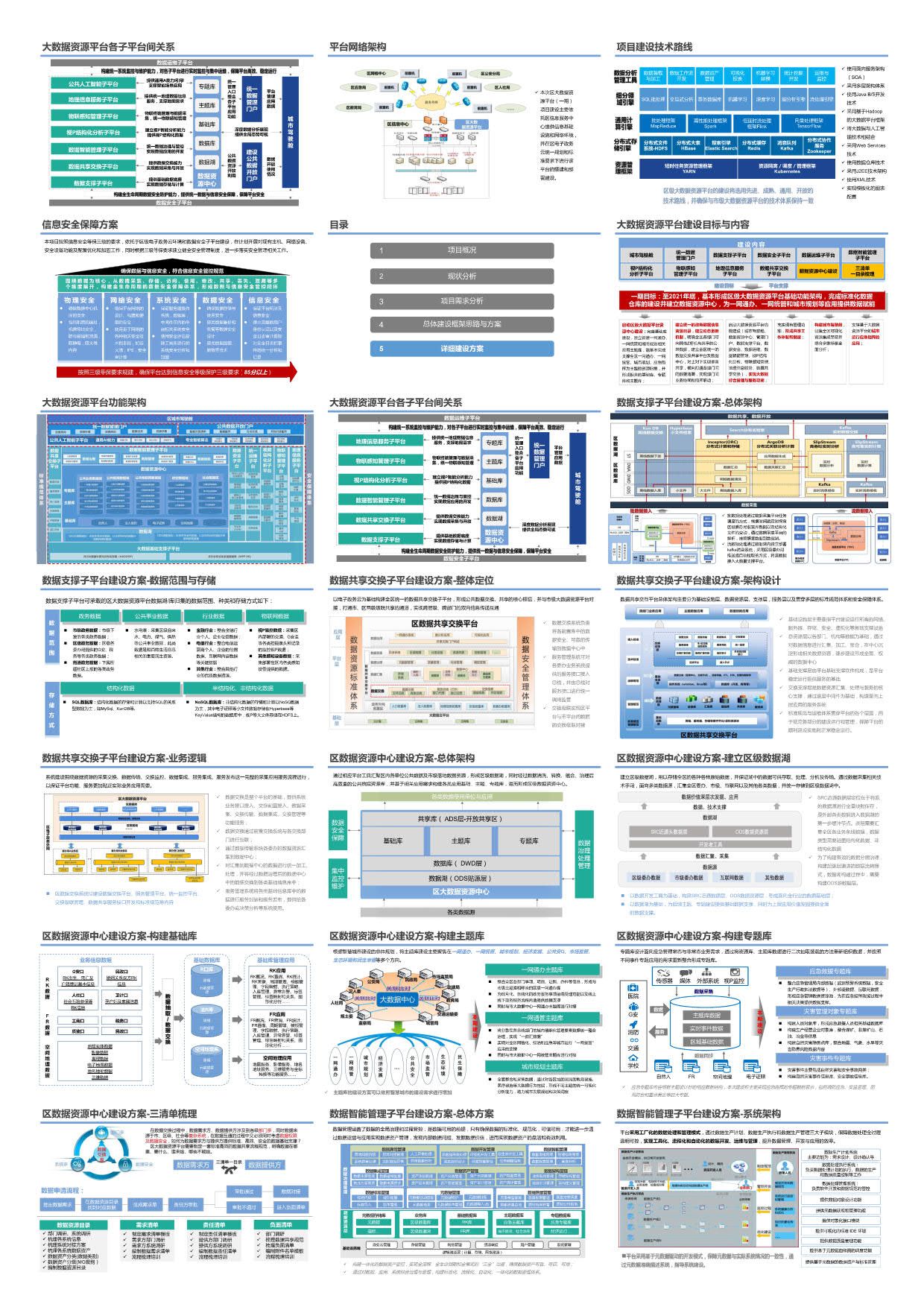
概述
队列,是一种基本的数据结构,也是一种数据适配器。它在底层上以链表方法实现。
队列的显著特点是他的添加元素与删除元素操作:先加入的元素总是被先弹出。
一个队列应该应该是这样的:
--------------QUEUE-------------
———— ———— ———— ————
pop() ←-- T1 ←-- T2 ←-- T3 ←-- T4 ←-- push()
———— ———— ———— ————
--------------------------------
front() back()
*注意*
-------------------------------→
队列的内部是一张由front指向back的链表Tn代表该元素被加入到队列的次序。
一个队列有以下四种基本行为:
front()表示对队列头元素的访问操作。如得到元素T1。
pop()表示对队列头元素的弹出操作。我们弹出T1
---------QUEUE---------
———— ———— ————
pop() ←-- T2 ←-- T3 ←-- T4 ←-- push()
———— ———— ————
-----------------------
front() back()现在T2成为队头元素。
back()表示对队列尾元素的访问操作。如当前会得到T4。
push()表示对队列尾部压入新元素。我们压入T5
--------------QUEUE-------------
———— ———— ———— ————
pop() ←-- T2 ←-- T3 ←-- T4 ←-- T5 ←-- push()
———— ———— ———— ————
--------------------------------
front() back()现在T5成为尾元素。
接下来我们通过封装queue类,实现队列的一些基本功能 。(Code和测试案例附后)
命名空间
C++有自己的std命名空间下的queue,为了进行区分,封装一个自己的动态数组命名空间custom_queue。
使用namespace关键字封装,使用时可以声明using namespace custom_queu;在作用域内声明,或custom_queue::局部声明。
namespace custom_queue{
...
}
//作用域内声明
using namespace custom_queue;
//局部声明
custom_queue::...成员变量
template <typename T>是泛型,作为数据适配器,他的数据单位应该是任意一种类型,此时暂用T表示,至于T为何物将在实例化时以<>告知。
定义class类queue,封装三个成员变量:queue_node<T>* val_front; queue_node<T>* val_back; size_t val_size;
(size_t 是C/C++标准在stddef.h中定义的(这个头文件通常不需要#include),size_t 类型专门用于表示长度,它是无符号整数。)
我们还要额外定义嵌套类queue_node,它只能被queue类使用,这就实现了结构功能的封装。
queue_node<T>* val_front是队头处的指针。
queue_node<T>* val_back是队尾处的指针。
size_t val_size用于记录当前队列的长度。
template<typename T>
class queue {
private:
template<typename T>
class queue_node {
private:
...
};
queue_node<T>* val_front;
queue_node<T>* val_back;
size_t val_size;
public:
...
}定义class类queue_node,封装两个成员变量:T val; queue_node*next
声明友员类friend class queu(queue为模版类,模版友员类前加泛型声明),这使得queue可以操控queue_node的私有成员,将queue_node的构造函数和析构函数定为私有,这样就只用queue能管理queue_node了。
T val当前节点值。
queue_node*next指向下一个节点
另有构造函数接受一个T elem,创建新节点。
析构函数无须函数体,完全由trie类代管,略去不表。
禁用拷贝构造和重载等于号:默认拷贝构造和等于号进行,指针变量赋值,这存在极大问题(两指针争抢堆上的数据同一块数据),另有深层拷贝解决,略去不表。
template<typename T>
class queue_node {
private:
template<typename T>
friend class queue;
T val;
queue_node* next;
queue_node(T elem) :val(elem), next(nullptr) {};
~queue_node(){};
queue_node(const queue_node& another)=delete;
queue_node& operator=(const queue_node& another) = delete;
};创建销毁
提供四种构造。
无参构造:创建空队列。
复制构造:用另一个队列进行深度拷贝。所谓深度拷贝就是以another指针指向的值作为参数创建新指针而不是让两指针指向同一值。让队头获得创新得到的第一个节点,然后以两个临时指针another_val与this_val进行同步,this_val时时构造与another_val指向的值相同的新节点。
最后队尾获得创建得到的最后一个节点。
析构函数:当队列非空,循环进行头结点弹出。后面实现判断空队列行为和弹出行为。
另有重载等于号:作用于复制构造相同。
queue() :val_front(nullptr), val_back(nullptr), val_size(0) {};
queue(const queue& another) :queue() {
int len = another.val_size;
val_size = len;
if (len) {
queue_node<T>* this_val=new queue_node<T>(another.val_front->val);
const queue_node<T>* another_val = another.val_front->next;
val_front = this_val;
while (--len) {
this_val->next= new queue_node<T>(another_val->val);
this_val = this_val->next;
another_val = another_val->next;
}
val_back = this_val;
}
}
~queue() {
while (!empty())pop();
}
queue& operator=(const queue& another){
val_front = val_back = nullptr;
int len = another.val_size;
val_size = len;
if (len) {
queue_node<T>* this_val = new queue_node<T>(another.val_front->val);
const queue_node<T>* another_val = another.val_front->next;
val_front = this_val;
while (--len) {
this_val->next = new queue_node<T>(another_val->val);
this_val = this_val->next;
another_val = another_val->next;
}
val_back = this_val;
}
return *this;
}数据控制
获取长度:返回val_size。
判断为空:返回val_size ? false : true。
队尾压入:如果是空队列,队头申请新节点node后,令队尾等于队头。否则在队尾后面申请新节点。
队头弹出:如果是空队列,抛出异常。否则获取当前头结点的next,删除头节点后将next作为头结点。如果队列大小为1,那么删除后应将头尾全部置为nullptr空节点。
size_t size() {
return val_size;
}
bool empty() {
return val_size ? false : true;
}
void push(const T elem) {
if (val_size == 0) {
val_front = new queue_node<T>(elem);
val_back = val_front;
}
else {
val_back->next = new queue_node<T>(elem);
val_back = val_back->next;
}
val_size++;
}
void pop(){
assert(val_size > 0);
queue_node<T>* temp = val_front->next;
delete val_front;
val_front = temp;
val_size--;
if (!val_size)val_front = val_back= nullptr;
}数据访问
访问队头:判断无异常后返回队头的常量引用。
访问队尾:判断无异常后返回队尾的常量引用。
我们的queue访问操作不支持接受方进行数据更改。
const T& front() {
assert(val_size > 0);
return (val_front->val);
}
const T& back() {
assert(val_size > 0);
return (val_back->val);
}Code
#pragma once
#include <cassert>
namespace custom_queue {
template<typename T>
class queue {
private:
template<typename T>
class queue_node {
private:
template<typename T>
friend class queue;
T val;
queue_node* next;
queue_node(T elem) :val(elem), next(nullptr) {};
~queue_node(){};
queue_node(const queue_node& another)=delete;
queue_node& operator=(const queue_node& another) = delete;
};
queue_node<T>* val_front;
queue_node<T>* val_back;
size_t val_size;
public:
queue() :val_front(nullptr), val_back(nullptr), val_size(0) {};
queue(const queue& another) :queue() {
int len = another.val_size;
val_size = len;
if (len) {
queue_node<T>* this_val=new queue_node<T>(another.val_front->val);
const queue_node<T>* another_val = another.val_front->next;
val_front = this_val;
while (--len) {
this_val->next= new queue_node<T>(another_val->val);
this_val = this_val->next;
another_val = another_val->next;
}
val_back = this_val;
}
}
~queue() {
while (!empty())pop();
}
queue& operator=(const queue& another){
val_front = val_back = nullptr;
int len = another.val_size;
val_size = len;
if (len) {
queue_node<T>* this_val = new queue_node<T>(another.val_front->val);
const queue_node<T>* another_val = another.val_front->next;
val_front = this_val;
while (--len) {
this_val->next = new queue_node<T>(another_val->val);
this_val = this_val->next;
another_val = another_val->next;
}
val_back = this_val;
}
return *this;
}
int size() {
return val_size;
}
bool empty() {
return val_size ? false : true;
}
void push(const T elem) {
if (val_size == 0) {
val_front = new queue_node<T>(elem);
val_back = val_front;
}
else {
val_back->next = new queue_node<T>(elem);
val_back = val_back->next;
}
val_size++;
}
void pop(){
assert(val_size > 0);
queue_node<T>* temp = val_front->next;
delete val_front;
val_front = temp;
val_size--;
if (!val_size)val_front = val_back= nullptr;
}
const T& front() {
assert(val_size > 0);
return (val_front->val);
}
const T& back() {
assert(val_size > 0);
return (val_back->val);
}
};
}测试
#include <iostream>
#include "queue.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
custom_queue::queue<char>que1;
que1.push('a'); que1.push('b'); que1.push('c');
custom_queue::queue<char>que2(que1);
while (!que1.empty()) {
cout << que1.front();
que1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
while (!que2.empty()) {
cout << que2.front();
que2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
que2.push('x');
cout <<que2.front()<<' '<< que2.back();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}