IO流体系

字节流
字节流: 字节输出流:FileOutputStream 程序---写--->文件 字节输入流:FileInputStream 程序<---读---文件
字节输出流(FileOutputStream)
@Test
public void testIO01() throws IOException {
/*
new FileOutputStream
文件不存在创建文件
父级文件夹不存在报错
*/
byte[] bytes = "我测匿名".getBytes();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\a.txt",true);//追加写模式
fos.write(bytes);
fos.close();
} @Test
public void testIO02() throws IOException {
/*
97=a 98=b 99=c ...
*/
byte[] bytes1={98,99,100};
byte[] bytes2={97,98,99,100,101,102};
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\b.txt");
fos.write('9'); //这样会写入字符9
fos.write(97);//一次写一个字节数据
fos.write(bytes1);//一次写一个字节数据的数据
fos.write(bytes2,4,2);//一次写一个字节数组中的部分数据
fos.close();
} @Test
public void testIO03() throws IOException {
/*
换行:
windows:\r\n
Linux:\n
Mac:\r
windows操作系统中,java对换行进行了优化,\r \n \r\n都可以表示换行 推荐\r\n
*/
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\c.txt",true);//追加写模式
byte[] bytes = "\r\nabcd\r\nefgh".getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);
fos.close();
}字节输入流(FileInputStream)
书写细节

read方法的使用

read方法指定字节缓冲区进行读需要注意的细节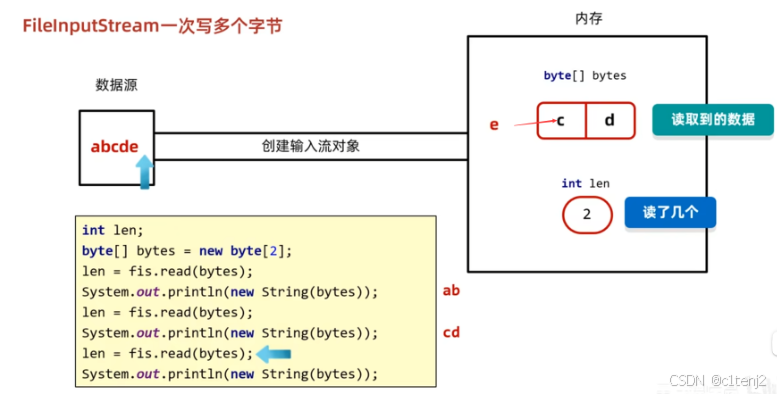
最后一次只读到一个e,但是没有指定读出字节数组的长度,最后读出的结果是ed

解决:读出的时候指定read方法返回的本次写入字节数据的字节数量

编码问题
字符集:
1.GB2312字符集:1980年发布,1981年5月1日实施的简体中文汉字编码国家标准。
2.BIG5字符集:台湾地区繁体中文标准字符集,共收录13053个中文字,1984年实施。
⚠3.GBK字符集:2000年3月17日发布,收录21003个汉字。(windows默认使用GBK)
3.1 GBK中,一个英文字母占1个字节,二进制第一位是0
3.2 GBK中,一个中文汉字占2个字节,二进制第一位是1
⚠4.国际标准字符集,它将世界各种语言的每个字符定义一个唯一的编码,以满足跨语言、跨平台的文本信息交换。
4.1一个英文占1个字节,二进制第一位是0
4.2一个汉字占3个字节,二进制第一位是1(如果编码是用GBK,解码用UTF-8,中文乱码的原因)


编码与解码:
Unicode字符集里面的UTF-8编码方式
GBK字符集里面的GBK编码方式


测试代码:
@Test
public void testIO05() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
/*
测试编码与解码
*/
String str="iam中国人啊";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//用UTF-8编码
//Unicode字符集中一个英文字母占1个字节,一个中文字符占3个字节,因此输出 3+12=15
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes)+"--"+"共"+bytes.length+"个字节");
byte[] gbkBytes = str.getBytes("GBK");//用GBK编码
//GBK中一个英文1个字节,一个中文2个字节 因此输出 3+8=11
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(gbkBytes)+"--"+"共"+gbkBytes.length+"个字节");
//UTF-8编码 GBK解码 出现乱码,英文字母还是一样的,归因于这两个编码方式对于英文字母都是用一个0开头的字节来编码的。
//iam涓浗浜哄晩
String errorStr = new String(bytes, "GBK");
System.out.println(errorStr);
}运行结果:

字节流练习
拷贝文件
package com.example.testIO;
import java.io.*;
public class demo01 {
//练习:拷贝文件
public static void copyFile(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
/*
fis.read() 每次一个字节一个字节地读太慢了
1byte=1B=8bit
创一个5MB的缓冲区
*/
int len=0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[5 * 1024 * 1024];
while ((len=fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len); //只把每次新读到的写到新文件
}
/*
关闭资源:
先开的后关,后开的先关
*/
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File source = new File("C:\\Users\\chen\\Desktop\\微信图片_20240322135504.jpg");
File dest = new File("D:\\testIO\\handsomeboy.jpg");
demo01.copyFile(source,dest);
}
}拷贝文件夹
package com.example.testIO;
import com.example.entity.Frog;
import java.io.*;
/*
用字节流来拷贝文件夹
*/
public class demo02 {
public static void copySrc(File source,File dest) throws IOException {
dest.mkdirs();
File[] files = source.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isFile()){
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest.getAbsolutePath(), file.getName()));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
int len=0;
while ((len=fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
else {
copySrc(file,new File(dest,file.getName()));// 这里的第一个参数是source目录下的文件夹 第二个参数是dest目录下的同级文件
//别想复杂了,就考虑最简单的两级情况
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File source = new File("D:\\rabbitMQ\\rabbitmq_server-3.7.4");
System.out.println(source.getName());
File dest = new File("D:\\rabbitMQ\\testIO");
// demo02.copySrc(source,dest);
}
}加密文件
在字节级别进行异或应该继续使用 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream。FileReader 和 FileWriter 会将字节转换为字符(使用平台的默认字符编码),这可能会引入不必要的字符编码问题,特别是在处理非文本文件时。
package com.example.testIO;
import java.io.*;
public class demo03 {
/*
异或 1^1=0 1^0=1 0^0=0
1100100
^ 0001010
————————————
1101110
^ 0001010
————————————
1100100
!!!!!一个数 被一个相同的数 异或两次 得到的结果是 它本身
*/
public static void encodeFile(File source,File dest) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
int ch=0;
while ((ch=fis.read())!=-1){
// System.out.println(ch);
fos.write(ch^114514);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
public static void decodeFile(File source,File dest) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
int ch=0;
while ((ch=fis.read())!=-1){
// System.out.println(ch);
fos.write(ch^114514);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File source = new File("D:\\testIO\\handsomeboy.jpg");
File encode = new File("D:\\testIO\\edcodehandsomeboy.jpg");
File decode = new File("D:\\testIO\\decodehandsomeboy.jpg");
demo03.encodeFile(source,encode);
demo03.decodeFile(encode,decode);
}
}
字符流(只能对纯文本文件进行操作,不能对文件夹进行操作)
字符输入流(FileReader)
@Test
public void testIO06() throws IOException {
/*
字符输出流FileReader
read方法:不同于字节流的每次读取一个字节,它每次读取一个字符
遇到英文一次读取一个字节,遇到中文一次读取2个字节(GBK)或三个字节(UTF-8)
//fr.read()
最终返回 这个字符在字符集的10进制
为空返回-1
//fr.read(buffer)
可以指定字符数组作为缓冲区(区分于字节流的字节缓冲区)
返回本次读到的字符数据到缓冲区上
为空返回 -1
*/
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\testIO\\e.txt");
// int ch=0;
// while ((ch=fr.read())!=-1){
// System.out.print((char) ch);
// }
int len=0;
char[] buffer = new char[2];
while ((len=fr.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
fr.close();
}字符输出流 (FileWriter)
@Test
public void testIO07() throws IOException {
char[] chars={98,99,100};
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\testIO\\f.txt",true);//追加写模式
fw.write(97);//写一个字符
fw.write(chars,0,3);//写一个字符数组的一部分
fw.write("v我");//写一个字符串
fw.write("最爱看电视剧",1,2);//写一个字符串的一部分
fw.close();
}字符流练习
文件内排序
package com.example.testIO;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/*
调整顺序:
5-3-1-4-9-8-10-2-6-7
1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10
*/
public class demo04 {
public static void sortFile(File file) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file,true);//不使用追加写模式会直接清空文件夹。
int ch=0;
while ((ch=fr.read())!=-1){
sb.append((char) ch);
}
String[] split = sb.toString().split("-");
Arrays.sort(split, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return Integer.parseInt(s1)-Integer.parseInt(s2);
}
});
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
for(int i=0;i<split.length;i++){
if(i==split.length-1){
fw.write(split[i]);
}
else {
fw.write(split[i]+"-");
}
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\testIO\\g.txt");
demo04.sortFile(file);
}
}
缓冲流
字节缓冲流(BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream)
字节缓冲流提高效率的原理(在内存中增设了缓冲区)


案例
@Test
public void testIO08() throws IOException {
/*
字节缓冲流
*/
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\testIO\\handsomeboy.jpg"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\copy.jpg"));
int ch;
while ((ch=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(ch);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}字符缓冲流
字符缓冲流的特有方法

案例
@Test
public void testIO09() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\testIO\\TodoList.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\testIO\\copyTodoList.txt"));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}总结

转换流
作用:字节流想要用字符流里面的方法了

@Test
public void testIO10() throws IOException {
/*
需求:用字节流读取文件(含中文)中的所有数据,每次读取一行
解析:文件含中文,要包装成字符流,每次读取一行,要包装成缓冲流
*/
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\testIO\\TodoList.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
//isr.read(); 转换为字符流,它里面有字符流里面的所有方法
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);//传入的isr本身就是一个字符流
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\testIO\\TodoList.txt")));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}序列化流和反序列化流
常用方法


细节汇总

测试案例
学生类实现序列化接口
package com.example.testIO;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student implements Serializable {
//serialVersionUID是java通过分析javabean中的成员和方法得到的一个专属版本号
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3944752278183804444L;
public String name;
public int age;
//transient:瞬态关键字 被它修饰的成员不会被序列化
public transient String address;
}
测试代码
package com.example.testIO;
import com.sun.corba.se.impl.orbutil.ObjectWriter;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class demo05 {
/*
测试序列化流和反序列化流
*/
public static void m1() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 123,"福建");
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 456,"安徽");
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 18,"辽宁");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\object.txt"));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.writeObject(s2);
oos.writeObject(s3);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\testIO\\object.txt"));
System.out.println((Student)ois.readObject());
System.out.println((Student)ois.readObject());
System.out.println((Student)ois.readObject());
ois.close();
oos.close();
}
public static void m2() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 123,"福建");
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 456,"安徽");
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 18,"辽宁");
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
/*
ArrayList内部也实现了序列化接口 用它存储Student可以实现一次性全部序列化
还有解决了反序列化时不知道里面多少个Student,要读多少次的问题
*/
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\testIO\\object.txt"));
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\testIO\\object.txt"));
oos.writeObject(students);
ArrayList<Student> stus = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();
stus.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
ois.close();
oos.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
demo05.m2();
}
}
测试结果


打印流(字节打印流PrintStream和字符打印流PrintWriter)

字节打印流


@Test
public void testIO11() throws FileNotFoundException {
/*
字节打印流
*/
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("D:\\testIO\\print.txt");
ps.write(97);
ps.print(97);
ps.println("97换行");
ps.printf("%s , %s","原始人","启动");
ps.close();
}字符打印流


@Test
public void testIO12() throws IOException {
/*
字符打印流
*/
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\testIO\\print2.txt"),true);
pw.write(97);
pw.print(97);
pw.println("97换行");
pw.printf("%s , %s","原始人","启动");
pw.close();
}总结

关于System.out
@Test
public void testIO13(){
//System.out是虚拟机启动的时候,由虚拟机创建的,指向控制台的字节打印流。在系统中是唯一的。
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.println("控制台输出数据");
ps.close();
ps.println("控制台输出数据");
System.out.println("控制台输出数据");
}测试结果
关流后sout失效

压缩流和解压缩流
解压
// 解压
public static void unzip(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
if (!dest.exists()) {
dest.mkdirs();
}
//构造解压缩流对象
ZipInputStream zis = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(source));
//一个ZipEntry代表压缩包内的一个对象,可以是文件或文件夹
//不断调用zis.getNextEntry()可以得到所有的文件和文件夹,不用递归
ZipEntry entry;
while ((entry = zis.getNextEntry()) != null) {
System.out.println(entry);
String entryStr = entry.toString();
String[] split = entryStr.split("/");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//有上级文件夹,创建完整文件夹路径
if (split.length > 1) {
System.out.println(1);
for (int i = 0; i < split.length - 1; i++) {
sb.append(split[i] + "/");
}
File dir = new File(dest, sb.toString());
dir.mkdirs();
}
File file = new File(dest, entry.toString());
file.createNewFile(); //创建文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b = zis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
zis.closeEntry();//当前文件处理完毕,关闭entry
// }
}
zis.close();
}压缩单个文件
//压缩一个文件
public static void zipOne(File source, File dest) throws IOException {
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest, source.getName().substring(0, source.getName().lastIndexOf(".")) + ".zip")));
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("a.txt");
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}压缩文件夹
//压缩文件夹
public static void zip(File source) throws IOException {
String root = source.getParent();//得到要压缩的文件夹的上一级目录,用于toZip方法中创建本地要读文件的字节流
FileOutputStream dest = new FileOutputStream(new File(root, source.getName() + ".zip"));
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(dest);//得到压缩流
toZip(zos,root,"",source);//遍历文件进行压缩,刚开始的所有文件没有上级目录
zos.close();
}
/*
参数:压缩流 压缩包根路径 压缩资源父路径 压缩资源(文件和文件夹)
*/
public static void toZip(ZipOutputStream zos,String root,String parent,File source) throws IOException {
File[] files = source.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(parent +"\\"+ file.getName());//拼接上级完整目录和文件名
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(root +"\\"+ parent +"\\"+ file.getName());//读取本地文件
int b;
while ((b=fis.read())!=-1){
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}
else {
toZip(zos,root,parent+"\\"+file.getName(),file); //拼接file文件夹的完整上级目录 传递file文件夹
}
}
}测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// File source1 = new File("D:\\testIO\\testZip.zip");//里面的文件名不能有中文
// File dest1 = new File("D:\\testIO\\testZip");
// demo06.unzip(source1, dest1);
// File source2 = new File("D:\\testIO\\a.txt");
// File dest2 = new File("D:\\testIO");
// demo06.zipOne(source2,dest2);
File source3 = new File("D:\\testIO\\testZip");
zip(source3);
}