0 环境准备
0.0 云服务器
阿里云、腾讯云、华为云 服务器开通; 按量付费,省钱省心
安装以下组件:docker、redis、kafka、prometheus、grafana
下载windterm:
https://github.com/kingToolbox/WindTerm/releases/download/2.5.0/WindTerm_2.5.0_Windows_Portable_x86_64.zip
重要:开通云服务器以后,请一定在安全组设置规则,放行端口
重要:开通云服务器以后,请一定在安全组设置规则,放行端口
重要:开通云服务器以后,请一定在安全组设置规则,放行端口
0.1 Docker安装
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
sudo systemctl enable docker --now
#测试工作
docker ps
# 批量安装所有软件
docker compose 创建 /prod 文件夹,准备以下文件
0.2 prometheus.yml
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
evaluation_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'prometheus'
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9090']
- job_name: 'redis'
static_configs:
- targets: ['redis:6379']
- job_name: 'kafka'
static_configs:
- targets: ['kafka:9092']0.3 docker-compose.yml
version: '3.9'
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
container_name: redis
restart: always
ports:
- "6379:6379"
networks:
- backend
zookeeper:
image: bitnami/zookeeper:latest
container_name: zookeeper
restart: always
environment:
ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181
ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000
networks:
- backend
kafka:
image: bitnami/kafka:3.4.0
container_name: kafka
restart: always
depends_on:
- zookeeper
ports:
- "9092:9092"
environment:
ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER: yes
KAFKA_CFG_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper:2181
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
networks:
- backend
kafka-ui:
image: provectuslabs/kafka-ui:latest
container_name: kafka-ui
restart: always
depends_on:
- kafka
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: dev
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: kafka:9092
networks:
- backend
prometheus:
image: prom/prometheus:latest
container_name: prometheus
restart: always
volumes:
- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
ports:
- "9090:9090"
networks:
- backend
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
container_name: grafana
restart: always
depends_on:
- prometheus
ports:
- "3000:3000"
networks:
- backend
networks:
backend:
name: backend0.4 启动环境
docker compose -f docker-compose.yml up -d0.5 验证
Redis:你的ip:6379
- 填写表单,下载官方可视化工具:
- RedisInsight - The Best Redis GUI
Kafka:你的ip:9092
- idea安装大数据插件
Prometheus:你的ip:9090
- 直接浏览器访问
Grafana:你的ip:3000
- 直接浏览器访问
1 NoSQL
Redis整合
1.1 场景整合
依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>配置
spring.data.redis.host=192.168.200.100
spring.data.redis.password=Lfy123!@!测试
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void redisTest(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("a","1234");
Assertions.assertEquals("1234",redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("a"));
}RedisTestController
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
//为了后来系统的兼容性,应该所有对象都是以json的方式进行保存
@Autowired //如果给redis中保存数据会使用默认的序列化机制,导致redis中保存的对象不可视
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/count")
public String count(){
Long hello = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("hello");
//常见数据类型 k: v value可以有很多类型
//string: 普通字符串 : redisTemplate.opsForValue()
//list: 列表: redisTemplate.opsForList()
//set: 集合: redisTemplate.opsForSet()
//zset: 有序集合: redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
//hash: map结构: redisTemplate.opsForHash()
return "访问了【"+hello+"】次";
}Boot309RedisApplicationTests
package com.atguigu.boot3.redis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.UUID;
@SpringBootTest
class Boot309RedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired //key.value 都是字符串
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* string: 普通字符串 : redisTemplate.opsForValue()
*/
@Test
void contextLoads() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("haha", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
String haha = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("haha");
System.out.println(haha);
}
/**
* list: 列表: redisTemplate.opsForList()
*/
@Test
void testList(){
String listName = "listtest";
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(listName,"1");
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(listName,"2");
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(listName,"3");
String pop = redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(listName);
Assertions.assertEquals("3",pop);
}
/**
* set: 集合: redisTemplate.opsForSet()
*/
@Test
void testSet(){
String setName = "settest";
//1、给集合中添加元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(setName,"1","2","3","3");
Boolean aBoolean = redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(setName, "2");
Assertions.assertTrue(aBoolean);
Boolean aBoolean1 = redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(setName, "5");
Assertions.assertFalse(aBoolean1);
}
/**
* zset: 有序集合: redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
*/
@Test
void testzset(){
String setName = "zsettest";
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(setName,"雷丰阳",90.00);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(setName,"张三",99.00);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(setName,"李四",9.00);
redisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(setName,"王五",97.10);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> popMax = redisTemplate.opsForZSet().popMax(setName);
String value = popMax.getValue();
Double score = popMax.getScore();
System.out.println(value + "==>" + score);
}
/**
* hash: map结构: redisTemplate.opsForHash()
*/
@Test
void testhash(){
String mapName = "amap";
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(mapName,"name","张三");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(mapName,"age","18");
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(mapName, "name"));
}
}1.2 自动配置原理
1 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports中导入了RedisAutoConfiguration、RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration和RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration。所有属性绑定在RedisProperties中
2 RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration属于响应式编程,不用管。RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration属于 JPA 操作,也不用管
3 RedisAutoConfiguration 配置了以下组件
a)LettuceConnectionConfiguration: 给容器中注入了连接工厂LettuceConnectionFactory,和操作 redis 的客户端DefaultClientResources。
b)RedisTemplate<Object, Object>: 可给 redis 中存储任意对象,会使用 jdk 默认序列化方式。
c)StringRedisTemplate: 给 redis 中存储字符串,如果要存对象,需要开发人员自己进行序列化。key-value都是字符串进行操作··
1.3 定制化
1.3.1 序列化机制
AppRedisConfiguration
@Configuration
public class AppRedisConfiguration {
/**
* 允许Object类型的key-value,都可以被转为json进行存储。
* @param redisConnectionFactory 自动配置好了连接工厂
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
//把对象转为json字符串的序列化工具
template.setDefaultSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
}Person
package com.atguigu.boot3.redis.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author lfy
* @Description
* @create 2023-04-28 16:05
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Person implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthDay;
}RedisTestController
package com.atguigu.boot3.redis.controller;
import com.atguigu.boot3.redis.entity.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author lfy
* @Description
* @create 2023-04-28 15:43
*/
@RestController
public class RedisTestController {
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
//为了后来系统的兼容性,应该所有对象都是以json的方式进行保存
@Autowired //如果给redis中保存数据会使用默认的序列化机制,导致redis中保存的对象不可视
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/person/save")
public String savePerson(){
Person person = new Person(1L,"张三",18,new Date());
//1、序列化: 对象转为字符串方式
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("person",person);
return "ok";
}
@GetMapping("/person/get")
public Person getPerson(){
Person person = (Person) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("person");
return person;
}
}1.3.2 redis客户端
RedisTemplate、StringRedisTemplate: 操作redis的工具类
● 以上2个工具类要从redis的连接工厂获取连接才能操作redis。redis的连接工厂Spring有两种:Lettuce和Jedis。RedisTemplate从底层客户端获取连接,进行操作
● Redis客户端
○ Lettuce: 默认
○ Jedis:可以使用以下切换
从默认Lettuce切换到Jedis,首先排除默认导入的lettuce包,并导入Jedis包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--切换 jedis 作为操作redis的底层客户端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>1.3.3 配置参考
spring.data.redis.host=8.130.74.183
spring.data.redis.port=6379
#spring.data.redis.client-type=lettuce
#设置lettuce的底层参数
#spring.data.redis.lettuce.pool.enabled=true
#spring.data.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
spring.data.redis.client-type=jedis
spring.data.redis.jedis.pool.enabled=true
spring.data.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=82 接口文档
OpenAPI 3 与 Swagger
Swagger 可以快速生成实时接口文档,方便前后开发人员进行协调沟通。遵循 OpenAPI 规范。
文档:https://springdoc.org/v2/
2.1 OpenAPI 3 架构

2.2 整合
导入场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>重启后,swagger默认访问地址 /swagger-ui/index.html
配置
# /api-docs endpoint custom path 默认 /v3/api-docs
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docs
# swagger 相关配置在 springdoc.swagger-ui
# swagger-ui custom path
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.html
springdoc.show-actuator=true2.3 使用
2.3.1 常用注解
| 注解 | 标注位置 | 作用 |
| @Tag | controller 类 | 标识 controller 作用 |
| @Parameter | 参数 | 标识参数作用 |
| @Parameters | 参数 | 参数多重说明 |
| @Schema | model 层的 JavaBean | 描述模型作用及每个属性 |
| @Operation | 方法 | 描述方法作用 |
| @ApiResponse | 方法 | 描述响应状态码等 |







package com.atguigu.boot3.crud.entity;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.media.Schema;
import lombok.Data;
@Schema(title = "部门信息")
@Data
public class Dept {
@Schema(title = "部门id")
private Long id;
@Schema(title = "部门名字")
private String deptName;
}

2.3.2 Docket配置
如果有多个Docket,配置如下
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi publicApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-public")
.pathsToMatch("/public/**")
.build();
}
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi adminApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-admin")
.pathsToMatch("/admin/**")
.addMethodFilter(method -> method.isAnnotationPresent(Admin.class))
.build();
}如果只有一个Docket,可以配置如下
springdoc.packagesToScan=package1, package2
springdoc.pathsToMatch=/v1, /api/balance/**分组方式的Open API
package com.atguigu.boot3.crud.config;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.ExternalDocumentation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.OpenAPI;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.Info;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.License;
import org.springdoc.core.models.GroupedOpenApi;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ApiUiConfig {
/**
* 分组设置
* @return
*/
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi empApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("员工管理")
.pathsToMatch("/emp/**","/emps")
.build();
}
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi deptApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("部门管理")
.pathsToMatch("/dept/**","/depts")
.build();
}
}

2.3.3 OpenAPI配置
@Bean
public OpenAPI springShopOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info().title("SpringShop API")
.description("Spring shop sample application")
.version("v0.0.1")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")))
.externalDocs(new ExternalDocumentation()
.description("SpringShop Wiki Documentation")
.url("https://springshop.wiki.github.org/docs"));
}package com.atguigu.boot3.crud.config;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.ExternalDocumentation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.OpenAPI;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.Info;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.License;
import org.springdoc.core.models.GroupedOpenApi;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ApiUiConfig {
/**
* 分组设置
* @return
*/
@Bean
public OpenAPI docsOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info()
.title("SpringBoot3-CRUD API")
.description("专门测试接口文件")
.version("v0.0.1")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")))
.externalDocs(new ExternalDocumentation()
.description("哈哈 Wiki Documentation")
.url("https://springshop.wiki.github.org/docs"));
}
}

注:Knife4j ,对swagger的增强,生成的文档是另外一个界面
2.4 Springfox迁移
2.4.1 注解变化
| 原注解 | 现注解 | 作用 |
| @Api | @Tag | 描述Controller |
| @ApiIgnore | @Parameter(hidden = true) | 描述忽略操作 |
| @ApiImplicitParam | @Parameter | 描述参数 |
| @ApiImplicitParams | @Parameters | 描述参数 |
| @ApiModel | @Schema | 描述对象 |
| @ApiModelProperty(hidden = true) | @Schema(accessMode = READ_ONLY) | 描述对象属性 |
| @ApiModelProperty | @Schema | 描述对象属性 |
| @ApiOperation(value = "foo", notes = "bar") | @Operation(summary = "foo", description = "bar") | 描述方法 |
| @ApiParam | @Parameter | 描述参数 |
| @ApiResponse(code = 404, message = "foo") | @ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "foo") | 描述响应 |
2.4.2 Docket配置
2.4.2.1 以前写法
@Bean
public Docket publicApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("org.github.springshop.web.public"))
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/public.*"))
.build()
.groupName("springshop-public")
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
@Bean
public Docket adminApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("org.github.springshop.web.admin"))
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/admin.*"))
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(Admin.class))
.build()
.groupName("springshop-admin")
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}2.4.2.2 新写法
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi publicApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-public")
.pathsToMatch("/public/**")
.build();
}
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi adminApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-admin")
.pathsToMatch("/admin/**")
.addOpenApiMethodFilter(method -> method.isAnnotationPresent(Admin.class))
.build();
}2.4.2.3 添加OpenAPI组件
@Bean
public OpenAPI springShopOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info().title("SpringShop API")
.description("Spring shop sample application")
.version("v0.0.1")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")))
.externalDocs(new ExternalDocumentation()
.description("SpringShop Wiki Documentation")
.url("https://springshop.wiki.github.org/docs"));
}3 远程调用
RPC(Remote Procedure Call):远程过程调用
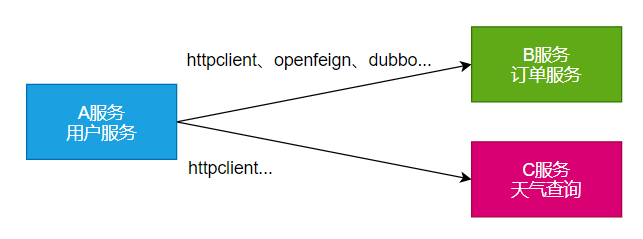
本地过程调用:a();b(); a() { b();}: 不同方法都在同一个JVM进程中运行
远程过程调用:
- 服务提供者:
- 服务消费者:
- 通过连接对方服务器进行请求\响应交互,来实现调用效果
API/SDK的区别是什么?
api:接口(Application Programming Interface)
- 远程提供功能;
sdk:工具包(Software Development Kit)
- 导入jar包,直接调用功能即可
开发过程中,我们经常需要调用别人写的功能
如果是内部微服务,可以通过依赖cloud、注册中心、openfeign等进行调用
如果是外部暴露的,可以发送 http 请求、或遵循外部协议进行调用
SpringBoot 整合提供了很多方式进行远程调用
轻量级客户端方式
RestTemplate: 普通开发
WebClient: 响应式编程开发
Http Interface: 声明式编程
Spring Cloud分布式解决方案方式
Spring Cloud OpenFeign
第三方框架
Dubbo
gRPC
...
3.1 WebClient
非阻塞、响应式HTTP客户端
3.1.1 创建与配置
发请求:
- 请求方式: GET\POST\DELETE\xxxx
- 请求路径: /xxx
- 请求参数:aa=bb&cc=dd&xxx
- 请求头: aa=bb,cc=ddd
- 请求体:
创建 WebClient 非常简单:
- WebClient.create()
- WebClient.create(String baseUrl)
还可以使用 WebClient.builder() 配置更多参数项:
- uriBuilderFactory: 自定义UriBuilderFactory ,定义 baseurl.
- defaultUriVariables: 默认 uri 变量.
- defaultHeader: 每个请求默认头.
- defaultCookie: 每个请求默认 cookie.
- defaultRequest: Consumer 自定义每个请求.
- filter: 过滤 client 发送的每个请求
- exchangeStrategies: HTTP 消息 reader/writer 自定义.
- clientConnector: HTTP client 库设置.
//获取响应完整信息
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");3.1.2 获取响应
retrieve()方法用来声明如何提取响应数据。比如
//获取响应完整信息
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");
Mono<ResponseEntity<Person>> result = client.get()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.toEntity(Person.class);
//只获取body
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");
Mono<Person> result = client.get()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Person.class);
//stream数据
Flux<Quote> result = client.get()
.uri("/quotes").accept(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM)
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(Quote.class);
//定义错误处理
Mono<Person> result = client.get()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is4xxClientError, response -> ...)
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is5xxServerError, response -> ...)
.bodyToMono(Person.class);3.1.3 定义请求体
//1、响应式-单个数据
Mono<Person> personMono = ... ;
Mono<Void> result = client.post()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(personMono, Person.class)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Void.class);
//2、响应式-多个数据
Flux<Person> personFlux = ... ;
Mono<Void> result = client.post()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_STREAM_JSON)
.body(personFlux, Person.class)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Void.class);
//3、普通对象
Person person = ... ;
Mono<Void> result = client.post()
.uri("/persons/{id}", id)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.bodyValue(person)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(Void.class);WeatherController
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.controller;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.ExpressApi;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.WeatherService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@RestController
public class WeatherController {
@Autowired
WeatherService weatherService;
@GetMapping("/weather")
public Mono<String> weather(@RequestParam("city") String city){
//查询天气
Mono<String> weather = weatherService.weather(city);
return weather;
}
}
WeatherService
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.support.WebClientAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.service.invoker.HttpServiceProxyFactory;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author lfy
* @Description
* @create 2023-05-07 12:16
*/
@Service
public class WeatherService {
@Autowired
WeatherInterface weatherInterface;
private static Mono<String> getByWebClient(String city) {
//1、创建WebClient
WebClient client = WebClient.create();
//2、准备数据
Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("area", city);
//3、定义发请求行为 CompletableFuture
Mono<String> mono = client.get()
.uri("https://ali-weather.showapi.com/area-to-weather-date?area={area}", params)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) //定义响应的内容类型
.header("Authorization", "APPCODE 93b7e19861a24c519a7548b17dc16d75") //定义请求头
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class);
return mono;
}
}
3.2 HTTP Interface
Spring 允许我们通过定义接口的方式,给任意位置发送 http 请求,实现远程调用,可以用来简化 HTTP 远程访问。需要webflux场景才可
3.2.1 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2.2 定义接口
public interface BingService {
@GetExchange(url = "/search")
String search(@RequestParam("q") String keyword);
}3.2.3 创建代理&测试
@SpringBootTest
class Boot05TaskApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() throws InterruptedException {
//1、创建客户端
WebClient client = WebClient.builder()
.baseUrl("https://cn.bing.com")
.codecs(clientCodecConfigurer -> {
clientCodecConfigurer
.defaultCodecs()
.maxInMemorySize(256*1024*1024);
//响应数据量太大有可能会超出BufferSize,所以这里设置的大一点
})
.build();
//2、创建工厂
HttpServiceProxyFactory factory = HttpServiceProxyFactory
.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(client)).build();
//3、获取代理对象
BingService bingService = factory.createClient(BingService.class);
//4、测试调用
Mono<String> search = bingService.search("尚硅谷");
System.out.println("==========");
search.subscribe(str -> System.out.println(str));
Thread.sleep(100000);
}
}com/atguigu/boot3/rpc/service/WeatherInterface.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.service.annotation.GetExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
public interface WeatherInterface {
@GetExchange(url = "https://ali-weather.showapi.com/area-to-weather-date",accept = "application/json")
Mono<String> getWeather(@RequestParam("area") String city);
}
com/atguigu/boot3/rpc/service/ExpressApi.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.service.annotation.GetExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
public interface ExpressApi {
@GetExchange(url = "https://express3.market.alicloudapi.com/express3",accept = "application/json")
Mono<String> getExpress(@RequestParam("number") String number);
}
application.properties
aliyun.appcode=93b7e19861a24c519a7548b17dc16d75
com/atguigu/boot3/rpc/config/WeatherConfiguration.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.config;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.ExpressApi;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.WeatherInterface;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.support.WebClientAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.service.invoker.HttpServiceProxyFactory;
@Configuration //最好起名为 AliyunApiConfiguration
public class WeatherConfiguration {
@Bean
HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory(@Value("${aliyun.appcode}") String appCode){
//1、创建客户端
WebClient client = WebClient.builder()
.defaultHeader("Authorization","APPCODE "+appCode)
.codecs(clientCodecConfigurer -> {
clientCodecConfigurer
.defaultCodecs()
.maxInMemorySize(256*1024*1024);
//响应数据量太大有可能会超出BufferSize,所以这里设置的大一点
})
.build();
//2、创建工厂
HttpServiceProxyFactory factory = HttpServiceProxyFactory
.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(client)).build();
return factory;
}
@Bean
WeatherInterface weatherInterface(HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory){
//3、获取代理对象
WeatherInterface weatherInterface = httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(WeatherInterface.class);
return weatherInterface;
}
@Bean
ExpressApi expressApi(HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory){
//3、获取代理对象
ExpressApi client = httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(ExpressApi.class);
return client;
}
}
com/atguigu/boot3/rpc/service/WeatherService.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.support.WebClientAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.service.invoker.HttpServiceProxyFactory;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class WeatherService {
@Autowired
WeatherInterface weatherInterface;
public Mono<String> weather(String city){
//远程调用阿里云API
// Mono<String> mono = getByWebClient(city);
Mono<String> weather = weatherInterface.getWeather(city);
return weather;
}
private static Mono<String> getByWebClient(String city) {
//1、创建WebClient
WebClient client = WebClient.create();
//2、准备数据
Map<String,String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("area", city);
//3、定义发请求行为 CompletableFuture
Mono<String> mono = client.get()
.uri("https://ali-weather.showapi.com/area-to-weather-date?area={area}", params)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) //定义响应的内容类型
.header("Authorization", "APPCODE 93b7e19861a24c519a7548b17dc16d75") //定义请求头
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class);
return mono;
}
}
com/atguigu/boot3/rpc/controller/WeatherController.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.controller;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.ExpressApi;
import com.atguigu.boot3.rpc.service.WeatherService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@RestController
public class WeatherController {
@Autowired
WeatherService weatherService;
@Autowired
ExpressApi expressApi;
@GetMapping("/weather")
public Mono<String> weather(@RequestParam("city") String city){
//查询天气
Mono<String> weather = weatherService.weather(city);
return weather;
}
@GetMapping("/express")
public Mono<String> express(@RequestParam("number") String number){
//获取物流
return expressApi.getExpress(number);
}
}
4 消息服务
Apache Kafka
4.1 消息队列-场景
4.1.1 异步
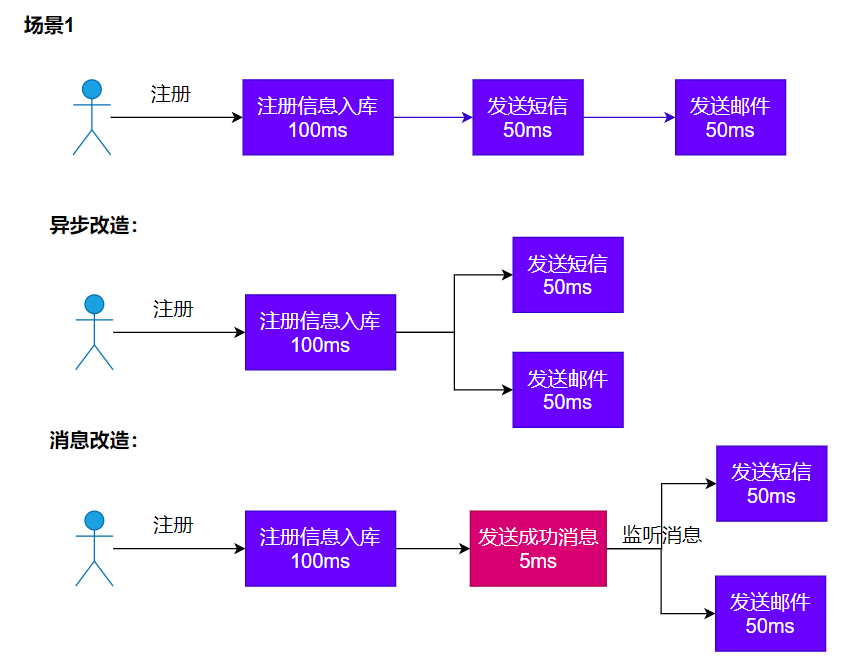
4.1.2 解耦
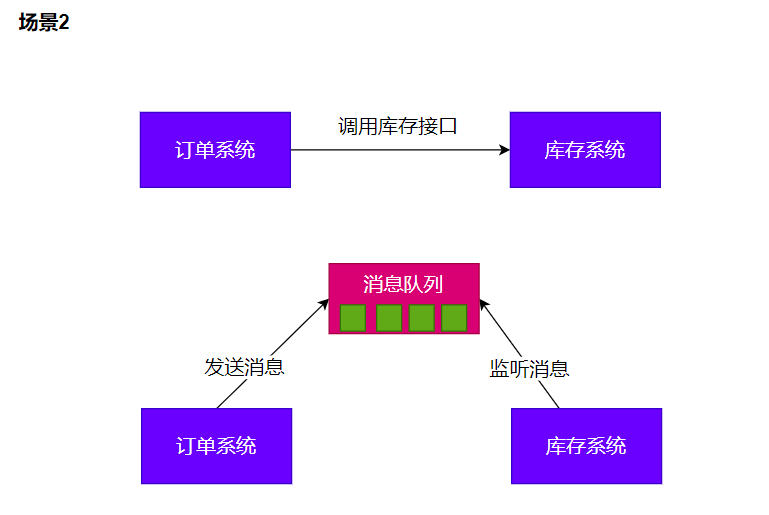
4.1.3 削峰

4.1.4 缓冲
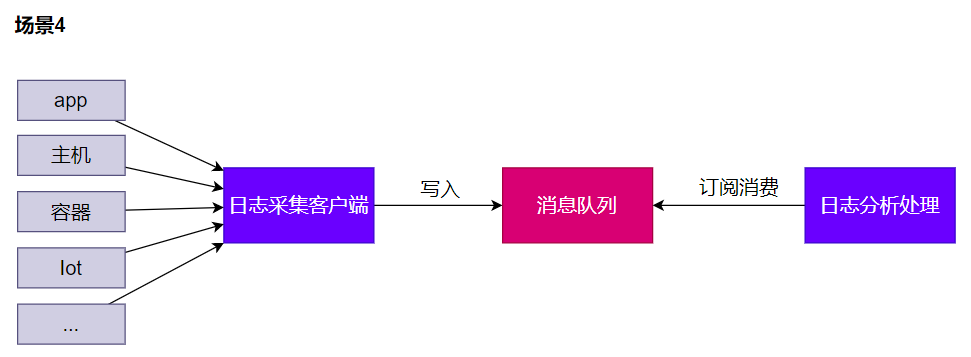
4.2 消息队列-Kafka
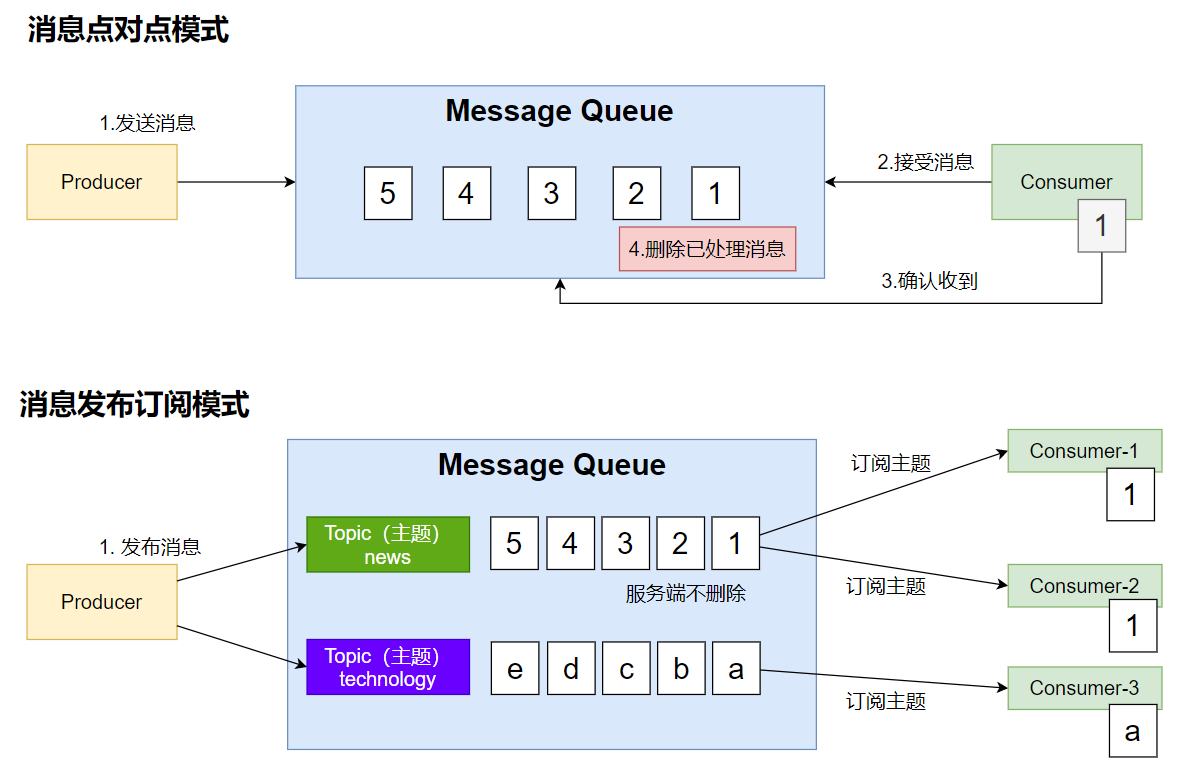
4.2.1 消息模式
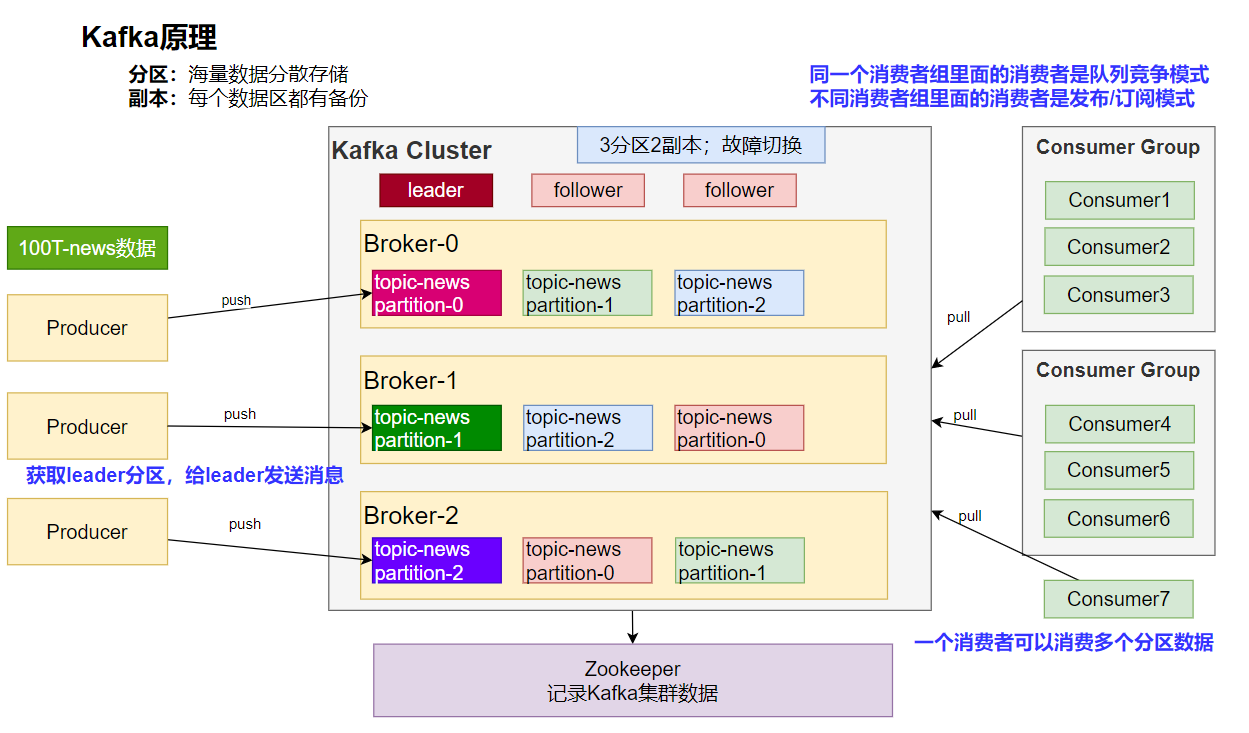
4.2.2 Kafka工作原理
/**
* KafkaAutoConfiguration提供如下功能
* 1、KafkaProperties:kafka的所有配置; 以 spring.kafka开始
* - bootstrapServers: kafka集群的所有服务器地址
* - properties: 参数设置
* - consumer: 消费者
* - producer: 生产者
* ...
* 2、@EnableKafka: 开启Kafka的注解驱动功能
* 3、KafkaTemplate: 收发消息
* 4、KafkaAdmin: 维护主题等...
* 5、@EnableKafka + @KafkaListener 接受消息
* 1)、消费者来接受消息,需要有group-id
* 2)、收消息使用 @KafkaListener + ConsumerRecord
* 3)、spring.kafka 开始的所有配置
* 6、核心概念
* 分区: 分散存储,1T的数据分散到N个节点
* 副本: 备份机制,每个小分区的数据都有备份
* 主题: topics; 消息是发送给某个主题
*/4.2.3 SpringBoot整合
参照:Overview :: Spring Kafka
<!--整合kafka-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>配置
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=172.20.128.1:9092修改C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件,配置8.130.32.70 kafka
4.2.4 消息发送
@SpringBootTest
class Boot07KafkaApplicationTests {
@Autowired
KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();
watch.start();
CompletableFuture[] futures = new CompletableFuture[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
CompletableFuture send = kafkaTemplate.send("order", "order.create."+i, "订单创建了:"+i);
futures[i]=send;
}
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();
watch.stop();
System.out.println("总耗时:"+watch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
}import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBean {
private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public MyBean(KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate) {
this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;
}
public void someMethod() {
this.kafkaTemplate.send("someTopic", "Hello");
}
}com/atguigu/boot3/message/entity/Person.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.message.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Person {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
}
com/atguigu/boot3/message/Boot312MessageApplicationTests.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.message;
import com.atguigu.boot3.message.entity.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
@SpringBootTest
class Boot312MessageApplicationTests {
@Autowired
KafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
CompletableFuture[] futures = new CompletableFuture[10000];
stopWatch.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
//JUC
CompletableFuture future = kafkaTemplate.send("newshaha", "haha-"+i, "哈哈哈-"+i);
futures[i] = future;
}
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures)
.join();
stopWatch.stop();
long millis = stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis();
System.out.println("10000消息发送完成:ms时间:"+millis);
}
@Test
void send(){
CompletableFuture future = kafkaTemplate.send("newshaha", "person", new Person(1L, "张三", "hjaha@qq.com"));
future.join();
System.out.println("消息发送成功...");
}
}application.properties
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=8.130.32.70:9092
#值的序列化规则
#默认是 StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonSerializer
4.2.5 消息监听
@Component
public class OrderMsgListener {
@KafkaListener(topics = "order",groupId = "order-service")
public void listen(ConsumerRecord record){
System.out.println("收到消息:"+record); //可以监听到发给kafka的新消息,以前的拿不到
}
@KafkaListener(groupId = "order-service-2",topicPartitions = {
@TopicPartition(topic = "order",partitionOffsets = {
@PartitionOffset(partition = "0",initialOffset = "0")
})
})
public void listenAll(ConsumerRecord record){
System.out.println("收到partion-0消息:"+record);
}
}package com.atguigu.boot3.message.listener;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.PartitionOffset;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.TopicPartition;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author lfy
* @Description
* @create 2023-05-08 16:39
*/
@Component
public class MyHahaTopicListener {
//默认的监听是从消息队列最后一个消息开始拿。新消息才能拿到
@KafkaListener(topics="newshaha",groupId="haha")
public void haha(ConsumerRecord record){
//1、获取消息的各种详细信息
// String topic = record.topic();
Object key = record.key();
Object value = record.value();
System.out.println("收到消息:key【"+key+"】 value【"+value+"】");
}
//拿到以前的完整消息;
@KafkaListener(groupId = "hehe",topicPartitions={
@TopicPartition(topic="newshaha",partitionOffsets={
@PartitionOffset(partition="0",initialOffset = "0")
})
})
public void hehe(ConsumerRecord record){
Object key = record.key();
Object value = record.value();
System.out.println("======收到消息:key【"+key+"】 value【"+value+"】");
}
}
4.2.6 参数配置
消费者
spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.properties[spring.json.value.default.type]=com.example.Invoice
spring.kafka.consumer.properties[spring.json.trusted.packages]=com.example.main,com.example.another生产者
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.properties[spring.json.add.type.headers]=false4.2.7 自动配置原理
kafka 自动配置在KafkaAutoConfiguration
- 容器中放了 KafkaTemplate 可以进行消息收发
- 容器中放了KafkaAdmin 可以进行 Kafka 的管理,比如创建 topic 等
- kafka 的配置在KafkaProperties中
- @EnableKafka可以开启基于注解的模式
5 Web安全
- Apache Shiro
- Spring Security
- 自研:Filter
Spring Security
5.1 安全架构
5.1.1 认证:Authentication
who are you?
登录系统,用户系统
5.1.2 授权:Authorization
what are you allowed to do?
权限管理,用户授权
5.1.3 攻击防护
XSS(Cross-site scripting)跨站脚本攻击
CSRF(Cross-site request forgery)跨站请求伪造
CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)跨域资源共享
SQL注入
...
5.1.4 扩展. 权限模型
5.1.4.1 RBAC(Role Based Access Controll)
用户(t_user)
id,username,password,xxx
1,zhangsan
2,lisi
用户_角色(t_user_role)【N对N关系需要中间表】
zhangsan, admin
zhangsan,common_user
lisi, hr
lisi, common_user
角色(t_role)
id,role_name
admin
hr
common_user
角色_权限(t_role_perm) 【N对N关系需要中间表】
admin, 文件r
admin, 文件w
admin, 文件执行
admin, 订单query,create,xxx
hr, 文件r
权限(t_permission)
id,perm_id
文件 r,w,x
订单 query,create,xxx
5.1.4.2 ACL(Access Controll List)
直接用户和权限挂钩
用户(t_user)
zhangsan
lisi
用户_权限(t_user_perm)
zhangsan,文件 r
zhangsan,文件 x
zhangsan,订单 query
权限(t_permission)
id,perm_id
文件 r,w,x
订单 query,create,xxx
@Secured("文件 r")
public void readFile(){
//读文件
}5.2 Spring Security原理
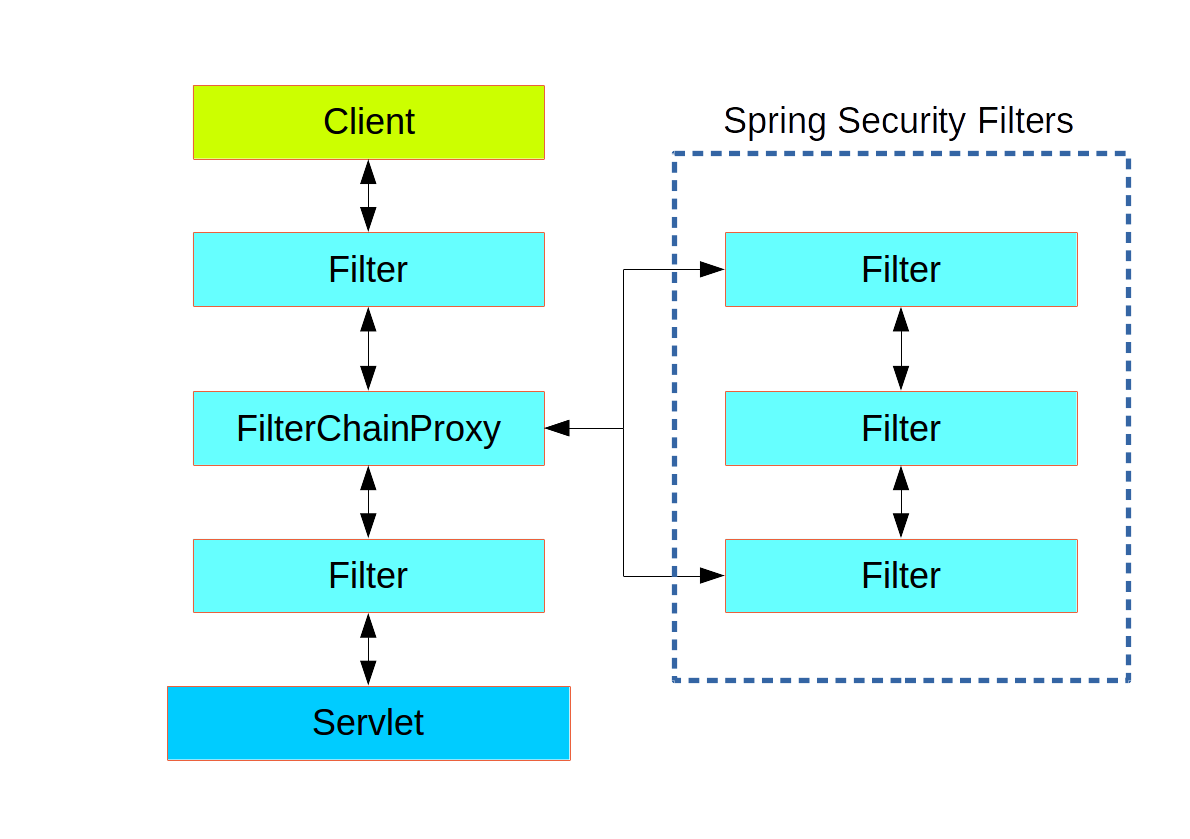
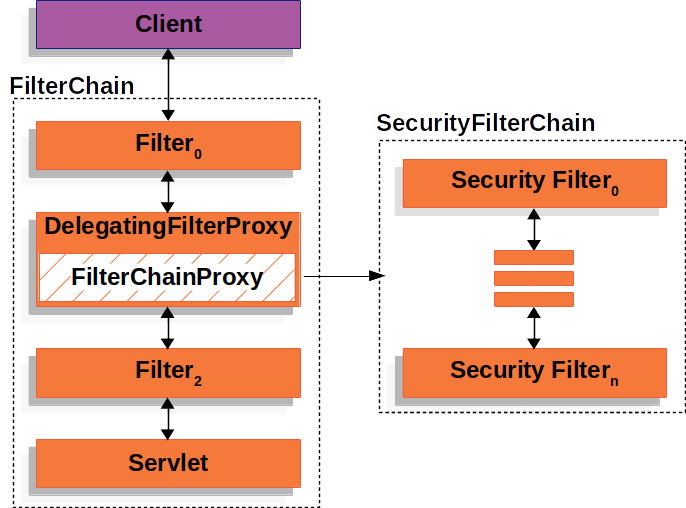
5.2.1 过滤器链架构
Spring Security利用 FilterChainProxy 封装一系列拦截器链,实现各种安全拦截功能
Servlet三大组件:Servlet、Filter、Listener
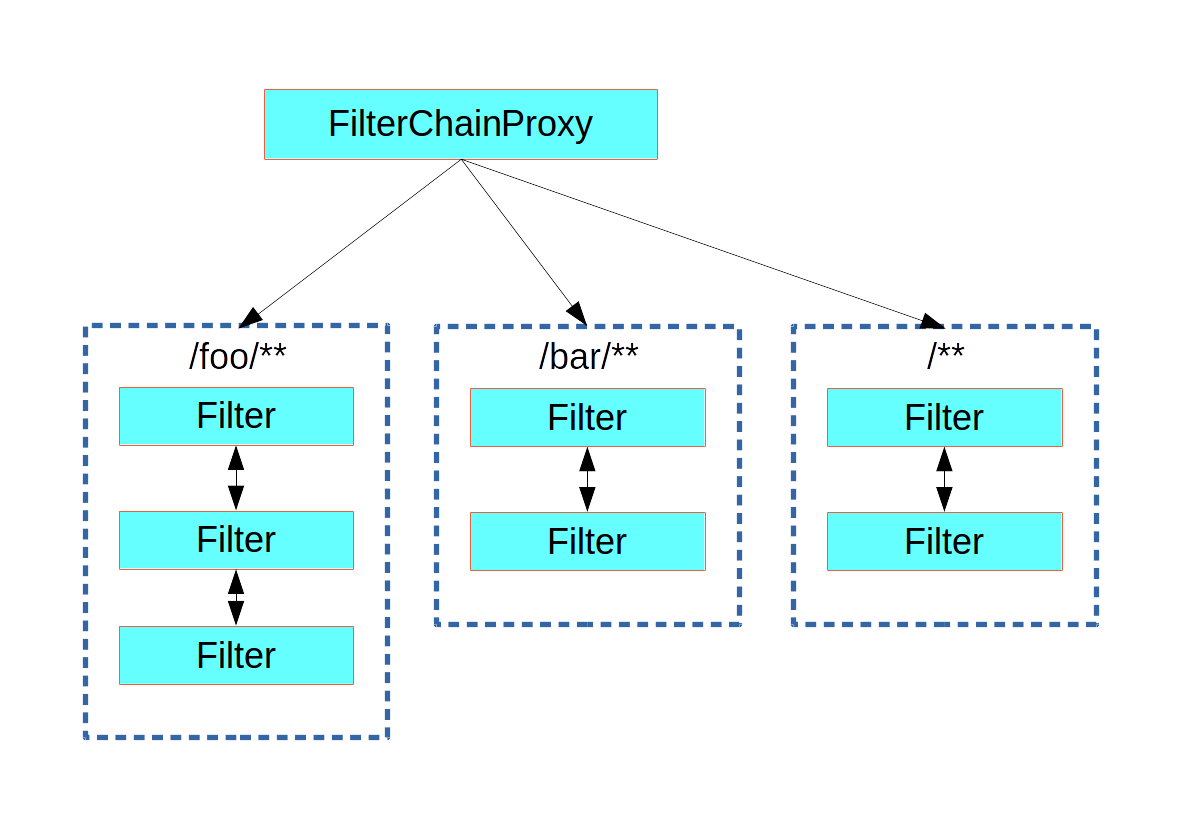
5.2.2 FilterChainProxy
5.2.3 SecurityFilterChain
5.3 使用
5.3.1 HttpSecurity
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/match1/**")
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/match1/user").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/match1/spam").hasRole("SPAM")
.anyRequest().isAuthenticated();
}
}5.3.2 MethodSecurity
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SampleSecureApplication {
}
@Service
public class MyService {
@Secured("ROLE_USER")
public String secure() {
return "Hello Security";
}
}核心
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
- @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity: 开启全局方法安全配置
- @Secured
- @PreAuthorize
- @PostAuthorize
- UserDetailService: 去数据库查询用户详细信息的service(用户基本信息、用户角色、用户权限)
5.4 实战
5.4.1 引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--引入security场景-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6</artifactId>
<!-- Temporary explicit version to fix Thymeleaf bug -->
<version>3.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>5.4.2 页面
5.4.2.1 首页
<p>Click <a th:href="@{/hello}">here</a> to see a greeting.</p>5.4.2.2 Hello页
<h1>Hello</h1>5.4.2.3 登录页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:if="${param.error}">Invalid username and password.</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">You have been logged out.</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<label> User Name : <input type="text" name="username" /> </label>
</div>
<div>
<label> Password: <input type="password" name="password" /> </label>
</div>
<div><input type="submit" value="登录" /></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>5.4.3 配置类
5.4.3.1 视图控制
package com.example.securingweb;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/home").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/hello").setViewName("hello");
registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");
}
}5.4.3.2 Security配置
package com.atguigu.security.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
/**
* @author lfy
* @Description
* @create 2023-03-08 16:54
*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests
.requestMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin((form) -> form
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
)
.logout((logout) -> logout.permitAll());
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
UserDetails user =
User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder()
.username("admin")
.password("admin")
.roles("USER")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
}5.4.4 改造Hello页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="https://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6"
>
<head>
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:inline="text">
Hello <span th:remove="tag" sec:authentication="name">thymeleaf</span>!
</h1>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Sign Out" />
</form>
</body>
</html>com/atguigu/boot3/security/Boot313SecurityApplication.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.security;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* Security场景的自动配置类:
* SecurityAutoConfiguration、SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration、SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration、
* 1、security的所有配置在 SecurityProperties: 以spring.security开头
* 2、默认SecurityFilterChain组件:
* - 所有请求都需要认证(登录)
* - 开启表单登录: spring security提供一个默认登录页,未经登录的所有请求都需要登录
* - httpbasic方式登录
* 3、@EnableWebSecurity 生效
* - WebSecurityConfiguration生效:web安全配置
* - HttpSecurityConfiguration生效:http安全规则
* - @EnableGlobalAuthentication生效:全局认证生效
* - AuthenticationConfiguration:认证配置
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Boot313SecurityApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot313SecurityApplication.class, args);
}
}
application.properties
spring.security.user.name=zhangsan
spring.security.user.password=123456
spring.security.user.roles=admin,common,hr
com/atguigu/boot3/security/config/AppSecurityConfiguration.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.security.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
/**
* 1、自定义请求授权规则:http.authorizeHttpRequests
* 2、自定义登录规则:http.formLogin
* 3、自定义用户信息查询规则:UserDetailsService
* 4、开启方法级别的精确权限控制:@EnableMethodSecurity + @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('world_exec')")
*/
@EnableMethodSecurity
@Configuration
public class AppSecurityConfiguration {
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//请求授权
http.authorizeHttpRequests(registry -> {
registry.requestMatchers("/").permitAll() //1、首页所有人都允许
.anyRequest().authenticated(); //2、剩下的任意请求都需要 认证(登录)
});
//表单登录
//3、表单登录功能:开启默认表单登录功能;Spring Security提供默认登录页
http.formLogin(formLogin -> {
formLogin.loginPage("/login").permitAll(); //自定义登录页位置,并且所有人都能访问
});
return http.build();
}
@Bean //查询用户详情;
UserDetailsService userDetailsService(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder){
UserDetails zhangsan = User.withUsername("zhangsan")
.password(passwordEncoder.encode("123456")) //使用密码加密器加密密码进行存储
.roles("admin", "hr")
.authorities("file_read", "file_write")
.build();
UserDetails lisi = User.withUsername("lisi")
.password(passwordEncoder.encode("123456"))
.roles("hr")
.authorities("file_read")
.build();
UserDetails wangwu = User.withUsername("wangwu")
.password(passwordEncoder.encode("123456"))
.roles("admin")
.authorities("file_write","world_exec")
.build();
//默认内存中保存所有用户信息
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(zhangsan,lisi,wangwu);
return manager;
}
@Bean //密码加密器
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
com/atguigu/boot3/security/controller/HelloController.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.security.controller;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello!Spring Security";
}
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('world_exec')")
@GetMapping("/world")
public String world(){
return "Hello World!!!";
}
}
com/atguigu/boot3/security/controller/LoginController.java
package com.atguigu.boot3.security.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String loginPage(){
return "login";
}
}
templates/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
Welcome To 尚硅谷 <br/>
<a th:href="@{/hello}">hello</a> <br/>
<a th:href="@{/world}">world</a> <br/>
</body>
</html>templates/login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:if="${param.error}">Invalid username and password.</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">You have been logged out.</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<label> User Name : <input type="text" name="username" /> </label>
</div>
<div>
<label> Password: <input type="password" name="password" /> </label>
</div>
<div><input type="submit" value="登录" /></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>6 可观测性
可观测性 Observability
对线上应用进行观测、监控、预警...
- 健康状况【组件状态、存活状态】Health
- 运行指标【cpu、内存、垃圾回收、吞吐量、响应成功率...】Metrics
- 链路追踪
- ...
6.1 SpringBoot Actuator
6.1.1 实战
6.1.1.1 场景引入
<!--可观测性场景启动器,线上指标监控、运行状态监控-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>6.1.1.2 暴露指标
management:
endpoints:
enabled-by-default: true #暴露所有端点信息
web:
exposure:
include: '*' #以web方式暴露6.1.1.3 访问数据
- 访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator;展示出所有可以用的监控端点
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/jvm.gc.pause
- http://localhost:8080/actuator/endpointName/detailPath
6.1.2 Endpoint
6.1.2.1 常用端点
| ID | 描述 |
|
| 暴露当前应用程序的审核事件信息。需要一个 |
|
| 显示应用程序中所有Spring Bean的完整列表。 |
|
| 暴露可用的缓存。 |
|
| 显示自动配置的所有条件信息,包括匹配或不匹配的原因。 |
|
| 显示所有 |
|
| 暴露Spring的属性 |
|
| 显示已应用的所有Flyway数据库迁移。 |
|
| 显示应用程序运行状况信息。 |
|
| 显示HTTP跟踪信息(默认情况下,最近100个HTTP请求-响应)。需要一个 |
|
| 显示应用程序信息。 |
|
| 显示Spring |
|
| 显示和修改应用程序中日志的配置。 |
|
| 显示已应用的所有Liquibase数据库迁移。需要一个或多个 |
|
| 显示当前应用程序的“指标”信息。 |
|
| 显示所有 |
|
| 显示应用程序中的计划任务。 |
|
| 允许从Spring Session支持的会话存储中检索和删除用户会话。需要使用Spring Session的基于Servlet的Web应用程序。 |
|
| 使应用程序正常关闭。默认禁用。 |
|
| 显示由 |
|
| 执行线程转储。 |
|
| 返回 |
|
| 通过HTTP暴露JMX bean(需要引入Jolokia,不适用于WebFlux)。需要引入依赖 |
|
| 返回日志文件的内容(如果已设置 |
|
| 以Prometheus服务器可以抓取的格式公开指标。需要依赖 |
threaddump、heapdump、metrics
6.1.2.2 定制端点
- 健康监控:返回存活、死亡
- 指标监控:次数、率
1. HealthEndpoint
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
int errorCode = check(); // perform some specific health check
if (errorCode != 0) {
return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code", errorCode).build();
}
return Health.up().build();
}
}
构建Health
Health build = Health.down()
.withDetail("msg", "error service")
.withDetail("code", "500")
.withException(new RuntimeException())
.build();management:
health:
enabled: true
show-details: always #总是显示详细信息。可显示每个模块的状态信息@Component
public class MyComHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
/**
* 真实的检查方法
* @param builder
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
//mongodb。 获取连接进行测试
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 检查完成
if(1 == 2){
// builder.up(); //健康
builder.status(Status.UP);
map.put("count",1);
map.put("ms",100);
}else {
// builder.down();
builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE);
map.put("err","连接超时");
map.put("ms",3000);
}
builder.withDetail("code",100)
.withDetails(map);
}
}application.properties
server.port=9999
#通过web方式暴露所有监控端点
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.enabled=true
management.endpoint.health.show-details=alwayscom.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component.MyHahaComponent
package com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Counter;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHahaComponent {
public int check(){
//业务代码判断这个组件是否该是存活状态
return 1;
}
}
com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.health.MyHahaHealthIndicator
package com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.health;
import com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component.MyHahaComponent;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.AbstractHealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
*
* 第一种:实现 HealthIndicator 接口来定制组件的健康状态对象(Health) 返回
* 第二种:继承 AbstractHealthIndicator抽象类,重写 doHealthCheck
*/
@Component
public class MyHahaHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
@Autowired
MyHahaComponent myHahaComponent;
/**
* 健康检查
* @param builder
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
//自定义检查方法
int check = myHahaComponent.check();
if(check == 1){
//存活
builder.up()
.withDetail("code","1000")
.withDetail("msg","活的很健康")
.withDetail("data","我的名字叫haha")
.build();
}else {
//下线
builder.down()
.withDetail("code","1001")
.withDetail("msg","死的很健康")
.withDetail("data","我的名字叫haha完蛋")
.build();
}
}
}
2. MetricsEndpoint
class MyService{
Counter counter;
public MyService(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){
counter = meterRegistry.counter("myservice.method.running.counter");
}
public void hello() {
counter.increment();
}
}
com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.controller.HelloController
package com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.controller;
import com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component.MyHahaComponent;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
MyHahaComponent myHahaComponent;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
//业务调用
myHahaComponent.hello();
return "哈哈哈";
}
}
com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component.MyHahaComponent
package com.atguigu.boot3.actuator.component;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.Counter;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHahaComponent {
Counter counter = null;
/**
* 注入 meterRegistry 来保存和统计所有指标
* @param meterRegistry
*/
public MyHahaComponent(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){
//得到一个名叫 myhaha.hello 的计数器
counter = meterRegistry.counter("myhaha.hello");
}
public int check(){
//业务代码判断这个组件是否该是存活状态
return 1;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
counter.increment();
}
}
6.2 监控案例落地
基于 Prometheus + Grafana

6.2.1 安装 Prometheus + Grafana
#安装prometheus:时序数据库
docker run -p 9090:9090 -d \
-v pc:/etc/prometheus \
prom/prometheus
#安装grafana;默认账号密码 admin:admin
docker run -d --name=grafana -p 3000:3000 grafana/grafana6.2.2 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
<version>1.10.6</version>
</dependency>management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure: #暴露所有监控的端点
include: '*'访问: http://localhost:8001/actuator/prometheus 验证,返回 prometheus 格式的所有指标
部署Java应用
#安装上传工具
yum install lrzsz
#安装openjdk
# 下载openjdk
wget https://download.oracle.com/java/17/latest/jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz
mkdir -p /opt/java
tar -xzf jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz -C /opt/java/
sudo vi /etc/profile
#加入以下内容
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/jdk-17.0.7
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
#环境变量生效
source /etc/profile
# 后台启动java应用
nohup java -jar boot3-14-actuator-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar > output.log 2>&1 &
确认可以访问到: http://8.130.32.70:9999/actuator/prometheus
6.2.3 配置 Prometheus 拉取数据
## 修改 prometheus.yml 配置文件
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'spring-boot-actuator-exporter'
metrics_path: '/actuator/prometheus' #指定抓取的路径
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.200.1:8001']
labels:
nodename: 'app-demo'6.2.4 配置 Grafana 监控面板
- 添加数据源(Prometheus)
- 添加面板。可去 dashboard 市场找一个自己喜欢的面板,也可以自己开发面板;Dashboards | Grafana Labs
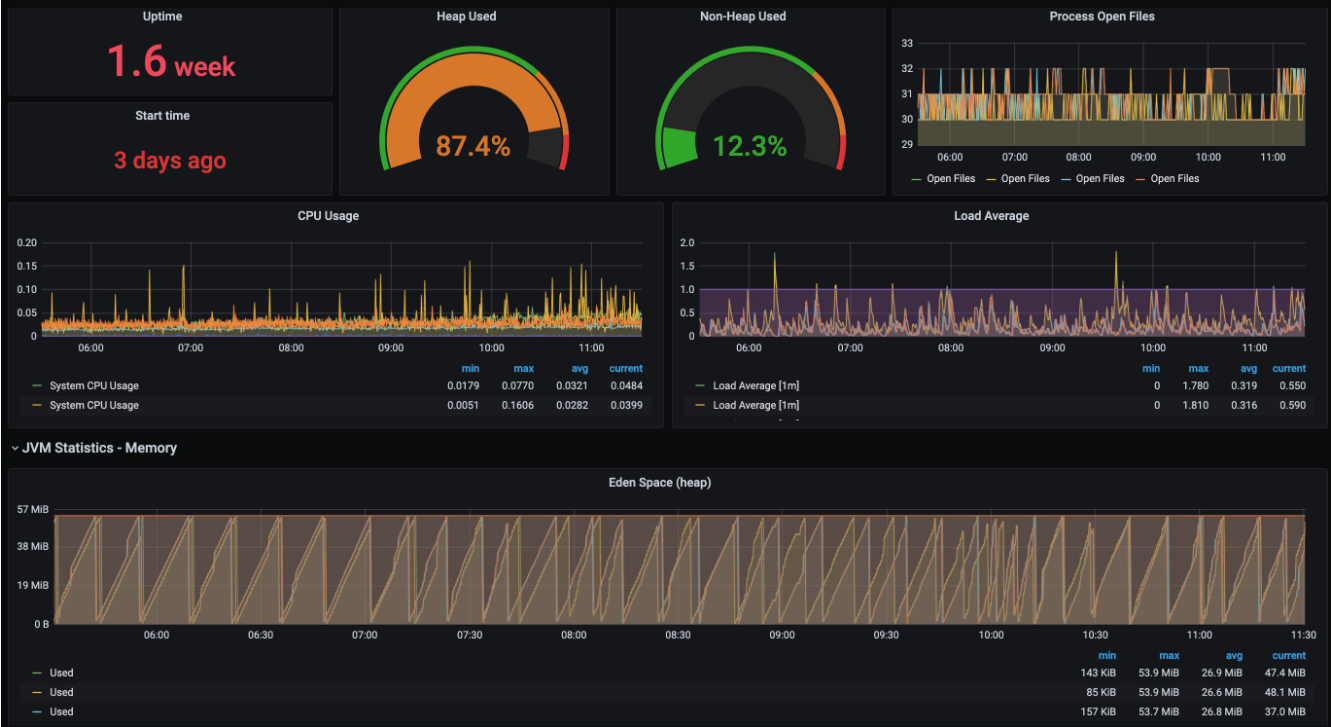
6.2.5 效果
package com.atguigu.boot3.actuator;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* 整合Prometheus+Grafana 完成线上应用指标监控系统
* 1、改造SpringBoot应用,产生Prometheus需要的格式数据
* - 导入 micrometer-registry-prometheus
* 2、部署java应用。在同一个机器内,访问 http://172.25.170.71:9999/actuator/prometheus 就能得到指标数据
* 在外部访问:http://8.130.32.70:9999/actuator/prometheus
* 3、修改prometheus配置文件,让他拉取某个应用的指标数据
* 4、去grafana添加一个prometheus数据源,配置好prometheus地址
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Boot314ActuatorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot314ActuatorApplication.class, args);
}
}
7 AOT
7.1 AOT与JIT
AOT:Ahead-of-Time(提前编译):程序执行前,全部被编译成机器码
JIT:Just in Time(即时编译): 程序边编译,边运行;
编译:
- 源代码(.c、.cpp、.go、.java。。。) ===编译=== 机器码
语言:
- 编译型语言:编译器
- 解释型语言:解释器
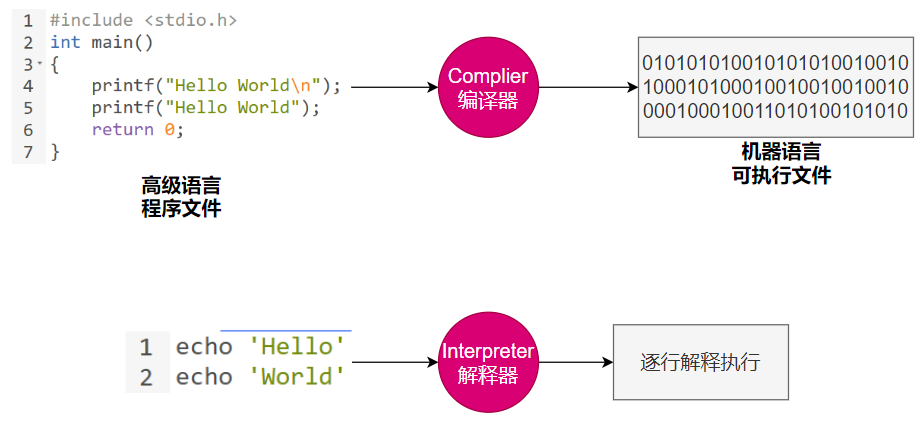
7.1.1 Complier 与 Interpreter
Java:半编译半解释
https://anycodes.cn/editor (在线编码)
| 对比项 | 编译器 | 解释器 |
| 机器执行速度 | 快,因为源代码只需被转换一次 | 慢,因为每行代码都需要被解释执行 |
| 开发效率 | 慢,因为需要耗费大量时间编译 | 快,无需花费时间生成目标代码,更快的开发和测试 |
| 调试 | 难以调试编译器生成的目标代码 | 容易调试源代码,因为解释器一行一行地执行 |
| 可移植性(跨平台) | 不同平台需要重新编译目标平台代码 | 同一份源码可以跨平台执行,因为每个平台会开发对应的解释器 |
| 学习难度 | 相对较高,需要了解源代码、编译器以及目标机器的知识 | 相对较低,无需了解机器的细节 |
| 错误检查 | 编译器可以在编译代码时检查错误 | 解释器只能在执行代码时检查错误 |
| 运行时增强 | 无 | 可以动态增强 |
7.1.2 AOT 与 JIT 对比
| JIT | AOT | |
| 优点 | 1.具备实时调整能力 | 1.速度快,优化了运行时编译时间和内存消耗 |
| 缺点 | 1.运行期边编译速度慢 | 1.程序第一次编译占用时间长 |
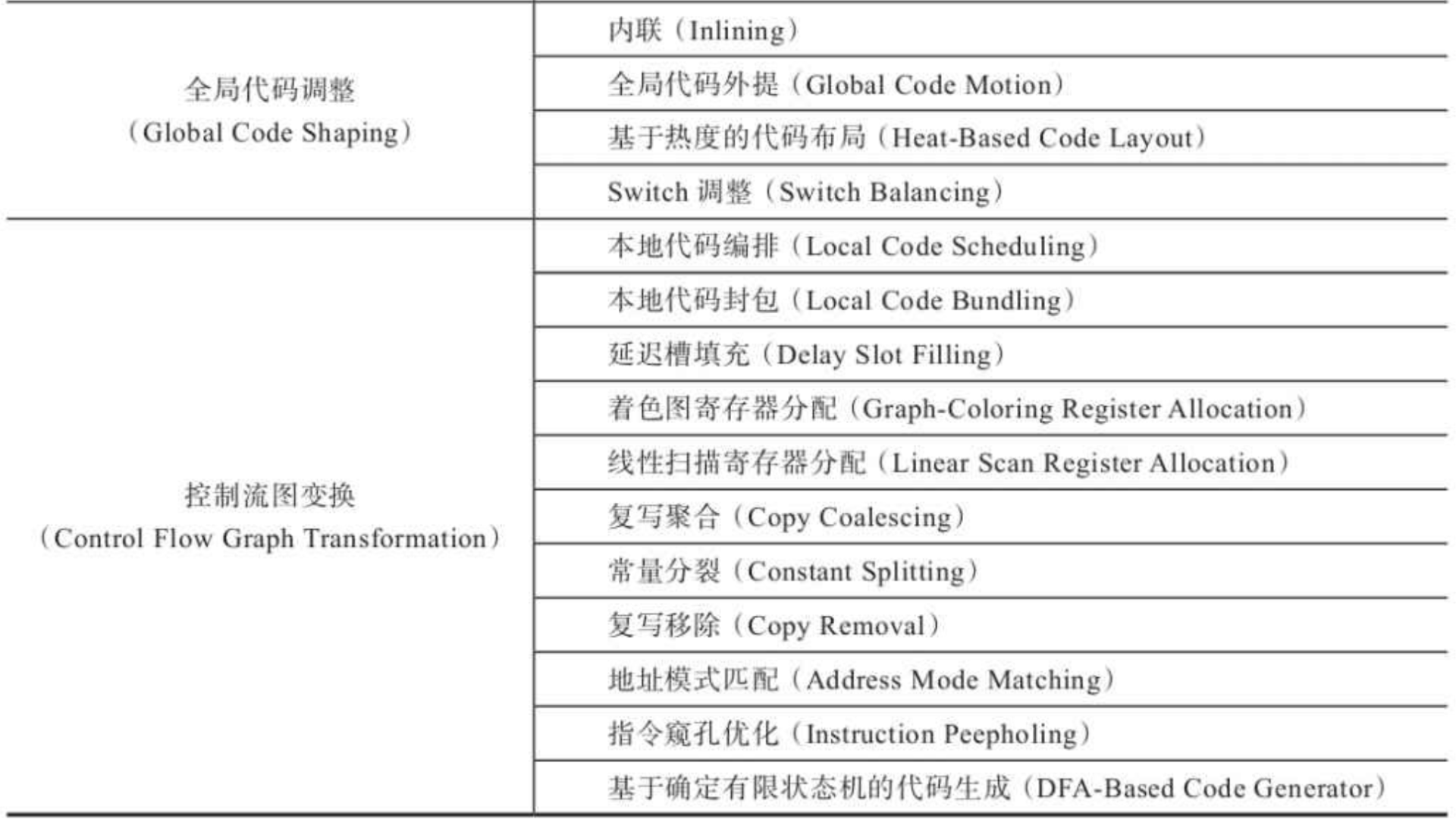
在 OpenJDK 的官方 Wiki 上,介绍了HotSpot 虚拟机一个相对比较全面的、即时编译器(JIT)中采用的优化技术列表。
可使用:-XX:+PrintCompilation 打印JIT编译信息
7.1.3 JVM架构
.java === .class === 机器码
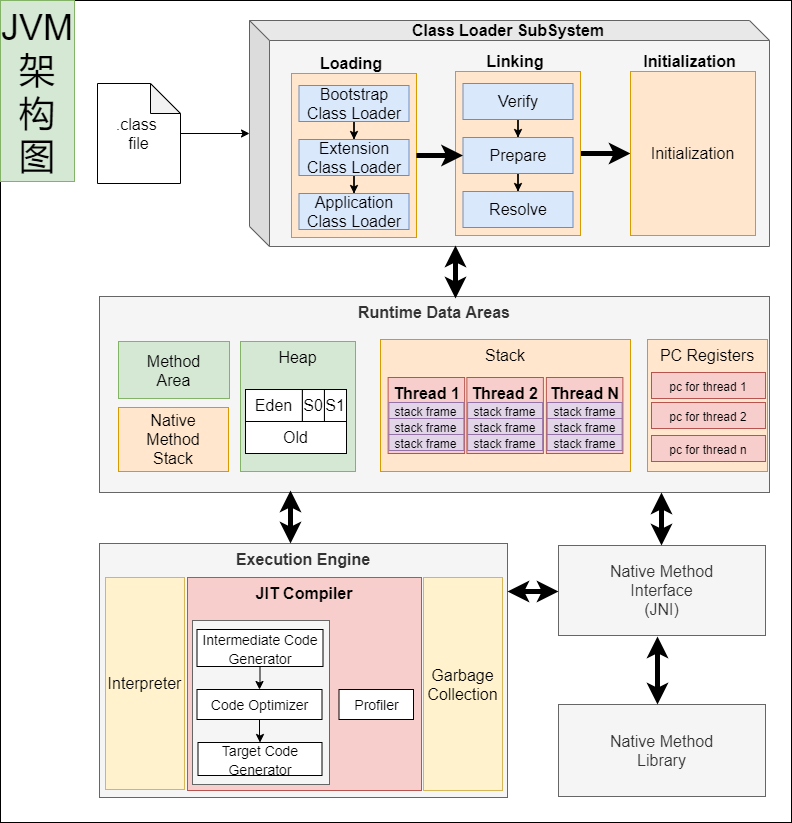
JVM: 既有解释器,又有编辑器(JIT:即时编译);
7.1.4 Java的执行过程
建议阅读:
- 美团技术:基本功 | Java即时编译器原理解析及实践 - 美团技术团队
- openjdk官网:Compiler - Compiler - OpenJDK Wiki
7.1.4.1 流程概要
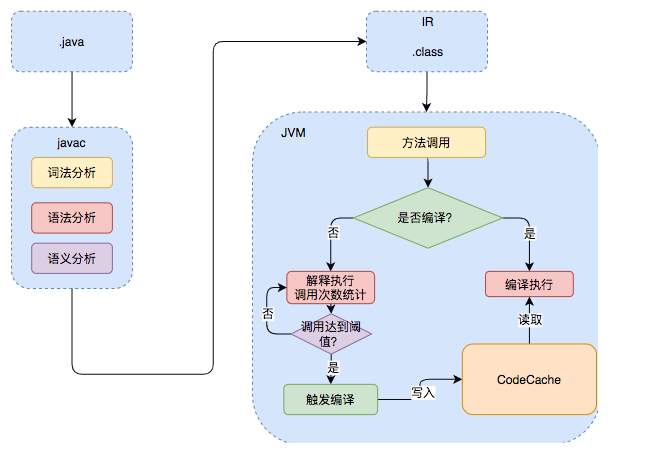
解释执行:
编译执行:
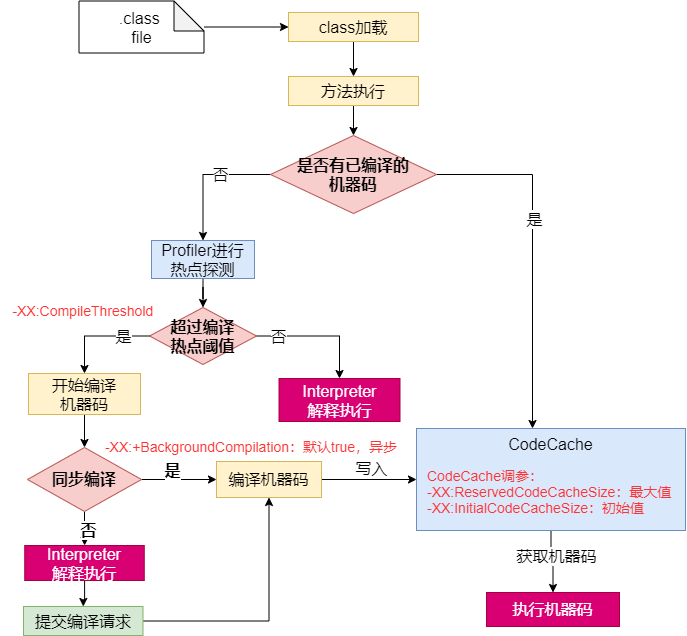
7.1.4.2 详细流程
热点代码:调用次数非常多的代码
7.1.5 JVM编译器
JVM中集成了两种编译器,Client Compiler 和 Server Compiler;
- Client Compiler注重启动速度和局部的优化
- Server Compiler更加关注全局优化,性能更好,但由于会进行更多的全局分析,所以启动速度会慢。
Client Compiler:
- HotSpot VM带有一个Client Compiler C1编译器
- 这种编译器启动速度快,但是性能比较Server Compiler来说会差一些。
- 编译后的机器码执行效率没有C2的高
Server Compiler:
- Hotspot虚拟机中使用的Server Compiler有两种:C2 和 Graal。
- 在Hotspot VM中,默认的Server Compiler是C2编译器。
7.1.6 分层编译
Java 7开始引入了分层编译(Tiered Compiler)的概念,它结合了C1和C2的优势,追求启动速度和峰值性能的一个平衡。分层编译将JVM的执行状态分为了五个层次。五个层级分别是:
- 解释执行。
- 执行不带profiling的C1代码。
- 执行仅带方法调用次数以及循环回边执行次数profiling的C1代码。
- 执行带所有profiling的C1代码。
- 执行C2代码。
profiling就是收集能够反映程序执行状态的数据。其中最基本的统计数据就是方法的调用次数,以及循环回边的执行次数。
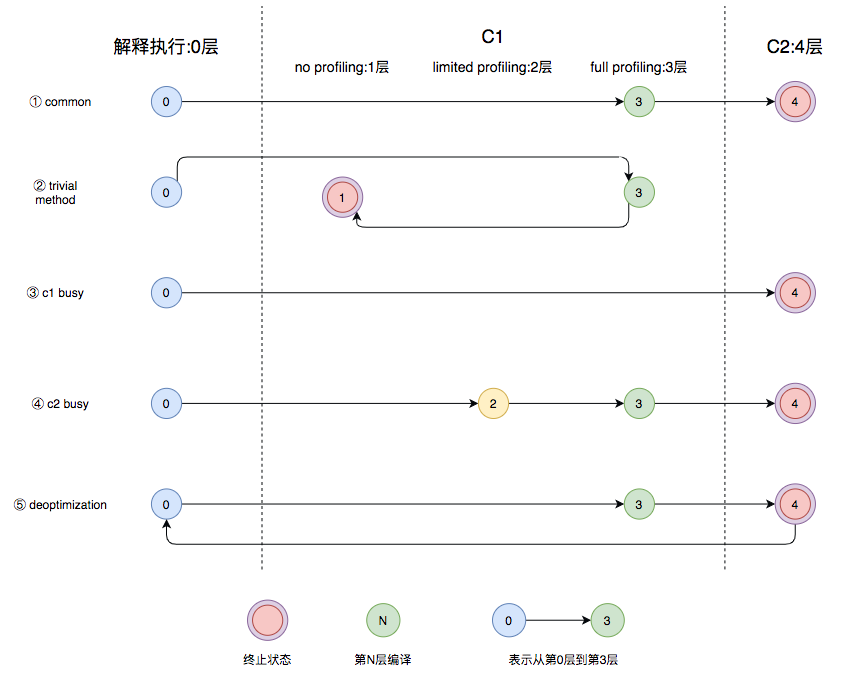
-
图中第①条路径,代表编译的一般情况,热点方法从解释执行到被3层的C1编译,最后被4层的C2编译。
-
如果方法比较小(比如Java服务中常见的getter/setter方法),3层的profiling没有收集到有价值的数据,JVM就会断定该方法对于C1代码和C2代码的执行效率相同,就会执行图中第②条路径。在这种情况下,JVM会在3层编译之后,放弃进入C2编译,直接选择用1层的C1编译运行。
-
在C1忙碌的情况下,执行图中第③条路径,在解释执行过程中对程序进行profiling ,根据信息直接由第4层的C2编译。
-
前文提到C1中的执行效率是1层>2层>3层,第3层一般要比第2层慢35%以上,所以在C2忙碌的情况下,执行图中第④条路径。这时方法会被2层的C1编译,然后再被3层的C1编译,以减少方法在3层的执行时间。
-
如果编译器做了一些比较激进的优化,比如分支预测,在实际运行时发现预测出错,这时就会进行反优化,重新进入解释执行,图中第⑤条执行路径代表的就是反优化。
总的来说,C1的编译速度更快,C2的编译质量更高,分层编译的不同编译路径,也就是JVM根据当前服务的运行情况来寻找当前服务的最佳平衡点的一个过程。从JDK 8开始,JVM默认开启分层编译。
云原生:Cloud Native; Java小改版;
最好的效果:
存在的问题:
- java应用如果用jar,解释执行,热点代码才编译成机器码;初始启动速度慢,初始处理请求数量少。
- 大型云平台,要求每一种应用都必须秒级启动。每个应用都要求效率高。
希望的效果:
- java应用也能提前被编译成机器码,随时急速启动,一启动就急速运行,最高性能
编译成机器码的好处:
Java应用如果打成一个jar包,部署到另外的服务器还需要安装Java环境;如果编译成机器码的,则可以在这个平台 Windows X64 直接运行。(0 1这种机器码,不需要什么环境,电脑通电就行)
原生镜像:native-image(机器码、本地镜像、直接的可执行程序)
- 把应用打包成能适配本机平台 的可执行文件(机器码、本地镜像)
7.2 GraalVM
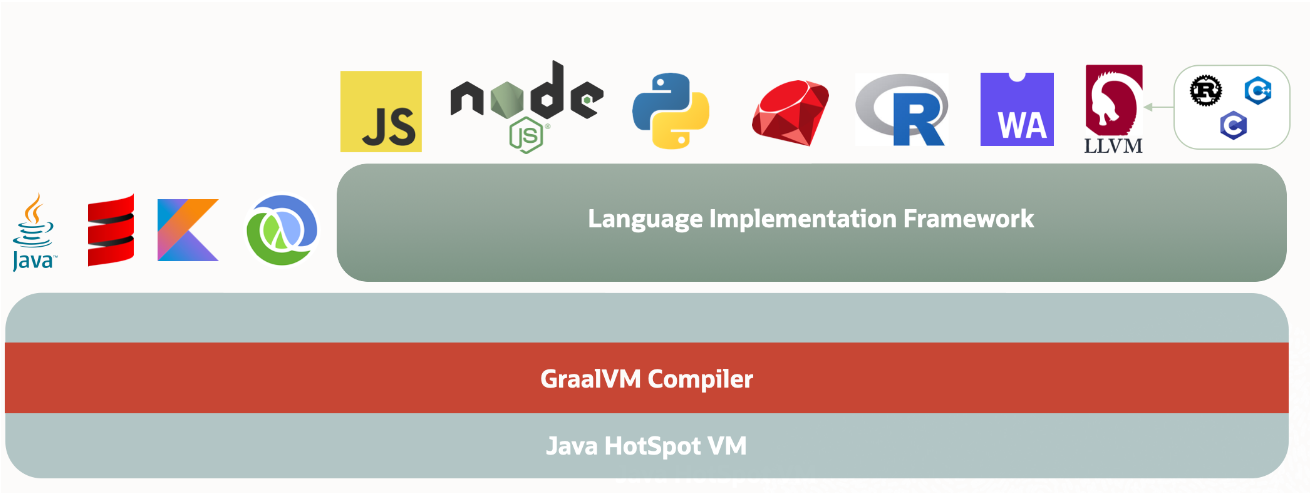
GraalVM
GraalVM是一个高性能的JDK,旨在加速用Java和其他JVM语言编写的应用程序的执行,同时还提供JavaScript、Python和许多其他流行语言的运行时。
GraalVM提供了两种运行Java应用程序的方式:
- 1. 在HotSpot JVM上使用Graal即时(JIT)编译器
- 2. 作为预先编译(AOT)的本机可执行文件运行(本地镜像)。
GraalVM的多语言能力使得在单个应用程序中混合多种编程语言成为可能,同时消除了外部语言调用的成本。
7.2.1 架构
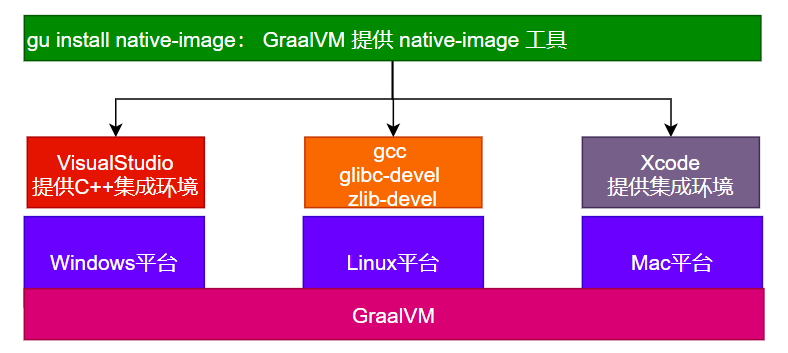
7.2.2 安装
跨平台提供原生镜像原理:
7.2.2.1 VisualStudio
免费的开发人员软件和服务 - Visual Studio
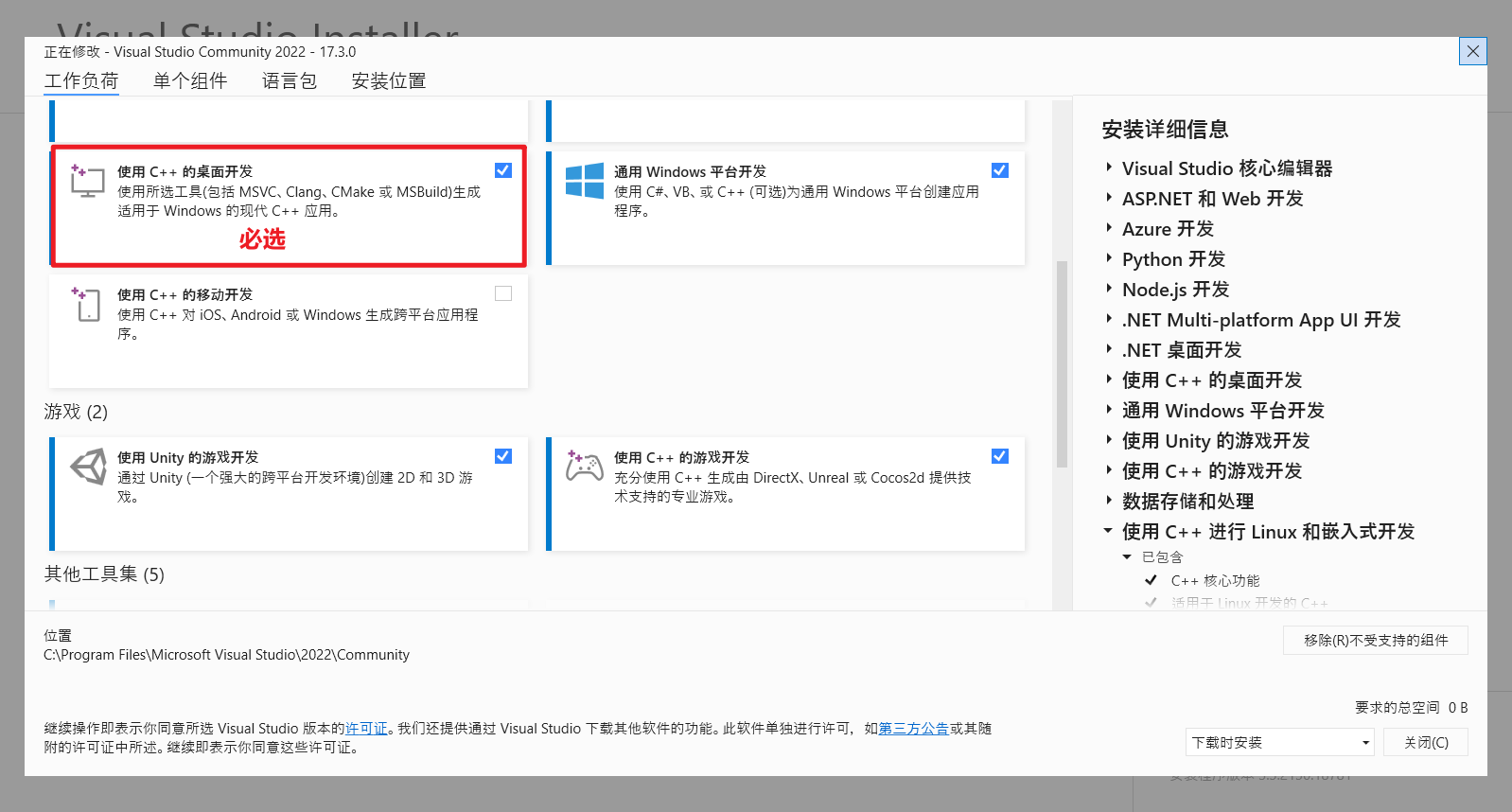
别选中文
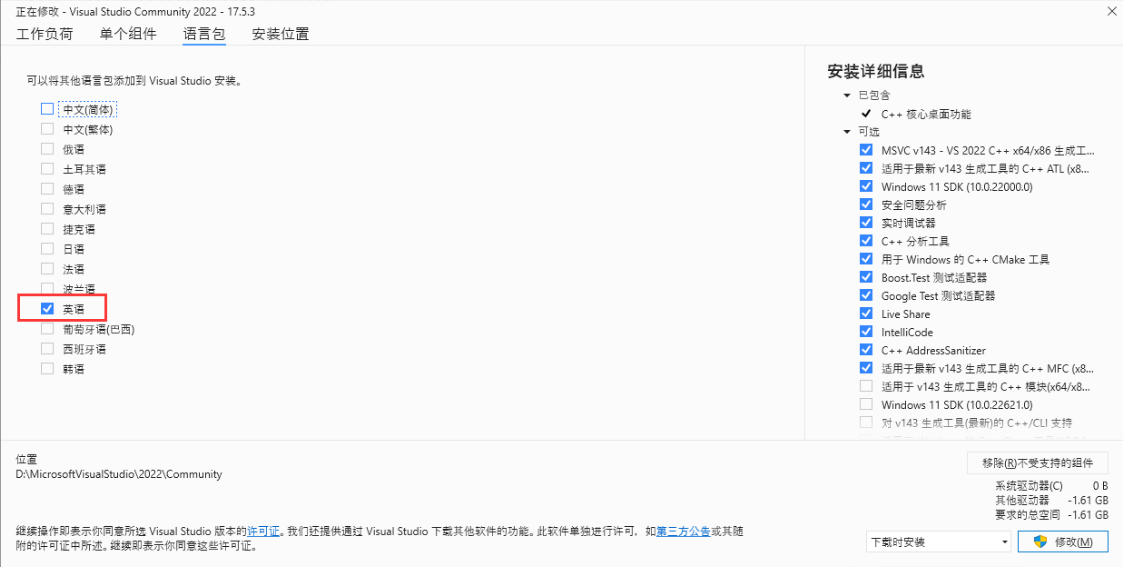
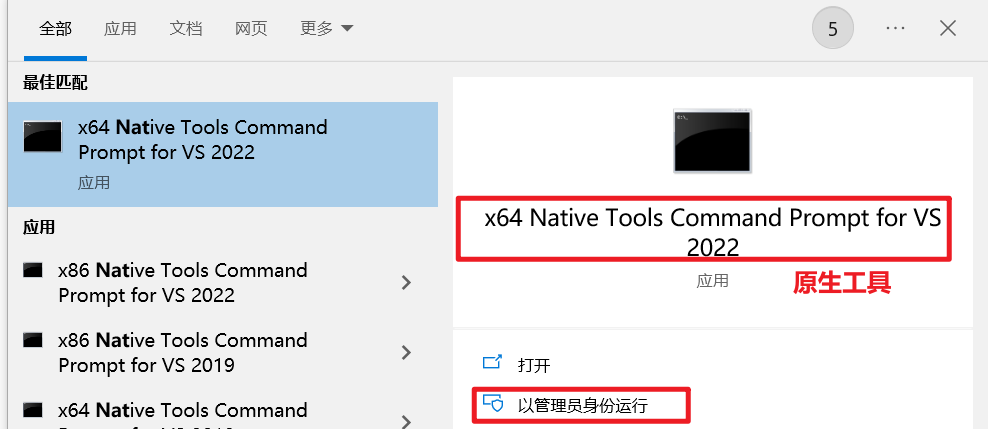
记住你安装的地址;
7.2.2.2 GraalVM
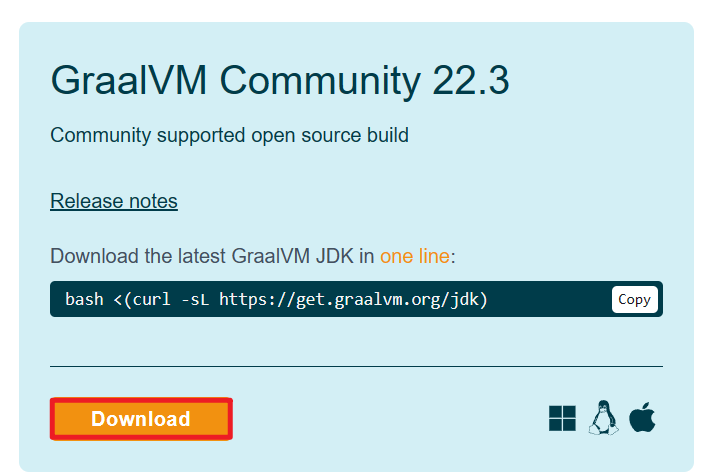
1 安装
下载 GraalVM + native-image
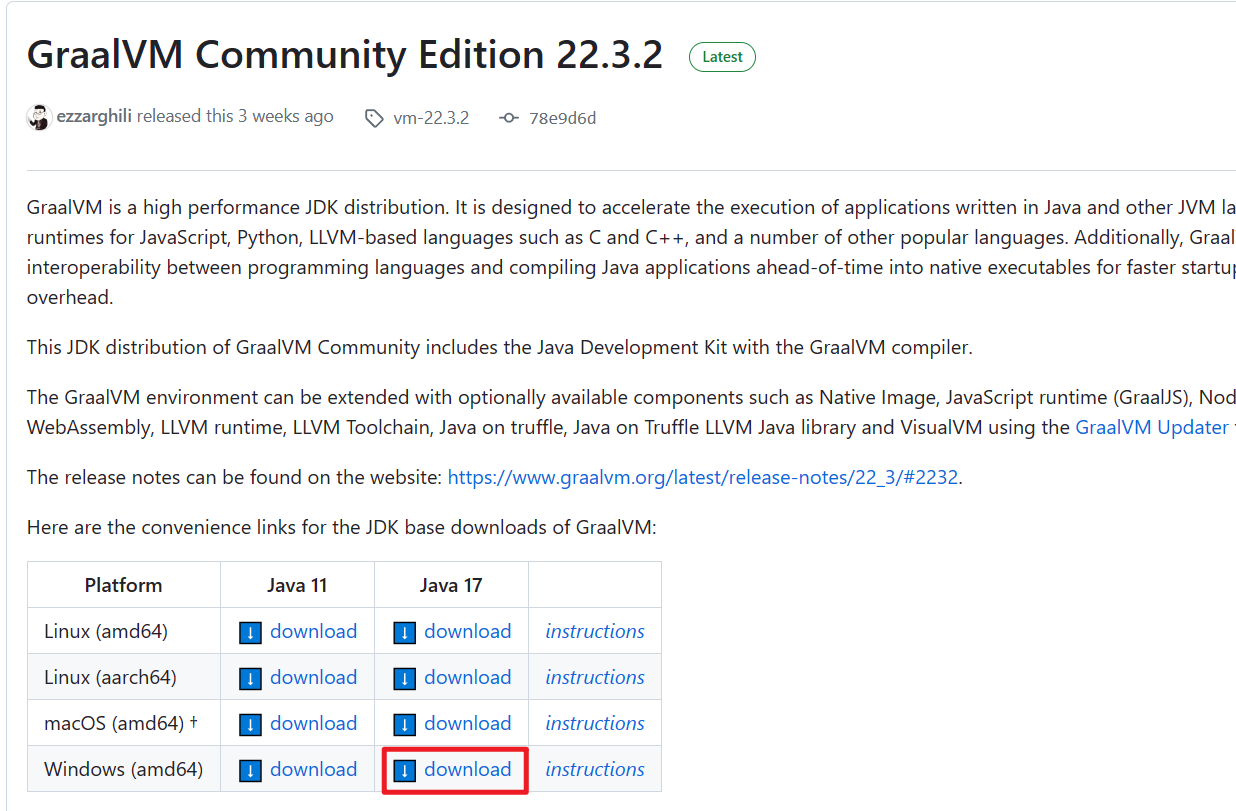
2 配置
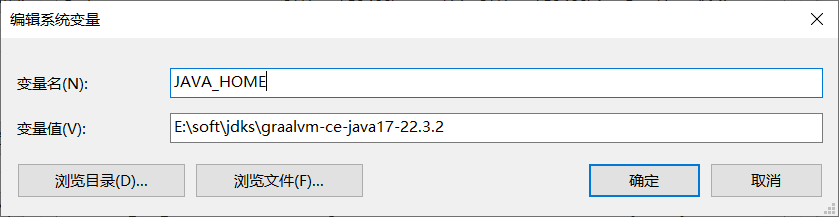
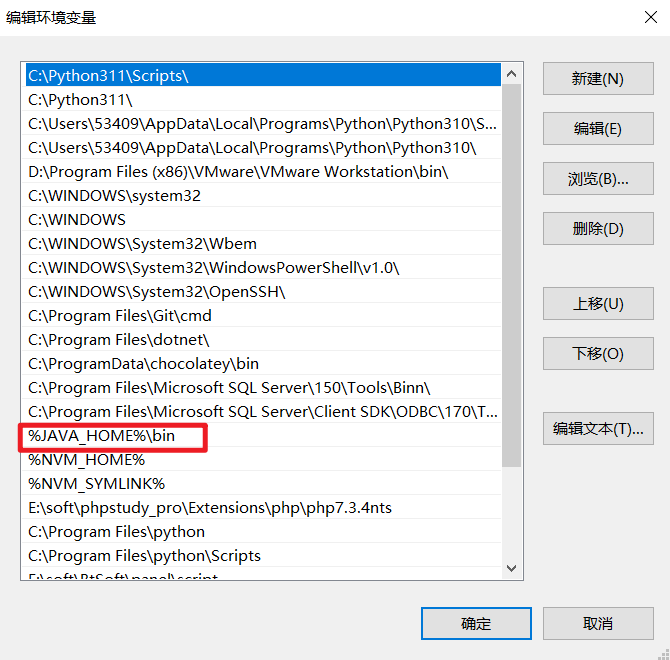
修改 JAVA_HOME 与 Path,指向新bin路径
验证JDK环境为GraalVM提供的即可:
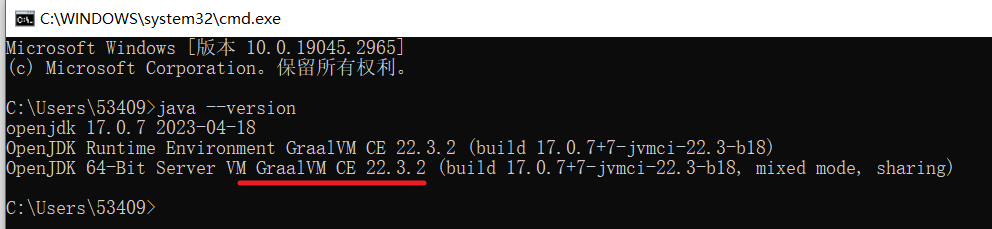
3 依赖
安装 native-image 依赖:
网络环境好:参考:Native Image
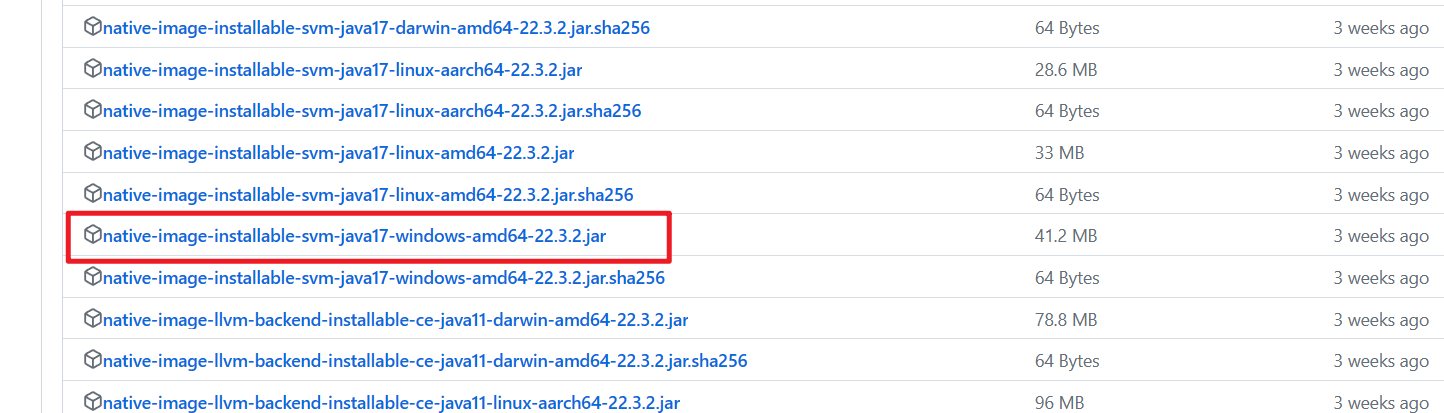
gu install native-image网络不好,使用我们下载的离线jar; native-image-xxx.jar 文件
gu install --file native-image-installable-svm-java17-windows-amd64-22.3.2.jar4 验证
native-image7.2.3 测试
7.2.3.1 创建项目
创建普通java项目。编写HelloWorld类;
- 使用mvn clean package进行打包
- 确认jar包是否可以执行java -jar xxx.jar
- 可能需要给 MANIFEST.MF添加 Main-Class: 你的主类
7.2.3.2 编译镜像
编译为原生镜像(native-image):使用native-tools终端
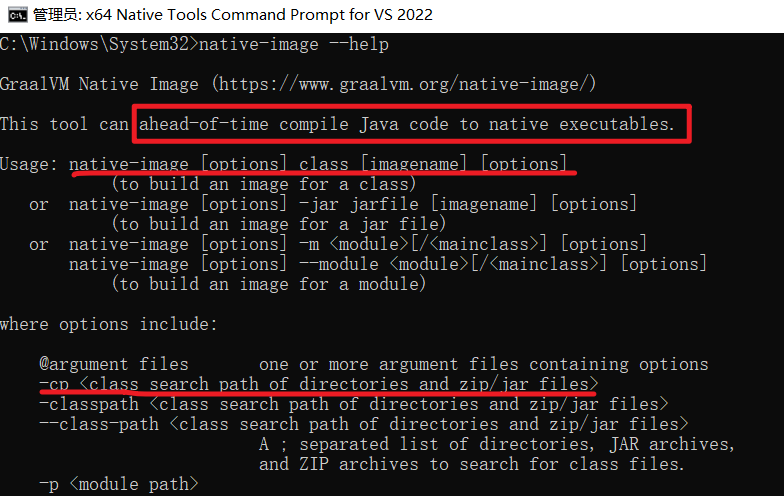
#第一种:从入口开始,编译整个jar
native-image -cp boot3-15-aot-common-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.atguigu.MainApplication -o Haha
#第二种:编译.class字节码文件,编译某个类【必须有main入口方法,否则无法编译】
native-image -cp .\classes com.atguigu.MainApplication -o Haha7.2.3.3 Linux平台测试
1 安装gcc等环境
yum install lrzsz
sudo yum install gcc glibc-devel zlib-devel2 下载安装配置Linux下的GraalVM、native-image
- 下载:https://www.graalvm.org/downloads/
- 安装:GraalVM、native-image
- 配置:JAVA环境变量为GraalVM
tar -zxvf graalvm-ce-java17-linux-amd64-22.3.2.tar.gz -C /opt/java/
sudo vim /etc/profile
#修改以下内容
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/graalvm-ce-java17-22.3.2
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
source /etc/profile3 安装native-image
gu install --file native-image-installable-svm-java17-linux-amd64-22.3.2.jar4 使用native-image编译jar为原生程序
#第一种:从入口开始,编译整个jar
native-image -cp boot3-15-aot-common-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.atguigu.MainApplication -o Demopackage com.atguigu;
/**
* 打包成本地镜像:
*
* 1、打成jar包: 注意修改 jar包内的 MANIFEST.MF 文件,指定Main-Class的全类名
* - java -jar xxx.jar 就可以执行。
* - 切换机器,安装java环境。默认解释执行,启动速度慢,运行速度慢
* 2、打成本地镜像(可执行文件):
* - native-image -cp 你的jar包/路径 你的主类 -o 输出的文件名
* - native-image -cp boot3-15-aot-common-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.atguigu.MainApplication -o Demo
*
* 并不是所有的Java代码都能支持本地打包;
* SpringBoot保证Spring应用的所有程序都能在AOT的时候提前告知graalvm怎么处理?
*
* - 动态能力损失:反射的代码:(动态获取构造器,反射创建对象,反射调用一些方法);
* 解决方案:额外处理(SpringBoot 提供了一些注解):提前告知 graalvm 反射会用到哪些方法、构造器
* - 配置文件损失:
* 解决方案:额外处理(配置中心):提前告知 graalvm 配置文件怎么处理
* - 【好消息:新版GraalVM可以自动进行预处理,不用我们手动进行补偿性的额外处理。】
* 二进制里面不能包含的,不能动态的都得提前处理;
*
* 不是所有框架都适配了 AOT特性;Spring全系列栈适配OK
*
* application.properties
* a(){
* //ssjsj bcde();
* //提前处理
* }
*/
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
}7.3 SpringBoot整合
7.3.1 依赖导入
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.graalvm.buildtools</groupId>
<artifactId>native-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>7.3.2 生成native-image
1、运行aot提前处理命令:mvn springboot:process-aot
2、运行native打包:mvn -Pnative native:build
# 推荐加上 -Pnative
mvn -Pnative native:build -f pom.xml
7.3.3 常见问题
可能提示如下各种错误,无法构建原生镜像,需要配置环境变量;
- 出现cl.exe找不到错误
- 出现乱码
- 提示no include path set
- 提示fatal error LNK1104: cannot open file 'LIBCMT.lib'
- 提示 LINK : fatal error LNK1104: cannot open file 'kernel32.lib'
- 提示各种其他找不到
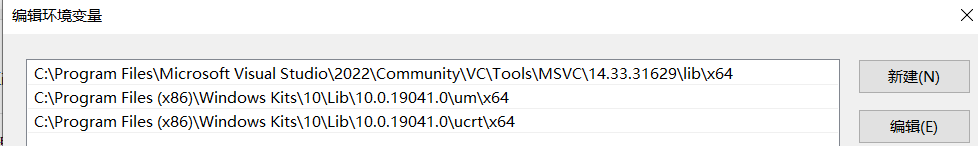
需要修改三个环境变量:Path、INCLUDE、lib
1、 Path:添加如下值
- C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.33.31629\bin\Hostx64\x64
2、新建INCLUDE环境变量:值为
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.33.31629\include;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.19041.0\shared;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.19041.0\ucrt;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.19041.0\um;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Include\10.0.19041.0\winrt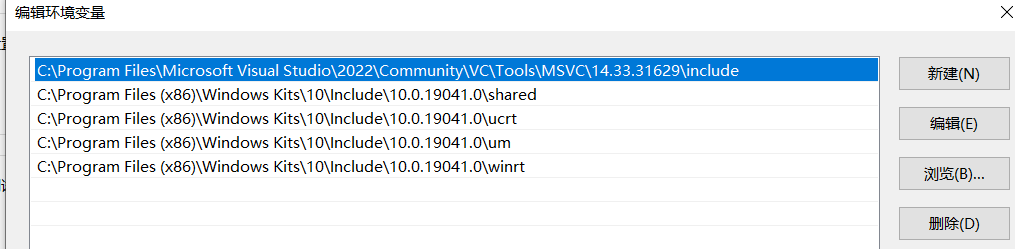
3、新建lib环境变量:值为
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\VC\Tools\MSVC\14.33.31629\lib\x64;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.19041.0\um\x64;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Lib\10.0.19041.0\ucrt\x64