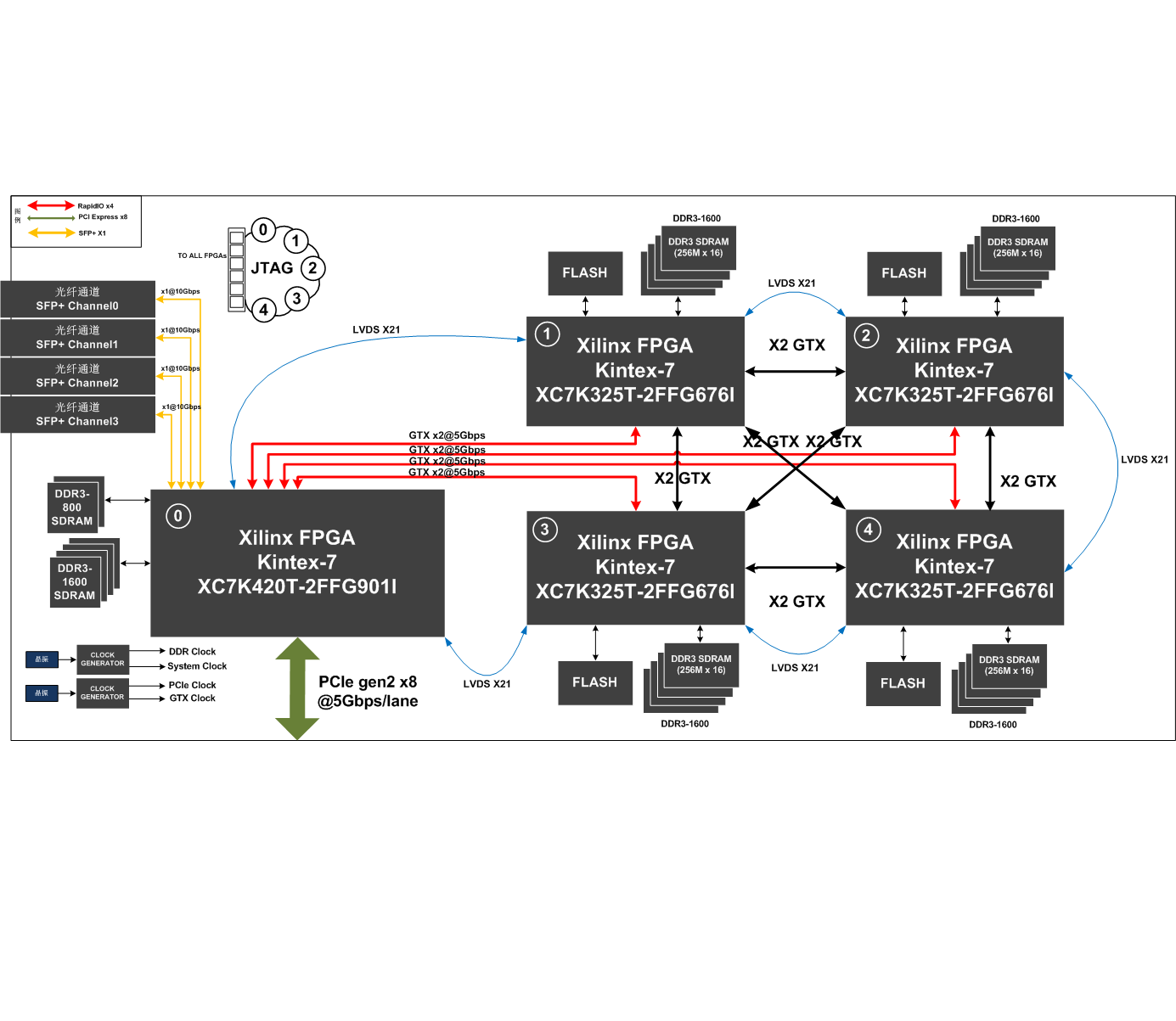
在实际应用场景中,由于训练数据集不足,所以很少有人会从头开始训练整个网络。普遍的做法是,在一个非常大的基础数据集上训练得到一个预训练模型,然后使用该模型来初始化网络的权重参数或作为固定特征提取器应用于特定的任务中。
一些通用的东西,可能会有大量的数据用来训练,但是大多数的行业应用,基本很难找到大量的数据提供给模型训练。如果是之前的分类模型,缺乏足够的数据很难得到一个比较理想的模型。由此,迁移学习产生了,带着强大的光环。她可以应用于这种数据量不足的场合和应用。

通过简单的添加狼和狗的数据集训练以后,可以看到训练后的模型对于狼狗的预测准确率还是不错的。
可以多次运行
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mindspore as ms
def visualize_model(best_ckpt_path, val_ds):
net = resnet50()
# 全连接层输入层的大小
in_channels = net.fc.in_channels
# 输出通道数大小为狼狗分类数2
head = nn.Dense(in_channels, 2)
# 重置全连接层
net.fc = head
# 平均池化层kernel size为7
avg_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7)
# 重置平均池化层
net.avg_pool = avg_pool
# 加载模型参数
param_dict = ms.load_checkpoint(best_ckpt_path)
ms.load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
model = train.Model(net)
# 加载验证集的数据进行验证
data = next(val_ds.create_dict_iterator())
images = data["image"].asnumpy()
labels = data["label"].asnumpy()
class_name = {0: "dogs", 1: "wolves"}
# 预测图像类别
output = model.predict(ms.Tensor(data['image']))
pred = np.argmax(output.asnumpy(), axis=1)
# 显示图像及图像的预测值
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i + 1)
# 若预测正确,显示为蓝色;若预测错误,显示为红色
color = 'blue' if pred[i] == labels[i] else 'red'
plt.title('predict:{}'.format(class_name[pred[i]]), color=color)
picture_show = np.transpose(images[i], (1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
picture_show = std * picture_show + mean
picture_show = np.clip(picture_show, 0, 1)
plt.imshow(picture_show)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
visualize_model(best_ckpt_path, dataset_val)
看每次的结果来看,基本可以准确预测。











![[MySQL][表的约束][二][主键][自增长][唯一键][外键]详细讲解](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1731cb055723451eafd5a076bfbbe001.png)





