
2.1 yum
yum install -y zlib-devel bzip2-devel \
openssl-devel ncurses-devel epel-release gcc gcc-c++ xz-devel readline-devel \
gdbm-devel sqlite-devel tk-devel db4-devel libpcap-devel libffi-devel2.2 python
# 下载
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.8.3/Python-3.8.3.tgz
tar -zxvf Python-3.8.3.tgz
# 安装
cd Python-3.8.3
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python38
make && make install
# 软链接
ln -s /usr/local/python38/bin/python3.8 /usr/bin/python38
ln -s /usr/local/python38/bin/pip3.8 /usr/bin/pip38
# 验证
python38 -V
pip38 -V
pip38 install --upgrade pip
2.3 Docker-Compose
vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"insecure-registries" : ["registry-1.docker.io/v2/"],
"data-root": "/rainbow/docker"
}
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl status docker.service
systemctl restart docker.service
# 配置yum的repo源头
yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
#安装docker
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
#下载docker-compose文件
curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.21.1/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
#将文件复制到/usr/local/bin环境变量下面
mv docker-compose /usr/local/bin
#给他一个执行权限
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
#查看是否安装成功
docker-compose -version2.4 datahub安装
pip38 install --upgrade pip
python38 -m pip uninstall datahub acryl-datahub || true # sanity check - ok if it
pip38 install acryl-datahub==0.10.5 -i https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple
# 报错1:包冲突
# 改为上面部署命令
pydantic-core 2.18.1 requires typing-extensions!=4.7.0,>=4.6.0
acryl-datahub 0.10.5 requires typing-extensions<4.6.0,>=3.10.0.2;
# 报错2
# 降级 ImportError: urllib3 v2 only supports OpenSSL 1.1.1+, currently the 'ssl' module is compiled with 'OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017'.
pip38 uninstall urllib3
pip38 install 'urllib3<2.0'
# 查看版本
python38 -m datahub version
# 下载docker镜像
wget https://github.com/datahub-project/datahub/blob/master/docker/quickstart/docker-compose.consumers-without-neo4j.quickstart.yml
docker pull acryldata/datahub-frontend-react:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-gms:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-kafka-setup:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-elasticsearch-setup:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-upgrade:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-mysgl-setup:v0.13.1
docker pull acryldata/datahub-actions:head
docker pull confluentinc/cp-schema-registry:7.4.0
docker pull confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.4.0
docker pull confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:7.4.0
docker pull elasticsearch:7.10.1
docker pull mysql:8.2
# 安装
python38 -m datahub version
# 参考版本 https://hub.docker.com/r/linkedin/datahub-gms/tags?page=1&page_size=&ordering=&name=0.1
export DATAHUB_VERSION='v0.13.1'
# 启动方式1:默认启动
python38 -m datahub docker quickstart --mysql-port 53306 --zk-port 52181 --kafka-broker-port 59092 --schema-registry-port 58081 --elastic-port 59200
python38 -m datahub docker quickstart --stop
# 启动方式2:配置文件启动(自定义挂载券、端口)
python38 -m datahub docker quickstart -f /opt/datahub/docker-compose-without-neo4j.quickstart-volumn.yml --version=v0.13.1 --no-pull-images -d
# 重新部署需要清理过期挂载券volumn!!!
docker volume ls
docker volume rm
docker container prune -f
docker volume prune -f
docker network prune -f
docker builder prune -f
docker ps -a
# 其他:清理所有未使用的镜像、容器、网络和存储卷
python38 -m docker system prune
2.5 导入hive元数据工具
# 安装摄入mysql插件
python38 -m datahub check plugins
pip38 install acryl-datahub[mysql]
python38 -m datahub ingest -c /root/datahub/mysql_to_datahub.yml
# 安装摄入hive插件
yum install cyrus-sasl cyrus-sasl-lib cyrus-sasl-plain cyrus-sasl-devel cyrus-sasl-gssapi cyrus-sasl-md5
pip38 install sasl
pip38 install acryl-datahub[hive]
# 编辑导入脚本
vim pro-hive.yaml
source:
type: hive
config:
host_port: 'hlj-bigdata-107-163:10000'
include_views: false
incremental_lineage: true
scheme: 'hive'
options:
connect_args:
auth: KERBEROS
kerberos_service_name: hive
sink:
type: "datahub-rest"
config:
server: 'http://dc2-bigdata-rainbow-sit01:58080'
# 执行命令
python38 -m datahub ingest -c pro-hive.yaml2.6 Sqllineage
pip38 install sqllineage
3.血缘解析
3.1核心解析脚本
思路:
项目是git代码,通过扫描文件夹下面的sql或shell文件,提供过sqllineage进行解析,最终api写入datahub,项目涉及到一些sql清洗逻辑。
问题:
- datahub血缘写入会覆盖之前的血缘,所以每次写入需要把当前表的血缘获取完整再写入,目前通过dict字典存储,最终再写入。
- 每个项目的区别不太一样, 非纯sql文件解析会有异常,但最终执行会有sql文件,处理方式是将最终执行sql输出到中间sql文件夹,再最终sqllineage解析该文件。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 多线程解析字段血缘到datahub
import json
from datetime import datetime
import os
import re
import subprocess
import sys
from sqllineage.runner import LineageRunner
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
from signal import SIGTERM
from multiprocessing import Pool, Manager
if sys.platform == 'linux':
from signal import alarm
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
from datahub.emitter.mce_builder import make_dataset_urn
from datahub.ingestion.graph.client import DatahubClientConfig, DataHubGraph
from datahub.metadata.com.linkedin.pegasus2avro.dataset import (
DatasetLineageType,
FineGrainedLineage,
FineGrainedLineageDownstreamType,
FineGrainedLineageUpstreamType,
Upstream,
UpstreamLineage,
)
def scan_directory(directory):
"""
扫描指定目录下的所有文件,并返回文件列表,如果传入不是文件夹,则转换成一个数组返回
"""
file_list = []
if os.path.isdir(directory):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
file_list.append(file_path)
else:
file_list.append(directory)
return file_list
def read_file(file_path):
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return file.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
return f"文件 {file_path} 未找到。"
except Exception as e:
return f"处理文件时发生错误: {e}"
def read_sql_file(file_path):
"""
读取sql文件,并去除测试环境关键字_sit或参数,注释行(可能有;导致sql异常)
"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
text = file.read()
text = re.sub(r'_sit', '', text, flags=re.IGNORECASE) # 库环境
text = re.sub(r'\$\{.{0,10}env.{0,10}\}', '', text, flags=re.IGNORECASE) # 库环境
text = re.sub(r'\$\{\w+(date|time)\}', '2024-01-01', text,
flags=re.IGNORECASE) # 日期变量 ${hiveconf:start_date}
text = re.sub(r'\$\{\w+[:]?\w+(date|time)\}', '2024-01-01', text, flags=re.IGNORECASE) # 日期变量
text = re.sub(r'where\s+\$\{.{0,20}\}', 'where 1=1', text) # where 变量 -> where 1=1
text = re.sub(r'\$\{.{0,10}filter.{0,10}\}', '', text) # 剔除where类型sql
text = re.sub(r'\'\$\{.{0,20}\}\'', '\'\'', text) # 替换'${变量}' -> ''
text = re.sub(r'\"\$\{.{0,20}\}\"', '\'\'', text) # 替换 ${变量} -> ''
text = re.sub(r'\$\{.{0,20}\}', '\'\'', text) # 替换 ${变量} -> ''
text = re.sub(r'^--.*\n?', '', text, flags=re.MULTILINE) # 剔除注解
text = re.sub(r'upsert\s+', 'insert ', text, flags=re.IGNORECASE) # 写入语法替换成标准语法
text = re.sub(r'\\;', '\\#', text) # sql语句中存在函数按;切割的符号,替换掉
return text
except FileNotFoundError:
return f"文件 {file_path} 未找到。"
except Exception as e:
return f"处理文件时发生错误: {e}"
def check_file(file_path):
def is_sql_exec_file(text):
"""
判断是否可执行文件:
1.包含"select" 关键字的sql文件,忽略大小写
2.包含sql执行命令
"""
# 定义关键字列表
keywords = ["select"]
# 对每个关键字使用正则表达式检查,忽略大小写
for keyword in keywords:
if not bool(re.compile(keyword, re.IGNORECASE).search(text)):
return False # 只要有一个关键字未找到,就返回False
# 判断是否找到sql执行命令
return bool(re.compile('batch_execute_', re.IGNORECASE).search(text)) # 所有关键字都找到,返回True
def is_danger_file(text):
"""
包含危险关键字
"""
keywords = ["spark-sql"]
# 对每个关键字使用正则表达式检查,忽略大小写
for keyword in keywords:
if bool(re.compile(keyword, re.IGNORECASE).search(text)):
return True # 只要有一个关键字找到,就返回True
return False # 所有关键字未找到一个,返回False
dir_name = os.path.dirname(file_path) # 获取目录路径
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path) # 获取文件名,包含扩展名
name_without_extension, extension = os.path.splitext(file_name) # 分离文件名和扩展名
if bool(re.compile('export', re.IGNORECASE).search(file_name)):
print('跳过导出执行文件:' + file_name + '\n')
return True
if bool(re.compile('check', re.IGNORECASE).search(file_name)):
print('跳过检查执行文件:' + file_name + '\n')
return True
if extension != '.sql' and not is_sql_exec_file(read_file(file_path)):
print('跳过无sql文件:' + file_name + '\n')
return True
if is_danger_file(read_file(file_path)):
print('跳过危险文件:' + file_name + '\n')
return True
return False
def parse_to_sqlfile(input_file_path, output_file_path, output_sqlflie_path):
"""
将文件中的执行命令替换成echo "sql参数",最终用于新文件
:param input_file_path: 旧文件
:param output_file_path: 新文件
:param output_sqlflie_path: 输出sql文件
:return:
"""
def is_exec_command(command):
"""
判断命令语句是否为可执行命令
"""
# 不过滤集合
shell_keywords = ["if", "then", "else", "fi", "for", "while", "do", "done", # "in",
"case", "esac", "function", "select", "try", "except", "finally", "#", "echo"
, "select", "as", ";", "{", "}", "--", "declare", "join", "set"]
if bool(re.compile('/opt/cloudera', re.IGNORECASE).search(command)):
print('跳过用户执行命令:' + command + '\n')
return True
if bool(re.compile('hadoop |hdfs ', re.IGNORECASE).search(command)):
print('跳过用户执行命令:' + command + '\n')
return True
if bool(re.compile('hive\s+-e', re.IGNORECASE).search(command)):
print('跳过用户执行命令:' + command + '\n')
return True
if bool(re.compile('<<\s+EOF', re.IGNORECASE).search(command)):
print('跳过多输入命令:' + command + '\n')
return True
# !! 跳过默认执行命令,跳过空字符串
if len(command.strip()) == 0:
return False
first_word = command.strip().split(maxsplit=1)[0]
cmd = ['bash', '-c', 'command -v {}'.format(first_word)]
result = subprocess.run(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, text=True)
# 检查命令是否存在
if result.returncode == 0:
# 排查shell关键字
if any(keyword in first_word for keyword in shell_keywords):
return False
return True
else:
# 命令不存在
return False
with open(input_file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as input_file, \
open(output_file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as output_file:
for line in input_file:
tmp_line = line.lower().strip()
# 1.检查替换用户执行:检查导包
if bool(re.compile('source .*sh', re.IGNORECASE).search(tmp_line)):
if bool(re.compile('date_setting\\.sh', re.IGNORECASE).search(tmp_line)):
# 保留日期工具
output_file.write(tmp_line + '\n')
else:
print('跳过导包命令:' + tmp_line + '\n')
continue
# 2.检查替换系统执行命令
# 因为存在 if xxx then: exit 0 fi ,不能直接替换为空
if is_exec_command(line):
print('跳过系统执行语句:' + line + '\n')
# output_file.write(f'echo''\n')
continue
# 3.检查sql:注释掉高风险sql
if tmp_line.startswith('truncate ') \
| tmp_line.startswith('drop ') \
| tmp_line.startswith('delete ') \
| tmp_line.startswith('alter '):
line = '--' + line
# 4.检查替换用户执行命令(自定义方法):echo "sql参数",输出sql到文件,将
# batch_execute_sql 参数A 参数B
# batch_execute_hive_sql
# batch_execute_spark_sql
# batch_execute_spark3_sql
if line.strip().startswith('batch_execute_') | line.strip().startswith('execute_sql'):
# 最多分割两次,取第二个参数
parts = line.split(maxsplit=2)
if len(parts) >= 2:
parameter_a = parts[1].strip()
transformed_line = f'echo {parameter_a} \';\' >> {output_sqlflie_path}\n'
output_file.write(transformed_line)
else:
print(f"提取参数失败: {line.strip()}")
else:
output_file.write(line)
def executor(script_path, timeout):
"""
运行指定的shell脚本,并在超时时终止执行。
参数:
script_path (str): 要执行的shell脚本的路径。
timeout (int): 脚本执行的超时时间(秒)。
返回:
tuple: 包含脚本的标准输出和标准错误的元组。如果脚本因超时而被终止,则返回None。
"""
def handler(signum, frame):
"""信号处理器,用于在接收到SIGALRM时终止子进程"""
raise Exception("Timed out!")
try:
# 使用Popen启动shell脚本,以便我们能够跟踪其进程
process = subprocess.Popen([script_path], shell=True, preexec_fn=os.setsid)
# 启动定时器
if sys.platform == 'linux':
alarm(timeout)
# 等待子进程完成
stdout, stderr = process.communicate()
except Exception as e:
# 超时处理
print(f"子进程执行异常: {e}")
# 终止子进程及其子进程组
os.killpg(os.getpgid(process.pid), SIGTERM)
process.wait()
return None
finally:
# 重置闹钟
if sys.platform == 'linux':
alarm(0)
# print()
# 检查stdout和stderr是否为None,以避免解码错误
stdout = stdout.decode('utf-8') if stdout is not None else ""
stderr = stderr.decode('utf-8') if stderr is not None else ""
# 如果没有异常,返回脚本的输出
return stdout, stderr
def parse_sqllineage(file_path, all_dict):
"""
解析sql脚本到全局字典
"""
def save_sql(target_tables, sql):
"""
保存sql到全局字典
"""
if all_dict.get(target_tables) is None:
all_dict[target_tables] = [sql]
if all_dict.get(target_tables) is not None:
all_dict[target_tables] = all_dict[target_tables] + [sql]
def parse_sqlfile(file_path):
print("开始解析sql文件:", file_path)
sqltext = read_sql_file(file_path).lower()
sqls = sqltext.split(';')
for idx, sql in enumerate(sqls):
# 跳过部分非查询语句
if bool(re.compile('^\s+update ', re.IGNORECASE).search(sql)):
continue
if not bool(re.compile('select', re.IGNORECASE).search(sql)):
continue
if bool(re.compile('kudu', re.IGNORECASE).search(sql)):
continue
try:
sqllineage = LineageRunner(sql, dialect="sparksql")
if sqllineage is not None and len(sqllineage.target_tables) > 0:
save_sql(sqllineage.target_tables[0], sql)
# send_sqllineage_datahub(sqllineage)
print(f"第{idx}条sql在sparksql解析血缘成功:", sqllineage)
continue
except Exception as spark_e:
print("SparkSql解析异常,进入HiveSQL解析.")
try:
sqllineage = LineageRunner(sql, dialect="hive")
if sqllineage is not None and len(sqllineage.target_tables) > 0:
save_sql(sqllineage.target_tables[0], sql)
# send_sqllineage_datahub(sqllineage)
print(f"第{idx}条sql在hivesql解析血缘成功:", sqllineage)
continue
except Exception as hive_e:
print(f"解析sql(SparkSql和HiveSQL)失败.", hive_e)
continue
# 调用核心方法
parse_sqlfile(file_path)
def send_coulumn_sqllineage_datahub(all_dict):
def query_sqllineage_datahub(table_name):
"""
返回当前上游血缘表
"""
graph = DataHubGraph(config=DatahubClientConfig(server=server_url))
dataset_urn = make_dataset_urn(name=table_name, platform="hive")
query = """
query searchAcrossLineage {
searchAcrossLineage(
input: {
query: "*"
urn: "$dataset_urn"
start: 0 # 分页
count: 100 # 条数
direction: UPSTREAM # 上游血缘
orFilters: [
{
and: [
{
condition: EQUAL
negated: false
field: "degree"
values: ["1"] # 血缘层级
}
]
}
]
}
) {
searchResults {
degree
entity {
urn
}
}
}
}
""".replace('$dataset_urn', dataset_urn)
result = graph.execute_graphql(query=query)
current_upstream_urn = []
for res in result['searchAcrossLineage']['searchResults']:
# [{'degree': 1, 'entity': {'urn': 'urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,dws.dws_shoppe_sale_detail_di,PROD)'}}]
current_upstream_urn.append(res['entity']['urn'])
return current_upstream_urn
def datasetUrn(dataType, tbl):
return builder.make_dataset_urn(dataType, tbl, "PROD")
def fldUrn(dataType, tbl, fld):
return builder.make_schema_field_urn(datasetUrn(dataType, tbl), fld)
def send_sqllineage_datahub(sqllineage, append_lineage=True):
"""
发送血缘到datahub,列字段血缘还需要调整.
:param sqllineage: 血缘
:param append_lineage: 是否追加之前的表血缘
:return:
"""
targetTableName = sqllineage.target_tables[0].__str__() # 获取sql中的下游表名
lineage = sqllineage.get_column_lineage # 获取列级血缘
fineGrainedLineageList = [] # 字段级血缘list
upStreamsList = [] # 用于冲突检查的上游list
# 把表血缘的加入到字段血缘
for upStreamTableName in sqllineage.source_tables:
upStreamsList.append(
Upstream(dataset=datasetUrn("hive", str(upStreamTableName)), type=DatasetLineageType.TRANSFORMED))
# 遍历列级血缘
for columnTuples in lineage():
upStreamStrList = []
downStreamStrList = []
# 逐个字段遍历
for column in columnTuples:
# 元组中最后一个元素为下游表名与字段名,其他元素为上游表名与字段名
# 遍历到最后一个元素,为下游表名与字段名
if columnTuples.index(column) == len(columnTuples) - 1:
# ['urn:li:schemaField:(urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,default.sinktb,PROD),id)']
downStreamFieldName = column.raw_name.__str__()
downStreamTableName = column.__str__().replace('.' + downStreamFieldName, '').__str__()
downStreamStrList.append(fldUrn("hive", downStreamTableName, downStreamFieldName))
else:
# 组装上游血缘List: ['urn:li:schemaField:(urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,default.sourcetb,PROD),name)']
upStreamFieldName = column.raw_name.__str__()
upStreamTableName = column.__str__().replace('.' + upStreamFieldName, '').__str__()
upStreamStrList.append(fldUrn("hive", upStreamTableName, upStreamFieldName))
# 用于检查上游血缘是否冲突
upStreamsList.append(
Upstream(dataset=datasetUrn("hive", upStreamTableName), type=DatasetLineageType.TRANSFORMED))
# print("upStreamsList:", upStreamsList)
# print("downStreamStrList:", downStreamStrList)
# 设置血缘级别
# DATASET 数据集级别
# FIELD_SET 字段级别
fineGrainedLineage = FineGrainedLineage(upstreamType=FineGrainedLineageUpstreamType.FIELD_SET,
upstreams=upStreamStrList,
downstreamType=FineGrainedLineageDownstreamType.FIELD,
downstreams=downStreamStrList)
fineGrainedLineageList.append(fineGrainedLineage)
fieldLineages = UpstreamLineage(
upstreams=upStreamsList, fineGrainedLineages=fineGrainedLineageList
)
lineageMcp = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=datasetUrn("hive", targetTableName), # 下游表名
aspect=fieldLineages
, changeType="UPSERT" # 新增或更新血缘
)
# 发送血缘
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=server_url)
# 发送列血缘
try:
# print(sqllineage)
# print(lineageMcp)
# 提取字段解析出来的上游表列表
data_dict = json.loads(lineageMcp.make_mcp().aspect.value)
# 提取upstreams数组
upstreams_list = data_dict.get('upstreams')
column_source_list = []
pattern = r'urn:li:dataset:\(urn:li:dataPlatform:\w+\,([^,]+),\w+\)'
for i in upstreams_list:
match = re.search(pattern, str(i))
if match:
column_source_list.append(match.group(1))
# 计算交集
set_table = set([str(table_name) for table_name in sqllineage.source_tables])
set_colums = set(column_source_list)
print("添加数仓表 【{}】血缘成功".format(targetTableName))
emitter.emit_mcp(lineageMcp)
except Exception as e:
print("添加数仓表 【{}】血缘失败".format(targetTableName))
print(e)
def scan_dict(all_dict):
for tableName, sql in all_dict.items():
result_sql = ';'.join(sql)
try:
sqllineage = LineageRunner(result_sql, dialect="sparksql")
# print(result_sql)
if sqllineage is not None and len(sqllineage.target_tables) > 0:
send_sqllineage_datahub(sqllineage)
continue
except Exception as spark_e:
print("最终Sql:SparkSql解析异常,进入HiveSQL解析.")
try:
sqllineage = LineageRunner(result_sql, dialect="hive")
if sqllineage is not None and len(sqllineage.target_tables) > 0:
send_sqllineage_datahub(sqllineage)
continue
except Exception as hive_e:
print(f"最终Sql:解析sql(SparkSql和HiveSQL)失败.", hive_e)
continue
# 核心方法!!
scan_dict(all_dict)
def parse_file(file_path, tmp_dir_name, all_dict):
# for file_path in scan_directory(file_paths):
# 分离出文件名和路径
dir_name = os.path.dirname(file_path) # 获取目录路径
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path) # 获取文件名,包含扩展名
name_without_extension, extension = os.path.splitext(file_name) # 分离文件名和扩展名
# 1.检查文件名及内容
if check_file(file_path):
return
# 2. 判断文件类型并生成血缘
formatted_now = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print(f'-------------{formatted_now} 开始解析文件:{file_path}.\n')
if extension == '.sql':
# 2.1 直接解析sql到字典
parse_sqllineage(file_path, all_dict)
print(f'解析{file_path}完成.\n')
elif extension == '.sh':
# 2.2.1 生成新shell文件
output_file_path = os.path.join(tmp_dir_name, name_without_extension + '.sh')
output_sqlflie_path = os.path.join(tmp_dir_name, name_without_extension + '.sql')
parse_to_sqlfile(file_path, output_file_path, output_sqlflie_path)
# 2.2.2 先清空文件,执行新shell文件生成sql,只给5秒解析
command = f"echo '' > {output_sqlflie_path} && sh {output_file_path}"
executor(command, 5)
# 2.2.3 解析sql到字典
parse_sqllineage(output_sqlflie_path, all_dict)
else:
return
print(f'-------------{formatted_now} 结束解析文件:{file_path}.\n')
def mult_parse_file(file_paths, tmp_dir_name, all_dict):
"""
多线程扫描所有路径生成sql缓存到字典里
"""
# 设置参数
params = []
for file_path in scan_directory(file_paths):
params.append((file_path, tmp_dir_name, all_dict))
pool = Pool(6) # 进程数
pool.starmap(parse_file, params)
pool.close()
pool.join() # 确保所有进程执行完毕
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1.获取命令行参数
args = sys.argv
server_url = ''
file_paths = ''
tmp_dir_name = ''
if sys.platform == 'linux':
server_url = "http://192.168.1.10:58080"
file_paths = args[1]
# file_paths = '/rainbow/bigdata-script/ads'
tmp_dir_name = '/home/caijiasheng/parsefile/'
# 刷新kerberos认证
cmd = "cd {};git pull".format(file_paths)
print("开始执行cmd命令(拉取最新git):{}".format(cmd))
subprocess.run(cmd, shell=True)
if sys.platform == 'win32':
# 测试环境
server_url = "http://192.168.1.10:58080"
file_paths = 'D:\workspace\pycharmworksapce\PyDemo\\resource\sqlfile'
tmp_dir_name = 'D:\workspace\pycharmworksapce\PyDemo\\resource\tmp'
all_dict = Manager().dict() # 这是一个可以在进程间共享的字典
# 2.解析文件->sql->全局字典(缓存sql)
mult_parse_file(file_paths, tmp_dir_name, all_dict)
# 3.写入全局字典->datahub字段血缘
send_coulumn_sqllineage_datahub(all_dict)
3.2 成果


4. 相关资料
开源元数据管理平台Datahub最新版本0.10.5——安装部署手册(附离线安装包)
【Datahub系列教程】Datahub入门必学——DatahubCLI之Docker命令详解
开源数据血缘和元数据管理框架DataHub的血缘摄取 V0.12.1版本
hive kerberos