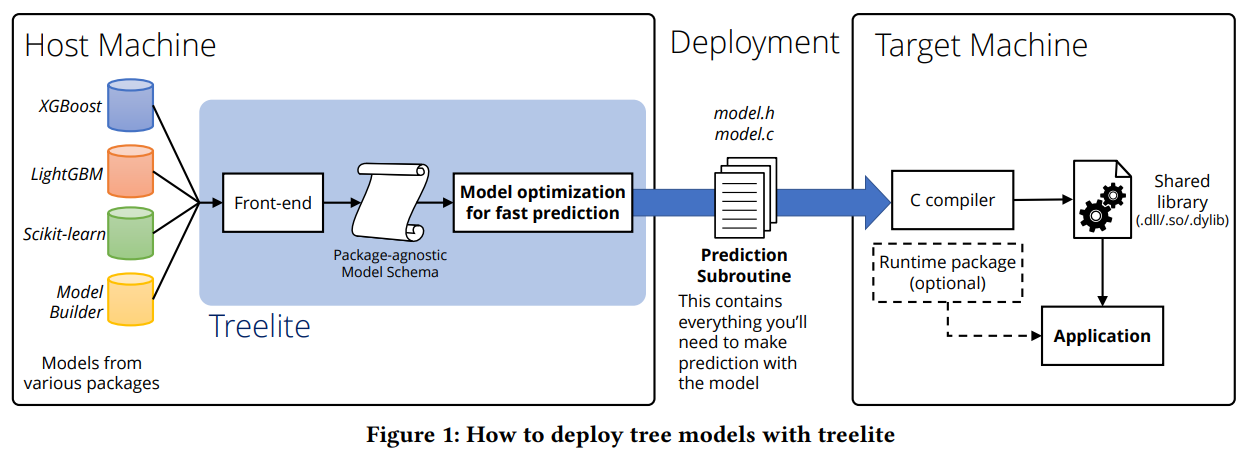
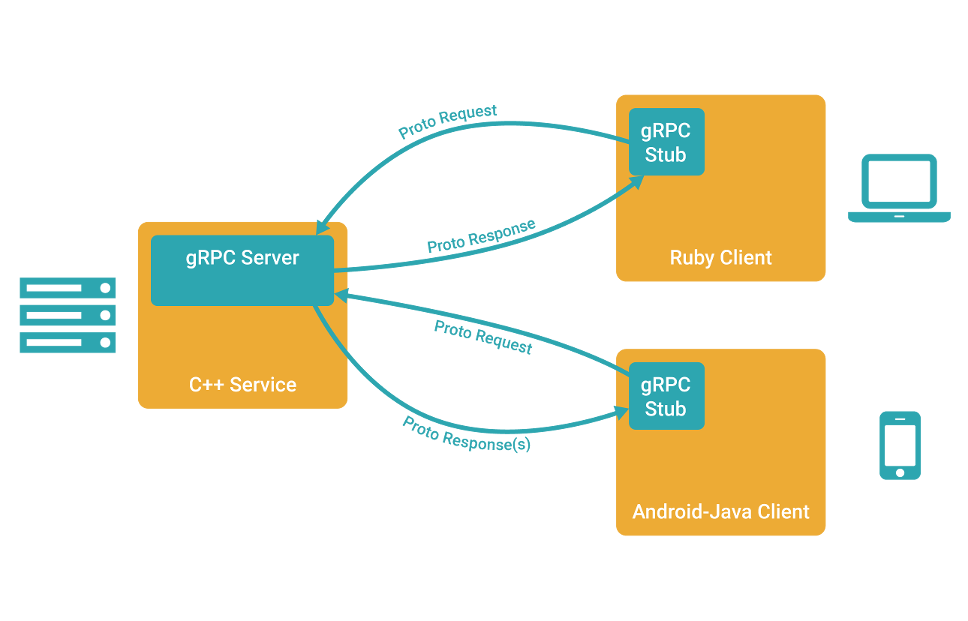
1.什么是GRPC?
gRPC 是一个高性能、开源、通用的RPC框架,由Google推出,基于HTTP2协议标准设计开发,默认采用Protocol Buffers数据序列化协议,支持多种开发语言。gRPC提供了一种简单的方法来精确的定义服务,并且为客户端和服务端自动生成可靠的功能库。 在gRPC客户端可以直接调用不同服务器上的远程程序,使用姿势看起来就像调用本地程序一样,很容易去构建分布式应用和服务。和很多RPC系统一样,服务端负责实现定义好的接口并处理客户端的请求,客户端根据接口描述直接调用需要的服务。客户端和服务端可以分别使用gRPC支持的不同语言实现。
主要特性
- 强大的IDLgRPC使用ProtoBuf来定义服务,ProtoBuf是由Google开发的一种数据序列化协议(类似于XML、JSON、hessian)。ProtoBuf能够将数据进行序列化,并广泛应用在数据存储、通信协议等方面。
- 多语言支持gRPC支持多种语言,并能够基于语言自动生成客户端和服务端功能库。目前已提供了C版本grpc、Java版本grpc-java 和 Go版本grpc-go,其它语言的版本正在积极开发中,其中,grpc支持C、C++、Node.js、Python、Ruby、Objective-C、PHP和C#等语言,grpc-java已经支持Android开发。
- HTTP2gRPC基于HTTP2标准设计,所以相对于其他RPC框架,gRPC带来了更多强大功能,如双向流、头部压缩、多复用请求等。这些功能给移动设备带来重大益处,如节省带宽、降低TCP链接次数、节省CPU使用和延长电池寿命等。同时,gRPC还能够提高了云端服务和Web应用的性能。gRPC既能够在客户端应用,也能够在服务器端应用,从而以透明的方式实现客户端和服务器端的通信和简化通信系统的构建。
2.代码工程
我们建议将您的项目分为2至3个不同的模块。
- grpc-api 项目 包含原始 protobuf 文件并生成 java model 和 service 类。 你可能会在不同的项目中会共享这个部分。
- grpc-Server 项目 包含项目的业务实现,并使用上面的 Interface 项目作为依赖项。
- grpc-Client 项目(可选,可能很多) 任何使用预生成的 stub 来访问服务器的客户端项目。
实验目的
定义了一个Hello Service,客户端发送包含字符串名字的请求,服务端返回Hello消息。
grpc-api
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>grpc</artifactId>
<groupId>com.et</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>grpc-api</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<protobuf.version>3.23.4</protobuf.version>
<protobuf-plugin.version>0.6.1</protobuf-plugin.version>
<grpc.version>1.58.0</grpc.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-stub</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-protobuf</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<!-- Java 9+ compatibility - Do NOT update to 2.0.0 -->
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5</version>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>kr.motd.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>os-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.xolstice.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${protobuf-plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<protocArtifact>com.google.protobuf:protoc:${protobuf.version}:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</protocArtifact>
<pluginId>grpc-java</pluginId>
<pluginArtifact>io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:${grpc.version}:exe:${os.detected.classifier}</pluginArtifact>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>compile-custom</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>proto
将您的 protobuf 定义/.proto文件放入src/main/proto。 有关编写 protobuf 文件的信息,请参阅官方的 protobuf 文档。 您的 .proto 文件跟如下的示例类似:
syntax = "proto3";
package net.devh.boot.grpc.example;
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib";
option java_outer_classname = "HelloWorldProto";
// The greeting service definition.
service MyService {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {
}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}生成文件,源码在target/generated-sources/protobuf
mvn protobuf:compile mvn protobuf:compile-custom
最后打包给server和client引用
grpc-server
protoc-gen-grpc-java 插件为你的每个 grpc 服务生成一个类。 例如:MyServiceGrpc 的 MyService 是 proto 文件中的 grpc 服务名称。 这个类 包含您需要扩展的客户端 stub 和服务端的 ImplicBase。 在这之后,你还有四个步骤:
- 请确保您的
MyServiceImp实现了MyServiceGrpc.MyServiceImpBase - 将
@GrpcService注解添加到您的MyServiceImp类上 - 请确保
MyServiceImplic已添加到您的应用程序上下文中。- 通过在您的
@Configuration类中创建@Bean - 或者将其放置在 spring 的自动检测到路径中(例如在您
Main类的相同或子包中)
- 通过在您的
- 实现 grpc 服务方法。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>grpc</artifactId>
<groupId>com.et</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>grpc-server</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.devh</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-server-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.et</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>service
/*
* Copyright (c) 2016-2023 The gRPC-Spring Authors
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.et.grpc.server;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.HelloReply;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.HelloRequest;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.MyServiceGrpc;
import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver;
import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.service.GrpcService;
/**
* @author Michael (yidongnan@gmail.com)
* @since 2016/11/8
*/
@GrpcService
public class GrpcServerService extends MyServiceGrpc.MyServiceImplBase {
@Override
public void sayHello(HelloRequest req, StreamObserver<HelloReply> responseObserver) {
HelloReply reply = HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("Hello ==> " + req.getName()).build();
responseObserver.onNext(reply);
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
}application.yaml
spring:
application:
name: local-grpc-server
grpc:
server:
port: 9898grpc-client
以下列表包含您可能在客户端使用到的的所有功能。 如果您不想使用任何高级功能,那么前两个元素可能都是您需要使用的。
- @GrpcClient: 在需要注入的客户端的字段或者 setter 方法上这个注解。 支持
Channel和各种类型的Stub。 请不要将@GrpcClient与@Autowireed或@Inject一起使用。 目前,它不支持构造函数和@Bean方法参数。 这种情况请查看后面@GrpcClientBean的使用文档。 注意: 同一应用程序提供的服务只能在 ` ApplicationStartedEvent之后访问/调用。 连接到外部服务的 Stubs 可以提前使用;从@PostConstruct/初始化Bean#afterPropertiesSet()` 开始。 - @GrpcClientBean: 注解会把使用
@GrpcClient注解的类型注册到 Spring Context 中,方便@Autowired和@Qualifier的使用。 这个注解可以重复添加到您的@Configuration类中。 - Channel: Channel 是单个地址的连接池。 目标服务器可能是多个 gRPC 服务。 该地址将使用
NameResolver做解析,最终它可能会指向一批固定数量或动态数量的服务端。 - ManagedChannel: ManagedChannel 是 Channel 的一种特殊变体,因为它允许对连接池进行管理操作,例如将其关闭。
- NameResolver、 NameResolver.Factory: 一个用于将地址解析为
SocketAddress列表的类 ,当与先前列出的服务端连表连接失败或通道空闲时,地址将会重新做解析。 参阅 Configuration -> Choosing the Target。 - ClientInterceptor: 在每个
Channel处理之前拦截它们。 可以用于日志、监测、元数据处理和请求/响应的重写。 grpc-spring-boot-starter 将自动接收所有带有 @GrpcGlobalClientInterceptor 注解以及手动注册在GlobalClientInterceptorRegistry 上的客户拦截器。 参阅 Configuration -> ClientInterceptor。 - CallCredentials: 管理身份验证的组件。 它可以用于存储凭据和会话令牌。 它还可以用来身份验证,并且使用返回的令牌(例如 OAuth) 来授权实际请求。 除此之外,如果令牌过期并且重新发送请求,它可以续签令牌。 如果您的应用程序上下文中只存在一个
CallCredentialsbean,那么 spring 将会自动将其附加到Stub( 非Channel)。 CallCredentialsHelper工具类可以帮助您创建常用的CallCredentials类型和相关的StubTransformer。 - StubFactory: 一个用于从
Channel创建特定Stub的工厂。 可以注册多个StubFactory,以支持不同类型的 stub。 参阅 Configuration -> StubFactory。 - StubTransformer: 所有客户端的
Stub的注入之前应用的转换器。 参阅 Configuration -> StubTransformer。
pom.xml
/*
* Copyright (c) 2016-2023 The gRPC-Spring Authors
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.et.grpc.client;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.HelloReply;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.HelloRequest;
import com.et.grpc.api.protobuf.lib.MyServiceGrpc;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import io.grpc.StatusRuntimeException;
import net.devh.boot.grpc.client.inject.GrpcClient;
/**
* @author Michael (yidongnan@gmail.com)
* @since 2016/11/8
*/
@Service
public class GrpcClientService {
@GrpcClient("local-grpc-server")
// @GrpcClient("cloud-grpc-server")
private MyServiceGrpc.MyServiceBlockingStub myServiceStub;
public String sendMessage(final String name) {
try {
final HelloReply response = this.myServiceStub.sayHello(HelloRequest.newBuilder().setName(name).build());
return response.getMessage();
} catch (final StatusRuntimeException e) {
return "FAILED with " + e.getStatus().getCode().name();
}
}
}controller
/*
* Copyright (c) 2016-2023 The gRPC-Spring Authors
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.et.grpc.client;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author Michael (yidongnan@gmail.com)
* @since 2016/12/4
*/
@RestController
public class GrpcClientController {
@Autowired
private GrpcClientService grpcClientService;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String printMessage(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "Michael") String name) {
return grpcClientService.sendMessage(name);
}
}application.yaml
server:
port: 8088
spring:
application:
name: local-grpc-client
grpc:
client:
local-grpc-server:
address: 'static://127.0.0.1:9898'
enableKeepAlive: true
keepAliveWithoutCalls: true
negotiationType: plaintext3.测试
- 启动服务端
- 启动客户端
- 调用服务http://127.0.0.1:8088/
测试服务
您可以通过运行 gRPCurl 命令来测试您的应用程序是否正常运行:
grpcurl --plaintext localhost:9898 list
grpcurl --plaintext localhost:9898 list net.devh.boot.grpc.example.MyService
# Linux (Static content)
grpcurl --plaintext -d '{"name": "test"}' localhost:9898 net.devh.boot.grpc.example.MyService/sayHello
# Windows or Linux (dynamic content)
grpcurl --plaintext -d "{\"name\": \"test\"}" localhost:9898 net.devh.boot.grpc.example.MyService/sayHello
gRPCurl 的示例命令输出以及其他信息请参考此 文档 。
4.引用
- 入门指南 | grpc-spring-boot-starter