1.pyc
使用pyc在线反编译得到python源码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# visit https://tool.lu/pyc/ for more information
# Version: Python 3.8
import random
def encrypt_file(file_path):
random.seed(114514)
# WARNING: Decompyle incomplete
file_path = "./flag"
encrypt_file(file_path)
然后使用AI分析可得到它对应的解密脚本
import random
import os
def decrypt_data(encrypted_data):
random.seed(114514)
decrypted_data = bytearray()
for byte in encrypted_data:
key = random.randint(0, 128)
decrypted_data.append(byte ^ key)
return decrypted_data
def read_file(file_path, mode='rb'):
with open(file_path, mode) as file:
return file.read()
def write_file(file_path, data, mode='wb'):
with open(file_path, mode) as file:
file.write(data)
def decrypt_file(encrypted_file_path, output_file_path):
encrypted_data = read_file(encrypted_file_path)
decrypted_data = decrypt_data(encrypted_data)
write_file(output_file_path, decrypted_data)
if __name__=='__main__':
encrypted_file_path = 'flag.enc'
output_file_path = 'flag_decrypted.txt'
decrypt_file(encrypted_file_path, output_file_path)
#flag{U_R_g00d_at_do1n_pyc}
2.MWatch
提示:数据安全研究员在分析智能设备实时采集的数据时,检测到有一台设备使用者曾出现过某数值过高的情况,请你协助分析该数值最高是多少。flag{md5(数据采集设备名称数据接收设备名称数值)}
多次出现Heart Rate,结合题目描述应该就是找这个,只查看Heart Rate相关
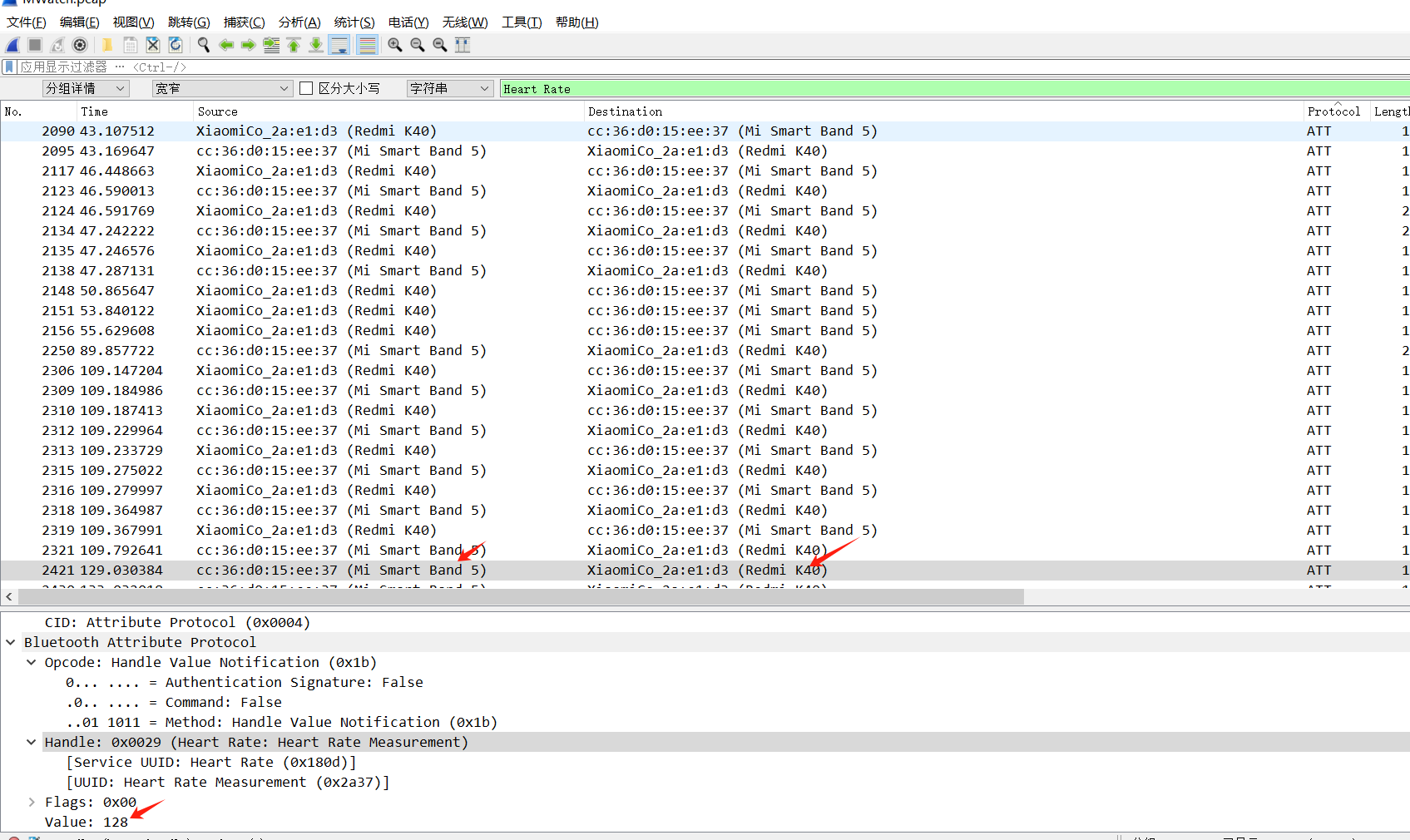
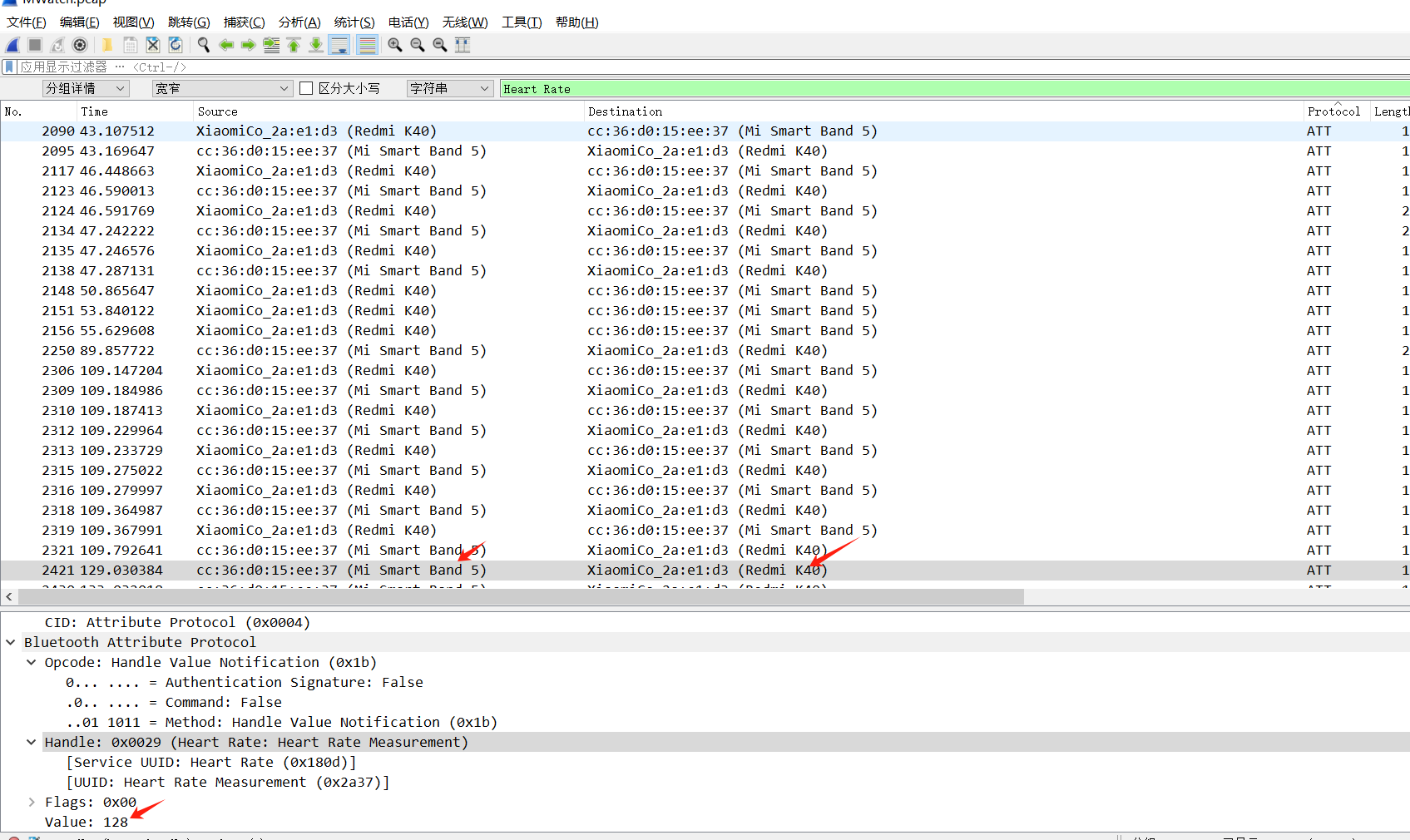
flag{md5(Mi Smart Band 5_Redmi K40_128)}
flag{453d8feda5adb6e7b4d54f71a9ce9e14}
3.BabyRSA
提示:某员工有一个生成素数的初始值,这个算法他跑了很长时间。程序不小心终端,还不小心删了了初始值,还能恢复明文吗
源码:
#task.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from secret import flag,init
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from sage.all import *
from gmpy2 import iroot
m = bytes_to_long(flag.encode())
r = getPrime(128)
p = init
# for i in range(r-1):
# p += next_prime(init)
# assert iroot(p,3)[1] == 1
q = getPrime(12)
# N = p*q*r
N = r**4*q
e = getPrime(17)
c = pow(m,e,N)
print(f"r = {r}")
print(f"e = {e}")
print(f"c = {c}")
# r = 287040188443069778047400125757341514899
# e = 96001
# c = 7385580281056276781497978538020227181009675544528771975750499295104237912389096731847571930273208146186326124578668216163319969575131936068848815308298035625
爆破12比特的素数得到q,然后解密即可
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, inverse
r = 287040188443069778047400125757341514899
e = 96001
c = 7385580281056276781497978538020227181009675544528771975750499295104237912389096731847571930273208146186326124578668216163319969575131936068848815308298035625
# Assuming the modulus for the exponentiation should indeed be r**4
n = r**4
# Compute the modular inverse of e mod φ(n), where φ(n) could be a function of r, like (r-1)*(r**3)
# We need the correct value of φ(n) for the RSA decryption formula m = c^d mod n, where d = e^(-1) mod φ(n)
# Here, assuming φ(n) = r^4 - r^3 as a simplification, you might need to adjust this based on actual RSA setup
phi_n = r**4 - r**3
d = inverse(e, phi_n)
# Decrypt message
m = pow(c, d, n)
# Convert number to bytes
message = long_to_bytes(m)
print(message)
#flag{3b0ce326141ea4f6b5bf2f37efbd1b42}
4.Backpack
背包加密,用BKZ算法可以求解到一组基
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from sage.all import *
from secret import flag
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from math import log2
class Knapsack:
def __init__(self,n,m):
self.M = []
self.n = n
self.m = self.pre(m)
self.A = 0
self.B = 0
def pre(self,m):
tmp_m = bin(m)[2:]
t = []
for tmp in tmp_m:
t.append(int(tmp))
return t
def get_M(self):
seq = [randint(2**34,2**35) for _ in range(self.n)]
self.M = seq
def calc_density(self):
t = log2(max(self.M))
d = self.n/t
print(d)
def enc(self):
self.get_M()
self.calc_density()
C = 0
for t in range(len(self.m)):
C += self.m[t] * self.M[t]
print(f"C = {C}")
print(f"M = {self.M}")
if __name__=="__main__":
m = bytes_to_long(flag.encode())
n = m.bit_length()
k = Knapsack(n,m)
k.enc()
# C = 231282844744
# M = [27811518167, 19889199464, 19122558731, 19966624823, 25670001067, 30690729665, 23936341812, 31011714749, 30524482330, 21737374993, 17530717152, 19140841231, 33846825616, 17334386491, 28867755886, 29354544582, 21758322019, 27261411361, 31465376167, 26145493792, 27075307455, 33514052206, 25397635665, 21970496142, 30801229475, 22405695620, 18486900933, 27071880304, 17919853256, 18072328152, 21108080920]
sagemath中执行:
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
C = 231282844744
M = [27811518167, 19889199464, 19122558731, 19966624823, 25670001067, 30690729665,
23936341812, 31011714749, 30524482330, 21737374993, 17530717152, 19140841231,
33846825616, 17334386491, 28867755886, 29354544582, 21758322019, 27261411361,
31465376167, 26145493792, 27075307455, 33514052206, 25397635665, 21970496142,
30801229475, 22405695620, 18486900933, 27071880304, 17919853256, 18072328152,
21108080920]
L = block_matrix([[1, matrix(ZZ, M).T], [0, C]]).LLL()
for row in L:
if row[-1] == 0 and len(set(row[:-1])) == 1:
# Assuming all elements in the row, except the last one, are the same
ans = [abs(i) for i in row[:-1]]
ans = int(''.join(map(str, ans)), 2)
print(long_to_bytes(ans))
5.定向数据采集
import openpyxl
import requests
import time
from urllib.parse import urlencode
burp0_url = "http://121.40.65.125:23328/submit"
def separate_name_and_id(input_file, output_file):
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(input_file)
ws = wb.active
for row in ws.iter_rows(min_row=1, max_col=1, max_row=ws.max_row, values_only=True):
if row[0]:
name, id_number = row[0].split('----') #提取名字和身份证
print(name, id_number)
age = 2024-int(id_number[6:10])
if(int(id_number[10:12])>4):
age -= 1
sexx=u"男"
burp0_json={"address": "asd", "age": str(age), "ethnicity": "as", "experience": "1", "idcard": id_number, "name": "a", "phonenumber": "12312331233", "position": "as", "sex": sexx}
sexx2 = u"女"
burp0_json1={"address": "asd", "age": str(age), "ethnicity": "as", "experience": "1", "idcard": id_number, "name": "a", "phonenumber": "12312331233", "position": "as", "sex": sexx2}
try:
r0=requests.post(burp0_url, json=burp0_json)
r1=requests.post(burp0_url, json=burp0_json1)
print(r0.request.body)
print(r0.text,r1.text)
#time.sleep(0.5)
except requests.exceptions:
print("err")
#time.sleep(2)
#ws.append([name.strip(), id_number.strip()])
#wb.save(output_file)
wb.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_file = "data1.xlsx"
output_file = "separated_data.xlsx" #没啥用,废弃掉了
separate_name_and_id(input_file, output_file)
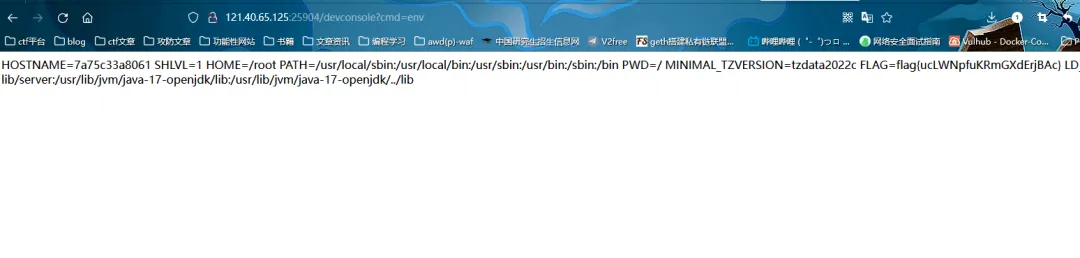
6.weather
审下bundle.js
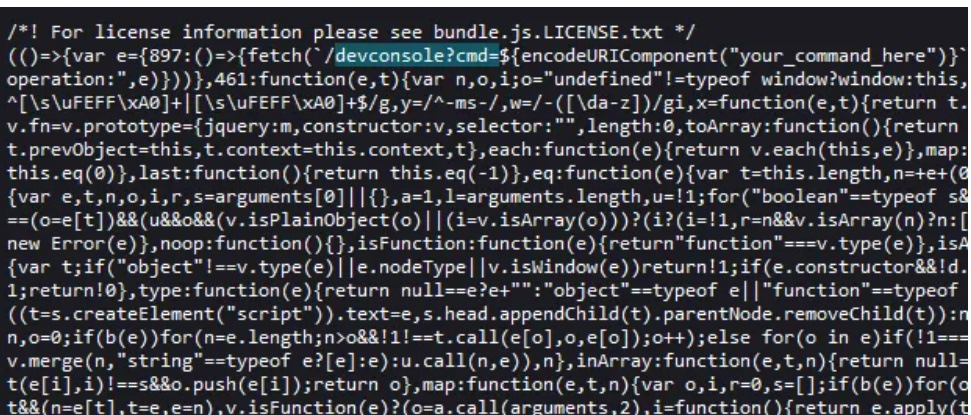
带参数去访问
7.mysql 清理
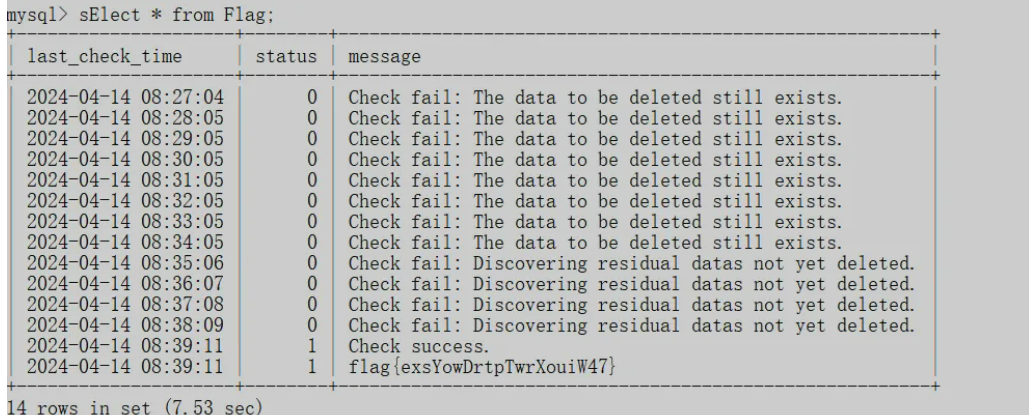
提示:
根据要求,现在要从数据库中彻底删除一些用户的数据,请连接提供的mysql容器,删除ctf所有表中,用户id为5142、2123、1169、8623这四个用户的数据。要求彻底清理这些用户,不能在服务器[中找到残留,同时不能改动其他用户数据。当操作成功后,系统会在ctf.flag表中录入flag数据。(mysql ctf用户密码 pswd@123)
DELETE FROM ShoppingCart WHERE user_id in ("5142","2123","1169","8623");
DELETE FROM TransactionHistory WHERE user_id in ("5142","2123","1169","8623");
DELETE FROM UserLog WHERE user_id in ("5142","2123","1169","8623");
DELETE FROM Wallet WHERE user_id in ("5142","2123","1169","8623");
DELETE FROM User WHERE id in ("5142","2123","1169","8623");
再重建一下表,清掉删除之后的残留数据
alter table User engine = innodb;
alter table UserLog engine = innodb;
alter table TransactionHistory engine = innodb;
alter table ShoppingCart engine = innodb;
alter table Orders engine = innodb;
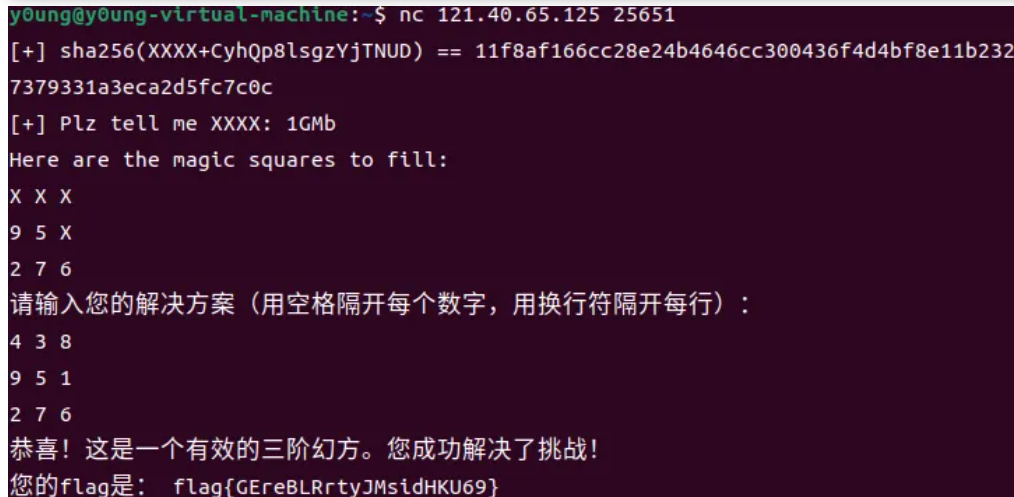
8.幻方
三阶幻方只有八种结果,认准一个多试几次就行
import hashlib
import random
import string
# Define the character set as alphanumeric characters
charset = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
while True:
# Generate a random 4-character string from the charset
rand_str = ''.join(random.choice(charset) for _ in range(4)) + 'CyhQp8lsgzYjTNUD'
# Calculate the SHA-256 hash of the string
hash_output = hashlib.sha256(rand_str.encode()).hexdigest()
# Check if the hash matches the target hash
if hash_output == '11f8af166cc28e24b4646cc300436f4d4bf8e11b2327379331a3eca2d5fc7c0c':
print(rand_str[:4]) # Print the first 4 characters if a match is found
break
'''
[2, 7, 6, 9, 5, 1, 4, 3, 8]
[2, 9, 4, 7, 5, 3, 6, 1, 8]
[4, 3, 8, 9, 5, 1, 2, 7, 6]
[4, 9, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 1, 6]
[6, 1, 8, 7, 5, 3, 2, 9, 4]
[6, 7, 2, 1, 5, 9, 8, 3, 4]
[8, 1, 6, 3, 5, 7, 4, 9, 2]
[8, 3, 4, 1, 5, 9, 6, 7, 2]
4 3 8
9 5 1
2 7 6
'''
9.Prime Conundrum
知道了delta可以对leak的那条式子进行二元copper求解s,t,通过hint和s求解p, 算私钥解密即可
import itertools
from tqdm import tqdm
def small_roots(f, bounds, m=1, d=None):
if not d:
d = f.degree()
R = f.base_ring()
N = R.cardinality()
f /= f.coefficients().pop(0)
f = f.change_ring(ZZ)
G = Sequence([], f.parent())
for i in range(m + 1):
base = N ^ (m - i) * f ^ i
for shifts in itertools.product(range(d), repeat=f.nvariables()):
g = base * prod(map(power, f.variables(), shifts))
G.append(g)
B, monomials = G.coefficient_matrix()
monomials = vector(monomials)
factors = [monomial(*bounds) for monomial in monomials]
for i, factor in enumerate(factors):
B.rescale_col(i, factor)
B = B.dense_matrix().LLL()
B = B.change_ring(QQ)
for i, factor in enumerate(factors):
B.rescale_col(i, 1 / factor)
H = Sequence([], f.parent().change_ring(QQ))
for h in filter(None, B * monomials):
H.append(h)
I = H.ideal()
if I.dimension() == -1:
H.pop()
elif I.dimension() == 0:
roots = []
for root in I.variety(ring=ZZ):
root = tuple(R(root[var]) for var in f.variables())
roots.append(root)
return roots
return []
P = 91307300383014465303389363075431698588933838431961163766796972428733255940234665671679789435258337578396879726483195947952476118985507696067550566875810703327064257916213956673893327976728584687137639337961422903593701591152074826447530099276756806166361533554689114264018344629905535188048343259754284652017
Q = 149089411480331249267443825847904508235946280550542428853480950085018092182435890098430254117786823782088885695848943795846175490059759543848516828825072642481794902650586147465149175976488985613001468444893241645390860978312924241181340390543064512602477917112031391367608345501790785857442379515898677467337
n = 97339579366356507946846401691835843338581994635020856947574389213640653953117584127557153363761256108433474475102197685296591968229050609482457622390855692102761025647645801250282912327521623082583744902369819132264725498938021235699466656447009532567358416017236962637028458839659218745744825556065623673913
N = 72077628115206161977315177371814064093288033362281459918751639032623658967593542855291047617938064177930014574391486973767462937337649946356572406647109942552336519343063401327708412361664750917582404375485334706345485264831286788789648126355202140531434534406410829696252616051882952860015344370516517084357909896281965899571934196572691
leak = 45439323369250400352006541741265096780554398472451037280607564706700682873365442581062404781075514235328183754475227917775810587457541607767765455164339314322631781126065808432845447798024685402323868389611285038950397054020330610558058133599416135943335731904873776868614834960217751934513462319743149481906
c = 31456530156035981140909630437789986968079386074106871160743980387785993275753486380185420818239283975922682050323918081691381897642776414263991442096807392948925867761878299044300335666219533277719472330029607869735373712681522022301659090108633692457216985013550482473362675907949633024047291607542103649091410575340884845190483766424507
hint = 13318665442465244206832303588726230530847297247590371628366697082014350966833522479782161994817212671730145702818662148370306660550486536176566012104254910
z = 740476059013240018009340328107
PR.<x,y>=PolynomialRing(Zmod(n))
f=P*x + Q*y + z -leak
ans=small_roots(f,bounds=(2^70,2^70),m=3,d=3)
ans
s = 30656796668419630391
t = 35875762848049841267
p = hint + s
q = n // p
assert p*q == n
e = 65537
from Crypto.Util.number import *
d = inverse(e,(p-1)*(q-1)*(z-1))
m = pow(c,d,n)
long_to_bytes(int(m))
10.fun
遍历爆破满足条件的x,y然后解密即可
# from z3 import *
A = []
for x in range(101):
for y in range(101):
z = x^y
if (x+y)*z == x**2 + y**2:
if x*y != z:
if x != y:
A.append([x,y,z])
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import random
# 与加密时相同的种子,确保生成相同的密钥
for i in A:
x,y,z = i
random.seed(x+y+z)
key = random.randbytes(16)
# print(key)
# 读取加密的数据
PATH = r"encrypted_flag.bin"
with open(PATH, "rb") as file_in:
nonce = file_in.read(16) # Nonce 的长度为 16 字节
tag = file_in.read(16) # Tag 通常与块大小相同,对于 AES 为 16 字节
ciphertext = file_in.read() # 读取剩余部分作为密文
# 解密过程
# print(nonce)
# print(tag)
# print(ciphertext)
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_EAX,nonce=nonce)
try:
decrypted_text = cipher.decrypt_and_verify(ciphertext, tag)
print("The flag is:", decrypted_text)
except:
pass
11.好大的公钥
boneh and durfee 一把梭
from libnum import *
N = 73662176635930217145588251109582598744318418885493494845859692592990304301546996154904097420724904838772056137908521735803973827790665774255932629529776216900362889972771913683024723128622502292694632281143536586986352764727899291750703185204118126673717387089701233154888606074285445820360105604776003690487
e = 26083019178473123328452230832076345302834454225396475868531519193551971982955975631443131705619185405190763284436613436828597887376946206551305947183212830810924956452635880343496593901027606468731840531964306285933726727512533644720818081124507069662781291949841231431546394148749720394411454774153995026037
c = 46149785989975097887441076951612740430034092652052333486778189200068487460813449057674051203125773261695615434443270333980225346411838188124458064365680435783802887397970067324393852247219619820813993601444322710186223021625645961186730735728928546458428244830359782270698452792224875596683123815246426241726
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = False
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii, ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii, jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
# print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(
bound - BB[ii, ii]):
# print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii - 1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u,x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
Q = PR.quotient(x * y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX * YY + 1
# x-shifts
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x ^ ii * modulus ^ (mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y) ^ kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# x-shifts list of monomials
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-shifts (selected by Herrman and May)
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm / tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y ^ jj * polZ(u, x, y) ^ kk * modulus ^ (mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# y-shifts list of monomials
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm / tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u ^ kk * y ^ jj)
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus ^ mm, nn - 1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0, 0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus ^ mm)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus ^ (mm * nn)
if det >= bound:
# print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
# print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
# print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus ^ mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w * z + 1, w, z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w * z + 1, w, z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU, XX, YY)
# resultant
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
# print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
# print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
# print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
#
return solx, soly
delta = .271 # this means that d < N^delta
m = 8 # size of the lattice (bigger the better/slower)
t = int((1 - 2 * delta) * m) # optimization from Herrmann and May
X = 2 * floor(N ^ delta) # this _might_ be too much
Y = floor(N ^ (1 / 2)) # correct if p, q are ~ same size
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
A = int((N + 1) / 2)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y)
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
d = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
print(d)
m = power_mod(c, d, N)
print(n2s(int(m)))
12.Notebook
复制文本到浏览器检索,发现有200C,所以直接零宽字符,用Cyberchef转换为Escape Unicode,发现大量出现了以下零宽字符
u202C\u200B\u2062\uFEFF最后找到了
https://lazzzaro.github.io/2020/05/24/misc-%E9%9B%B6%E5%AE%BD%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%97%E7%AC%A6%E9%9A%90%E5%86%99/index.html
发现330k有自定义码表的功能
http://330k.github.io/misc_tools/unicode_steganography.html
最后发现MACOSX_里面里面其实hint了330k.github.io。
https://www.mzy0.com/ctftools/zerowidth1/
也可以处理。
选中需要的编码之后即可解析,解析后如下:
K|2+YG3-hfl|&_U8检索一整段之后没有什么信息,放入随波逐流里面发现该编码可以被base92解码解码后可知泄露源。
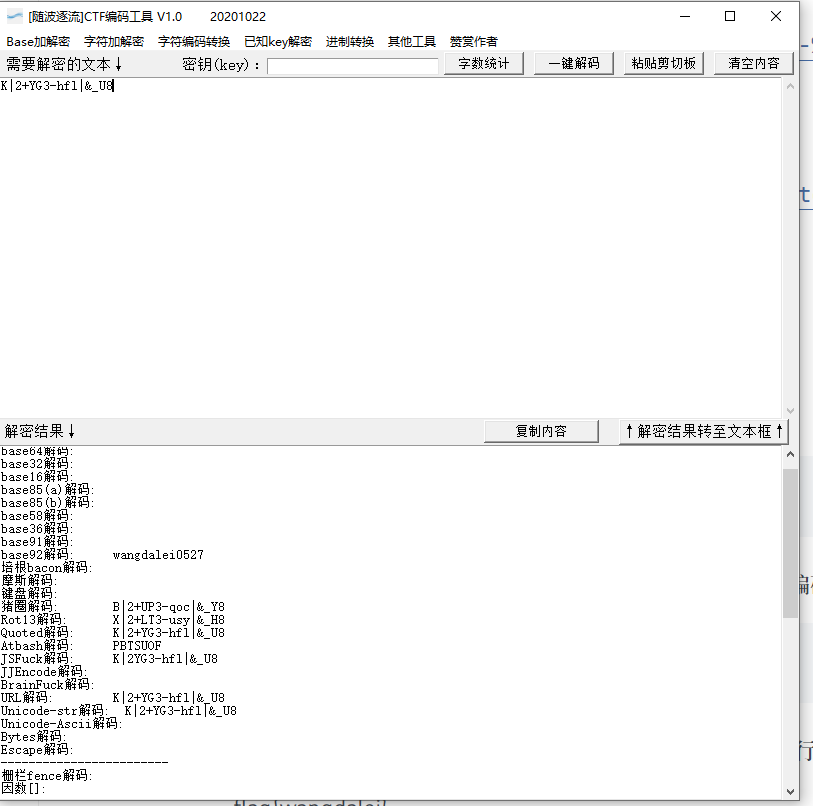
wangdalei0527然后找了半天flag提交格式结果发现只用提交wangdalei就行,0527猜测是手机尾号
flag{wangdalei}
13.UnsetData
发现是一个类似于内存镜像的东西,使用R-studio进行恢复找到了data.jpg,发现左上角有东西,有隐隐约约的字符,使用盲水印发现flag,然后调十几次参数找到相对清晰的图片之后抄10分钟flag即可得
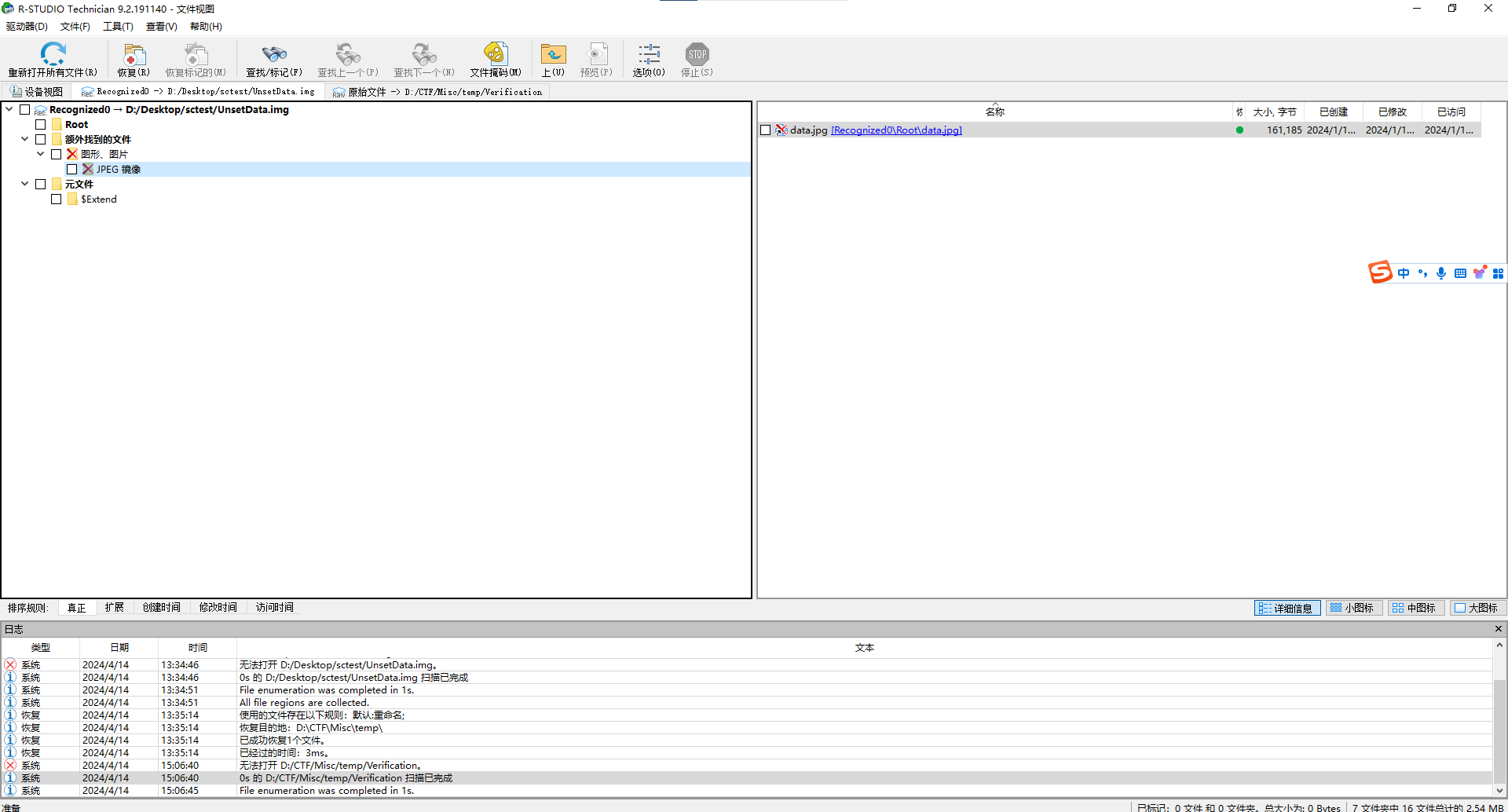
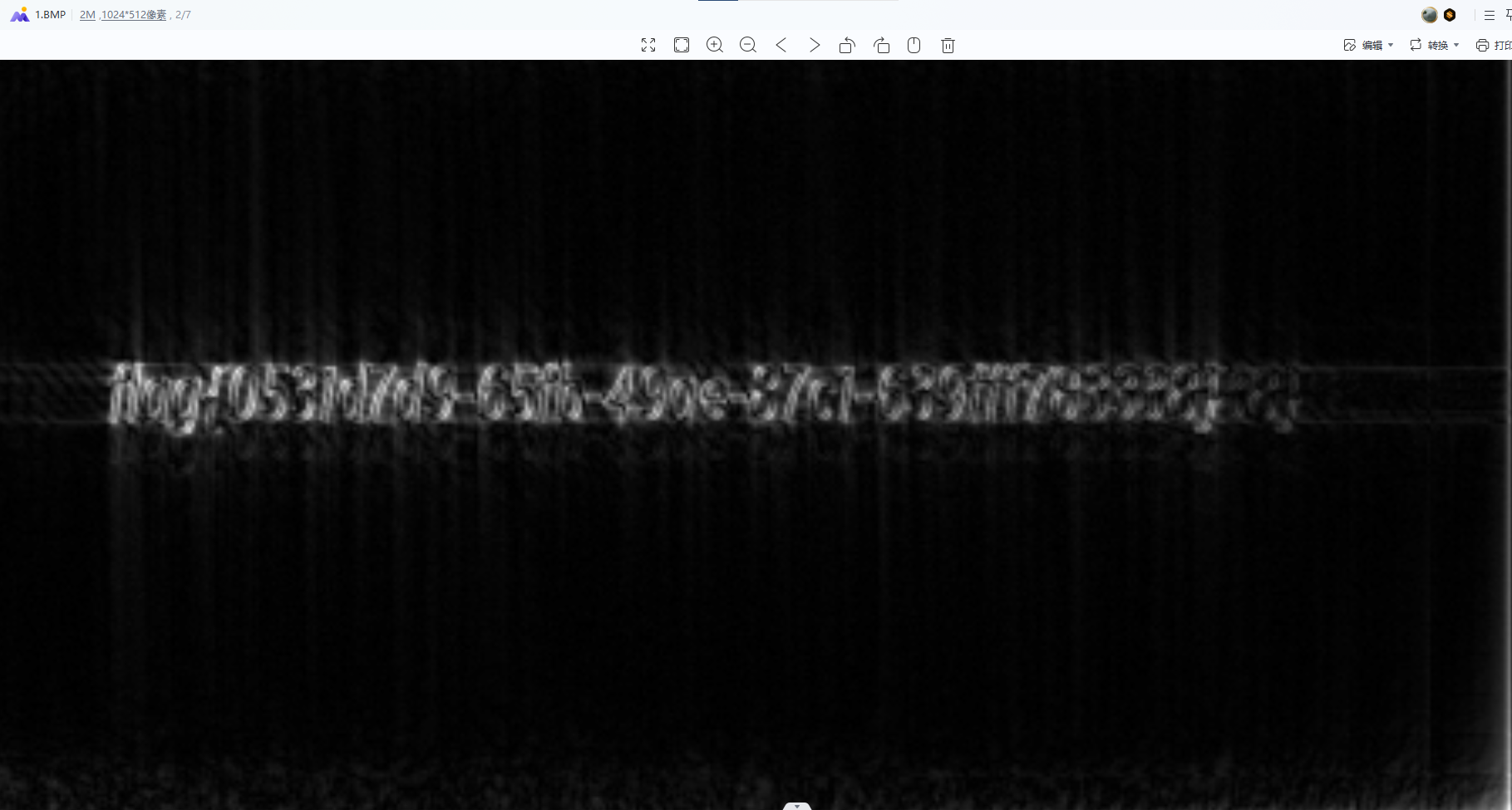
flag{0531d7d9-65fb-49ae-87c1-639fff783338}
14.RWZIP
发现该压缩包数据校验不通过,说明包体被修改过,修改前发现压缩加密格式为ZipCrypto没找到其他信息,使用passware toolkit爆破,可得压缩包密码为114514,再观察下包体发现他被ZipCrypto加密后却不需要输入密码,将加密为从08改为09正常输入密码即可解压解压后发现采用了特殊的字符集,目测是将左右进行翻转替换后可得flag
ʇlɒϱ{85ɘdɒʇ8245754b9ɘd09045087ʇɘ28392}
flag{85ebaf8245754d9eb09045087fe28392}
15.USBHacker
wireshark打开后USBHID长度为16,知道该流量为键盘流量
过滤Source 1.5.1之后,导出json,
import json
datainput = open('USB3.json', "r", encoding="utf-8")
output = open("USB3.txt", "w",encoding="utf-8")
d = json.load(datainput)
for i in d:
print(i["_source"]["layers"]["usbhid.data"])
output.write(i["_source"]["layers"]["usbhid.data"]+'\n')
然后再进行解析
normalKeys = {
"04":"a", "05":"b", "06":"c", "07":"d", "08":"e",
"09":"f", "0a":"g", "0b":"h", "0c":"i", "0d":"j",
"0e":"k", "0f":"l", "10":"m", "11":"n", "12":"o",
"13":"p", "14":"q", "15":"r", "16":"s", "17":"t",
"18":"u", "19":"v", "1a":"w", "1b":"x", "1c":"y",
"1d":"z","1e":"1", "1f":"2", "20":"3", "21":"4",
"22":"5", "23":"6","24":"7","25":"8","26":"9",
"27":"0","28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t",
"2c":"<SPACE>","2d":"-","2e":"=","2f":"[","30":"]","31":"\\",
"32":"<NON>","33":";","34":"'","35":"<GA>","36":",","37":".",
"38":"/","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>","3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>",
"3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>","41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>",
"44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}
shiftKeys = {
"04":"A", "05":"B", "06":"C", "07":"D", "08":"E",
"09":"F", "0a":"G", "0b":"H", "0c":"I", "0d":"J",
"0e":"K", "0f":"L", "10":"M", "11":"N", "12":"O",
"13":"P", "14":"Q", "15":"R", "16":"S", "17":"T",
"18":"U", "19":"V", "1a":"W", "1b":"X", "1c":"Y",
"1d":"Z","1e":"!", "1f":"@", "20":"#", "21":"$",
"22":"%", "23":"^","24":"&","25":"*","26":"(","27":")",
"28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t","2c":"<SPACE>",
"2d":"_","2e":"+","2f":"{","30":"}","31":"|","32":"<NON>","33":"\"",
"34":":","35":"<GA>","36":"<","37":">","38":"?","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>",
"3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>","3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>",
"41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>","44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}
output = []
keys = open('usb2.txt','r')
for line in keys:
try:
if line[0]!='0' or (line[1]!='0' and line[1]!='2') or line[3]!='0' or line[4]!='0' or line[9]!='0' or line[10]!='0' or line[12]!='0' or line[13]!='0' or line[15]!='0' or line[16]!='0' or line[18]!='0' or line[19]!='0' or line[21]!='0' or line[22]!='0' or line[6:8]=="00":
continue
if line[6:8] in normalKeys.keys():
output += [[normalKeys[line[6:8]]],[shiftKeys[line[6:8]]]][line[1]=='2']
else:
output += ['[unknown]']
except:
pass
keys.close()
flag=0
print("".join(output))
for i in range(len(output)):
try:
a=output.index('<DEL>')
del output[a]
del output[a-1]
except:
pass
for i in range(len(output)):
try:
if output[i]=="<CAP>":
flag+=1
output.pop(i)
if flag==2:
flag=0
if flag!=0:
output[i]=output[i].upper()
except:
pass
print ('output :' + "".join(output))
发现是身份证号,缺失校验位,计算得出校验位为3,md5后即为flag


















