1. 执行命令的入口方法
redis也是通过hook执行命令,initHooks时,会将redis的hook放在第一个
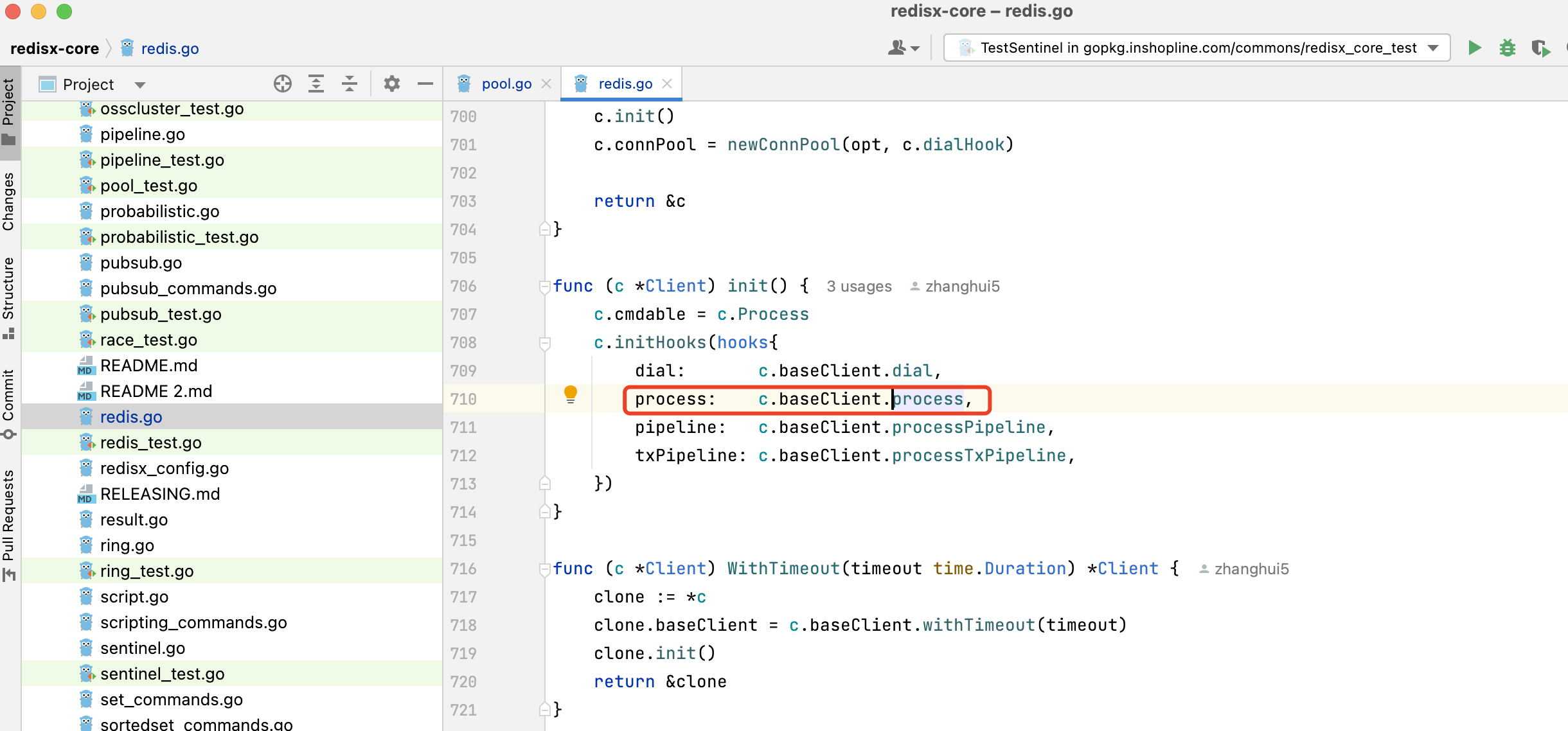
通过hook调用到process方法,process方法内部再调用_process
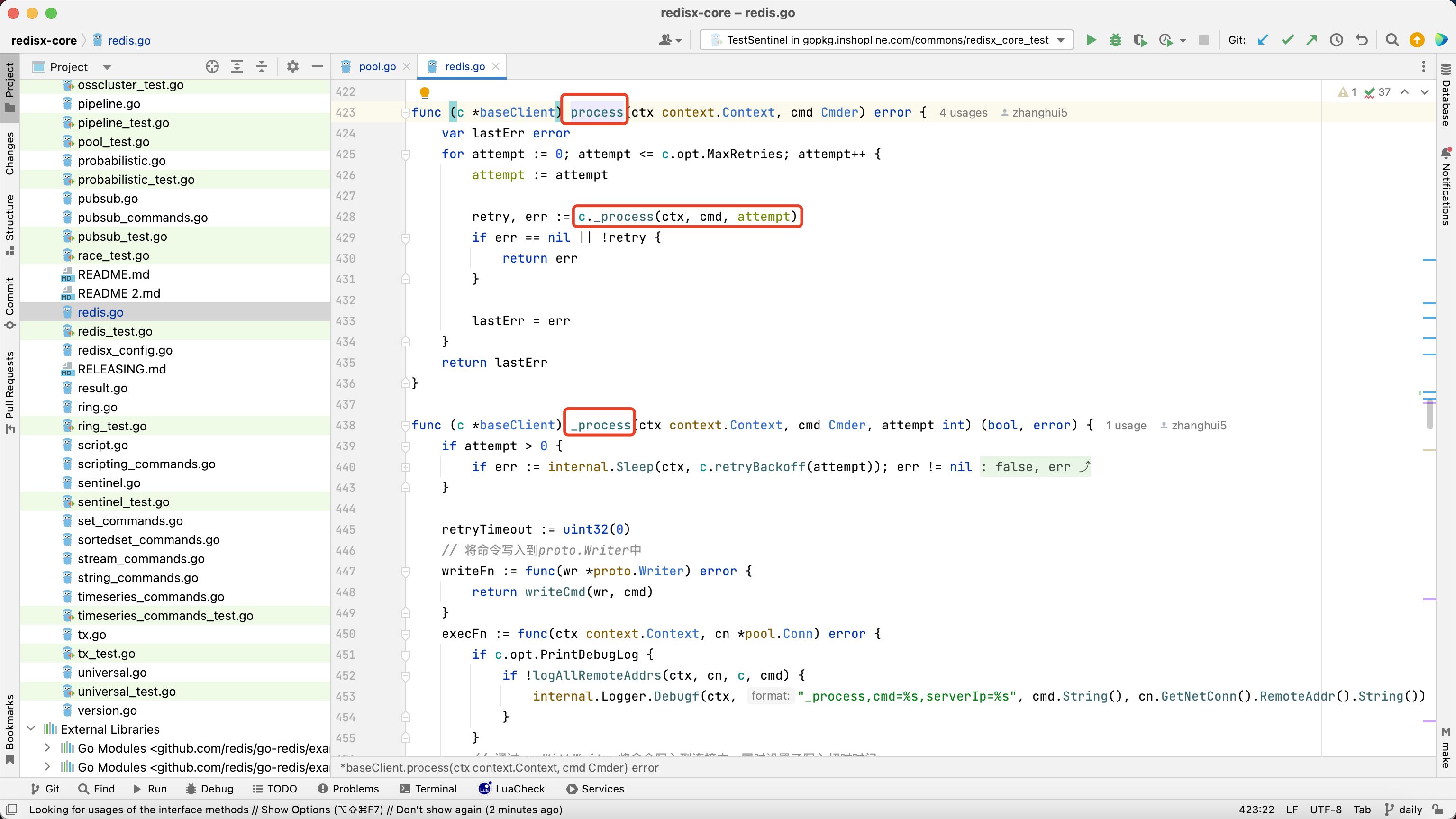
2. 线程池初始化
redis在新建单客户端、sentinel客户端、cluster客户端等,都会newConnPool初始化线程池
2.1.1. NewClient方式初始化连接池
// NewClient returns a client to the Redis Server specified by Options.
func NewClient(opt *Options) *Client {
opt.init()
c := Client{
baseClient: &baseClient{
opt: opt,
},
}
c.init()
// 初始化线程池
c.connPool = newConnPool(opt, c.dialHook)
return &c
}
2.1.2. NewFailoverClient方式初始化连接池
// NewFailoverClient returns a Redis client that uses Redis Sentinel
// for automatic failover. It's safe for concurrent use by multiple
// goroutines.
// zhmark 2024/6/13 NewFailoverClient
func NewFailoverClient(failoverOpt *FailoverOptions) *Client {
if failoverOpt.RouteByLatency {
panic("to route commands by latency, use NewFailoverClusterClient")
}
if failoverOpt.RouteRandomly {
panic("to route commands randomly, use NewFailoverClusterClient")
}
sentinelAddrs := make([]string, len(failoverOpt.SentinelAddrs))
copy(sentinelAddrs, failoverOpt.SentinelAddrs)
// todo:2024/6/26 有问题,每次都是换成1、3、2
// 将 sentinelAddrs 切片中的元素顺序随机打乱,实现随机化效果
rand.Shuffle(len(sentinelAddrs), func(i, j int) {
//交换 sentinelAddrs 中第 i 个和第 j 个元素
sentinelAddrs[i], sentinelAddrs[j] = sentinelAddrs[j], sentinelAddrs[i]
})
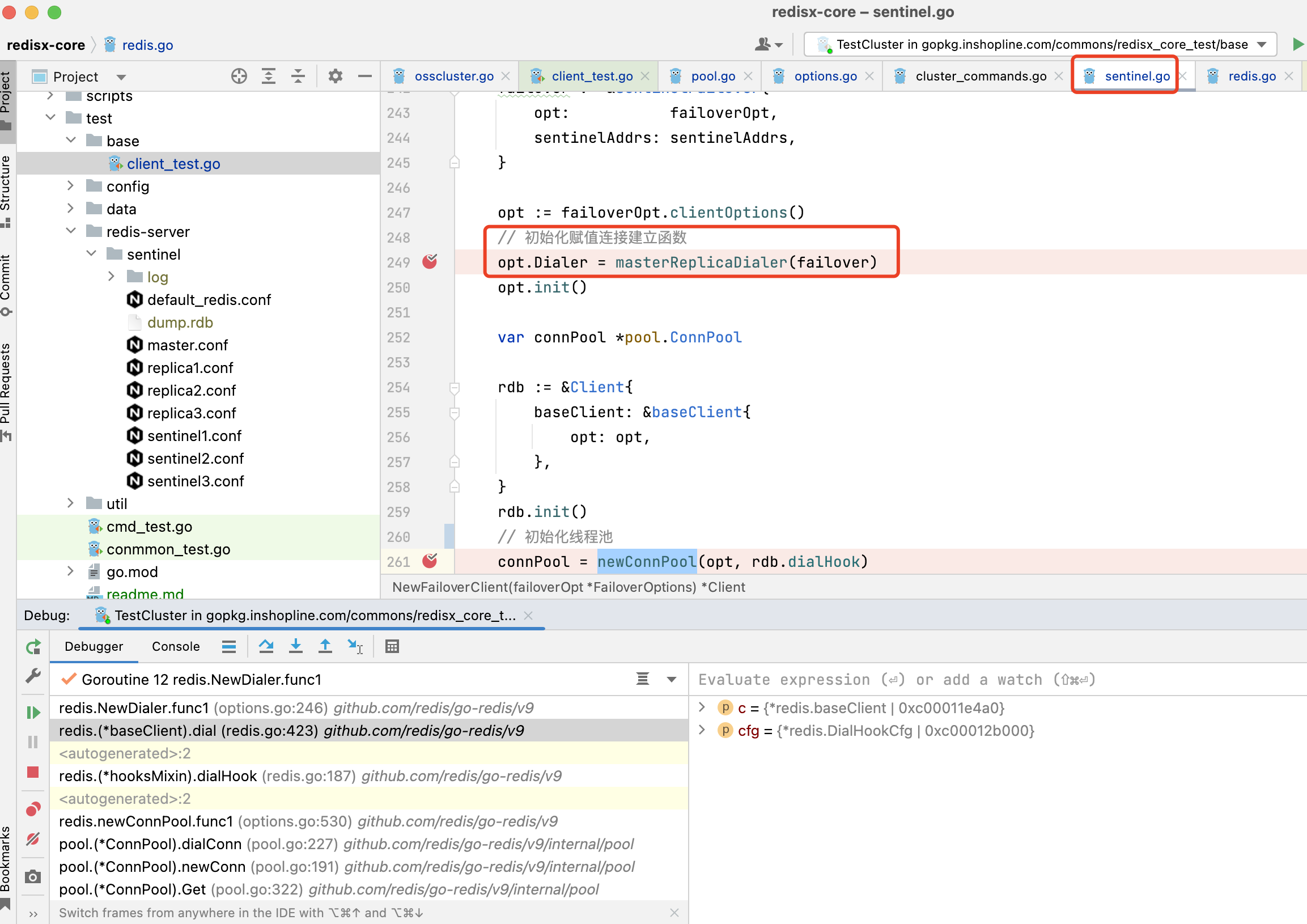
failover := &sentinelFailover{
opt: failoverOpt,
sentinelAddrs: sentinelAddrs,
}
opt := failoverOpt.clientOptions()
// 初始化赋值连接建立函数
opt.Dialer = masterReplicaDialer(failover)
opt.init()
var connPool *pool.ConnPool
rdb := &Client{
baseClient: &baseClient{
opt: opt,
},
}
rdb.init()
// 初始化线程池
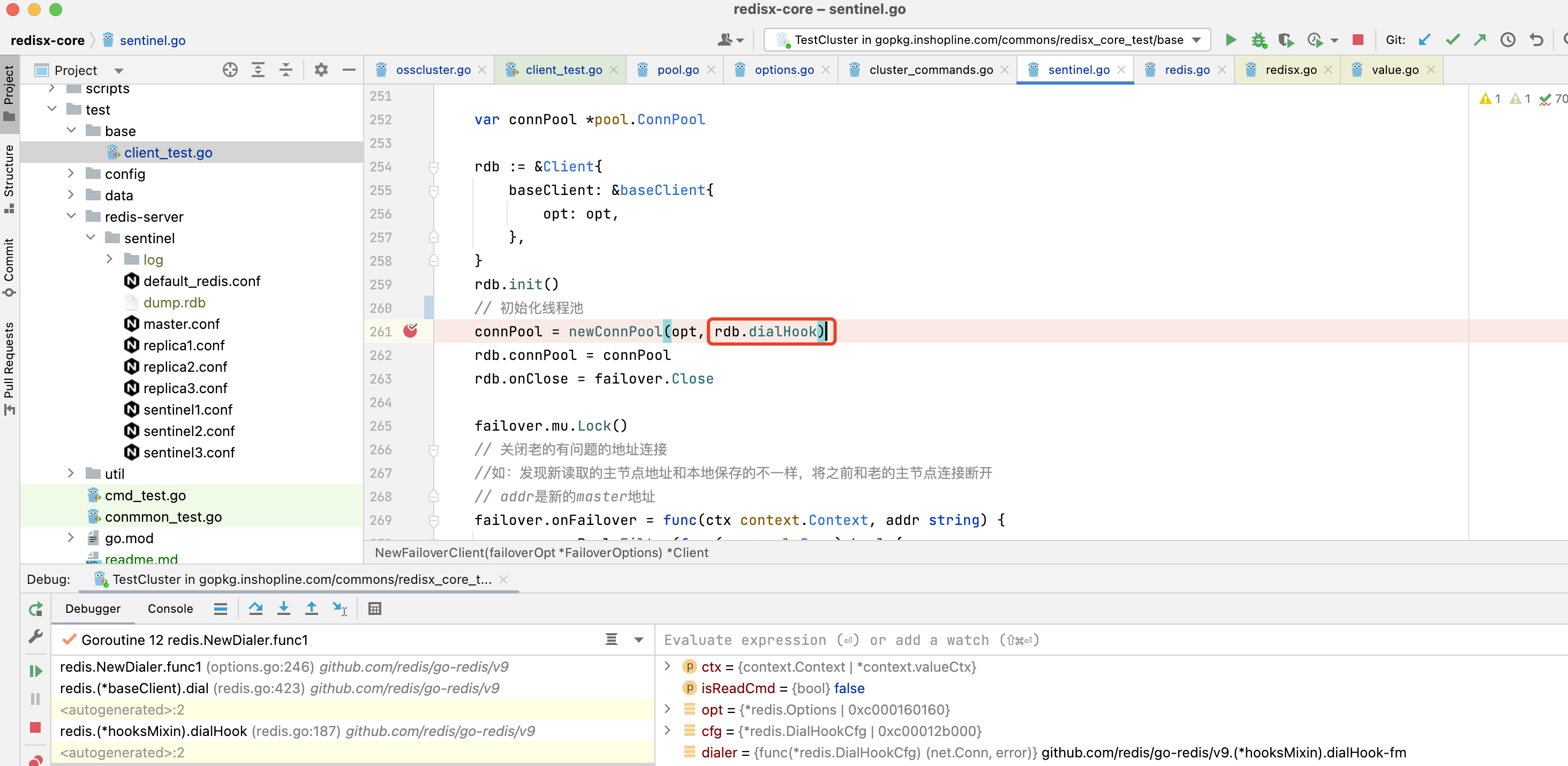
connPool = newConnPool(opt, rdb.dialHook)
rdb.connPool = connPool
rdb.onClose = failover.Close
failover.mu.Lock()
// 关闭老的有问题的地址连接
//如:发现新读取的主节点地址和本地保存的不一样,将之前和老的主节点连接断开
// addr是新的master地址
failover.onFailover = func(ctx context.Context, addr string) {
_ = connPool.Filter(func(cn *pool.Conn) bool {
// 如果连接的远程地址与 addr 不同,则返回 true,表示要关闭此连接;否则返回 false,表示保留该连接
return cn.RemoteAddr().String() != addr
})
}
failover.mu.Unlock()
return rdb
}
2.1. NewClusterClient方式初始化线程池
cluster模式和上面的NewClient、NewFailoverClient不一样。cluster模式new的时候不会初始化连接池,而是等执行命令时,获取所有节点,每个节点新建一个redisClient,每个client单独一个连接池
2.1.1. 初始化NewClusterClient时不会新建连接池
// NewClusterClient returns a Redis Cluster client as described in
// http://redis.io/topics/cluster-spec.
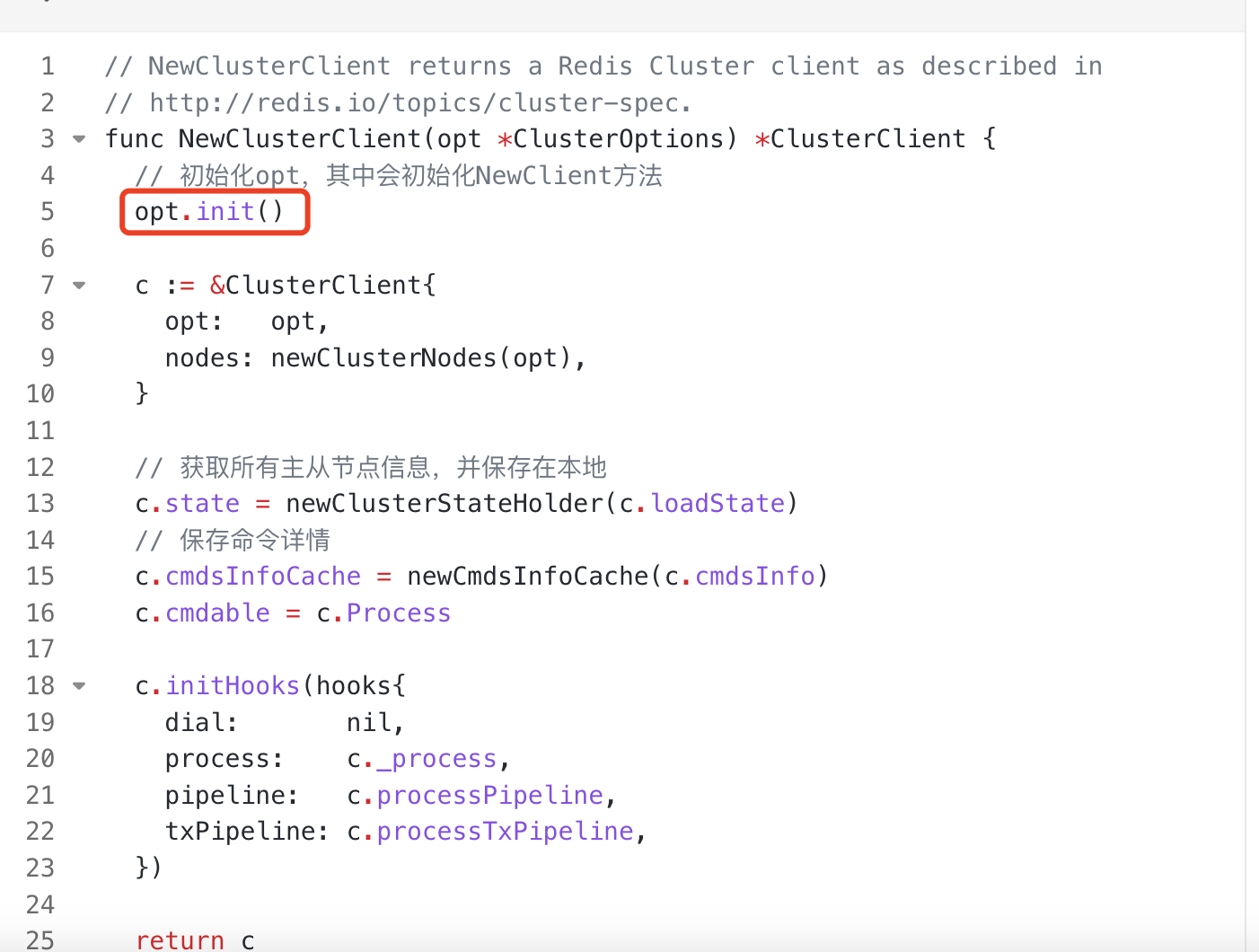
func NewClusterClient(opt *ClusterOptions) *ClusterClient {
// 初始化opt,其中会初始化NewClient方法
opt.init()
c := &ClusterClient{
opt: opt,
nodes: newClusterNodes(opt),
}
// 获取所有主从节点信息,并保存在本地
c.state = newClusterStateHolder(c.loadState)
// 保存命令详情
c.cmdsInfoCache = newCmdsInfoCache(c.cmdsInfo)
c.cmdable = c.Process
c.initHooks(hooks{
dial: nil,
process: c._process,
pipeline: c.processPipeline,
txPipeline: c.processTxPipeline,
})
return c
}
2.1.2. 执行命令时,通过cmdNode执行到NewClient,初始化线程池
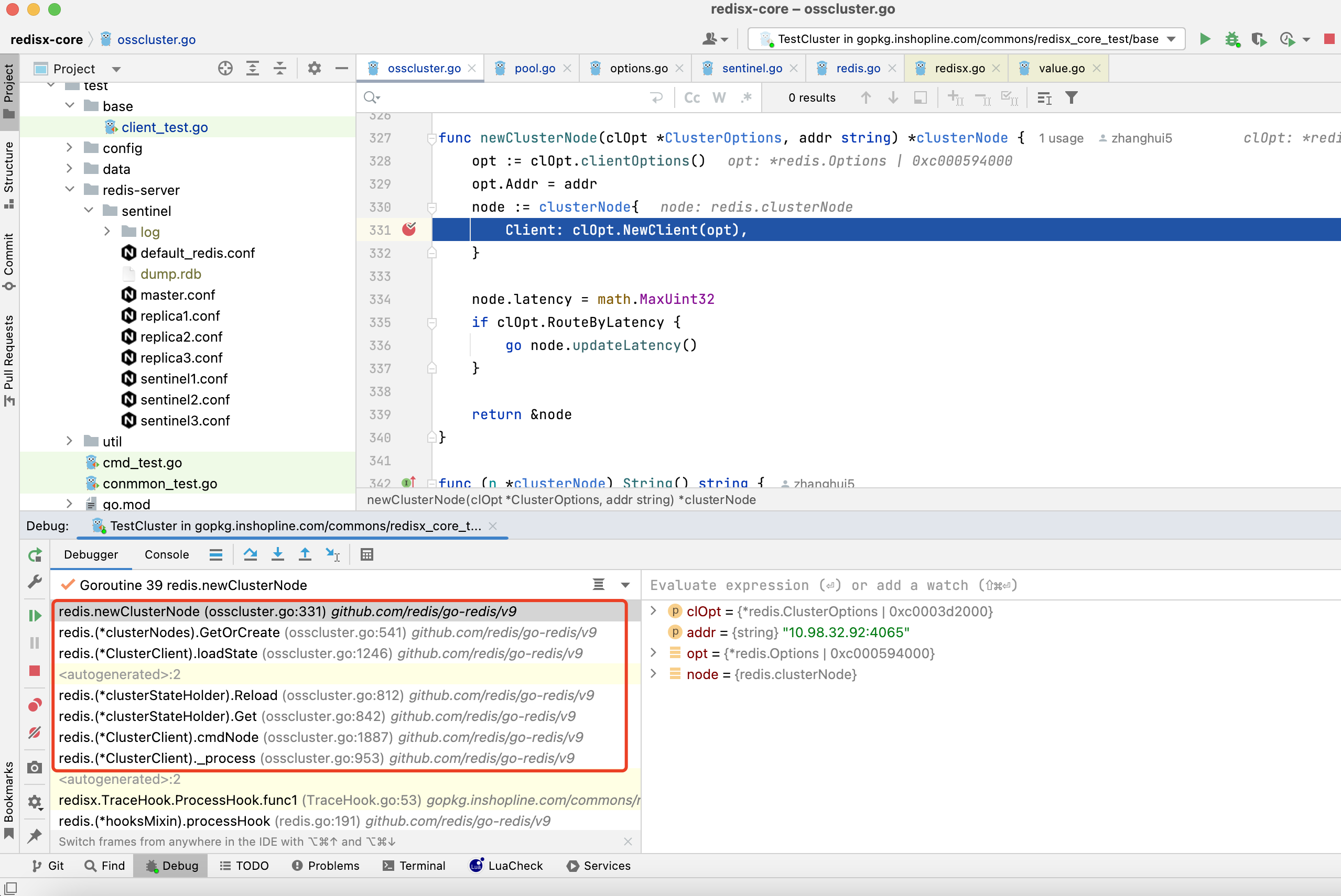
通过clOpt的NewClient方法,初始化client,进而初始化线程池
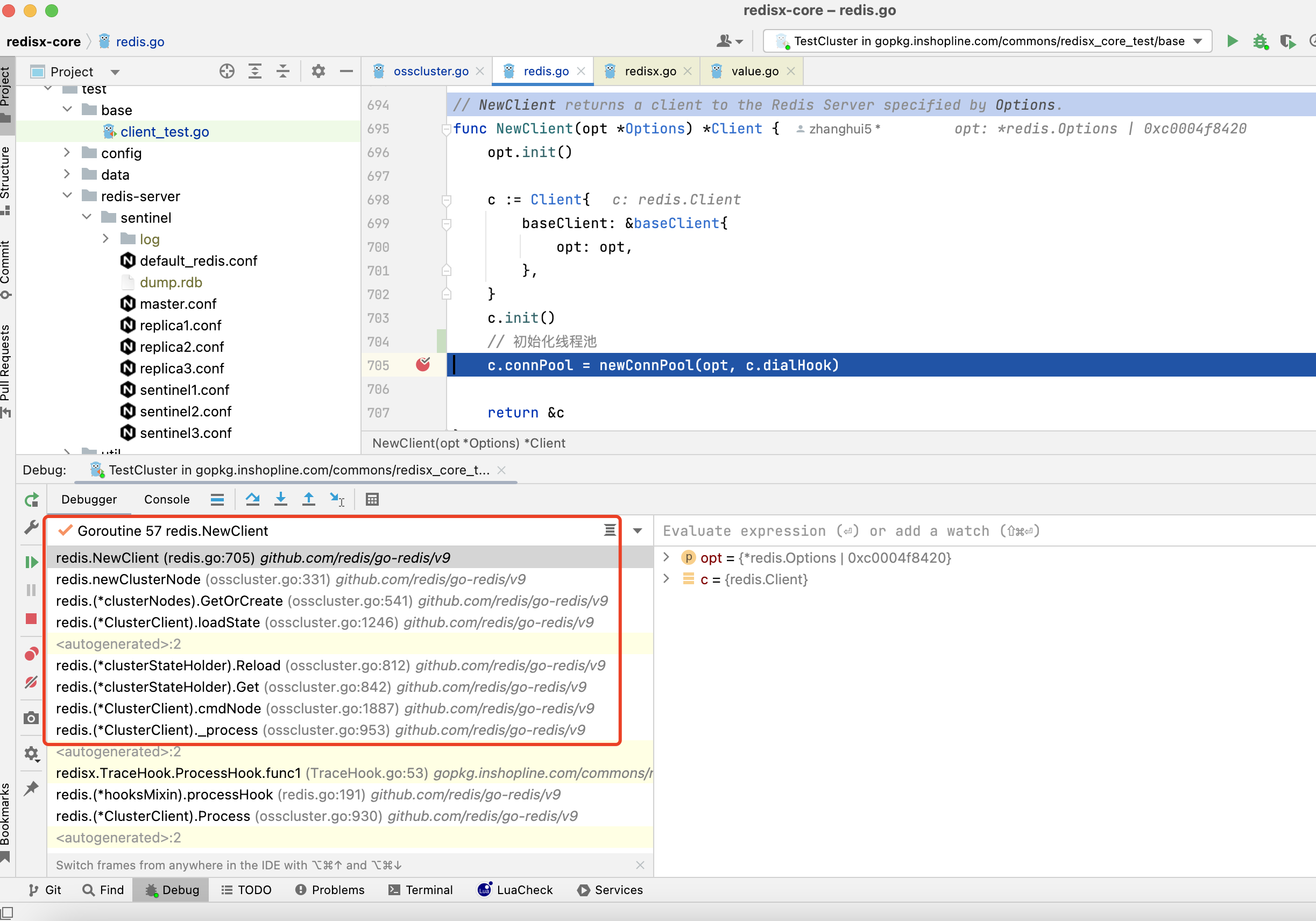
2.1.3. 然而clOpt的NewClient方法什么时候初始化赋值的呢
在NewClusterClient方法的opt.init()中
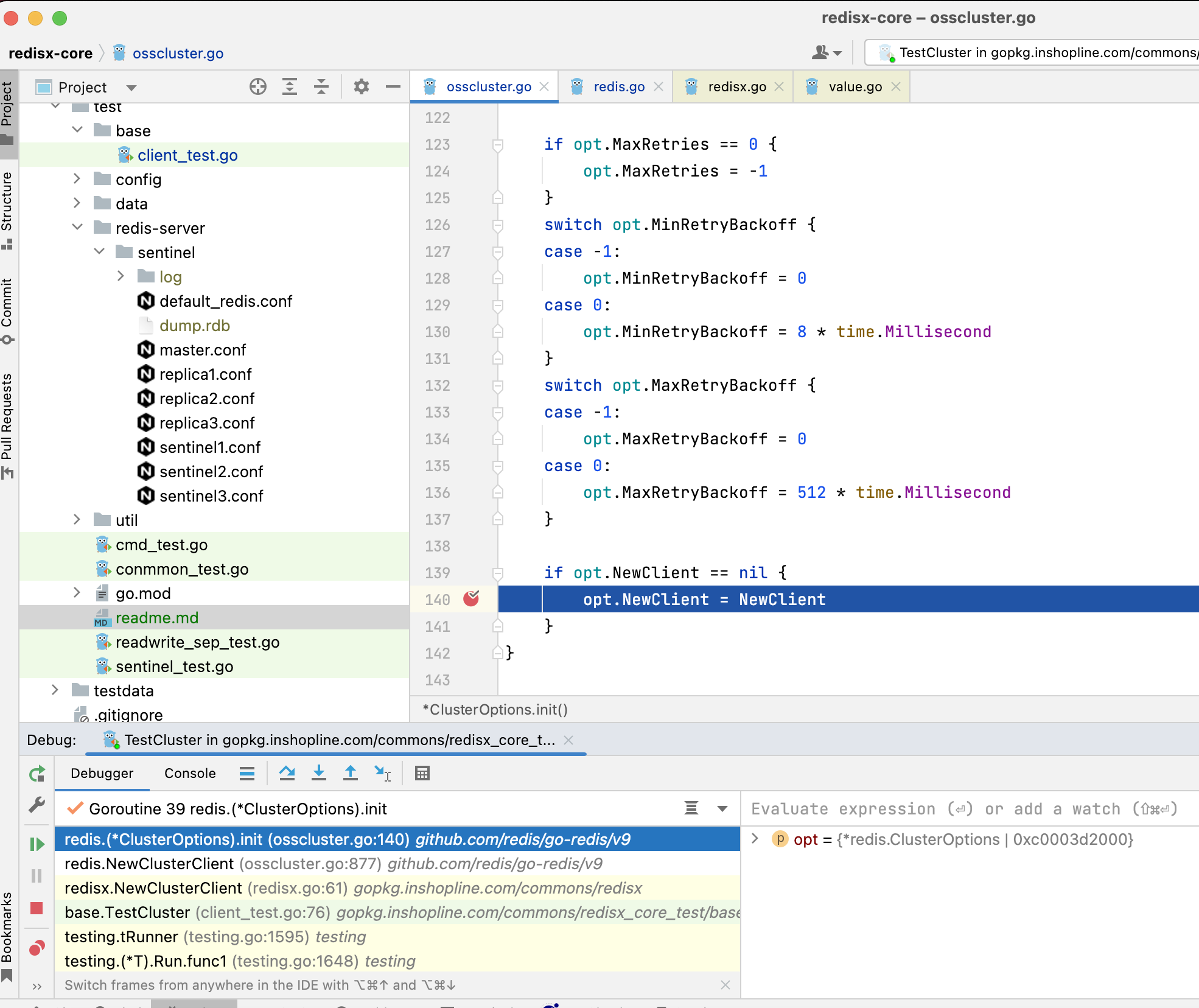
3. 如何新建连接
总览图
3.1.1. 第一次执行命令时,go-redis会先通过cmdNode方法,获取所有的节点信息
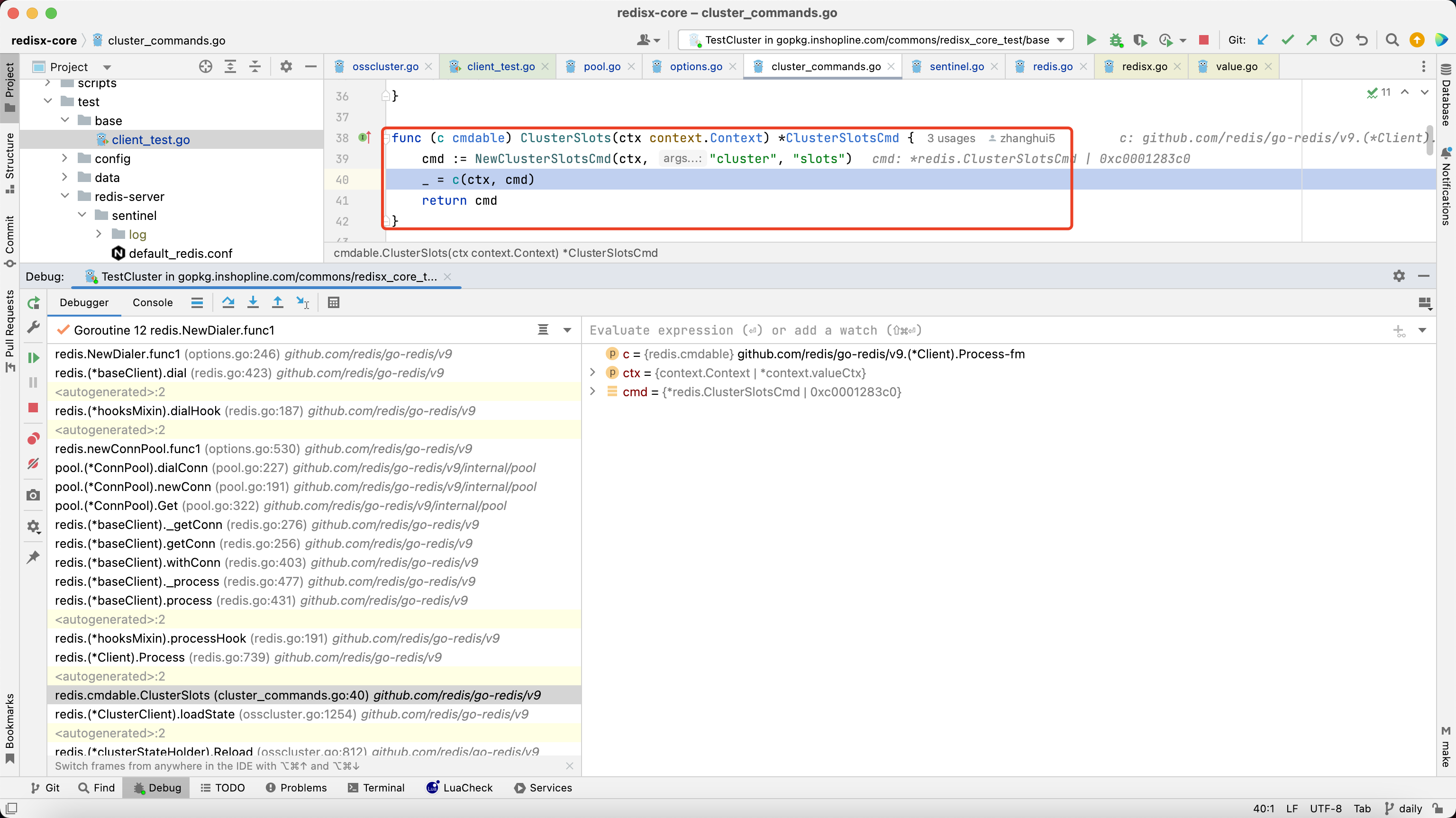
3.1.2. 底层调用到ClusterSlots方法,触发redis.go中_process方法,内部调用_withConn方法,通过getConn方法获取可用连接
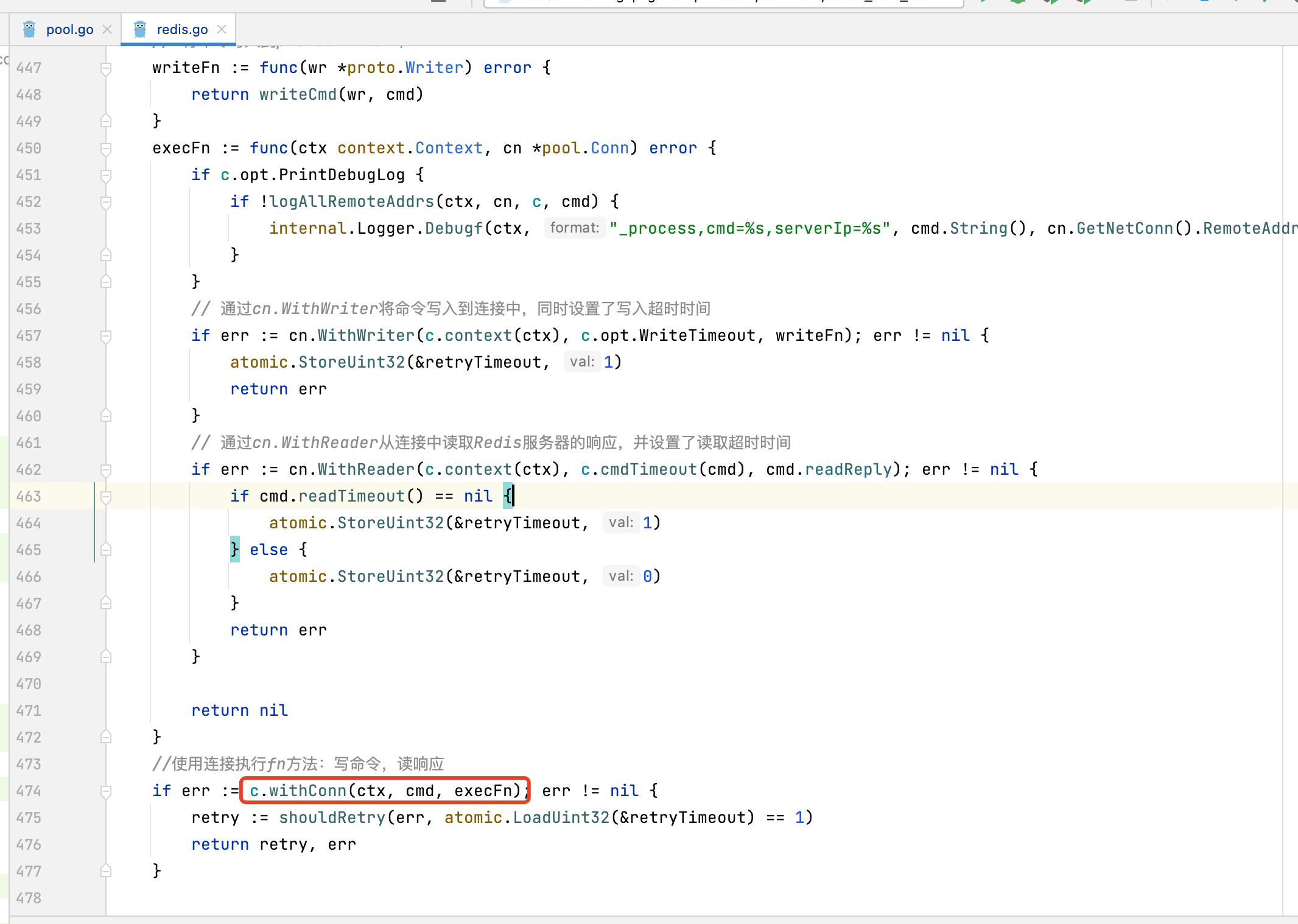
3.1.3. getConn方法内部发现无可用连接,则会调用newConn
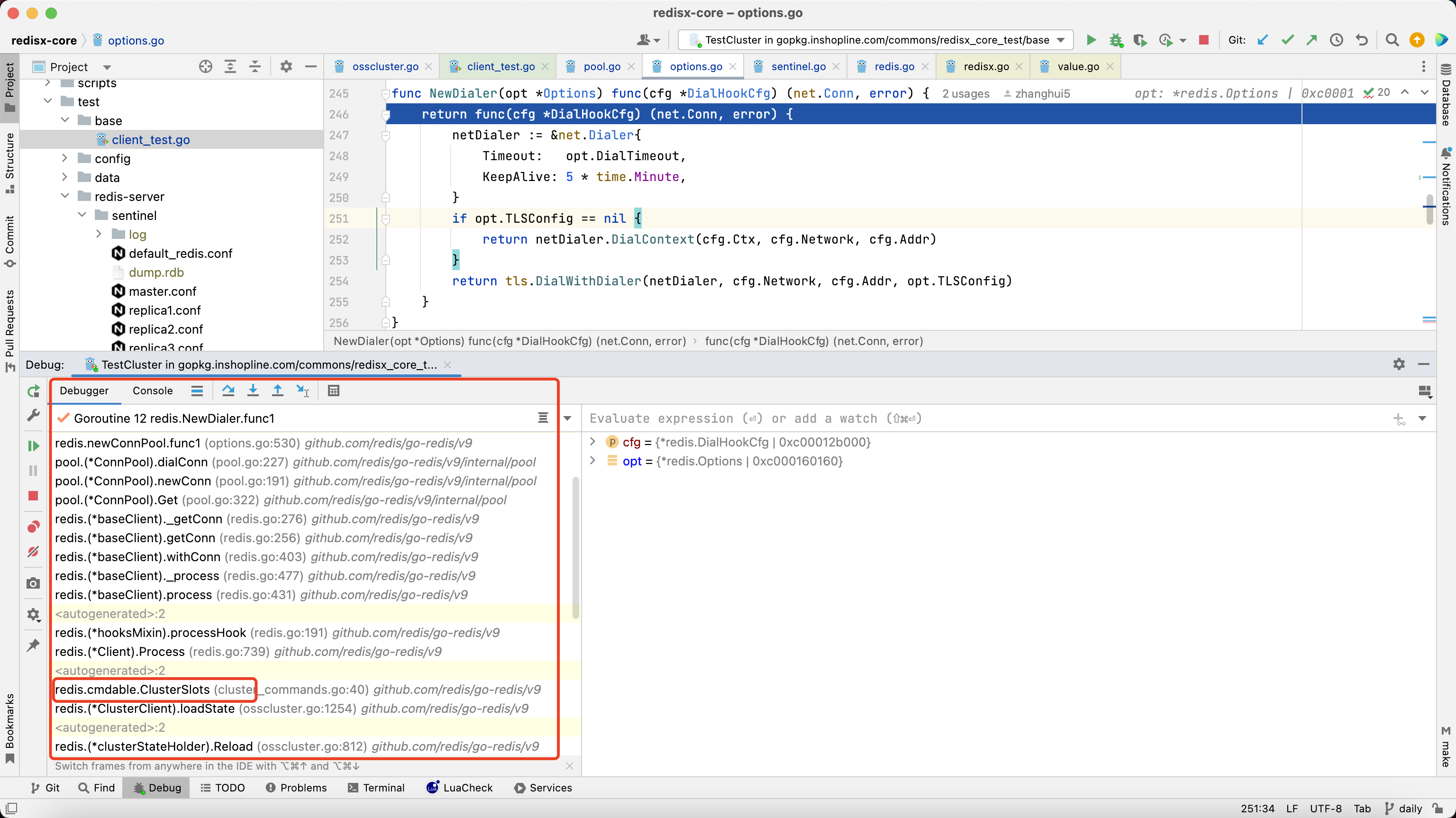
3.1.4. newConn内部,调用连接池的dialConn方法触发调用
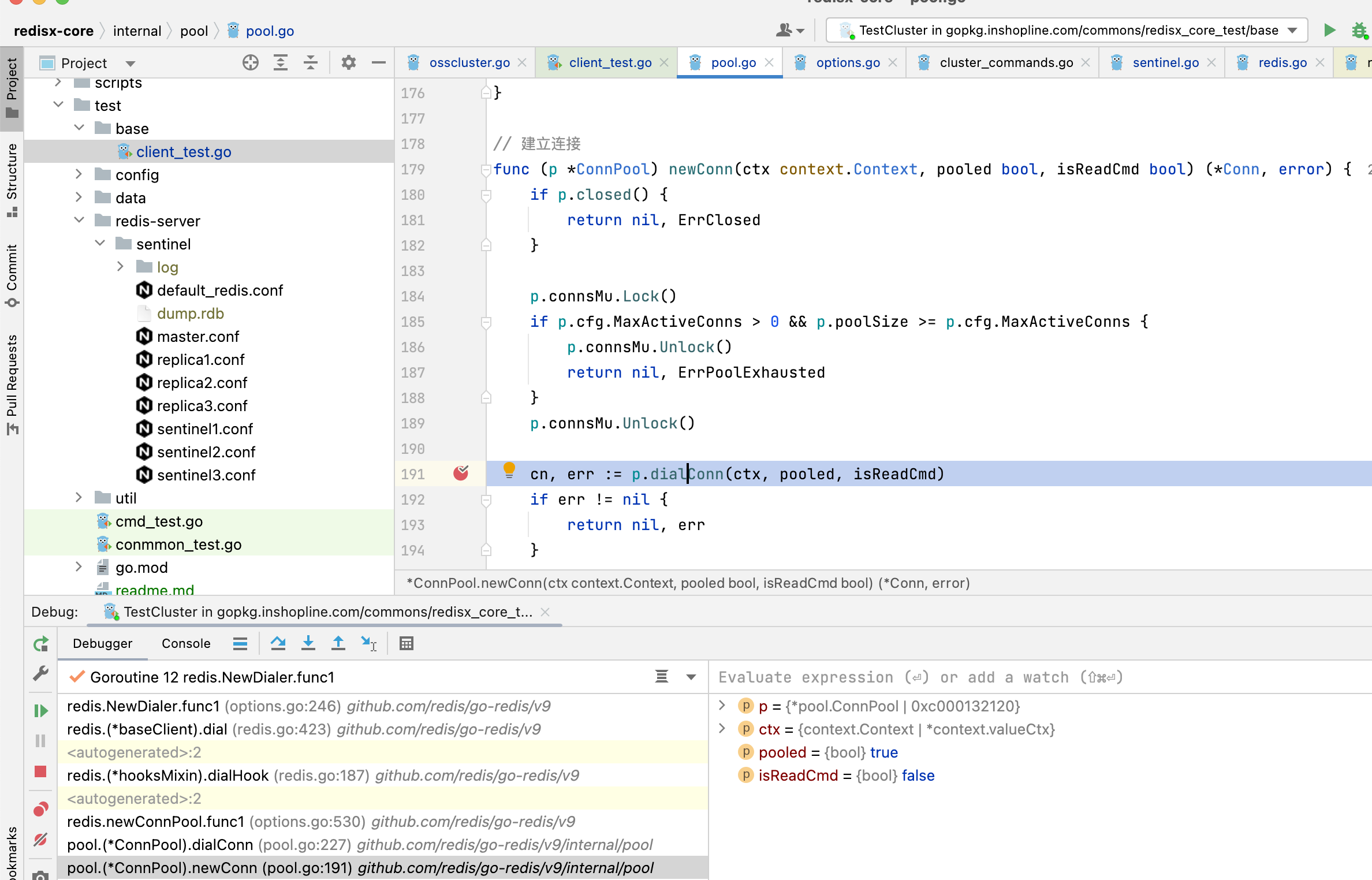
3.1.5. dialConn调用配置项的Dialer方法
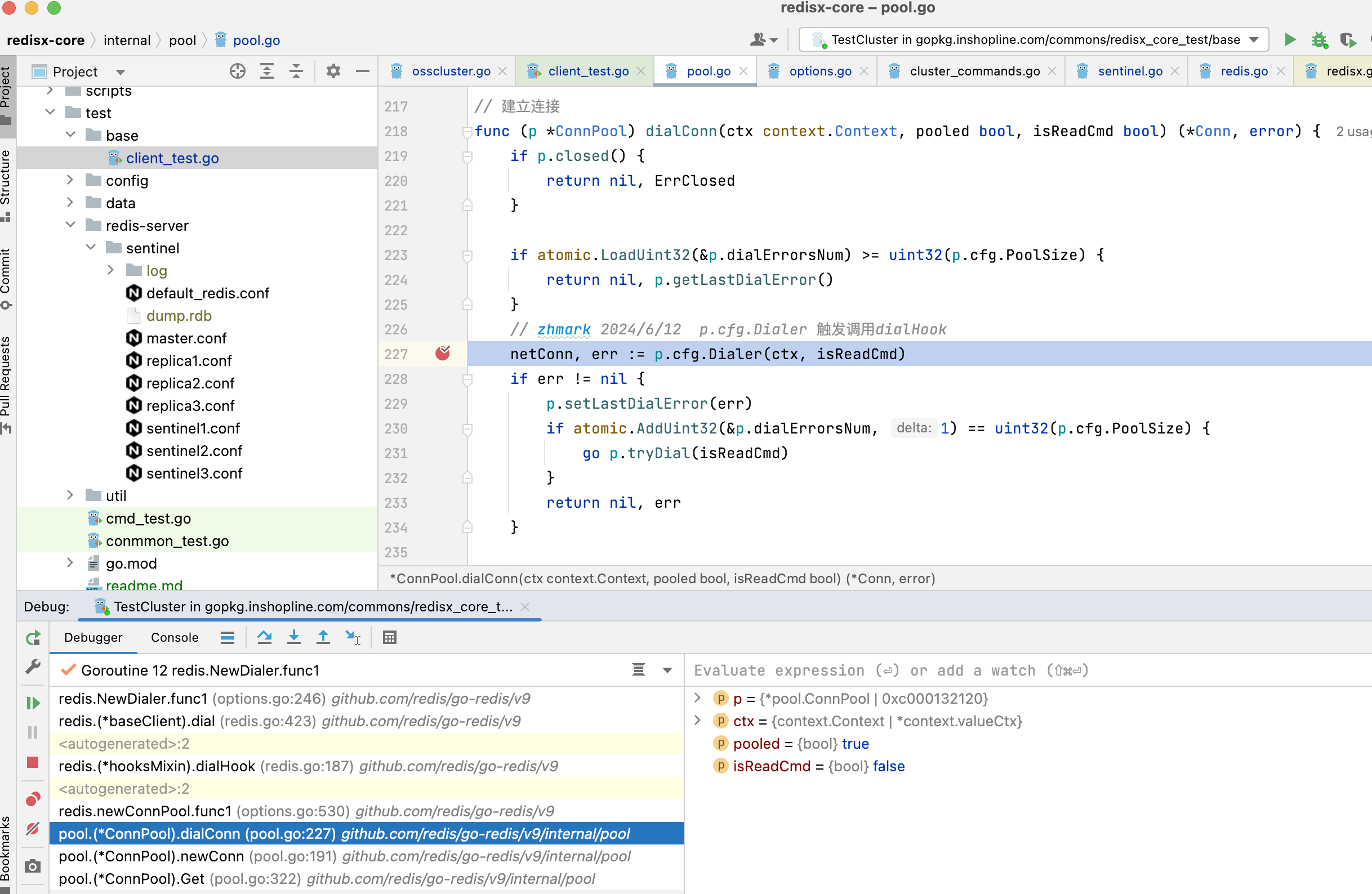
3.1.6. p.cfg.Dialer在newConnPool时候初始化的,通过Dialer方法,触发dialer
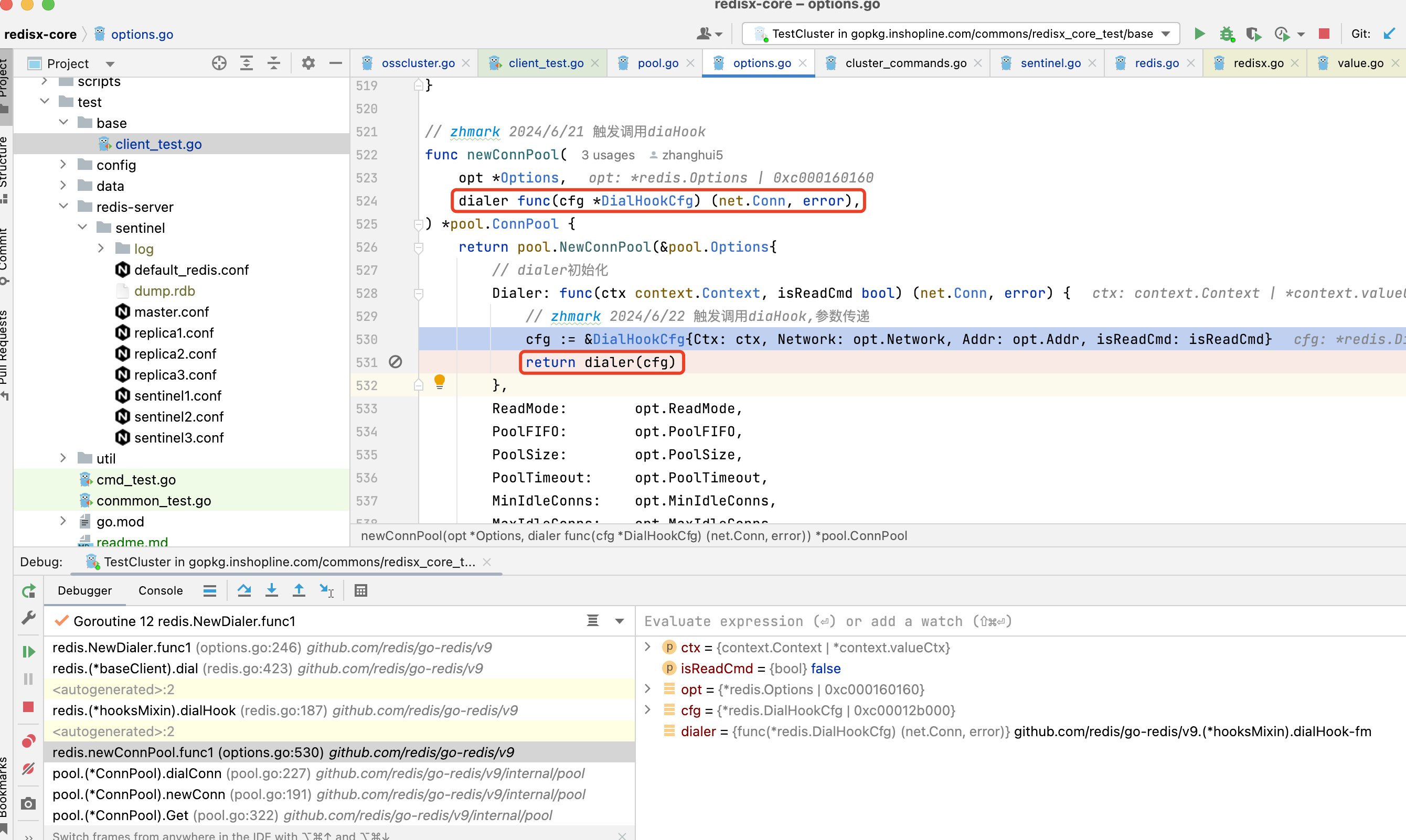
3.1.7. 而dialer是newClient时传入的dialhook,至此直接触发了dialhook
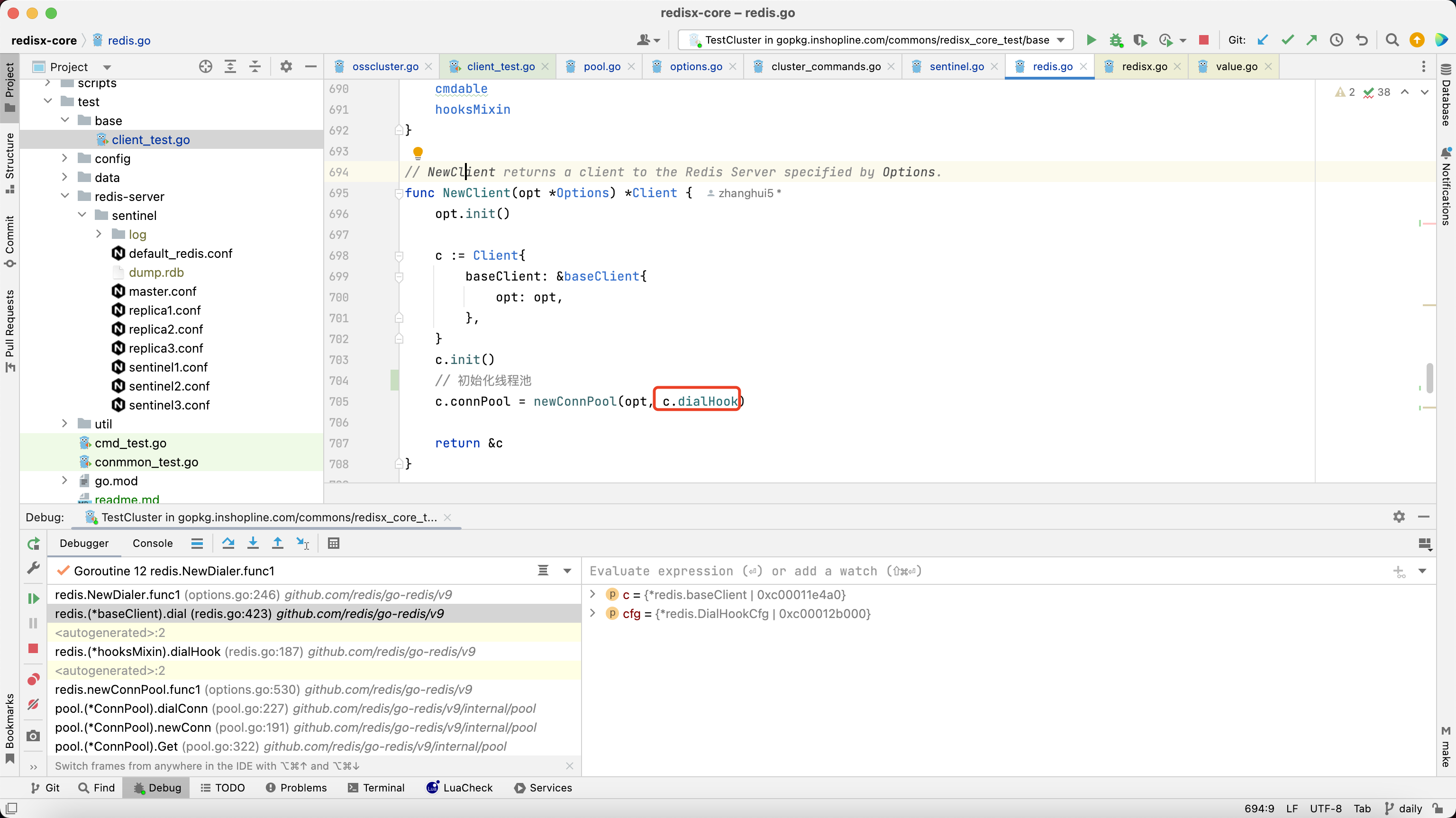
3.1.8. sentinel模式也是在NewFailoverClient时传入的dialhook
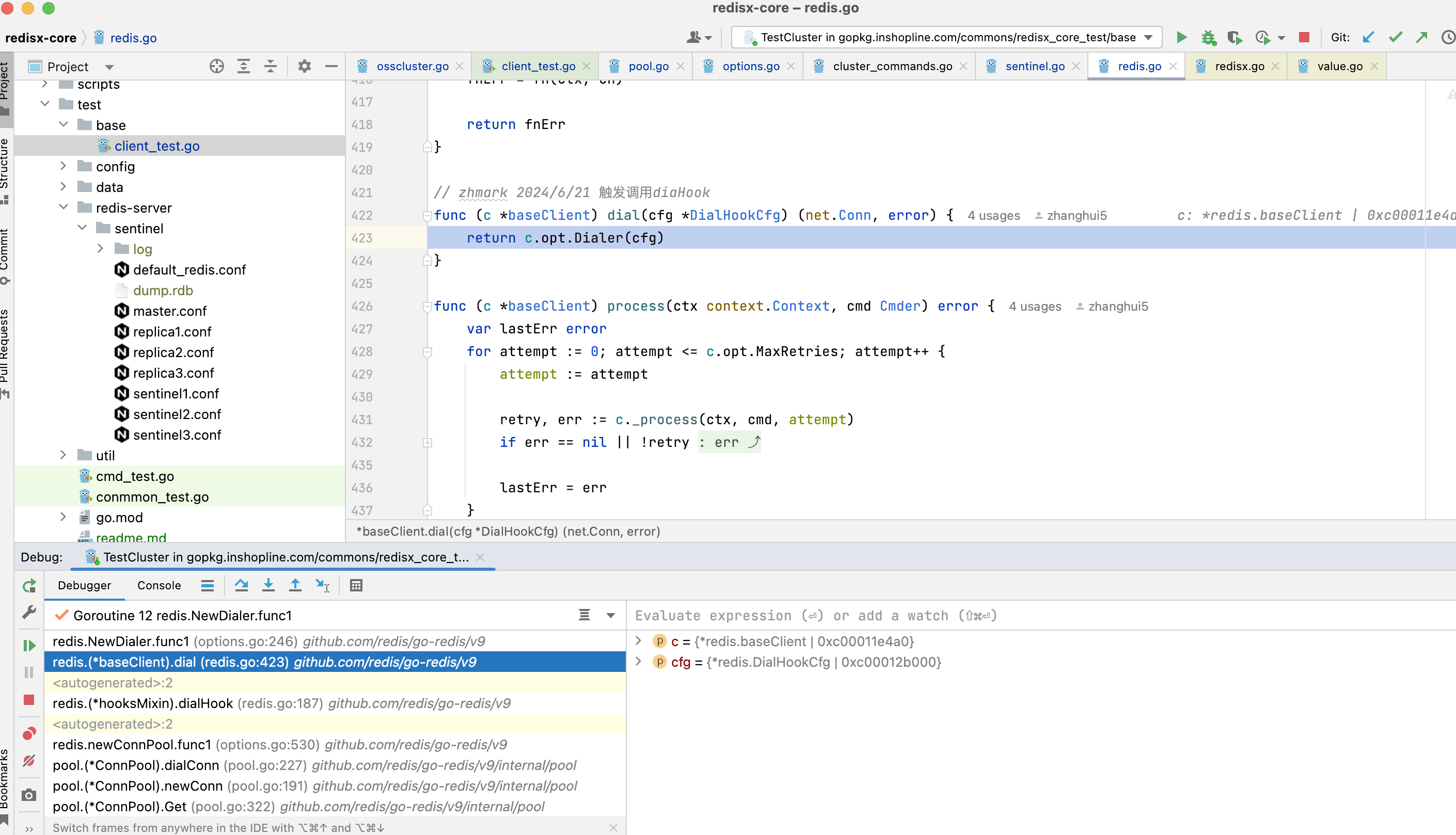
3.1.9. redis自己的dialHook内部,执行的是opt的Dialer方法
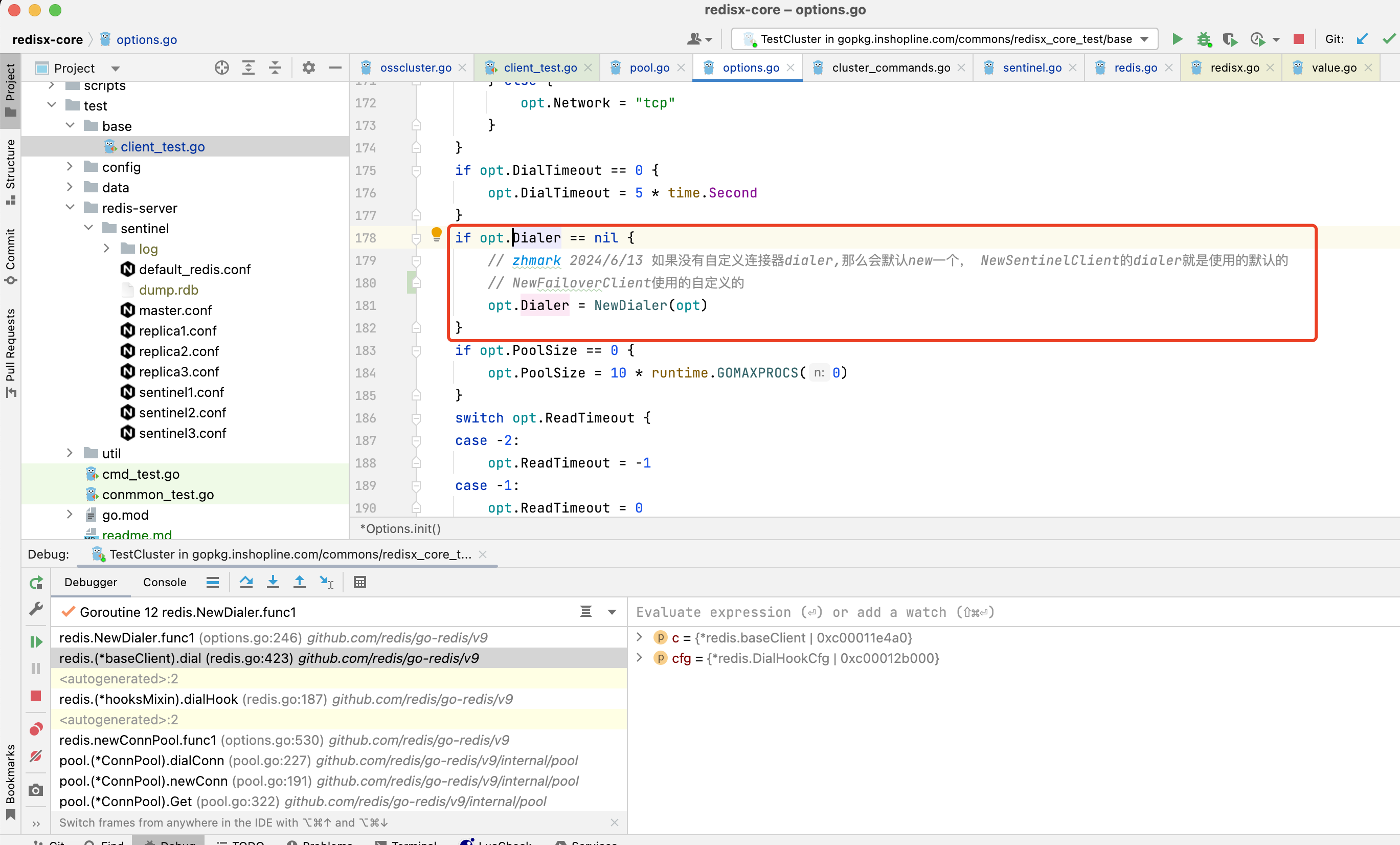
3.1.10. 此Dialer方法是在NewClient中opt.init()初始化方法中赋值的,如果没有自定义,就用默认的建连方法
3.1.11. 默认的建连方法很简单,调用go底层的net建立连接
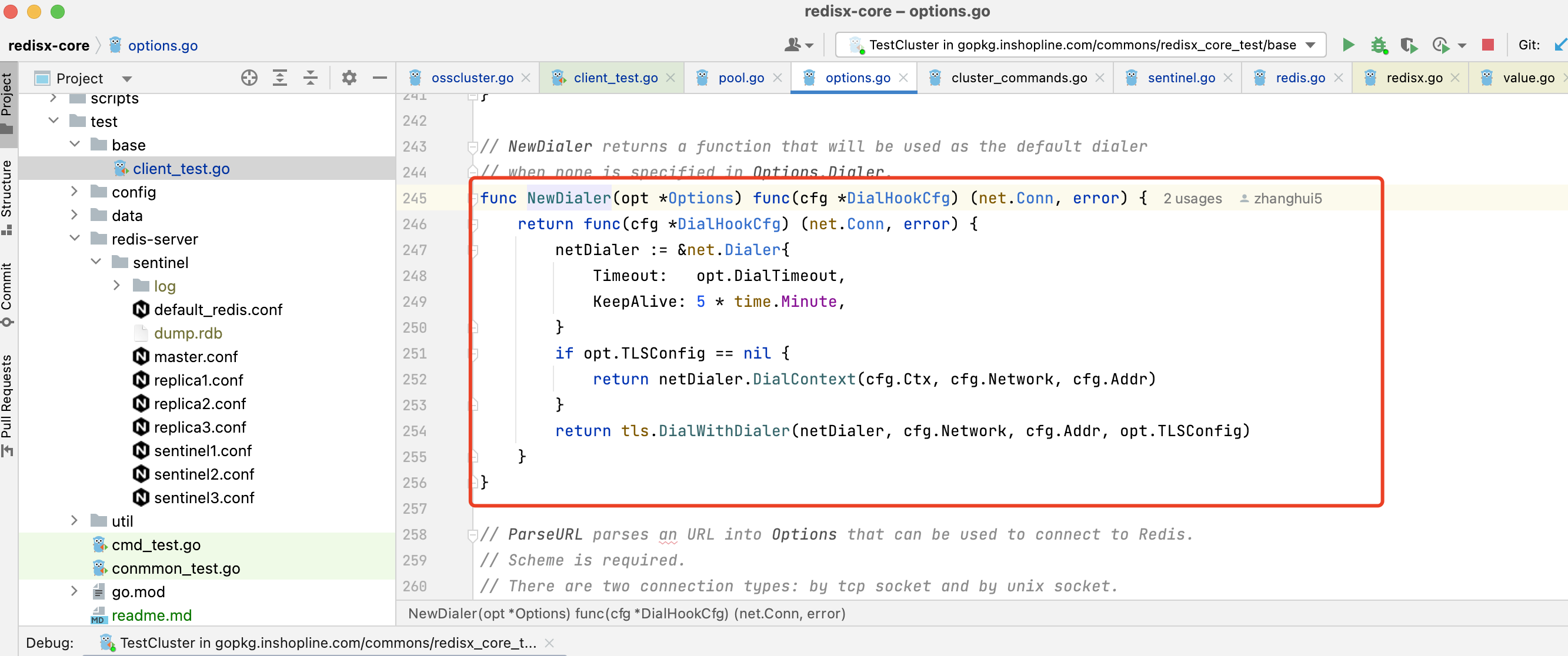
3.1.12. sentinel模式不一样,NewFailoverClient方法有自定义建连方法
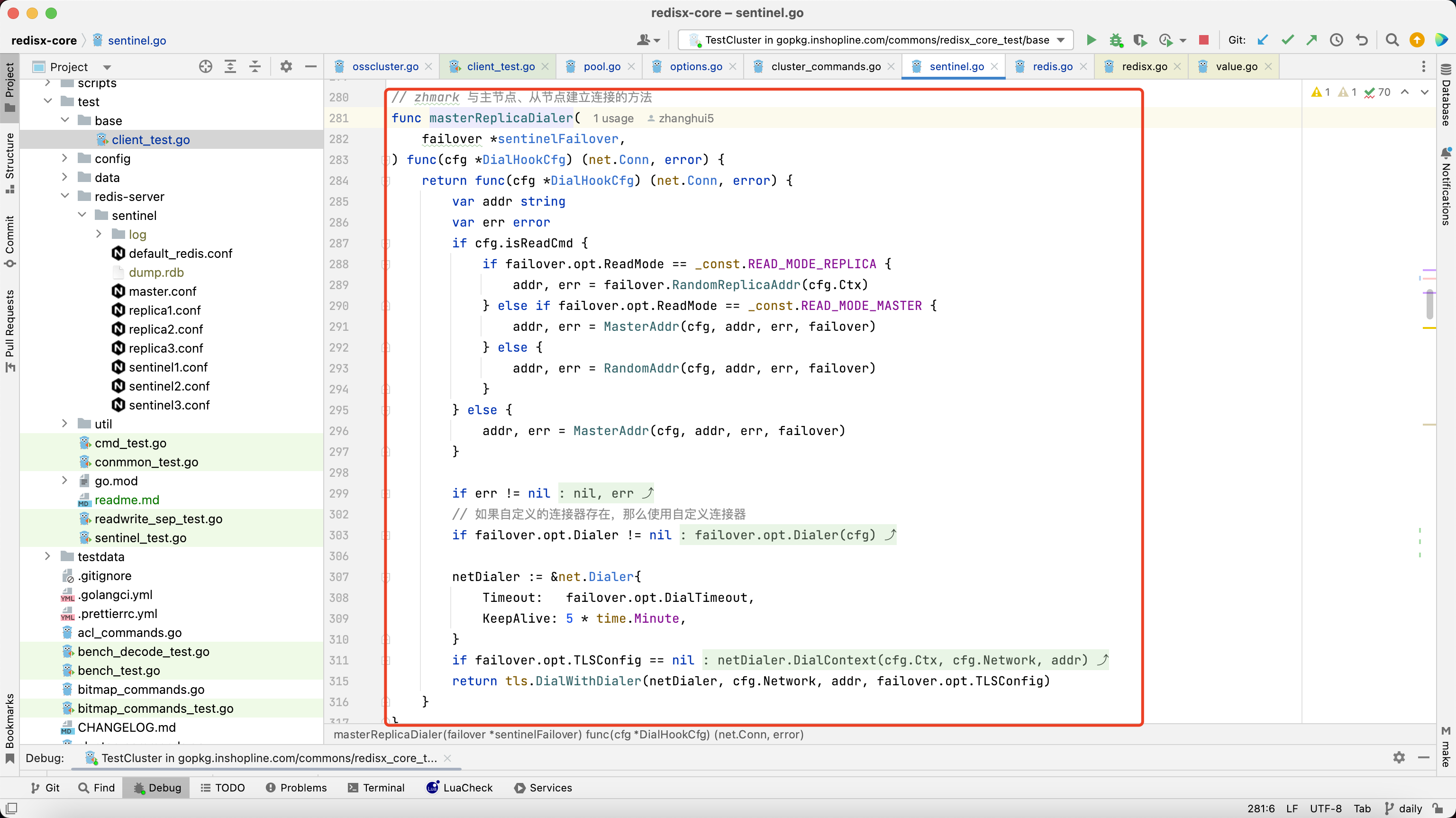
3.1.13. 里面实现了读写分离
4. 闲置连接如何关闭
看是否有配置MinIdleConns和MaxIdleConns。如果有配置了MinIdleConns,那么在NewConnPool、popIdle、removeConn时,都会调用checkMinIdleConns补充创建最低闲置连接数
// Minimum number of idle connections which is useful when establishing
// new connection is slow.
// Default is 0. the idle connections are not closed by default.
MinIdleConns int
// Maximum number of idle connections.
// Default is 0. the idle connections are not closed by default.
MaxIdleConns int
每次执行完方法,会释放连接
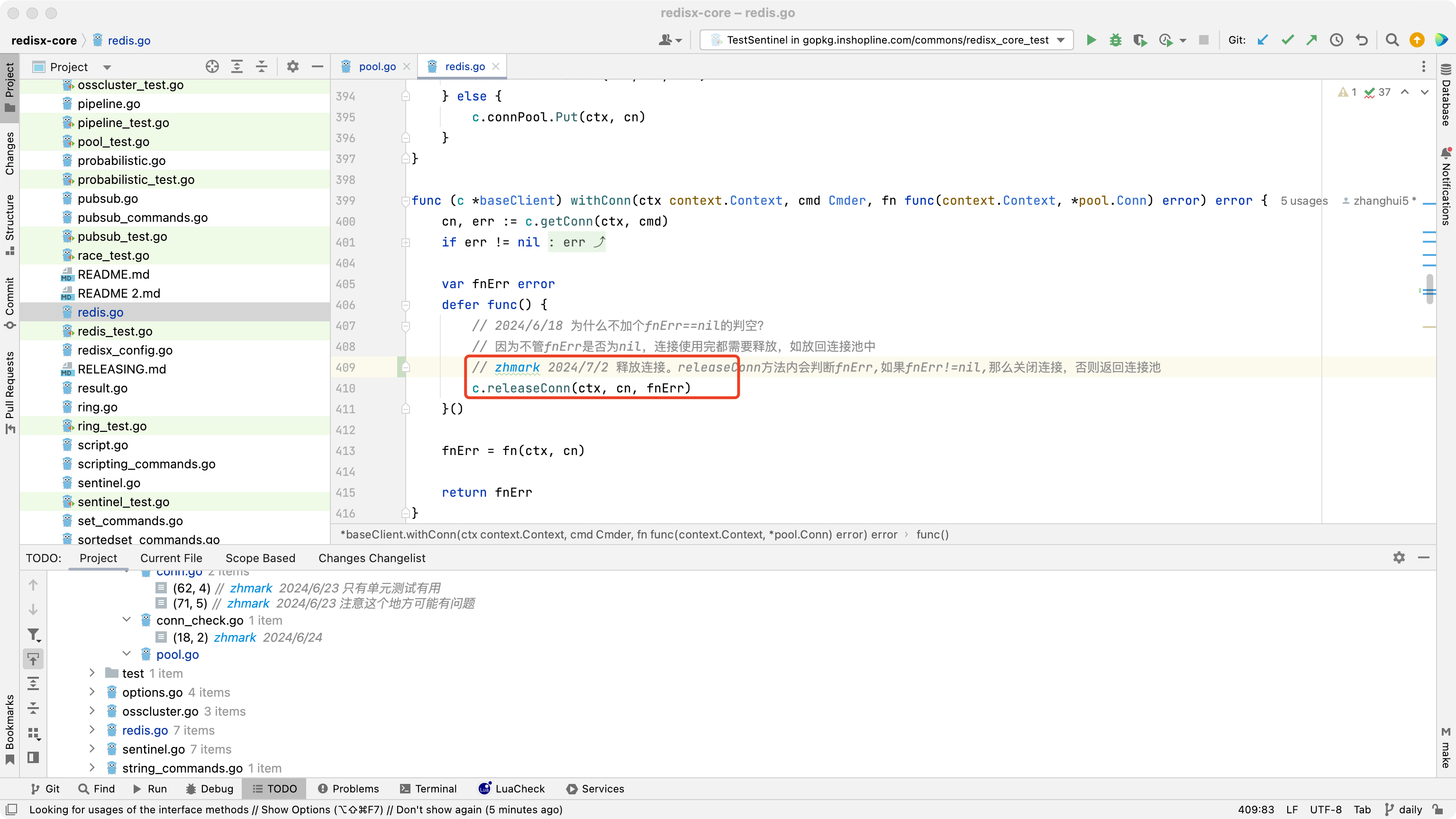
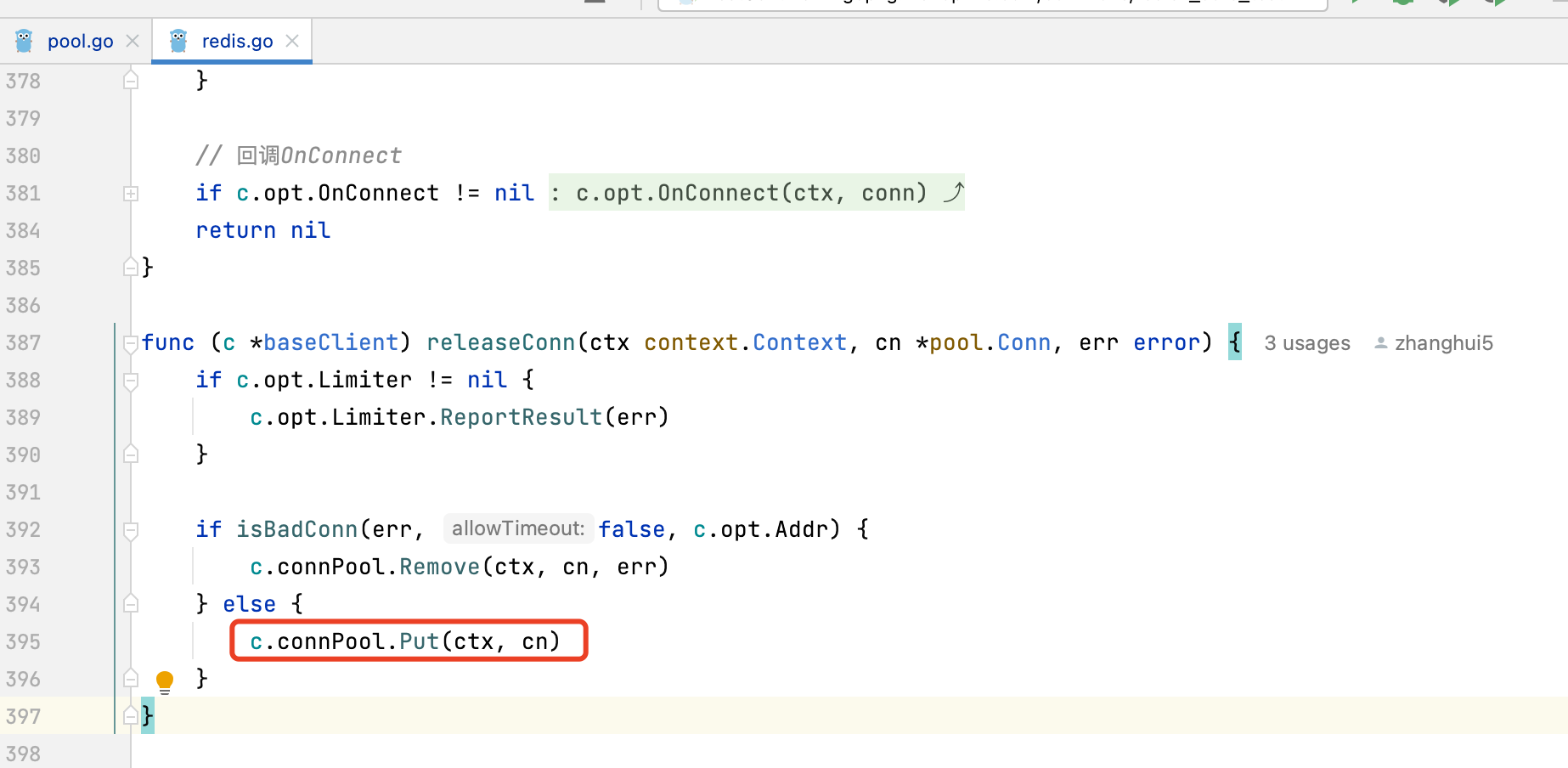
5. 如何控制闲置连接数大小
6. 如何控制总连接数
poolSize:控制最大并发量
turn可能为0,闲置连接数为最大poolSize
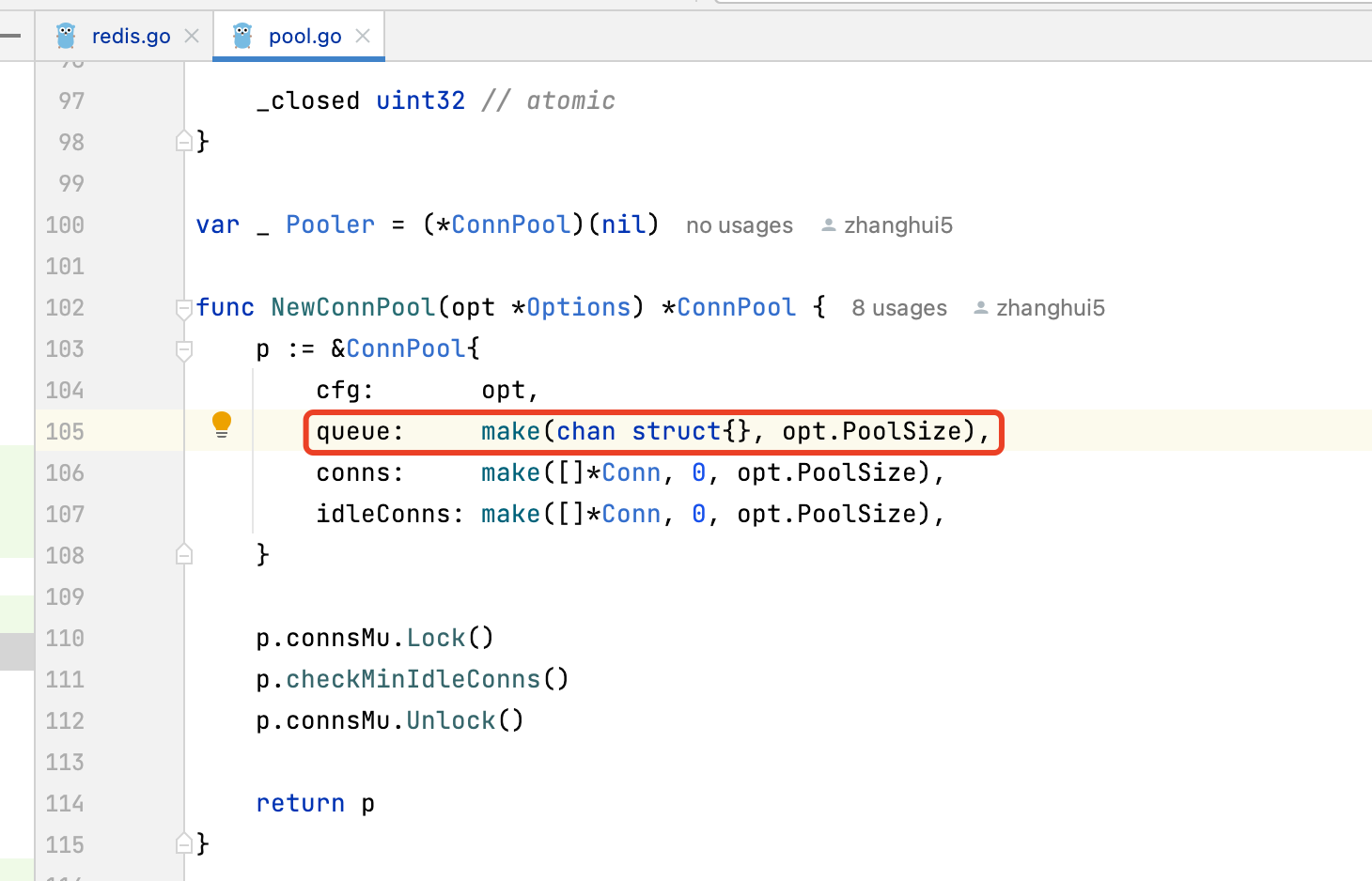
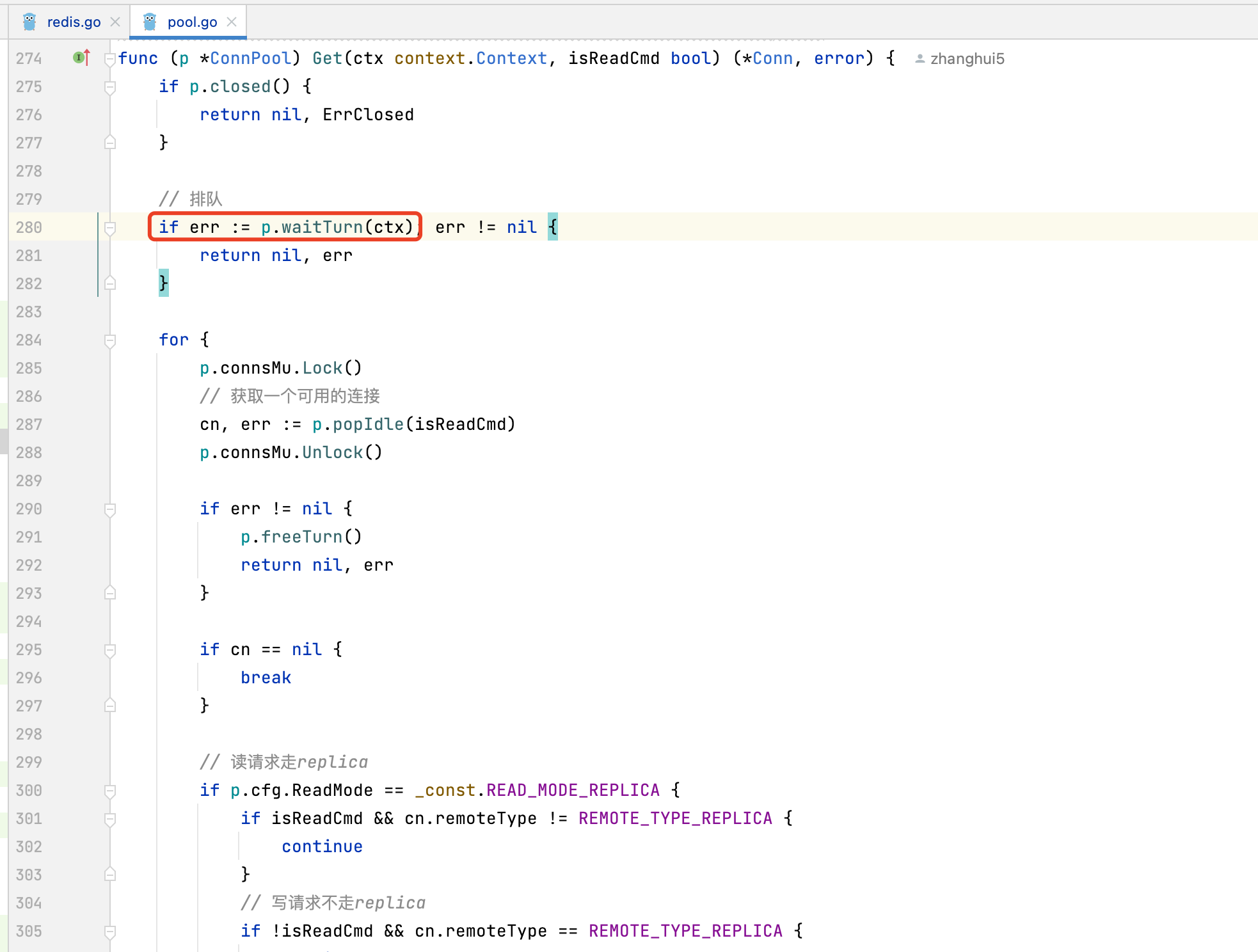
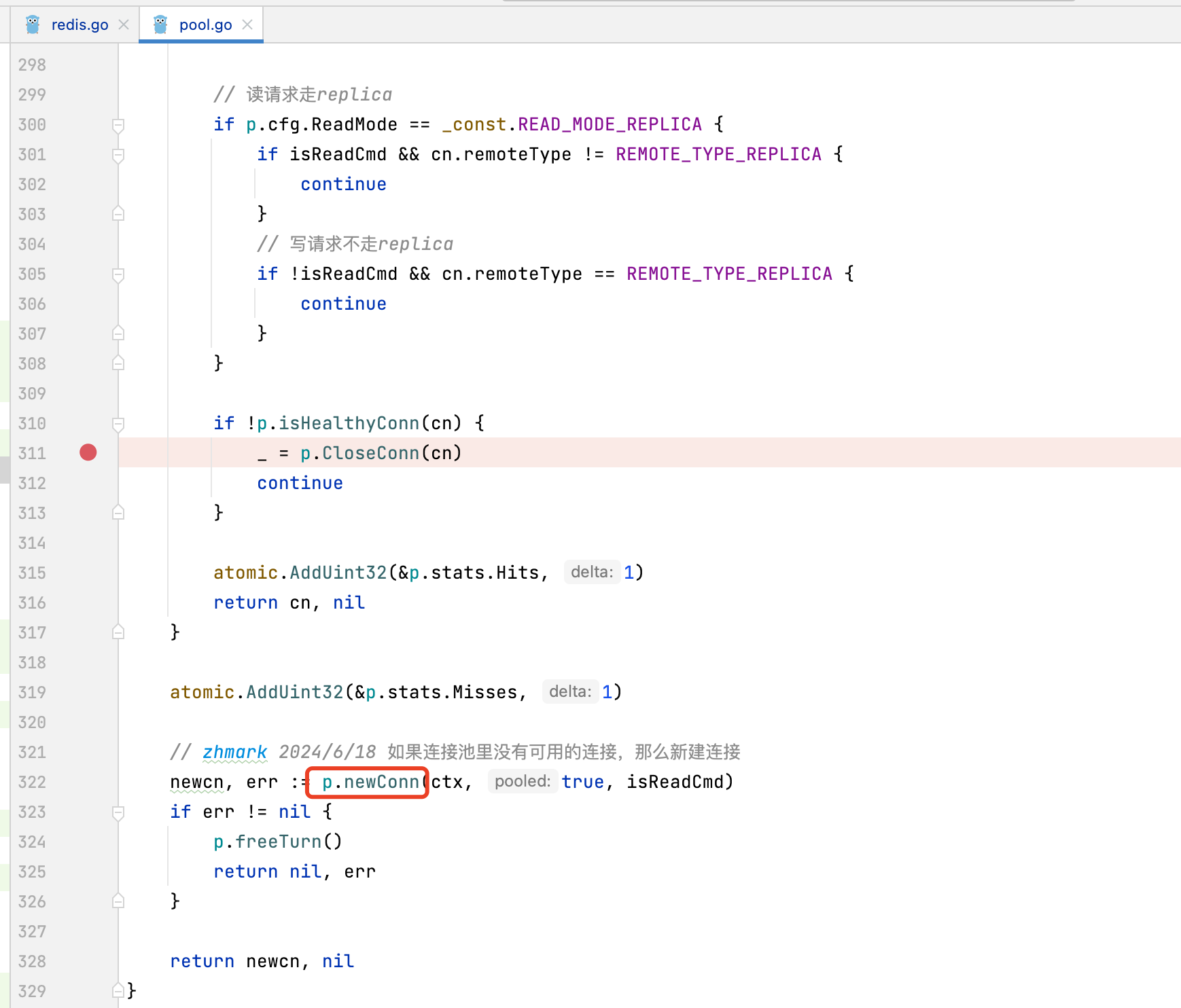
7. 如何保持连接池内的连接健康
每次Get连接时,会检查连接是否健康
func (p *ConnPool) Get(ctx context.Context, isReadCmd bool) (*Conn, error) {
if p.closed() {
return nil, ErrClosed
}
// 排队
if err := p.waitTurn(ctx); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
for {
p.connsMu.Lock()
// 获取一个可用的连接
cn, err := p.popIdle(isReadCmd)
p.connsMu.Unlock()
if err != nil {
p.freeTurn()
return nil, err
}
if cn == nil {
break
}
// 读请求走replica,只是多一层保护
if p.cfg.ReadMode == _const.READ_MODE_REPLICA {
if isReadCmd && cn.remoteType != REMOTE_TYPE_REPLICA {
continue
}
// 写请求不走replica
if !isReadCmd && cn.remoteType == REMOTE_TYPE_REPLICA {
continue
}
}
if !p.isHealthyConn(cn) {
_ = p.CloseConn(cn)
continue
}
atomic.AddUint32(&p.stats.Hits, 1)
return cn, nil
}
atomic.AddUint32(&p.stats.Misses, 1)
// zhmark 2024/6/18 如果连接池里没有可用的连接,那么新建连接
newcn, err := p.newConn(ctx, true, isReadCmd)
if err != nil {
p.freeTurn()
return nil, err
}
return newcn, nil
}
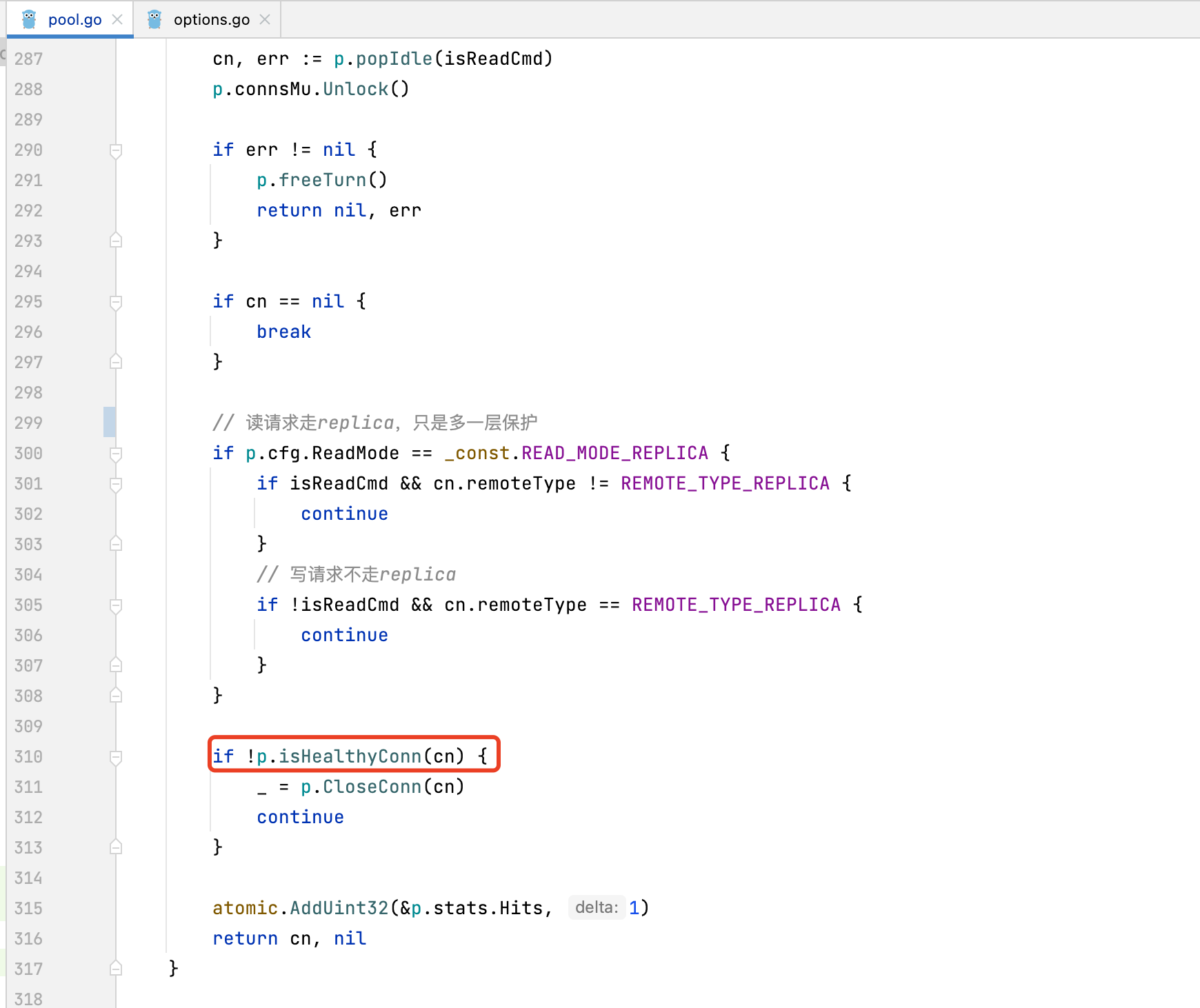
7.1. isHealthyConn内方法解析
// zhmark 2024/7/8 连接关键检查,维护连接池连接健康
func (p *ConnPool) isHealthyConn(cn *Conn) bool {
now := time.Now()
// ConnMaxLifetime 默认为0
if p.cfg.ConnMaxLifetime > 0 && now.Sub(cn.createdAt) >= p.cfg.ConnMaxLifetime {
return false
}
// ConnMaxIdleTime Default is 30 minutes. -1 disables idle timeout check
if p.cfg.ConnMaxIdleTime > 0 && now.Sub(cn.UsedAt()) >= p.cfg.ConnMaxIdleTime {
return false
}
if connCheck(cn.netConn) != nil {
return false
}
cn.SetUsedAt(now)
return true
}
7.1.1. 连接使用时长检验
-
- ConnMaxLifetime默认为0,如果配置了ConnMaxLifetime,那么如果当前时间离连接创建时间超过ConnMaxLifetime,则会判定连接为不健康,进而关闭连接
7.1.2. 连接空闲时长检验
-
- ConnMaxIdleTime,默认为30分钟,如果连接超过ConnMaxIdleTime时间未使用,则会判定连接为不健康
7.1.3. 检查底层网络连接状态
func connCheck(conn net.Conn) error {
// Reset previous timeout.
_ = conn.SetDeadline(time.Time{})
sysConn, ok := conn.(syscall.Conn)
if !ok {
return nil
}
rawConn, err := sysConn.SyscallConn()
if err != nil {
return err
}
var sysErr error
if err := rawConn.Read(func(fd uintptr) bool {
var buf [1]byte
n, err := syscall.Read(int(fd), buf[:])
switch {
case n == 0 && err == nil:
sysErr = io.EOF
case n > 0:
sysErr = errUnexpectedRead
case err == syscall.EAGAIN || err == syscall.EWOULDBLOCK:
sysErr = nil
default:
sysErr = err
}
return true
}); err != nil {
return err
}
return sysErr
}
8. 如何实时监控连接池状态
PoolStats