什么是线性表
线性表是最简单、最基本、最常用的数据结构。线性表是线性结构的抽象(Abstract),线性结构的特点是结构中的数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系。这种一对一的关系指的是数据元素之间的位置关系,即:(1)除第一个位置的数据元素外,其它数据元素位置的前面都只有一个数据元素;(2)除最后一个位置的数据元素外,其它数据元素位置的后面都只有一个元素。也就是说,数据元素是一个接一个的排列。因此,可以把线性表想象为一种数据元素序列的数据结构。
线性表就是位置有先后关系,一个接着一个排列的数据结构。
C#提供了一个非泛型接口IList 接口中的项是object,实现了lList解扣子的类有ArrayList,ListDictionary,StringCollection,StringDictionary.
c#2.0提供了泛型的IList<T>接
c#1.1 提供了一个非泛型接lList接接,实现了List<T>接口的类有List<T>
使用List<>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//1.使用BCL中的List线性表
List<string> list = new List<string>();
list.Add("123");//索引为0
list.Add("456");//索引为1
}
}
}
线性表的接口定义
public interface IListDS<T> {
int GetLength(;//求长度
void Clear(;//清空操作
bool IsEmpty0;//判断线性表是否为空
void Append(T item);//附加操作
void Insert(T item,int i);//插八操作
T Delete(int i);//刪除操作
T GetElem(int i);//取表元
int Locate(T value);//按值查找
}
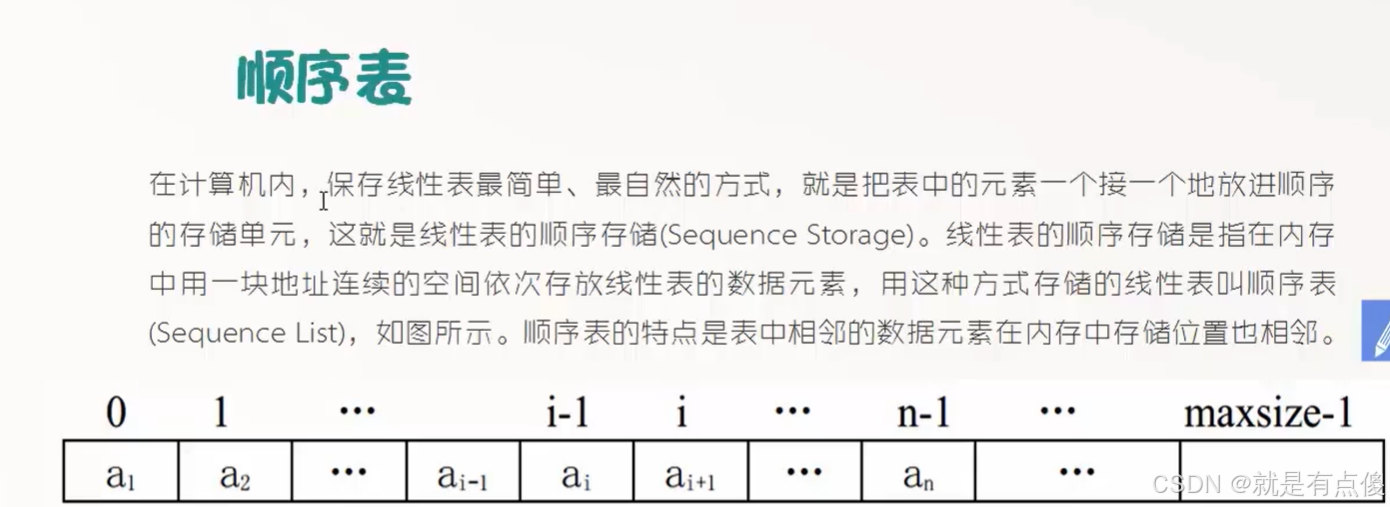
顺序表

自定义自己实现List
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal interface IlistDS<T>
{
int GetLength();
void Clear();
bool IsEmpty();
void Add(T item);
void Insert(int index, T item);
T Delete(int index);
T this[int index] { get; }
T GetEle(int index);
int Locate(T value);
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal class SeqList<T> : IlistDS<T>
{
private T[] data;//用来存储数据
private int count = 0;//表示存了多少个数据
public SeqList(int size)//size就是最大容量
{
data = new T[size];
count = 0;
}
public SeqList() : this(10)//默认构造函数的大小为10
{
}
public T this[int index]
{
get { return GetEle(index); }
}
public void Add(T item)
{
if (count == data.Length)//说明当前数组已经存满
{
Console.WriteLine("当前顺序表已经存满,不允许再存");
}
else
{
data[count] = item;
count++;
}
}
public void Clear()
{
count = 0;
}
public T Delete(int index)
{
T temp = data[index];
for (int i = index + 1; i < count; i++)
{
data[i - 1] = data[i];//把数据向前移动
}
count--;
return temp;
}
public T GetEle(int index)
{
if (index >= 0 && index <= count - 1)//说明所以存在
{
return data[index];
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("索引不存在");
return default(T);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 取得数据的个数
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
/// <exception cref="NotImplementedException"></exception>
public int GetLength()
{
return count;
}
public void Insert(int index, T item)
{
for (int i = count - 1; i >= index; i--)
{
data[i + 1] = data[i];
}
data[index] = item;
count++;
}
public bool IsEmpty()
{
return (count == 0);
}
public int Locate(T value)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
{
if (data[i].Equals(value))
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SeqList<string> list = new SeqList<string>();
list.Add("123");
list.Add("456");
list.Add("789");
Console.WriteLine(list.GetEle(0));
Console.WriteLine(list[0]);
list.Insert(1,"777");
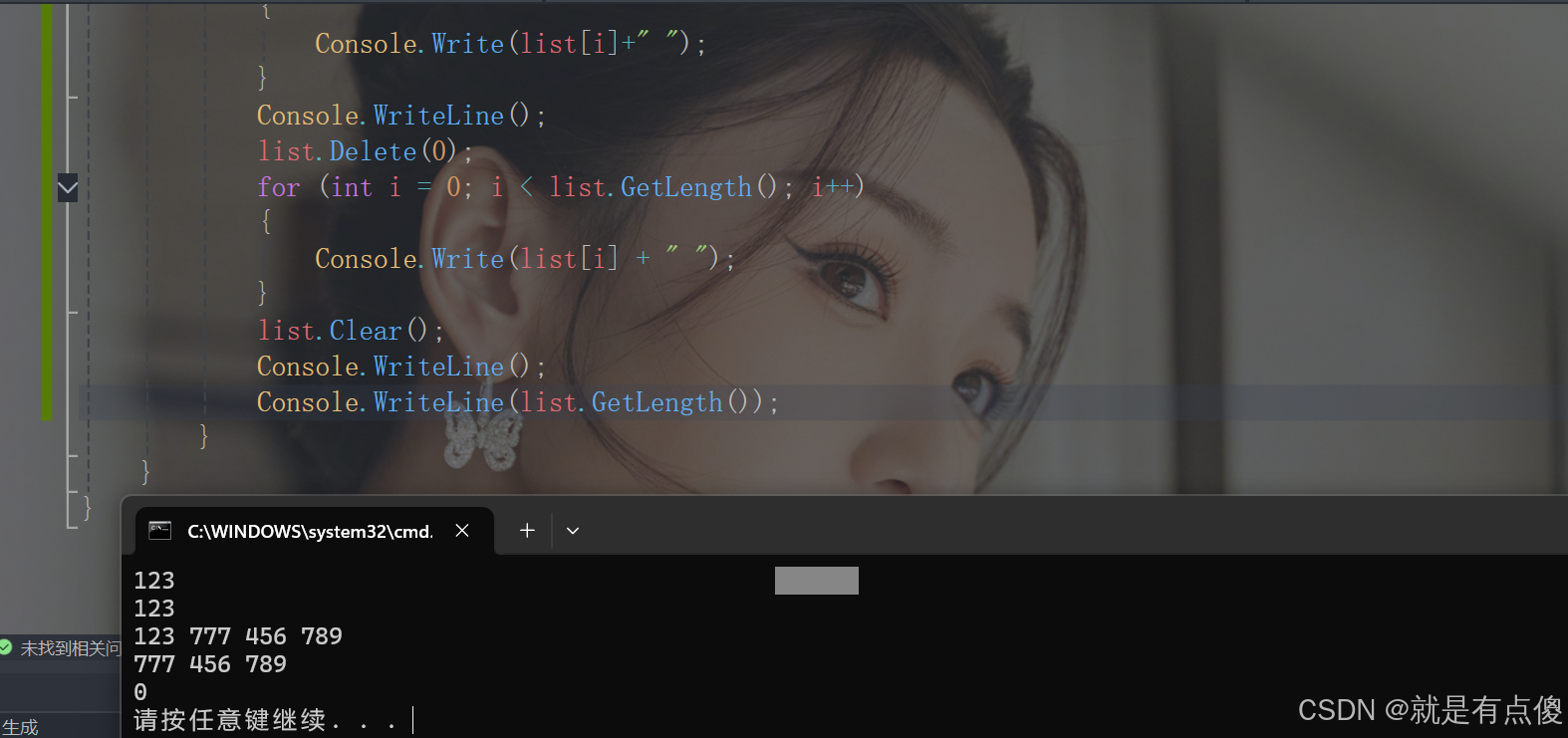
for (int i = 0; i < list.GetLength(); i++)
{
Console.Write(list[i]+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
list.Delete(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list.GetLength(); i++)
{
Console.Write(list[i] + " ");
}
list.Clear();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(list.GetLength());
}
}
}
链表


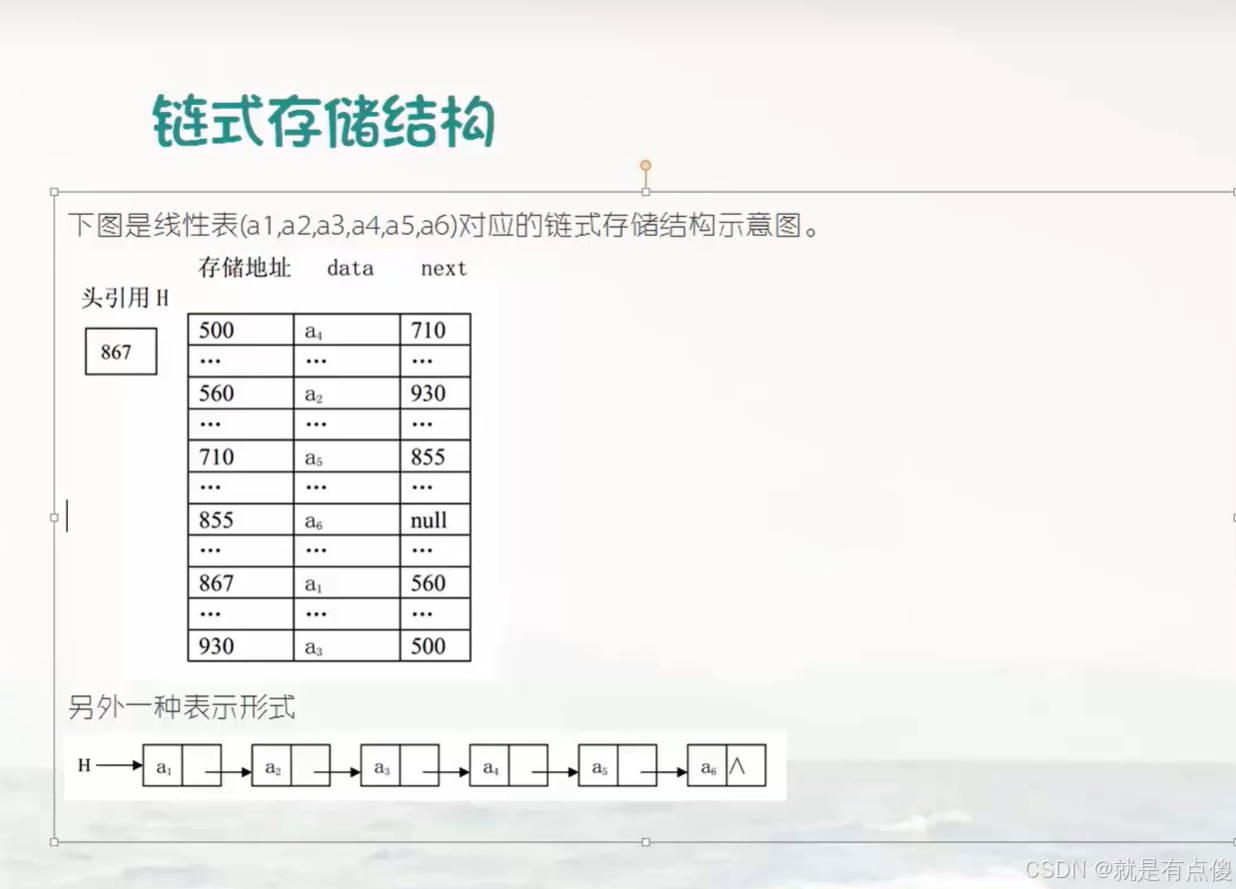
自定义代码实现
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
/// <summary>
/// 单链表的结点
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
internal class Node<T>
{
private T data; //存储数据
private Node<T> next;//指针 用来指向下一个元素
public Node()
{
data = default(T);
next = null;
}
public Node(T value)
{
data = value;
next = null;
}
public Node(T value, Node<T> next)
{
this.data = value;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(Node<T> node)
{
this.next = next;
}
public T Data
{
get { return data; }
set { data = value; }
}
public Node<T> Next
{
get { return next; }
set { next = value; }
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal interface IlistDS<T>
{
int GetLength();
void Clear();
bool IsEmpty();
void Add(T item);
void Insert(int index, T item);
T Delete(int index);
T this[int index] { get; }
T GetEle(int index);
int Locate(T value);
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal class LinkList<T> : IlistDS<T>
{
private Node<T> head;
public LinkList()
{
head = null;
}
public T this[int index]
{
get
{
Node<T> temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index; i++)
{
temp = temp.Next;
}
return temp.Data;
}
}
public void Add(T item)
{
Node<T> newnode = new Node<T>(item);//根据新的数据创建一个新的节点
//如果头节点为空,那么这个新的节点就是头节点
if (head == null)
{
head = newnode;
}
else
{//把新来的节点放在链表的尾部
//要访问到链表的尾节点
Node<T> temp = head;
while (true)
{
if (temp.Next != null)
{
temp = temp.Next;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
temp.Next = newnode;//把新来的节点放在链表的尾部
}
}
public void Clear()
{
head = null;
}
public T Delete(int index)
{
T data = default(T);
if (index == 0) //删除头节点
{
data = head.Data;
head = head.Next;
}
else
{
Node<T> temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index - 1; i++)
{
temp = temp.Next;
}
Node<T> perNode = temp;
Node<T> currentNode = temp.Next;
data = currentNode.Data;
Node<T> nextNode = temp.Next.Next;
perNode.Next = nextNode;
}
return data;
}
public T GetEle(int index)
{
return this[index];
}
public int GetLength()
{
if (head == null)
{
return 0;
}
Node<T> temp = head;
int count = 1;
while (true)
{
if (temp.Next != null)
{
count++;
temp = temp.Next;
}
else { break; }
}
return count;
}
public void Insert(int index, T item)
{
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item);
if (index == 0)//插入头节点
{
newNode.Next = head;
head = newNode;
}
else
{
Node<T> temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i <= index - 1; i++)
{
//让temp向后移动一个位置
temp = temp.Next;
}
Node<T> perNode = temp;
Node<T> currentNode = temp.Next;
perNode.Next = newNode;
newNode.Next = currentNode;
}
}
public bool IsEmpty()
{
return head == null;
}
public int Locate(T value)
{
Node<T> temp = head;
if (temp == null)
{
return - 1;
}
else
{
int index = 0;
while (true)
{
if (temp.Data.Equals(value))
{
return index;
}
else
{
if(temp.Next == null)
{
temp=temp.Next;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 线性表
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LinkList<string> list = new LinkList<string>();
list.Add("123");
list.Add("456");
list.Add("789");
Console.WriteLine(list.GetEle(0));
Console.WriteLine(list[0]);
list.Insert(1,"777");
for (int i = 0; i < list.GetLength(); i++)
{
Console.Write(list[i]+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
list.Delete(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list.GetLength(); i++)
{
Console.Write(list[i] + " ");
}
list.Clear();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine(list.GetLength());
}
}
}
双向链表

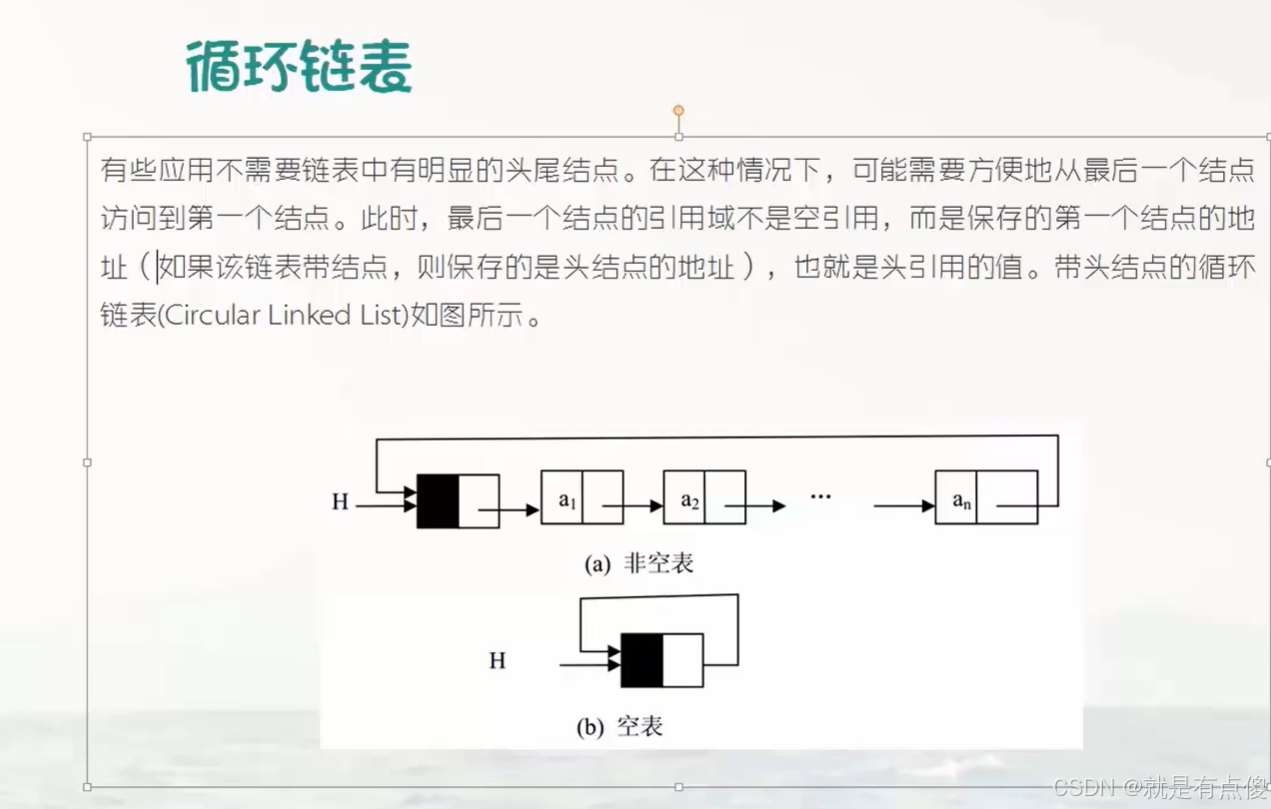
循环链表
课程: 201-线性表介绍List-T_哔哩哔哩_bilibili