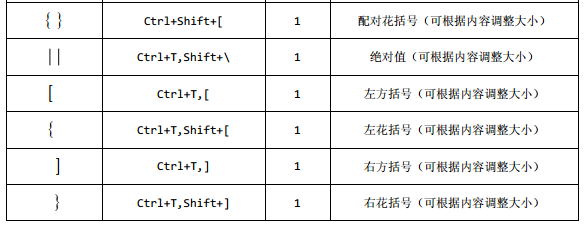
1. CompletableFuture简介
1.1 异步编程的概念
异步编程是一种编程范式,允许程序在等待某些操作完成时,继续执行其他任务。这在处理I/O密集型任务,如网络请求或文件读写时尤其有用。异步编程可以提高程序的响应性和效率,避免在等待I/O操作时浪费CPU资源。
1.2 CompletableFuture的作用
CompletableFuture 是Java 8引入的一个类,位于java.util.concurrent包中。它提供了一种更加强大和灵活的方式来处理异步编程。CompletableFuture 可以表示一个异步操作的最终结果,并且可以对其进行链式调用,实现复杂的异步逻辑。
以下是一些常用的CompletableFuture API的使用示例:
1.2.1 创建CompletableFuture
// 创建一个已经完成的CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> completedFuture = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("已完成");
// 创建一个异步任务,supplyAsync会在另一个线程中执行给定的Supplier
CompletableFuture<String> future future = CompletableFuture -> {
// 模拟长时间运行的任务
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "异步结果";
});
1.2.2 处理CompletableFuture的结果
// thenApply用于处理CompletableFuture的结果,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture
future.thenApply(result -> {
System.out.println("处理结果: " + result);
return result.toUpperCase(); // 转换为大写
}).thenAccept(upperCaseResult -> {
System.out.println("接收到的大写结果: " + upperCaseResult);
});
1.2.3 组合CompletableFuture
// thenCombine用于组合两个CompletableFuture的结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 10);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 20);
future1.thenCombine(future2, (a, b) -> a + b).thenAccept(sum -> {
System.out.println("两个结果的和: " + sum);
});
1.2.4 异常处理
// exceptionally用于处理CompletableFuture中的异常
CompletableFuture<String> failedFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
throw new RuntimeException("发生异常");
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
System.out.println("捕获到异常: " + throwable.getMessage());
return "异常处理结果";
});
1.2.5 等待所有任务完成
// allOf用于等待多个CompletableFuture全部完成
CompletableFuture<Void> combined = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
combined.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("所有任务都已完成");
});
1.2.6 应用案例
以下是CompletableFuture在实际应用中的一些案例:
1.2.6.1 网络请求
CompletableFuture<String> fetchData = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟网络请求
return "从服务器获取的数据";
});
// 处理获取到的数据
fetchData.thenApply(data -> {
// 对数据进行处理
return data + " 经过处理";
}).thenAccept(processedData -> {
System.out.println("处理后的数据: " + processedData);
});
1.2.6.2 文件读写
CompletableFuture<Void> readFile = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 模拟从文件中读取数据
String content = "文件内容";
// 对文件内容进行处理
System.out.println("读取并处理文件内容: " + content);
});
CompletableFuture<Void> writeFile = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 模拟将数据写入文件
System.out.println("将数据写入文件");
});
// 等待读写操作完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(readFile, writeFile).join();
1.2.6.3 数据库操作
CompletableFuture<List<User>> fetchUsers = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟从数据库中获取用户列表
return Arrays.asList(new User("Alice"), new User("Bob"));
});
// 处理用户数据
fetchUsers.thenApply(users -> {
users.forEach(user -> System.out.println("处理用户: " + user.getName()));
return users;
});
这些示例展示了CompletableFuture在不同场景下的应用,包括创建异步任务、处理结果、异常处理、组合任务以及在网络请求、文件读写和数据库操作中的应用。通过这些示例,可以更深入地理解CompletableFuture的用法和强大之处。
2. CompletableFuture的创建和基本用法
2.1 使用supplyAsync创建异步任务
supplyAsync 方法是 CompletableFuture 中用于创建带有返回结果的异步任务的静态工厂方法。此方法接受一个 Supplier 函数接口参数,该参数代表异步执行的任务,并返回一个 CompletableFuture 对象。
以下是 supplyAsync 方法的基本使用示例:
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return "任务结果";
});
// 通过 thenAccept 方法处理异步任务的结果
future.thenAccept(result -> {
System.out.println("异步任务结果: " + result);
});
// 通过 join 方法等待异步任务完成并获取结果
try {
String result = future.join();
System.out.println("通过 join 获取的异步任务结果: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
2.2 使用runAsync执行无返回值的任务
与 supplyAsync 类似,runAsync 方法用于创建并执行无返回结果的异步任务。此方法接受一个 Runnable 函数接口参数。
以下是 runAsync 方法的使用示例:
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务正在执行...");
// 模拟耗时操作
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
System.out.println("异步任务执行完毕.");
});
// 使用 thenRun 方法在异步任务完成后执行其他操作
future.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("异步任务之后的操作.");
});
// 由于 runAsync 创建的 CompletableFuture 无返回值,因此无法通过 join 获取结果
// 但可以通过 isDone 判断任务是否完成
future.isDone();
以上代码展示了如何使用 CompletableFuture 的 supplyAsync 和 runAsync 方法来创建和执行异步任务,并提供了如何获取异步任务结果和在任务完成后执行其他操作的示例。这些是异步编程中非常基础且常用的用法。在实际应用中,可以结合 thenApply, thenAccept, thenRun, whenComplete 等方法进一步扩展异步任务链,实现更复杂的逻辑。
3. CompletableFuture的链式调用
3.1 thenApply和thenApplyAsync
thenApply 方法用于对 CompletableFuture 的结果进行处理,并返回一个新的 CompletableFuture,其结果为处理函数的返回值。这个方法会阻塞等待前一个任务完成,然后同步执行提供的函数。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
.thenApply(s -> s + " World")
.thenAccept(System.out::println);
相对的,thenApplyAsync 方法同样用于处理结果,但是它会异步执行提供的函数,可以使用自定义的 Executor 来指定执行线程池。
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello", executorService)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> s + " World", executorService)
.thenAccept(System.out::println);
3.2 thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
thenAccept 方法用于消费 CompletableFuture 的结果,不返回新的结果,适合在完成某个操作后执行一些副作用操作。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
.thenAccept(System.out::println);
thenAcceptAsync 方法也是消费结果,但是异步执行,允许在不同的线程中处理结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello", executorService)
.thenAcceptAsync(System.out::println, executorService);
3.3 thenRun和thenRunAsync
thenRun 方法在前一个 CompletableFuture 完成后执行一个动作,不接收任何输入参数,也不产生结果。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("World"));
而 thenRunAsync 方法则是异步执行动作,可以在不同的线程中完成。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello", executorService)
.thenRunAsync(() -> System.out.println("World"), executorService);
应用案例
以下是一些 CompletableFuture 在实际应用中的代码示例:
1. 异步处理链式调用
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟数据库查询操作
return "Data from DB";
})
.thenApply(data -> {
// 对数据进行处理
return data.toUpperCase();
})
.thenAccept(processedData -> {
// 打印处理后的数据
System.out.println(processedData);
});
2. 并发执行多个任务并汇总结果
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 任务1
});
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 任务2
});
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).thenRun(() -> {
// 两个任务都完成后执行
System.out.println("Both tasks are completed.");
});
3. 异常处理
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (Math.random() > 0.5) {
throw new RuntimeException("Random failure");
}
return "Success";
})
.exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 处理可能发生的异常
System.out.println("An error occurred: " + throwable.getMessage());
return "Error";
})
.thenAccept(result -> {
// 打印结果
System.out.println(result);
});
4. 结果转换和组合
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
future.thenApply(s -> s + " World") // 字符串拼接
.thenAccept(System.out::println); // 打印结果
5. 使用自定义线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello", executorService)
.thenApplyAsync(s -> s + " World", executorService)
.thenAcceptAsync(System.out::println, executorService);
executorService.shutdown();
这些示例展示了 CompletableFuture 在不同场景下的应用,包括异步处理、任务组合、异常处理等。通过链式调用,可以构建复杂的异步逻辑,同时保持代码的清晰和可维护性。
4. 异常处理和任务组合
CompletableFuture提供了多种方法来处理异步编程中的异常情况和组合多个任务。以下是一些常用的API使用实例和应用案例,以及大量的代码示例。
4.1 exceptionally方法
exceptionally方法用于异常处理,当CompletableFuture中的计算发生异常时,可以调用此方法来提供异常的处理逻辑。
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
throw new RuntimeException("Error occurred");
});
future.exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println("Exception caught: " + ex.getMessage());
return 0; // 返回默认值
});
4.2 allOf和anyOf方法
allOf方法用于等待多个CompletableFuture任务全部完成,而anyOf方法则是等待其中一个任务完成。
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Result 1");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 42);
CompletableFuture<Void> allFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);
allFuture.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("Both futures are completed"));
CompletableFuture<Object> anyFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
anyFuture.thenAccept(result -> System.out.println("One of the futures is completed with result: " + result));
4.3 thenCombine和thenAcceptBoth
thenCombine方法允许将两个CompletableFuture的结果合并为一个新的结果,而thenAcceptBoth方法则是将两个任务的结果合并后执行一个动作。
CompletableFuture<String> futureA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<Integer> futureB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 5);
futureA.thenCombine(futureB, (str, num) -> str + " " + num)
.thenAccept(System.out::println); // 输出: Hello 5
futureA.thenAcceptBoth(futureB, (str, num) -> System.out.println(str + " " + num)); // 同上
4.4 任务组合的其他方法
除了上述方法,CompletableFuture还提供了其他一些用于任务组合的方法,如runAfterBoth、applyToEither等。
CompletableFuture<Void> bothFuture = futureA.runAfterBoth(futureB, () -> {
System.out.println("Both futures completed");
});
CompletableFuture<String> eitherFuture = futureA.applyToEither(futureB, str -> str + " (from either)");
eitherFuture.thenAccept(System.out::println); // 输出第一个完成的任务的结果
4.5 异常处理和任务组合的高级应用
在实际应用中,我们可能需要更复杂的异常处理和任务组合逻辑,以下是一些高级应用示例。
// 异常处理,使用handle方法
future.handle((result, ex) -> {
if (ex != null) {
System.out.println("Error: " + ex.getMessage());
return null; // 或者进行其他错误恢复操作
}
return result;
});
// 组合多个任务,使用CompletableFuture.join
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3).join();
// 并行执行多个任务,并在所有任务完成后获取结果列表
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = Arrays.asList(
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 1 result"),
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 2 result"),
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Task 3 result")
);
CompletableFuture<Void> allTasksFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]));
allTasksFuture.thenRun(() -> {
futures.forEach(future -> System.out.println(future.join()));
});
以上代码示例涵盖了CompletableFuture在异常处理和任务组合方面的多种使用场景,展示了如何通过链式调用和组合方法来实现复杂的异步编程逻辑。在实际开发中,可以根据具体需求选择合适的方法来处理异步任务。
5. 应用案例分析
5.1 并发获取多个数据源
在现代应用开发中,经常需要从多个数据源并发获取数据,以提高应用的响应速度和系统的整体性能。CompletableFuture提供了一种简洁高效的方式来实现这一需求。
5.1.1 并发查询数据库
假设我们有一个电子商务应用,需要从不同的数据库中查询商品信息、库存数据和用户评价。使用CompletableFuture,我们可以并发执行这些查询,并将结果汇总。
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<List<Product>> productFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟数据库查询操作
return productDao.getProducts();
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<List<Stock>> stockFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟数据库查询操作
return stockDao.getStocks();
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<List<Review>> reviewFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟数据库查询操作
return reviewDao.getReviews();
}, executor);
CompletableFuture.allOf(productFuture, stockFuture, reviewFuture)
.thenAcceptBoth(productFuture, (stocks, products) -> {
// 处理库存和商品信息
})
.thenAcceptBoth(reviewFuture, (reviews, stockProductsPair) -> {
// 处理用户评价和库存商品信息对
})
.thenRun(() -> {
// 所有数据查询完成,执行后续操作
});
5.2 异步任务的顺序执行与并行执行
在某些场景下,我们需要按照特定的顺序执行异步任务,同时利用并行执行来优化性能。CompletableFuture提供了丰富的API来支持这种模式。
5.2.1 顺序执行
考虑一个场景,我们需要先从服务器下载数据,然后处理数据,最后将处理结果保存到数据库。这些任务必须顺序执行,但每个任务内部可以并行处理。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟从服务器下载数据
return fetchDataFromServer();
}).thenApplyAsync(data -> {
// 模拟数据处理操作
return processData(data);
}).thenAcceptAsync(result -> {
// 模拟将结果保存到数据库
saveResultToDatabase(result);
});
5.2.2 并行执行
在另一个场景中,我们可能需要同时执行多个独立的任务,比如发送多个异步请求,然后汇总结果。
CompletableFuture<String> request1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟发送异步请求1
return sendRequest1();
});
CompletableFuture<String> request2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟发送异步请求2
return sendRequest2();
});
request1.thenCombine(request2, (result1, result2) -> {
// 合并两个请求的结果
return combineResults(result1, result2);
}).thenAccept(combinedResult -> {
// 使用合并后的结果进行进一步操作
furtherProcess(combinedResult);
});
5.2.3 异常处理
在异步编程中,异常处理是非常重要的。CompletableFuture提供了exceptionally方法来处理异步任务中的异常。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟可能抛出异常的操作
return potentiallyFailingOperation();
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 处理异常,返回默认值或进行恢复操作
return handleException(throwable);
});
5.2.4 超时处理
在某些情况下,我们可能需要对异步操作设置超时限制。CompletableFuture的get方法可以接收超时时间参数,以避免无限期地等待异步操作完成。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟长时间运行的异步任务
return longRunningAsyncOperation();
}).get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 设置5秒超时
5.2.5 结果转换
使用thenApply方法,我们可以在异步操作完成后对结果进行转换。
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟获取原始数据
return fetchData();
}).thenApply(data -> {
// 转换数据格式
return transformData(data);
});
5.2.6 结果消费
在某些情况下,我们可能只关心异步操作的结果消费,而不关心返回值。这时可以使用thenAccept方法。
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 模拟执行某些操作
performAction();
}).thenAccept(result -> {
// 消费结果
consumeResult(result);
});
5.2.7 多个异步操作的组合
当需要等待多个异步操作都完成后再执行某个操作时,可以使用allOf方法。
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::action1);
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::action2);
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2).thenRun(() -> {
// 两个异步操作都完成后执行
performCombinedAction();
});
这些示例展示了CompletableFuture在实际开发中的多样化应用,包括并发数据获取、顺序与并行任务执行、异常处理、超时处理、结果转换和消费,以及多个异步操作的组合使用。通过这些API的使用,可以大大提高异步编程的效率和灵活性。
6. 线程池的使用和自定义
6.1 默认线程池的局限性
默认线程池,如 Executors 提供的几种快捷线程池,虽然使用方便,但存在一些局限性:
-
FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadExecutor:允许任务队列长度无界,可能导致内存溢出。
-
CachedThreadPool:可创建的线程数量无限制,可能导致系统资源耗尽。
-
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor:适用于定时任务,但可能存在资源浪费。
示例代码:使用FixedThreadPool的潜在问题
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class FixedThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
6.2 自定义线程池的应用
自定义线程池可以更精确地控制线程数量、任务队列、拒绝策略等,适用于不同的应用场景。
示例代码:自定义线程池的创建和使用
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class CustomThreadPoolDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5, // corePoolSize
10, // maximumPoolSize
60L, // keepAliveTime
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(100), // workQueue
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // handler
);
// handler
);
0; i < 50; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 2000));
System.out.println("Task " + i + " executed by " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
应用案例:异步处理日志记录
在实际应用中,可以使用自定义线程池来异步处理日志记录,提高应用性能。
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AsyncLogHandler {
private static final ExecutorService logExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static void log(String message) {
logExecutor.execute(() -> {
// 模拟日志记录操作
try {
Thread.sleep(500); // 模拟耗时的日志写入操作
System.out.println("Logged: " + message);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
log("This is an asynchronous log message.");
}
}
应用案例:批量图像处理
在图像处理应用中,可以利用线程池来并行处理图像,提高处理速度。
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class ImageProcessor {
private static final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
public static void processImage(String imagePath) {
executor.execute(() -> {
// 模拟图像处理操作
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟耗时的图像处理
System.out.println("Processed image: " + imagePath);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String imagePath = "image_" + i + ".jpg";
processImage(imagePath);
latch.countDown();
}
latch.await(); // 等待所有图像处理完成
executor.shutdown();
}
}
以上示例展示了自定义线程池在不同场景下的应用,通过合理配置线程池参数,可以有效提升程序性能和资源利用率。