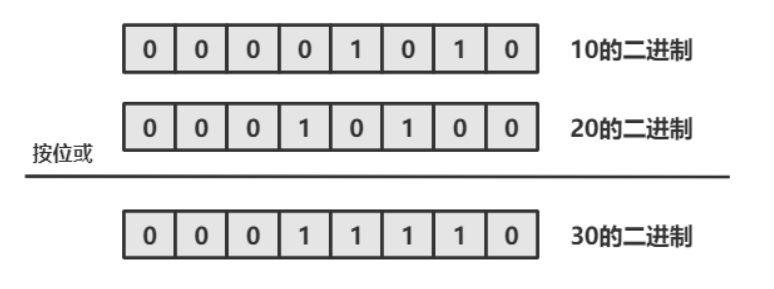
如果是磁盘自检出错,进入救援模式emergency mode,可以参考如下。
chatgpt给出提示:
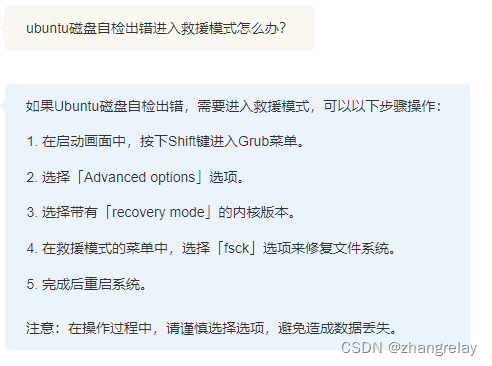
如果Ubuntu磁盘自检出错,需要进入救援模式,可以以下步骤操作:
在启动画面中,按下Shift键进入Grub菜单。
选择「Advanced options」选项。
选择带有「recovery mode」的内核版本。
在救援模式的菜单中,选择「fsck」选项来修复文件系统。
完成后重启系统。
注意:在操作过程中,请谨慎选择选项,避免造成数据丢失。
实验室旧电脑,大概都是10年之前的设备吧。
系统都是ubuntu20.04、22.04,预装的ROS1、ROS2,批量维护升级到最新版本后,遇到如下现象:
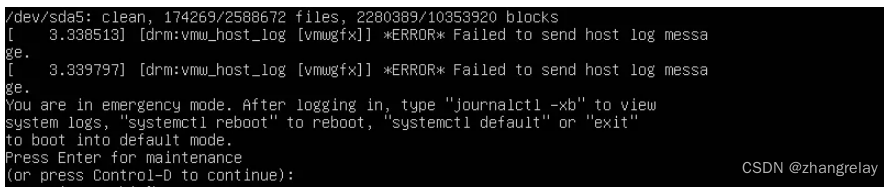
如果原来系统是中文,可能会有乱码。
如果root没有密码,直接回车即可
如果root有密码,输入合适密码。
猜测问题可能由于磁盘故障导致。
使用ros2go启动恢复模式手工修复。
过程比较简单,关键指令fsck。
哪个盘有问题就修复哪个磁盘。
记录全部命令:
1 reboot
2 exit
3 systemctl default
4 exit
5 journalctl -xb
6 exit
7 systemctl reboot
8 exit
9 A\[\[AB[B[
10 ls /dev/
11 journalctl -xb
12 vim /etc/fstab
13 vi /etc/fstab
14 umount /dev/sda5
15 umount /dev/sda6
16 fsck -y /dev/sda6
17 fsck -y /dev/sda5
18 exit
19 systemctl reboot
20 journalctl -xb
21 exit
22 mount -o remount,rw /
23 df -h
24 systemctl reboot
25 df -h
26 mount -o remount,rw /
27 passwd root
28 systemctl reboot
29 ros
30 df -h
31 fsck -y /dev/sda5
32 umount /dev/sda5关于fsck的使用参考如下:
fsck from util-linux 2.34
fsck.ext4: invalid option -- 'h'
Usage: fsck.ext4 [-panyrcdfktvDFV] [-b superblock] [-B blocksize]
[-l|-L bad_blocks_file] [-C fd] [-j external_journal]
[-E extended-options] [-z undo_file] device
Emergency help:
-p Automatic repair (no questions)
-n Make no changes to the filesystem
-y Assume "yes" to all questions
-c Check for bad blocks and add them to the badblock list
-f Force checking even if filesystem is marked clean
-v Be verbose
-b superblock Use alternative superblock
-B blocksize Force blocksize when looking for superblock
-j external_journal Set location of the external journal
-l bad_blocks_file Add to badblocks list
-L bad_blocks_file Set badblocks list
-z undo_file Create an undo file
修复完成就可以进入系统了。
fsck -p /dev/sdb1
fsck from util-linux 2.34
/dev/sdb1: clean, 388486/4071424 files, 3681422/16275712 blocks
没有问题就是如上。
有问题会刷屏问题,并修复。
Intel® Core™ i3 CPU M 380 @ 2.53GHz × 4
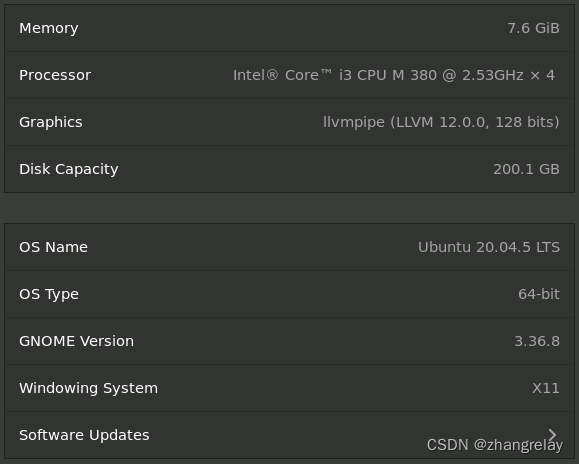
大概这个批次电脑都是2010-2011左右的。
fsck是一个文件系统检查工具,可以扫描和修复磁盘错误。使用方法如下:
进入终端(terminal)。
使用root权限运行fsck。
在终端中输入以下命令:
fsck /dev/sda1其中/dev/sda1是要检查的磁盘分区,替换为实际的磁盘分区名称。
NAME
fsck - check and repair a Linux filesystem
SYNOPSIS
fsck [-lsAVRTMNP] [-r [fd]] [-C [fd]] [-tfstype] [filesystem...] [--] [fs-specific-options]
DESCRIPTION
fsck is used to check and optionally repair one or more Linux filesystems. filesys can be
a device name (e.g. /dev/hdc1, /dev/sdb2), a mount point (e.g. /, /usr, /home), or an
ext2 label or UUID specifier (e.g. UUID=8868abf6-88c5-4a83-98b8-bfc24057f7bd or
LABEL=root). Normally, the fsck program will try to handle filesystems on different
physical disk drives in parallel to reduce the total amount of time needed to check all of
them.
If no filesystems are specified on the command line, and the -A option is not specified,
fsck will default to checking filesystems in /etc/fstab serially. This is equivalent to
the -As options.
The exit code returned by fsck is the sum of the following conditions:
0 No errors
1 Filesystem errors corrected
2 System should be rebooted
4 Filesystem errors left uncorrected
8 Operational error
16 Usage or syntax error
32 Checking canceled by user request
128 Shared-library error
The exit code returned when multiple filesystems are checked is the bit-wise OR of the
exit codes for each filesystem that is checked.
In actuality, fsck is simply a front-end for the various filesystem checkers (fsck.fstype)
available under Linux. The filesystem-specific checker is searched for in the PATH
environment variable. If the PATH is undefined then fallback to "/sbin".
Please see the filesystem-specific checker manual pages for further details.
OPTIONS
-l Create an exclusive flock(2) lock file (/run/fsck/<diskname>.lock) for whole-disk
device. This option can be used with one device only (this means that -A and -l
are mutually exclusive). This option is recommended when more fsck(8) instances
are executed in the same time. The option is ignored when used for multiple
devices or for non-rotating disks. fsck does not lock underlying devices when
executed to check stacked devices (e.g. MD or DM) – this feature is not implemented
yet.
-r [fd]
Report certain statistics for each fsck when it completes. These statistics
include the exit status, the maximum run set size (in kilobytes), the elapsed all-
clock time and the user and system CPU time used by the fsck run. For example:
/dev/sda1: status 0, rss 92828, real 4.002804, user 2.677592, sys 0.86186
GUI front-ends may specify a file descriptor fd, in which case the progress bar
information will be sent to that file descriptor in a machine parseable format.
For example:
/dev/sda1 0 92828 4.002804 2.677592 0.86186
-s Serialize fsck operations. This is a good idea if you are checking multiple
filesystems and the checkers are in an interactive mode. (Note: e2fsck(8) runs in
an interactive mode by default. To make e2fsck(8) run in a non-interactive mode,
you must either specify the -p or -a option, if you wish for errors to be corrected
automatically, or the -n option if you do not.)
-tfslist
Specifies the type(s) of filesystem to be checked. When the -A flag is specified,
only filesystems that match fslist are checked. The fslist parameter is a comma-
separated list of filesystems and options specifiers. All of the filesystems in
this comma-separated list may be prefixed by a negation operator 'no' or '!', which
requests that only those filesystems not listed in fslist will be checked. If none
of the filesystems in fslist is prefixed by a negation operator, then only those
listed filesystems will be checked.
Options specifiers may be included in the comma-separated fslist. They must have
the format opts=fs-option. If an options specifier is present, then only
filesystems which contain fs-option in their mount options field of /etc/fstab will
be checked. If the options specifier is prefixed by a negation operator, then only
those filesystems that do not have fs-option in their mount options field of
/etc/fstab will be checked.
For example, if opts=ro appears in fslist, then only filesystems listed in
/etc/fstab with the ro option will be checked.
For compatibility with Mandrake distributions whose boot scripts depend upon an
unauthorized UI change to the fsck program, if a filesystem type of loop is found
in fslist, it is treated as if opts=loop were specified as an argument to the -t
option.
Normally, the filesystem type is deduced by searching for filesys in the /etc/fstab
file and using the corresponding entry. If the type can not be deduced, and there
is only a single filesystem given as an argument to the -t option, fsck will use
the specified filesystem type. If this type is not available, then the default
filesystem type (currently ext2) is used.
-A Walk through the /etc/fstab file and try to check all filesystems in one run. This
option is typically used from the /etc/rc system initialization file, instead of
multiple commands for checking a single filesystem.
The root filesystem will be checked first unless the -P option is specified (see
below). After that, filesystems will be checked in the order specified by the
fs_passno (the sixth) field in the /etc/fstab file. Filesystems with a fs_passno
value of 0 are skipped and are not checked at all. Filesystems with a fs_passno
value of greater than zero will be checked in order, with filesystems with the
lowest fs_passno number being checked first. If there are multiple filesystems
with the same pass number, fsck will attempt to check them in parallel, although it
will avoid running multiple filesystem checks on the same physical disk.
fsck does not check stacked devices (RAIDs, dm-crypt, ...) in parallel with any
other device. See below for FSCK_FORCE_ALL_PARALLEL setting. The /sys filesystem
is used to detemine dependencies between devices.
Hence, a very common configuration in /etc/fstab files is to set the root
filesystem to have a fs_passno value of 1 and to set all other filesystems to have
a fs_passno value of 2. This will allow fsck to automatically run filesystem
checkers in parallel if it is advantageous to do so. System administrators might
choose not to use this configuration if they need to avoid multiple filesystem
checks running in parallel for some reason – for example, if the machine in
question is short on memory so that excessive paging is a concern.
fsck normally does not check whether the device actually exists before calling a
filesystem specific checker. Therefore non-existing devices may cause the system
to enter filesystem repair mode during boot if the filesystem specific checker
returns a fatal error. The /etc/fstab mount option nofail may be used to have fsck
skip non-existing devices. fsck also skips non-existing devices that have the
special filesystem type auto.
-C [fd]
Display completion/progress bars for those filesystem checkers (currently only for
ext[234]) which support them. fsck will manage the filesystem checkers so that
only one of them will display a progress bar at a time. GUI front-ends may specify
a file descriptor fd, in which case the progress bar information will be sent to
that file descriptor.
-M Do not check mounted filesystems and return an exit code of 0 for mounted
filesystems.
-N Don't execute, just show what would be done.
-P When the -A flag is set, check the root filesystem in parallel with the other
filesystems. This is not the safest thing in the world to do, since if the root
filesystem is in doubt things like the e2fsck(8) executable might be corrupted!
This option is mainly provided for those sysadmins who don't want to repartition
the root filesystem to be small and compact (which is really the right solution).
-R When checking all filesystems with the -A flag, skip the root filesystem. (This is
useful in case the root filesystem has already been mounted read-write.)
-T Don't show the title on startup.
-V Produce verbose output, including all filesystem-specific commands that are
executed.
fs-specific-options
Options which are not understood by fsck are passed to the filesystem-specific
checker. These options must not take arguments, as there is no way for fsck to be
able to properly guess which options take arguments and which don't.
Options and arguments which follow the -- are treated as filesystem-specific
options to be passed to the filesystem-specific checker.
Please note that fsck is not designed to pass arbitrarily complicated options to
filesystem-specific checkers. If you're doing something complicated, please just
execute the filesystem-specific checker directly. If you pass fsck some horribly
complicated options and arguments, and it doesn't do what you expect, don'tbotherreportingitasabug. You're almost certainly doing something that you shouldn't
be doing with fsck.
Options to different filesystem-specific fsck's are not standardized. If in doubt, please
consult the man pages of the filesystem-specific checker. Although not guaranteed, the
following options are supported by most filesystem checkers:
-a Automatically repair the filesystem without any questions (use this option with
caution). Note that e2fsck(8) supports -a for backward compatibility only. This
option is mapped to e2fsck's -p option which is safe to use, unlike the -a option
that some filesystem checkers support.
-n For some filesystem-specific checkers, the -n option will cause the fs-specific
fsck to avoid attempting to repair any problems, but simply report such problems to
stdout. This is however not true for all filesystem-specific checkers. In
particular, fsck.reiserfs(8) will not report any corruption if given this option.
fsck.minix(8) does not support the -n option at all.
-r Interactively repair the filesystem (ask for confirmations). Note: It is generally
a bad idea to use this option if multiple fsck's are being run in parallel. Also
note that this is e2fsck's default behavior; it supports this option for backward
compatibility reasons only.
-y For some filesystem-specific checkers, the -y option will cause the fs-specific
fsck to always attempt to fix any detected filesystem corruption automatically.
Sometimes an expert may be able to do better driving the fsck manually. Note that
not all filesystem-specific checkers implement this option. In particular
fsck.minix(8) and fsck.cramfs(8) do not support the -y option as of this writing.
FILES
/etc/fstab.
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
The fsck program's behavior is affected by the following environment variables:
FSCK_FORCE_ALL_PARALLEL
If this environment variable is set, fsck will attempt to check all of the
specified filesystems in parallel, regardless of whether the filesystems appear to
be on the same device. (This is useful for RAID systems or high-end storage
systems such as those sold by companies such as IBM or EMC.) Note that the
fs_passno value is still used.
FSCK_MAX_INST
This environment variable will limit the maximum number of filesystem checkers that
can be running at one time. This allows configurations which have a large number
of disks to avoid fsck starting too many filesystem checkers at once, which might
overload CPU and memory resources available on the system. If this value is zero,
then an unlimited number of processes can be spawned. This is currently the
default, but future versions of fsck may attempt to automatically determine how
many filesystem checks can be run based on gathering accounting data from the
operating system.
PATH The PATH environment variable is used to find filesystem checkers.
FSTAB_FILE
This environment variable allows the system administrator to override the standard
location of the /etc/fstab file. It is also useful for developers who are testing
fsck.
LIBBLKID_DEBUG=all
enables libblkid debug output.
LIBMOUNT_DEBUG=all
enables libmount debug output.

![[Spring Boot]11 使用@Cacheable注解实现Redis缓存](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/64f490b72c7e4abbb6e5cf09fb177c05.png)