目录
一、关于昨天的补充
1.final关键字
2.toString()方法
二、今日代码实现
1.顺序表的查找操作
2.顺序表的插入操作
3.顺序表的删除操作
4.数据测试
总结
一、关于昨天的补充
1.final关键字
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;在昨天的这行代码中,用到了final关键字,这里我们进行一些补充。
关键字final,中文意思“最终的”,在java中声明类、方法、变量时,我们可以用它来进行修饰,表示该引用不能被改变,具体规则如下:
- final修饰的类不能被继承,比如String类、System类、StringBuffer类
- final修饰的方法不能被重写,但可以被重载
- final修饰的变量(成员变量或局部变量)不可以被更改,相当于常量(注:命名时全大写,单词之间用下划线隔开)
2.toString()方法
在java中,Object类是所有类的根基类,相当于所有类的“老祖宗”,因此每个类都直接或间接地继承Object类。而在Object类中,定义有public String toString()方法,其返回值为String类型。
如果没有重写toString()方法,那么就会调用默认的toString()方法,如下:
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}但在大多数情况下,默认toString()方法的输出都不是我们想要的,所以我们会根据需要对其进行重写, 得到自己想要的格式,比如在昨天的代码中,我们就对toString()方法进行了如下的重写:
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
if (length == 0) {
return "empty";
} // Of if
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + ", ";
} // Of for i
resultString += data[length - 1];
return resultString;
}// Of toString在使用String与其他数据类型进行拼接操作时,系统会自动调用该对象类的toString()方法。
例如:在昨天的主函数代码中,System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());与System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);的输出格式是完全一样的,这是由于字符串类型与tempFirstList相拼接,所以系统会自动调用tempFirstList.toString()方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempArray = {1,4,6,9};
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempFirstList.reset();
System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // of main
二、今日代码实现
昨天我们学习了顺序表的一些基本概念,今天继续深入,进一步学习顺序表的相关操作。顺序表具有查找、插入、删除的功能,在昨天代码的基础上,下面进行相关方法的创建,利用java来实现这些功能。
1.顺序表的查找操作
首先是顺序表的查找操作,即给定一个元素,查找该元素在顺序表中的位置(用数组来解释就是查找该元素在数组中的索引值)。在大部分情况下,要实现顺序表的查找功能,使用的方法都是顺序查找,即按次序(一般是从头部到尾部)遍历整个数组,并在遍历的过程中将数组元素与给定元素一一进行比较,如果相同,则返回该数组元素的索引值,如果不同,则继续进行遍历。但是在查找的过程中,不可避免地会面临以下两个问题:
- 如果在顺序表找不到该元素怎么办?
- 如果在顺序表有两个及以上的位置都对应该元素,那么该元素的位置是哪一个呢?
对于第一个问题,我们采取一个很常见的小技巧,就是利用非法值-1,如果在顺序表中我们没有找到该元素,那么则返回-1;而第二个问题,普遍的处理方式就是以首次出现的为准。
下面进行方法创建:
/**
*********************
*Find the index of the given value. If it appears in multiple positions,
*simply return the first one.
*
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return The position. -1 for not found.
*********************
*/
public int indexOf(int paraValue) {
int tempPosition = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (data[i] == paraValue) {
tempPosition = i;
break;
} // of if
} // of for i
return tempPosition;
} // of indexOf在上述代码中, 我们需要注意三个点:
- if语句中,判断数组元素与给定元素是否相等时,用的是==,而不是赋值运算符=
- 为了避免输出多个位置,我们规定以首次出现的为准,所以在if语句中,需要利用break来中断循环,即当数组元素与给定元素首次相等时,就立马跳出循环,输出此时数组元素对应的索引值
- 由于定义方法时,规定了返回值类型为int型,所以最后一定不要忘记写上return语句
2.顺序表的插入操作
顺序表的插入操作一般包括在头部插入元素、在尾部插入元素以及在指定位置插入元素,显然,在指定位置插入元素的方法也可以实现“头插”、“尾插”,所以这里我们直接创建在指定位置插入元素的方法。不过,在此之前,我们需要考虑两个问题:
- 在插入元素之前,顺序表如果已经达到最大长度了怎么办?
- 所指定的位置非法怎么办?
为使得所创建的顺序表插入的方法能够正常运行,必须排除以上两个问题的干扰。第一个问题,直接用if语句进行一个判断即可,如下:
if (length == MAX_LENGTH) {
System.out.println("List full.");
return false;
} // of if而针对第二个问题,我们首先要知道什么是“非法位置”,当指定位置小于最小索引值0时,显然非法;当指定位置大于顺序表此时(插入前)的长度length时,也是非法的,这是因为顺序表此时(插入前)的长度为length,则顺序表此时(插入前)的最大索引值为length-1,而我们最多在尾部进行插入,所以指定位置最大达到索引值length,不可能比length还大。
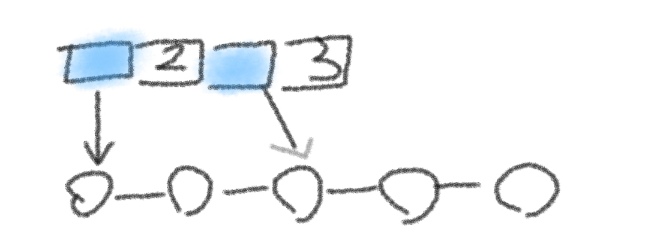
解决这两个问题后,就可以进行插入操作了。顺序表的插入操作其实就是将指定位置的原数组元素用给定的元素进行覆盖,然后把从指定位置开始一直到尾部的原数组元素通通往后移,为方便理解,我们用图解法来说明这个过程,如下图:

弄清楚顺序表的插入过程后,再用代码来模拟这个过程,如下:
// From tail to head. The last one is moved to a new position. Because length < MAX_LENGTH, no exceeding occurs.
for (int i = length; i > paraPosition; i--) {
data[i] = data[i - 1];
} // of for i
data[paraPosition] = paraValue;
length++;
return true;首先,利用for循环从尾部到指定位置进行遍历(因为指定位置之前的元素并没有发生改变,所以只需遍历至指定位置即可),然后data[i] = data[i - 1]实现了从尾部到指定位置的原数组元素的后移,再将给定元素赋给指定位置即可完成顺序表的插入操作。
//注意是从尾部开始遍历,而不是从头部开始,因为只有从尾部开始遍历,才能实现向后覆盖
//注意最后length要增加一
完整的方法创建代码如下:
/**
*********************
*Insert a value to a position. If the list is already full, do nothing.
*
* @param paraPosition The given position.
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return Success or not.
*********************
*/
public boolean insert(int paraPosition, int paraValue) {
if (length == MAX_LENGTH) {
System.out.println("List full.");
return false;
} // of if
if ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition > length)) {
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of the bound.");
return false;
} // of if
// From tail to head. The last one is moved to a new position. Because length < MAX_LENGTH, no exceeding occurs.
for (int i = length; i > paraPosition; i--) {
data[i] = data[i - 1];
} // of for i
data[paraPosition] = paraValue;
length++;
return true;
} // of insert3.顺序表的删除操作
和顺序表的插入操作一样,顺序表的删除操作也分为“头删”、“尾删”和删除指定位置的元素,这里我们同样只创建在指定位置进行删除操作的方法。因为删除操作不需要考虑顺序表是否已满(不过好像可以考虑一下顺序表长度是否为0?),所以我们直接判断指定位置是否非法即可,判断代码和顺序表插入操作中的并无二异。
判断完毕之后,进行删除操作,顺序表的删除操作其实说白了就是用后一个位置的元素去覆盖前一个位置的元素,图解如下:

与顺序表的插入操作不同,这里我们需要从指定位置开始遍历到尾部,代码模拟如下:
/**
*********************
*Delete a value at a position.
*
* @param paraPosition The given position.
* @return Success or not.
*********************
*/
public boolean delete(int paraPosition) {
if ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition >= length)) {
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of the bound.");
return false;
} // of if
// From head to tail.
for (int i = paraPosition; i < length - 1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i + 1];
} // of for i
length--;
return true;
} // of delete在代码中,语句data[i] = data[i + 1];就实现了向前覆盖,不过,需要注意到其中for循环的循环条件为i < length - 1,这是因为length是顺序表的长度,所以length - 1就是删除前的最大索引值,i < length - 1则说明i最大可以取到倒数第二个位置的索引值,i + 1最大可以取得最后一个位置的索引值,这样就保证了指定位置之后的所有元素都可以实现向前覆盖。
4.数据测试
创建好以上三个方法之后,我们利用一个数组进行数据测试,如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempArray = {1,4,6,9};
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);
System.out.println("After initialization, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
int tempValue = 4;
int tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempValue = 5;
tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempPosition = 2;
tempValue = 5;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 8;
tempValue = 10;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 3;
tempFirstList.delete(tempPosition);
System.out.println("After deleting data at position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
tempFirstList.insert(i, i);
System.out.println("After inserting " + i + " to position " + i + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // Of for i
tempFirstList.reset();
System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // of main结合今天的三个方法与数据测试以及昨天的代码,得到完整的程序代码:
package datastructure.list;
/**
*Sequential list.
*
*@auther Xin Lin 3101540094@qq.com.
*/
public class SequentialList {
/**
* The maximal length of the list. It is a constant.
*/
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
/**
* The actual length not exceeding MAX_LENGTH. Attention:length is not only
* the member variable of Sequential list, but also the member variable of
* Array. In fact, a name can be the member variable of different classes.
*/
int length;
/**
* The data stored in an array.
*/
int[] data;
/**
*********************
*Construct an empty sequential list.
*********************
*/
public SequentialList() {
length = 0;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
} // of the first constructor
/**
*********************
*Construct a sequential list using an array.
*
* @param paraArray
* The given array. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH.
* For simplicity now we do not check it.
*********************
*/
public SequentialList(int[] paraArray) {
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
length = paraArray.length;
// Copy data.
for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {
data[i] = paraArray[i];
} // of for i
} // of the second constructor
/**
*********************
*Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
if (length == 0) {
return "empty";
} // of if
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + ",";
} // of for i
resultString += data[length - 1];
return resultString;
} // of toString
/**
*********************
*Reset to empty.
*********************
*/
public void reset() {
length = 0;
} // of reset
/**
*********************
*Find the index of the given value. If it appears in multiple positions,
*simply return the first one.
*
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return The position. -1 for not found.
*********************
*/
public int indexOf(int paraValue) {
int tempPosition = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (data[i] == paraValue) {
tempPosition = i;
break;
} // of if
} // of for i
return tempPosition;
} // of indexOf
/**
*********************
*Insert a value to a position. If the list is already full, do nothing.
*
* @param paraPosition The given position.
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return Success or not.
*********************
*/
public boolean insert(int paraPosition, int paraValue) {
if (length == MAX_LENGTH) {
System.out.println("List full.");
return false;
} // of if
if ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition > length)) {
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of the bound.");
return false;
} // of if
// From tail to head. The last one is moved to a new position. Because length < MAX_LENGTH, no exceeding occurs.
for (int i = length; i > paraPosition; i--) {
data[i] = data[i - 1];
} // of for i
data[paraPosition] = paraValue;
length++;
return true;
} // of insert
/**
*********************
*Delete a value at a position.
*
* @param paraPosition The given position.
* @return Success or not.
*********************
*/
public boolean delete(int paraPosition) {
if ((paraPosition < 0) || (paraPosition >= length)) {
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of the bound.");
return false;
} // of if
// From head to tail.
for (int i = paraPosition; i < length - 1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i + 1];
} // of for i
length--;
return true;
} // of delete
/**
*********************
*The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempArray = {1,4,6,9};
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);
System.out.println("After initialization, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
int tempValue = 4;
int tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempValue = 5;
tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempPosition = 2;
tempValue = 5;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 8;
tempValue = 10;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 3;
tempFirstList.delete(tempPosition);
System.out.println("After deleting data at position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
tempFirstList.insert(i, i);
System.out.println("After inserting " + i + " to position " + i + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // Of for i
tempFirstList.reset();
System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // of main
} // of class SequentialList运行结果:

总结
今天我们主要通过顺序表查找、插入、删除这三个操作来深入理解和学习顺序表,可以发现顺序表的查找操作较迅速,其时间复杂度为O(1),这也是顺序表的优势所在。但是顺序表的缺点也是显而易见的,由于顺序表是顺序存储结构,要求其内的元素在存储时必须紧密相连,不能出现“空白”,所以这就造成了顺序表不能随意、直接地进行插入和删除,必须通过一大段元素移动覆盖的方式间接完成,因此其时间复杂度就为O(n)。