目录
系统版本说明
hive安装包下载及解压
上传mysql-connector-java的jar包
配置环境变量
进入conf配置文件中,将文件重命名
在hadoop集群上创建文件夹
创建本地目录
修改hive-site.xml文件
同步到其他的节点服务器
修改node02中的配置 hive-site.xml
修改node03节点中的配置文件
修改hive-env.xml文件
同步此文件到其他 的服务器
初始化hive
进入hive
启动hiveserver2
Metastore 高可用
系统版本说明
| 软件 | 版本 |
| Linux | centos3.10.0-1160.71.1.el7.x86_64 |
| hadoop | 2.6.0-cdh5.14.2 |
| JDK | 1.8.0_202 |
| MYSQL | 5.7.44 |
hive安装包下载及解压
本次项目安装的hive版本为:apache-hive-2.2.0-bin.tar.gz
hadoop集群节点的说明:

解压安装包的命令
tar -zxvf apache-hive-2.2.0-bin.tar.gz
上传mysql-connector-java的jar包
上传路径:/opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/lib

本项目使用jar包版本为如图所示的版本。
配置环境变量
Linux脚本命令
vi /etc/profile 或 vim /etc/profile增加hive的路径,这个每个项目存放的位置不同那么路径也不一样。

增加的内容
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin更新环境变量使七生效
source /etc/profile进入conf配置文件中,将文件重命名
mv hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
mv hive-default.xml.template hive-default.xml
mv hive-log4j2.properties.template hive-log4j2.properties
mv hive-exec-log4j2.properties.template hive-exec-log4j2.properties
cp hive-default.xml hive-site.xml
在hadoop集群上创建文件夹
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/tmp
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/hive/log
hdfs dfs -chmod -R 777 /user
创建本地目录
mkdir -p /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/tmp
chmod -R 777 /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/tmp修改hive-site.xml文件
vim hive-site.xml 或用上传工具下载到本地进行更改
这里我们选择下载到本地进行修改较为方便,然后修改完毕后上传覆盖即可
修改hive.exec.scratchdir一项
<property>
<name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name>
<value>/user/hive/tmp</value>
<description>HDFS root scratch dir for Hive jobs which gets created with write all (733) permission. For each connecting user, an HDFS scratch dir: ${hive.exec.scratchdir}/<username> is created, with ${hive.scratch.dir.permission}.</description>
</property>
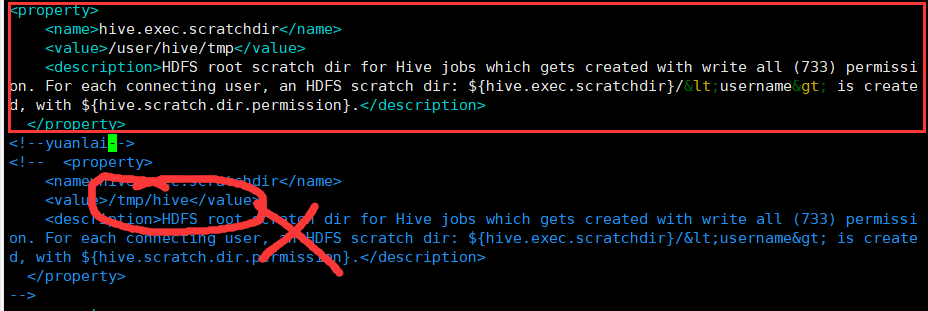
修改 hive.metastore.warehouse.dir
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name>
<value>/user/hive/warehouse</value>
<description>location of default database for the warehouse</description>
</property>
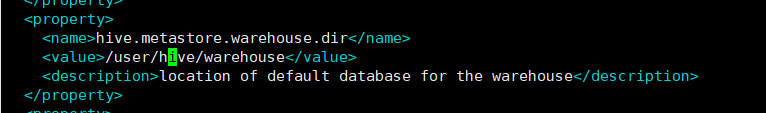
修改hive.querylog.location
<property>
<name>hive.querylog.location</name>
<value>/user/hive/log</value>
<description>Location of Hive run time structured log file</description>
</property>
修改javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false</value>
<description>
JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore.
To use SSL to encrypt/authenticate the connection, provide database-specific SSL flag in the connection URL.
For example, jdbc:postgresql://myhost/db?ssl=true for postgres database.
</description>
</property>
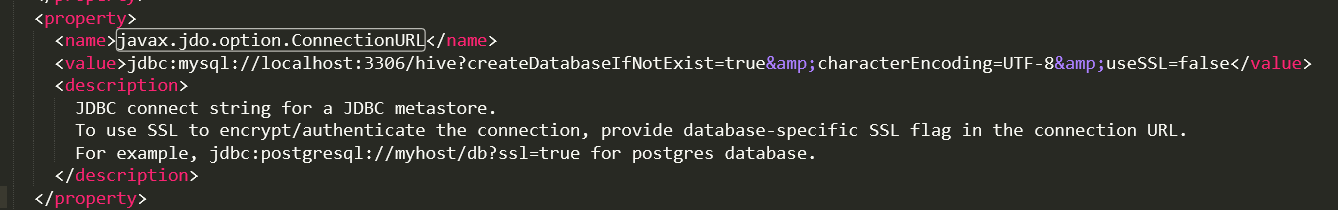
修改javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
<description>Driver class name for a JDBC metastore</description>
</property>
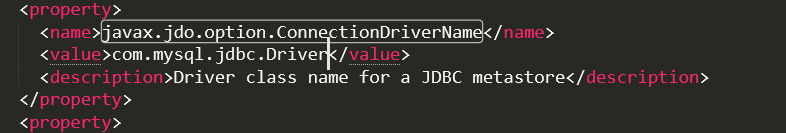
修改javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
<description>Username to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
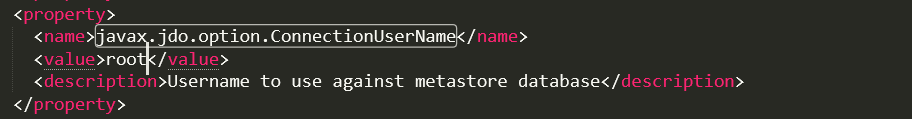
修改javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>root</value>
<description>password to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
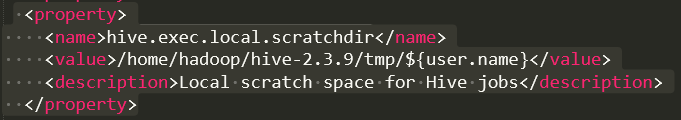
修改hive.exec.local.scratchdir
将文件中的${system:java.io.tmpdir}替换为 /home/hadoop/hive-2.3.9/tmp (对应自己创建的tmp目录位置)
{system:user.name} 改成 {user.name}
<property>
<name>hive.exec.local.scratchdir</name>
<value>/home/hadoop/hive-2.3.9/tmp/${user.name}</value>
<description>Local scratch space for Hive jobs</description>
</property>
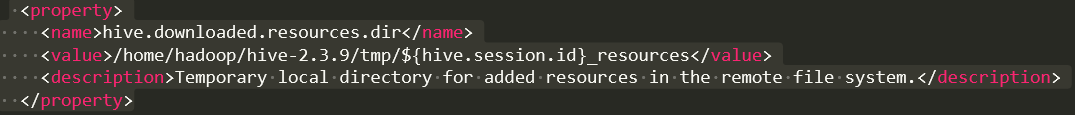
修改hive.downloaded.resources.dir
<property>
<name>hive.downloaded.resources.dir</name>
<value>/home/hadoop/hive-2.3.9/tmp/${hive.session.id}_resources</value>
<description>Temporary local directory for added resources in the remote file system.</description>
</property>
修改hive.server2.logging.operation.log.location
<property>
<name>hive.server2.logging.operation.log.location</name>
<value>/home/hadoop/hive-2.3.9/tmp/${user.name}/operation_logs</value>
<description>Top level directory where operation logs are stored if logging functionality is enabled</description>
</property>

高可用的配置还需要修改如下的内容:
<property>
<name>hive.server2.support.dynamic.service.discovery</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.zookeeper.namespace</name>
<value>hiveserver2_zk</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>node01,node02,node03</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.client.port</name>
<value>2181</value>
</property>
<property>
修改完毕之后,用上传工具将文件上传至原文件夹中覆盖即可.
同步到其他的节点服务器
cd /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/conf
xsync hive-site.xml
修改node02中的配置 hive-site.xml
修改如下内容:
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name>
<value>node02</value>
</property>修改node03节点中的配置文件
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name>
<value>node03</value>
</property>修改hive-env.xml文件
添加如下:
export HADOOP_HOME=/kkb/install/hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.14.2
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin同步此文件到其他 的服务器
cd /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/conf
xsync hive-env.xml初始化hive
cd /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/lib
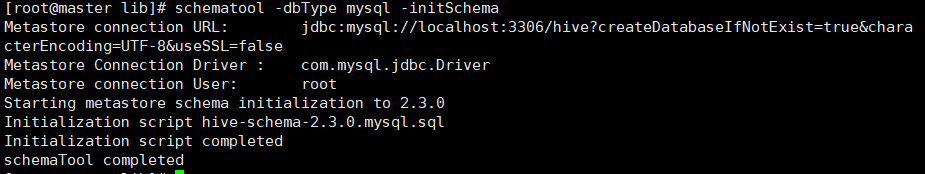
schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema 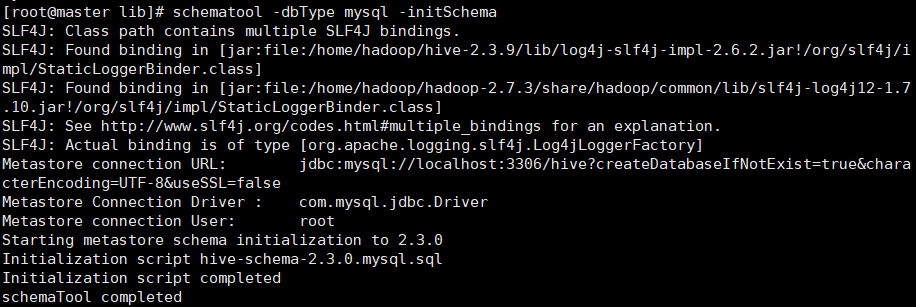
我们这里出现了jar包重复,进入到hive文件夹里的lib根据提示删除log4j-slf4j-impl-2.6.2.jar即可,可用上传工具直接删除,然后进入到mysql中删除hive表,之后退出:exit,再重新进行初始化hive 即可
出现下图即可
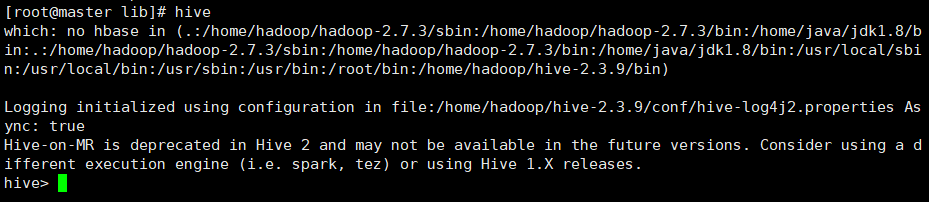
进入hive
直接输入hive即可
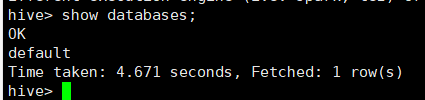
查看数据库
show databases
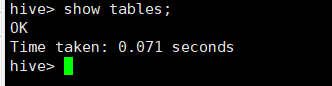
查看表
show tables
退出hive
exit;
启动hiveserver2
### 启动hive 服务
xcall /opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/bin/hive --service hiveserver2Metastore 高可用
同时也需要更修改三个节点的hive-site.xml文件
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.uris</name>
<value>thrift://node01:9083,thrift://node02:9083,thrift://node03:9083<value/>
</property>修改完以上内容,再重启hive。全部部署完成了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?><!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
--><configuration>
<!-- WARNING!!! This file is auto generated for documentation purposes ONLY! -->
<!-- WARNING!!! Any changes you make to this file will be ignored by Hive. -->
<!-- WARNING!!! You must make your changes in hive-site.xml instead. -->
<!-- Hive Execution Parameters -->
<property>
<name>hive.exec.script.wrapper</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.plan</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.stagingdir</name>
<value>.hive-staging</value>
<description>Directory name that will be created inside table locations in order to support HDFS encryption. This is replaces ${hive.exec.scratchdir} for query results with the exception of read-only tables. In all cases ${hive.exec.scratchdir} is still used for other temporary files, such as job plans.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.scratchdir</name>
<value>/user/hive/tmp</value>
<description>HDFS root scratch dir for Hive jobs which gets created with write all (733) permission. For each connecting user, an HDFS scratch dir: ${hive.exec.scratchdir}/<username> is created, with ${hive.scratch.dir.permission}.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.rootdir</name>
<value>/user/hive/repl/</value>
<description>HDFS root dir for all replication dumps.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.cm.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Turn on ChangeManager, so delete files will go to cmrootdir.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.cmrootdir</name>
<value>/user/hive/cmroot/</value>
<description>Root dir for ChangeManager, used for deleted files.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.cm.retain</name>
<value>24h</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is hour if not specified.
Time to retain removed files in cmrootdir.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.cm.interval</name>
<value>3600s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Inteval for cmroot cleanup thread.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.local.scratchdir</name>
<value>/opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/tmp/${user.name}</value>
<description>Local scratch space for Hive jobs</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.downloaded.resources.dir</name>
<value>/opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/tmp/${hive.session.id}_resources</value>
<description>Temporary local directory for added resources in the remote file system.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.scratch.dir.permission</name>
<value>700</value>
<description>The permission for the user specific scratch directories that get created.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.submitviachild</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.submit.local.task.via.child</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Determines whether local tasks (typically mapjoin hashtable generation phase) runs in
separate JVM (true recommended) or not.
Avoids the overhead of spawning new JVM, but can lead to out-of-memory issues.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.script.maxerrsize</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of bytes a script is allowed to emit to standard error (per map-reduce task).
This prevents runaway scripts from filling logs partitions to capacity
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.script.allow.partial.consumption</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When enabled, this option allows a user script to exit successfully without consuming
all the data from the standard input.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>stream.stderr.reporter.prefix</name>
<value>reporter:</value>
<description>Streaming jobs that log to standard error with this prefix can log counter or status information.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>stream.stderr.reporter.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enable consumption of status and counter messages for streaming jobs.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.compress.output</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This controls whether the final outputs of a query (to a local/HDFS file or a Hive table) is compressed.
The compression codec and other options are determined from Hadoop config variables mapred.output.compress*
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.compress.intermediate</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This controls whether intermediate files produced by Hive between multiple map-reduce jobs are compressed.
The compression codec and other options are determined from Hadoop config variables mapred.output.compress*
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.intermediate.compression.codec</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.intermediate.compression.type</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer</name>
<value>256000000</value>
<description>size per reducer.The default is 256Mb, i.e if the input size is 1G, it will use 4 reducers.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.reducers.max</name>
<value>1009</value>
<description>
max number of reducers will be used. If the one specified in the configuration parameter mapred.reduce.tasks is
negative, Hive will use this one as the max number of reducers when automatically determine number of reducers.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.pre.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated list of pre-execution hooks to be invoked for each statement.
A pre-execution hook is specified as the name of a Java class which implements the
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.hooks.ExecuteWithHookContext interface.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.post.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated list of post-execution hooks to be invoked for each statement.
A post-execution hook is specified as the name of a Java class which implements the
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.hooks.ExecuteWithHookContext interface.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.failure.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated list of on-failure hooks to be invoked for each statement.
An on-failure hook is specified as the name of Java class which implements the
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.hooks.ExecuteWithHookContext interface.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.query.redactor.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated list of hooks to be invoked for each query which can
tranform the query before it's placed in the job.xml file. Must be a Java class which
extends from the org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.hooks.Redactor abstract class.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.client.stats.publishers</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated list of statistics publishers to be invoked on counters on each job.
A client stats publisher is specified as the name of a Java class which implements the
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.stats.ClientStatsPublisher interface.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ats.hook.queue.capacity</name>
<value>64</value>
<description>
Queue size for the ATS Hook executor. If the number of outstanding submissions
to the ATS executor exceed this amount, the Hive ATS Hook will not try to log queries to ATS.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.parallel</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to execute jobs in parallel</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.parallel.thread.number</name>
<value>8</value>
<description>How many jobs at most can be executed in parallel</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapred.reduce.tasks.speculative.execution</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether speculative execution for reducers should be turned on. </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.counters.pull.interval</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>
The interval with which to poll the JobTracker for the counters the running job.
The smaller it is the more load there will be on the jobtracker, the higher it is the less granular the caught will be.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.dynamic.partition</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether or not to allow dynamic partitions in DML/DDL.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode</name>
<value>strict</value>
<description>
In strict mode, the user must specify at least one static partition
in case the user accidentally overwrites all partitions.
In nonstrict mode all partitions are allowed to be dynamic.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Maximum number of dynamic partitions allowed to be created in total.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>Maximum number of dynamic partitions allowed to be created in each mapper/reducer node.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.max.created.files</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>Maximum number of HDFS files created by all mappers/reducers in a MapReduce job.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.default.partition.name</name>
<value>__HIVE_DEFAULT_PARTITION__</value>
<description>
The default partition name in case the dynamic partition column value is null/empty string or any other values that cannot be escaped.
This value must not contain any special character used in HDFS URI (e.g., ':', '%', '/' etc).
The user has to be aware that the dynamic partition value should not contain this value to avoid confusions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lockmgr.zookeeper.default.partition.name</name>
<value>__HIVE_DEFAULT_ZOOKEEPER_PARTITION__</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.show.job.failure.debug.info</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If a job fails, whether to provide a link in the CLI to the task with the
most failures, along with debugging hints if applicable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.job.debug.capture.stacktraces</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether or not stack traces parsed from the task logs of a sampled failed task
for each failed job should be stored in the SessionState
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.job.debug.timeout</name>
<value>30000</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.tasklog.debug.timeout</name>
<value>20000</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.output.file.extension</name>
<value/>
<description>
String used as a file extension for output files.
If not set, defaults to the codec extension for text files (e.g. ".gz"), or no extension otherwise.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.mode.local.auto</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Let Hive determine whether to run in local mode automatically</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.mode.local.auto.inputbytes.max</name>
<value>134217728</value>
<description>When hive.exec.mode.local.auto is true, input bytes should less than this for local mode.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.mode.local.auto.input.files.max</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>When hive.exec.mode.local.auto is true, the number of tasks should less than this for local mode.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.drop.ignorenonexistent</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Do not report an error if DROP TABLE/VIEW/Index/Function specifies a non-existent table/view/index/function</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ignore.mapjoin.hint</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Ignore the mapjoin hint</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.file.max.footer</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>maximum number of lines for footer user can define for a table file</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.resultset.use.unique.column.names</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Make column names unique in the result set by qualifying column names with table alias if needed.
Table alias will be added to column names for queries of type "select *" or
if query explicitly uses table alias "select r1.x..".
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>fs.har.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.shims.HiveHarFileSystem</value>
<description>The implementation for accessing Hadoop Archives. Note that this won't be applicable to Hadoop versions less than 0.20</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name>
<value>/user/hive/warehouse</value>
<description>location of default database for the warehouse</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.uris</name>
<value/>
<description>Thrift URI for the remote metastore. Used by metastore client to connect to remote metastore.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.fastpath</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Used to avoid all of the proxies and object copies in the metastore. Note, if this is set, you MUST use a local metastore (hive.metastore.uris must be empty) otherwise undefined and most likely undesired behavior will result</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.fshandler.threads</name>
<value>15</value>
<description>Number of threads to be allocated for metastore handler for fs operations.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.catalog.cache.size</name>
<value>50000</value>
<description>Maximum number of objects we will place in the hbase metastore catalog cache. The objects will be divided up by types that we need to cache.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggregate.stats.cache.size</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Maximum number of aggregate stats nodes that we will place in the hbase metastore aggregate stats cache.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggregate.stats.max.partitions</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Maximum number of partitions that are aggregated per cache node.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggregate.stats.false.positive.probability</name>
<value>0.01</value>
<description>Maximum false positive probability for the Bloom Filter used in each aggregate stats cache node (default 1%).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggregate.stats.max.variance</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>Maximum tolerable variance in number of partitions between a cached node and our request (default 10%).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.cache.ttl</name>
<value>600s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds for a cached node to be active in the cache before they become stale.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.cache.max.writer.wait</name>
<value>5000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Number of milliseconds a writer will wait to acquire the writelock before giving up.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.cache.max.reader.wait</name>
<value>1000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Number of milliseconds a reader will wait to acquire the readlock before giving up.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.cache.max.full</name>
<value>0.9</value>
<description>Maximum cache full % after which the cache cleaner thread kicks in.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.cache.clean.until</name>
<value>0.8</value>
<description>The cleaner thread cleans until cache reaches this % full size.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.connection.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.hbase.VanillaHBaseConnection</value>
<description>Class used to connection to HBase</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggr.stats.cache.entries</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>How many in stats objects to cache in memory</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggr.stats.memory.ttl</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds stats objects live in memory after they are read from HBase.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggr.stats.invalidator.frequency</name>
<value>5s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
How often the stats cache scans its HBase entries and looks for expired entries
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.aggr.stats.hbase.ttl</name>
<value>604800s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds stats entries live in HBase cache after they are created. They may be invalided by updates or partition drops before this. Default is one week.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.hbase.file.metadata.threads</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Number of threads to use to read file metadata in background to cache it.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.connect.retries</name>
<value>3</value>
<description>Number of retries while opening a connection to metastore</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.failure.retries</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Number of retries upon failure of Thrift metastore calls</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.port</name>
<value>9083</value>
<description>Hive metastore listener port</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.client.connect.retry.delay</name>
<value>1s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds for the client to wait between consecutive connection attempts
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.client.socket.timeout</name>
<value>600s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
MetaStore Client socket timeout in seconds
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.client.socket.lifetime</name>
<value>0s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
MetaStore Client socket lifetime in seconds. After this time is exceeded, client
reconnects on the next MetaStore operation. A value of 0s means the connection
has an infinite lifetime.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>asd123</value>
<description>password to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.ds.connection.url.hook</name>
<value/>
<description>Name of the hook to use for retrieving the JDO connection URL. If empty, the value in javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL is used</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.Multithreaded</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Set this to true if multiple threads access metastore through JDO concurrently.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.108:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false</value>
<description>
JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore.
To use SSL to encrypt/authenticate the connection, provide database-specific SSL flag in the connection URL.
For example, jdbc:postgresql://myhost/db?ssl=true for postgres database.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.dbaccess.ssl.properties</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma-separated SSL properties for metastore to access database when JDO connection URL
enables SSL access. e.g. javax.net.ssl.trustStore=/tmp/truststore,javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=pwd.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hmshandler.retry.attempts</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>The number of times to retry a HMSHandler call if there were a connection error.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hmshandler.retry.interval</name>
<value>2000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
The time between HMSHandler retry attempts on failure.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hmshandler.force.reload.conf</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to force reloading of the HMSHandler configuration (including
the connection URL, before the next metastore query that accesses the
datastore. Once reloaded, this value is reset to false. Used for
testing only.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.server.max.message.size</name>
<value>104857600</value>
<description>Maximum message size in bytes a HMS will accept.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.server.min.threads</name>
<value>200</value>
<description>Minimum number of worker threads in the Thrift server's pool.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.server.max.threads</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Maximum number of worker threads in the Thrift server's pool.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.server.tcp.keepalive</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable TCP keepalive for the metastore server. Keepalive will prevent accumulation of half-open connections.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.archive.intermediate.original</name>
<value>_INTERMEDIATE_ORIGINAL</value>
<description>
Intermediate dir suffixes used for archiving. Not important what they
are, as long as collisions are avoided
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.archive.intermediate.archived</name>
<value>_INTERMEDIATE_ARCHIVED</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.archive.intermediate.extracted</name>
<value>_INTERMEDIATE_EXTRACTED</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.kerberos.keytab.file</name>
<value/>
<description>The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the metastore Thrift server's service principal.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.kerberos.principal</name>
<value>hive-metastore/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM</value>
<description>
The service principal for the metastore Thrift server.
The special string _HOST will be replaced automatically with the correct host name.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.sasl.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If true, the metastore Thrift interface will be secured with SASL. Clients must authenticate with Kerberos.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.thrift.framed.transport.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If true, the metastore Thrift interface will use TFramedTransport. When false (default) a standard TTransport is used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.thrift.compact.protocol.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If true, the metastore Thrift interface will use TCompactProtocol. When false (default) TBinaryProtocol will be used.
Setting it to true will break compatibility with older clients running TBinaryProtocol.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.token.signature</name>
<value/>
<description>The delegation token service name to match when selecting a token from the current user's tokens.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cluster.delegation.token.store.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.thrift.MemoryTokenStore</value>
<description>The delegation token store implementation. Set to org.apache.hadoop.hive.thrift.ZooKeeperTokenStore for load-balanced cluster.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cluster.delegation.token.store.zookeeper.connectString</name>
<value/>
<description>
The ZooKeeper token store connect string. You can re-use the configuration value
set in hive.zookeeper.quorum, by leaving this parameter unset.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cluster.delegation.token.store.zookeeper.znode</name>
<value>/hivedelegation</value>
<description>
The root path for token store data. Note that this is used by both HiveServer2 and
MetaStore to store delegation Token. One directory gets created for each of them.
The final directory names would have the servername appended to it (HIVESERVER2,
METASTORE).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cluster.delegation.token.store.zookeeper.acl</name>
<value/>
<description>
ACL for token store entries. Comma separated list of ACL entries. For example:
sasl:hive/host1@MY.DOMAIN:cdrwa,sasl:hive/host2@MY.DOMAIN:cdrwa
Defaults to all permissions for the hiveserver2/metastore process user.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.cache.pinobjtypes</name>
<value>Table,StorageDescriptor,SerDeInfo,Partition,Database,Type,FieldSchema,Order</value>
<description>List of comma separated metastore object types that should be pinned in the cache</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.connectionPoolingType</name>
<value>BONECP</value>
<description>
Expects one of [bonecp, dbcp, hikaricp, none].
Specify connection pool library for datanucleus
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.rdbms.initializeColumnInfo</name>
<value>NONE</value>
<description>initializeColumnInfo setting for DataNucleus; set to NONE at least on Postgres.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.schema.validateTables</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>validates existing schema against code. turn this on if you want to verify existing schema</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.schema.validateColumns</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>validates existing schema against code. turn this on if you want to verify existing schema</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.schema.validateConstraints</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>validates existing schema against code. turn this on if you want to verify existing schema</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.storeManagerType</name>
<value>rdbms</value>
<description>metadata store type</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.schema.autoCreateAll</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Auto creates necessary schema on a startup if one doesn't exist. Set this to false, after creating it once.To enable auto create also set hive.metastore.schema.verification=false. Auto creation is not recommended for production use cases, run schematool command instead.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.schema.verification</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Enforce metastore schema version consistency.
True: Verify that version information stored in is compatible with one from Hive jars. Also disable automatic
schema migration attempt. Users are required to manually migrate schema after Hive upgrade which ensures
proper metastore schema migration. (Default)
False: Warn if the version information stored in metastore doesn't match with one from in Hive jars.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.schema.verification.record.version</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When true the current MS version is recorded in the VERSION table. If this is disabled and verification is
enabled the MS will be unusable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.transactionIsolation</name>
<value>read-committed</value>
<description>Default transaction isolation level for identity generation.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.cache.level2</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Use a level 2 cache. Turn this off if metadata is changed independently of Hive metastore server</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.cache.level2.type</name>
<value>none</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.identifierFactory</name>
<value>datanucleus1</value>
<description>
Name of the identifier factory to use when generating table/column names etc.
'datanucleus1' is used for backward compatibility with DataNucleus v1
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.rdbms.useLegacyNativeValueStrategy</name>
<value>true</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>datanucleus.plugin.pluginRegistryBundleCheck</name>
<value>LOG</value>
<description>Defines what happens when plugin bundles are found and are duplicated [EXCEPTION|LOG|NONE]</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.batch.retrieve.max</name>
<value>300</value>
<description>
Maximum number of objects (tables/partitions) can be retrieved from metastore in one batch.
The higher the number, the less the number of round trips is needed to the Hive metastore server,
but it may also cause higher memory requirement at the client side.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.batch.retrieve.table.partition.max</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Maximum number of objects that metastore internally retrieves in one batch.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.init.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>
A comma separated list of hooks to be invoked at the beginning of HMSHandler initialization.
An init hook is specified as the name of Java class which extends org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.MetaStoreInitListener.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.pre.event.listeners</name>
<value/>
<description>List of comma separated listeners for metastore events.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.listeners</name>
<value/>
<description>A comma separated list of Java classes that implement the org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.MetaStoreEventListener interface. The metastore event and corresponding listener method will be invoked in separate JDO transactions. Alternatively, configure hive.metastore.transactional.event.listeners to ensure both are invoked in same JDO transaction.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.transactional.event.listeners</name>
<value/>
<description>A comma separated list of Java classes that implement the org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.MetaStoreEventListener interface. Both the metastore event and corresponding listener method will be invoked in the same JDO transaction.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.db.listener.timetolive</name>
<value>86400s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
time after which events will be removed from the database listener queue
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.authorization.storage.checks</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Should the metastore do authorization checks against the underlying storage (usually hdfs)
for operations like drop-partition (disallow the drop-partition if the user in
question doesn't have permissions to delete the corresponding directory
on the storage).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.authorization.storage.check.externaltable.drop</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Should StorageBasedAuthorization check permission of the storage before dropping external table.
StorageBasedAuthorization already does this check for managed table. For external table however,
anyone who has read permission of the directory could drop external table, which is surprising.
The flag is set to false by default to maintain backward compatibility.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.clean.freq</name>
<value>0s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Frequency at which timer task runs to purge expired events in metastore.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.expiry.duration</name>
<value>0s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Duration after which events expire from events table
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.event.message.factory</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.messaging.json.JSONMessageFactory</value>
<description>Factory class for making encoding and decoding messages in the events generated.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.execute.setugi</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
In unsecure mode, setting this property to true will cause the metastore to execute DFS operations using
the client's reported user and group permissions. Note that this property must be set on
both the client and server sides. Further note that its best effort.
If client sets its to true and server sets it to false, client setting will be ignored.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.partition.name.whitelist.pattern</name>
<value/>
<description>Partition names will be checked against this regex pattern and rejected if not matched.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.integral.jdo.pushdown</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Allow JDO query pushdown for integral partition columns in metastore. Off by default. This
improves metastore perf for integral columns, especially if there's a large number of partitions.
However, it doesn't work correctly with integral values that are not normalized (e.g. have
leading zeroes, like 0012). If metastore direct SQL is enabled and works, this optimization
is also irrelevant.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.try.direct.sql</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether the Hive metastore should try to use direct SQL queries instead of the
DataNucleus for certain read paths. This can improve metastore performance when
fetching many partitions or column statistics by orders of magnitude; however, it
is not guaranteed to work on all RDBMS-es and all versions. In case of SQL failures,
the metastore will fall back to the DataNucleus, so it's safe even if SQL doesn't
work for all queries on your datastore. If all SQL queries fail (for example, your
metastore is backed by MongoDB), you might want to disable this to save the
try-and-fall-back cost.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.direct.sql.batch.size</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
Batch size for partition and other object retrieval from the underlying DB in direct
SQL. For some DBs like Oracle and MSSQL, there are hardcoded or perf-based limitations
that necessitate this. For DBs that can handle the queries, this isn't necessary and
may impede performance. -1 means no batching, 0 means automatic batching.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.try.direct.sql.ddl</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Same as hive.metastore.try.direct.sql, for read statements within a transaction that
modifies metastore data. Due to non-standard behavior in Postgres, if a direct SQL
select query has incorrect syntax or something similar inside a transaction, the
entire transaction will fail and fall-back to DataNucleus will not be possible. You
should disable the usage of direct SQL inside transactions if that happens in your case.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.direct.sql.max.query.length</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>
The maximum
size of a query string (in KB).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.direct.sql.max.elements.in.clause</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>
The maximum number of values in a IN clause. Once exceeded, it will be broken into
multiple OR separated IN clauses.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.direct.sql.max.elements.values.clause</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>The maximum number of values in a VALUES clause for INSERT statement.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.orm.retrieveMapNullsAsEmptyStrings</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Thrift does not support nulls in maps, so any nulls present in maps retrieved from ORM must either be pruned or converted to empty strings. Some backing dbs such as Oracle persist empty strings as nulls, so we should set this parameter if we wish to reverse that behaviour. For others, pruning is the correct behaviour</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.disallow.incompatible.col.type.changes</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If true (default is false), ALTER TABLE operations which change the type of a
column (say STRING) to an incompatible type (say MAP) are disallowed.
RCFile default SerDe (ColumnarSerDe) serializes the values in such a way that the
datatypes can be converted from string to any type. The map is also serialized as
a string, which can be read as a string as well. However, with any binary
serialization, this is not true. Blocking the ALTER TABLE prevents ClassCastExceptions
when subsequently trying to access old partitions.
Primitive types like INT, STRING, BIGINT, etc., are compatible with each other and are
not blocked.
See HIVE-4409 for more details.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.table.parameters.default</name>
<value/>
<description>Default property values for newly created tables</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ddl.createtablelike.properties.whitelist</name>
<value/>
<description>Table Properties to copy over when executing a Create Table Like.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.rawstore.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.ObjectStore</value>
<description>
Name of the class that implements org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.rawstore interface.
This class is used to store and retrieval of raw metadata objects such as table, database
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.txn.store.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.CompactionTxnHandler</value>
<description>Name of class that implements org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.txn.TxnStore. This class is used to store and retrieve transactions and locks</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
<description>Driver class name for a JDBC metastore</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.PersistenceManagerFactoryClass</name>
<value>org.datanucleus.api.jdo.JDOPersistenceManagerFactory</value>
<description>class implementing the jdo persistence</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.expression.proxy</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.optimizer.ppr.PartitionExpressionForMetastore</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.DetachAllOnCommit</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Detaches all objects from session so that they can be used after transaction is committed</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.NonTransactionalRead</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Reads outside of transactions</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>hive</value>
<description>Username to use against metastore database</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.end.function.listeners</name>
<value/>
<description>List of comma separated listeners for the end of metastore functions.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.partition.inherit.table.properties</name>
<value/>
<description>
List of comma separated keys occurring in table properties which will get inherited to newly created partitions.
* implies all the keys will get inherited.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.filter.hook</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.DefaultMetaStoreFilterHookImpl</value>
<description>Metastore hook class for filtering the metadata read results. If hive.security.authorization.manageris set to instance of HiveAuthorizerFactory, then this value is ignored.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.dml.events</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If true, the metastore will be asked to fire events for DML operations</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.client.drop.partitions.using.expressions</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Choose whether dropping partitions with HCatClient pushes the partition-predicate to the metastore, or drops partitions iteratively</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether aggregate stats caching is enabled or not.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.size</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Maximum number of aggregate stats nodes that we will place in the metastore aggregate stats cache.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.max.partitions</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Maximum number of partitions that are aggregated per cache node.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.fpp</name>
<value>0.01</value>
<description>Maximum false positive probability for the Bloom Filter used in each aggregate stats cache node (default 1%).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.max.variance</name>
<value>0.01</value>
<description>Maximum tolerable variance in number of partitions between a cached node and our request (default 1%).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.ttl</name>
<value>600s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds for a cached node to be active in the cache before they become stale.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.max.writer.wait</name>
<value>5000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Number of milliseconds a writer will wait to acquire the writelock before giving up.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.max.reader.wait</name>
<value>1000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Number of milliseconds a reader will wait to acquire the readlock before giving up.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.max.full</name>
<value>0.9</value>
<description>Maximum cache full % after which the cache cleaner thread kicks in.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.aggregate.stats.cache.clean.until</name>
<value>0.8</value>
<description>The cleaner thread cleans until cache reaches this % full size.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.metrics.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Enable metrics on the metastore.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.initial.metadata.count.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enable a metadata count at metastore startup for metrics.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metadata.export.location</name>
<value/>
<description>
When used in conjunction with the org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.parse.MetaDataExportListener pre event listener,
it is the location to which the metadata will be exported. The default is an empty string, which results in the
metadata being exported to the current user's home directory on HDFS.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metadata.move.exported.metadata.to.trash</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
When used in conjunction with the org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.parse.MetaDataExportListener pre event listener,
this setting determines if the metadata that is exported will subsequently be moved to the user's trash directory
alongside the dropped table data. This ensures that the metadata will be cleaned up along with the dropped table data.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.errors.ignore</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.current.db</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to include the current database in the Hive prompt.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.prompt</name>
<value>hive</value>
<description>
Command line prompt configuration value. Other hiveconf can be used in this configuration value.
Variable substitution will only be invoked at the Hive CLI startup.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.pretty.output.num.cols</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
The number of columns to use when formatting output generated by the DESCRIBE PRETTY table_name command.
If the value of this property is -1, then Hive will use the auto-detected terminal width.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.fs.handler.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.HiveMetaStoreFsImpl</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.session.id</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.session.silent</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.session.history.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to log Hive query, query plan, runtime statistics etc.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.query.string</name>
<value/>
<description>Query being executed (might be multiple per a session)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.query.id</name>
<value/>
<description>ID for query being executed (might be multiple per a session)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.jobname.length</name>
<value>50</value>
<description>max jobname length</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.jar.path</name>
<value/>
<description>The location of hive_cli.jar that is used when submitting jobs in a separate jvm.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.aux.jars.path</name>
<value/>
<description>The location of the plugin jars that contain implementations of user defined functions and serdes.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.reloadable.aux.jars.path</name>
<value/>
<description>
The locations of the plugin jars, which can be a comma-separated folders or jars. Jars can be renewed
by executing reload command. And these jars can be used as the auxiliary classes like creating a UDF or SerDe.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.added.files.path</name>
<value/>
<description>This an internal parameter.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.added.jars.path</name>
<value/>
<description>This an internal parameter.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.added.archives.path</name>
<value/>
<description>This an internal parameter.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.progress.timeout</name>
<value>0s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
How long to run autoprogressor for the script/UDTF operators.
Set to 0 for forever.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.auto.progress</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether Hive Transform/Map/Reduce Clause should automatically send progress information to TaskTracker
to avoid the task getting killed because of inactivity. Hive sends progress information when the script is
outputting to stderr. This option removes the need of periodically producing stderr messages,
but users should be cautious because this may prevent infinite loops in the scripts to be killed by TaskTracker.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.operator.id.env.var</name>
<value>HIVE_SCRIPT_OPERATOR_ID</value>
<description>
Name of the environment variable that holds the unique script operator ID in the user's
transform function (the custom mapper/reducer that the user has specified in the query)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.operator.truncate.env</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Truncate each environment variable for external script in scripts operator to 20KB (to fit system limits)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.operator.env.blacklist</name>
<value>hive.txn.valid.txns,hive.script.operator.env.blacklist</value>
<description>Comma separated list of keys from the configuration file not to convert to environment variables when envoking the script operator</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.strict.checks.large.query</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Enabling strict large query checks disallows the following:
Orderby without limit.
No partition being picked up for a query against partitioned table.
Note that these checks currently do not consider data size, only the query pattern.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.strict.checks.type.safety</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Enabling strict type safety checks disallows the following:
Comparing bigints and strings.
Comparing bigints and doubles.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.strict.checks.cartesian.product</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Enabling strict large query checks disallows the following:
Cartesian product (cross join).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapred.mode</name>
<value>nonstrict</value>
<description>Deprecated; use hive.strict.checks.* settings instead.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.alias</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.map.aggr</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to use map-side aggregation in Hive Group By queries</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.groupby.skewindata</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether there is skew in data to optimize group by queries</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.join.emit.interval</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>How many rows in the right-most join operand Hive should buffer before emitting the join result.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.join.cache.size</name>
<value>25000</value>
<description>How many rows in the joining tables (except the streaming table) should be cached in memory.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.enable</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Flag to control enabling Cost Based Optimizations using Calcite framework.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.cnf.maxnodes</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>When converting to conjunctive normal form (CNF), fail ifthe expression exceeds this threshold; the threshold is expressed in terms of number of nodes (leaves andinterior nodes). -1 to not set up a threshold.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.returnpath.hiveop</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Flag to control calcite plan to hive operator conversion</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.extended</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Flag to control enabling the extended cost model based onCPU, IO and cardinality. Otherwise, the cost model is based on cardinality.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.cpu</name>
<value>0.000001</value>
<description>Default cost of a comparison</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.network</name>
<value>150.0</value>
<description>Default cost of a transfering a byte over network; expressed as multiple of CPU cost</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.local.fs.write</name>
<value>4.0</value>
<description>Default cost of writing a byte to local FS; expressed as multiple of NETWORK cost</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.local.fs.read</name>
<value>4.0</value>
<description>Default cost of reading a byte from local FS; expressed as multiple of NETWORK cost</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.hdfs.write</name>
<value>10.0</value>
<description>Default cost of writing a byte to HDFS; expressed as multiple of Local FS write cost</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.costmodel.hdfs.read</name>
<value>1.5</value>
<description>Default cost of reading a byte from HDFS; expressed as multiple of Local FS read cost</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cbo.show.warnings</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Toggle display of CBO warnings like missing column stats</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.transpose.aggr.join</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>push aggregates through join</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.semijoin.conversion</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>convert group by followed by inner equi join into semijoin</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.order.columnalignment</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Flag to control whether we want to try to aligncolumns in operators such as Aggregate or Join so that we try to reduce the number of shuffling stages</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.bucket.cache.size</name>
<value>100</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether Hive should use memory-optimized hash table for MapJoin.
Only works on Tez and Spark, because memory-optimized hashtable cannot be serialized.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable.probe.percent</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>Probing space percentage of the optimized hashtable</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.hybridgrace.hashtable</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to use hybridgrace hash join as the join method for mapjoin. Tez only.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.hybridgrace.memcheckfrequency</name>
<value>1024</value>
<description>For hybrid grace hash join, how often (how many rows apart) we check if memory is full. This number should be power of 2.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.hybridgrace.minwbsize</name>
<value>524288</value>
<description>For hybrid graceHash join, the minimum write buffer size used by optimized hashtable. Default is 512 KB.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.hybridgrace.minnumpartitions</name>
<value>16</value>
<description>ForHybrid grace hash join, the minimum number of partitions to create.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable.wbsize</name>
<value>8388608</value>
<description>
Optimized hashtable (see hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable) uses a chain of buffers to
store data. This is one buffer size. HT may be slightly faster if this is larger, but for small
joins unnecessary memory will be allocated and then trimmed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.hybridgrace.bloomfilter</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to use BloomFilter in Hybrid grace hash join to minimize unnecessary spilling.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.smbjoin.cache.rows</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>How many rows with the same key value should be cached in memory per smb joined table.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.groupby.mapaggr.checkinterval</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>Number of rows after which size of the grouping keys/aggregation classes is performed</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.map.aggr.hash.percentmemory</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>Portion of total memory to be used by map-side group aggregation hash table</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.followby.map.aggr.hash.percentmemory</name>
<value>0.3</value>
<description>Portion of total memory to be used by map-side group aggregation hash table, when this group by is followed by map join</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.map.aggr.hash.force.flush.memory.threshold</name>
<value>0.9</value>
<description>
The max memory to be used by map-side group aggregation hash table.
If the memory usage is higher than this number, force to flush data
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.map.aggr.hash.min.reduction</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>
Hash aggregation will be turned off if the ratio between hash table size and input rows is bigger than this number.
Set to 1 to make sure hash aggregation is never turned off.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.multigroupby.singlereducer</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to optimize multi group by query to generate single M/R job plan. If the multi group by query has
common group by keys, it will be optimized to generate single M/R job.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.map.groupby.sorted</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If the bucketing/sorting properties of the table exactly match the grouping key, whether to perform
the group by in the mapper by using BucketizedHiveInputFormat. The only downside to this
is that it limits the number of mappers to the number of files.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.groupby.position.alias</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable using Column Position Alias in Group By</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orderby.position.alias</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable using Column Position Alias in Order By</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.groupby.orderby.position.alias</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to enable using Column Position Alias in Group By or Order By (deprecated).
Use hive.orderby.position.alias or hive.groupby.position.alias instead
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.new.job.grouping.set.cardinality</name>
<value>30</value>
<description>
Whether a new map-reduce job should be launched for grouping sets/rollups/cubes.
For a query like: select a, b, c, count(1) from T group by a, b, c with rollup;
4 rows are created per row: (a, b, c), (a, b, null), (a, null, null), (null, null, null).
This can lead to explosion across map-reduce boundary if the cardinality of T is very high,
and map-side aggregation does not do a very good job.
This parameter decides if Hive should add an additional map-reduce job. If the grouping set
cardinality (4 in the example above), is more than this value, a new MR job is added under the
assumption that the original group by will reduce the data size.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.groupby.limit.extrastep</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This parameter decides if Hive should
create new MR job for sorting final output
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.copyfile.maxsize</name>
<value>33554432</value>
<description>Maximum file size (in Mb) that Hive uses to do single HDFS copies between directories.Distributed copies (distcp) will be used instead for bigger files so that copies can be done faster.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.udtf.auto.progress</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether Hive should automatically send progress information to TaskTracker
when using UDTF's to prevent the task getting killed because of inactivity. Users should be cautious
because this may prevent TaskTracker from killing tasks with infinite loops.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.default.fileformat</name>
<value>TextFile</value>
<description>
Expects one of [textfile, sequencefile, rcfile, orc].
Default file format for CREATE TABLE statement. Users can explicitly override it by CREATE TABLE ... STORED AS [FORMAT]
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.default.fileformat.managed</name>
<value>none</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, textfile, sequencefile, rcfile, orc].
Default file format for CREATE TABLE statement applied to managed tables only. External tables will be
created with format specified by hive.default.fileformat. Leaving this null will result in using hive.default.fileformat
for all tables.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.query.result.fileformat</name>
<value>SequenceFile</value>
<description>
Expects one of [textfile, sequencefile, rcfile, llap].
Default file format for storing result of the query.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.fileformat.check</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to check file format or not when loading data files</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.default.rcfile.serde</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.columnar.LazyBinaryColumnarSerDe</value>
<description>The default SerDe Hive will use for the RCFile format</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.default.serde</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe</value>
<description>The default SerDe Hive will use for storage formats that do not specify a SerDe.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.serdes.using.metastore.for.schema</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.orc.OrcSerde,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.columnar.ColumnarSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.dynamic_type.DynamicSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.MetadataTypedColumnsetSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.columnar.LazyBinaryColumnarSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.parquet.serde.ParquetHiveSerDe,org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazybinary.LazyBinarySerDe</value>
<description>SerDes retrieving schema from metastore. This is an internal parameter.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.querylog.location</name>
<value>/user/hive/log</value>
<description>Location of Hive run time structured log file</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.querylog.enable.plan.progress</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to log the plan's progress every time a job's progress is checked.
These logs are written to the location specified by hive.querylog.location
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.querylog.plan.progress.interval</name>
<value>60000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
The interval to wait between logging the plan's progress.
If there is a whole number percentage change in the progress of the mappers or the reducers,
the progress is logged regardless of this value.
The actual interval will be the ceiling of (this value divided by the value of
hive.exec.counters.pull.interval) multiplied by the value of hive.exec.counters.pull.interval
I.e. if it is not divide evenly by the value of hive.exec.counters.pull.interval it will be
logged less frequently than specified.
This only has an effect if hive.querylog.enable.plan.progress is set to true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.serde</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.lazy.LazySimpleSerDe</value>
<description>The default SerDe for transmitting input data to and reading output data from the user scripts. </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.recordreader</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.TextRecordReader</value>
<description>The default record reader for reading data from the user scripts. </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.script.recordwriter</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.TextRecordWriter</value>
<description>The default record writer for writing data to the user scripts. </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.transform.escape.input</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This adds an option to escape special chars (newlines, carriage returns and
tabs) when they are passed to the user script. This is useful if the Hive tables
can contain data that contains special characters.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.binary.record.max.length</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>
Read from a binary stream and treat each hive.binary.record.max.length bytes as a record.
The last record before the end of stream can have less than hive.binary.record.max.length bytes
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hwi.listen.host</name>
<value>0.0.0.0</value>
<description>This is the host address the Hive Web Interface will listen on</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hwi.listen.port</name>
<value>9999</value>
<description>This is the port the Hive Web Interface will listen on</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hwi.war.file</name>
<value>${env:HWI_WAR_FILE}</value>
<description>This sets the path to the HWI war file, relative to ${HIVE_HOME}. </description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapred.local.mem</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>mapper/reducer memory in local mode</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize</name>
<value>25000000</value>
<description>
The threshold for the input file size of the small tables; if the file size is smaller
than this threshold, it will try to convert the common join into map join
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.schema.evolution</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Use schema evolution to convert self-describing file format's data to the schema desired by the reader.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.sample.seednumber</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>A number used to percentage sampling. By changing this number, user will change the subsets of data sampled.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.mode</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether Hive is running in test mode. If yes, it turns on sampling and prefixes the output tablename.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.mode.prefix</name>
<value>test_</value>
<description>In test mode, specfies prefixes for the output table</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.mode.samplefreq</name>
<value>32</value>
<description>
In test mode, specfies sampling frequency for table, which is not bucketed,
For example, the following query:
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE dest SELECT col1 from src
would be converted to
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE test_dest
SELECT col1 from src TABLESAMPLE (BUCKET 1 out of 32 on rand(1))
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.mode.nosamplelist</name>
<value/>
<description>In test mode, specifies comma separated table names which would not apply sampling</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.dummystats.aggregator</name>
<value/>
<description>internal variable for test</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.dummystats.publisher</name>
<value/>
<description>internal variable for test</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.currenttimestamp</name>
<value/>
<description>current timestamp for test</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.rollbacktxn</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>For testing only. Will mark every ACID transaction aborted</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.fail.compaction</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>For testing only. Will cause CompactorMR to fail.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.test.fail.heartbeater</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>For testing only. Will cause Heartbeater to fail.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.mapfiles</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Merge small files at the end of a map-only job</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.mapredfiles</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Merge small files at the end of a map-reduce job</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.tezfiles</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Merge small files at the end of a Tez DAG</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.sparkfiles</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Merge small files at the end of a Spark DAG Transformation</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.size.per.task</name>
<value>256000000</value>
<description>Size of merged files at the end of the job</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.smallfiles.avgsize</name>
<value>16000000</value>
<description>
When the average output file size of a job is less than this number, Hive will start an additional
map-reduce job to merge the output files into bigger files. This is only done for map-only jobs
if hive.merge.mapfiles is true, and for map-reduce jobs if hive.merge.mapredfiles is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.rcfile.block.level</name>
<value>true</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.orcfile.stripe.level</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
When hive.merge.mapfiles, hive.merge.mapredfiles or hive.merge.tezfiles is enabled
while writing a table with ORC file format, enabling this config will do stripe-level
fast merge for small ORC files. Note that enabling this config will not honor the
padding tolerance config (hive.exec.orc.block.padding.tolerance).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.rcfile.use.explicit.header</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If this is set the header for RCFiles will simply be RCF. If this is not
set the header will be that borrowed from sequence files, e.g. SEQ- followed
by the input and output RCFile formats.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.rcfile.use.sync.cache</name>
<value>true</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.io.rcfile.record.interval</name>
<value>2147483647</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.io.rcfile.column.number.conf</name>
<value>0</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.io.rcfile.tolerate.corruptions</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.io.rcfile.record.buffer.size</name>
<value>4194304</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>parquet.memory.pool.ratio</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>
Maximum fraction of heap that can be used by Parquet file writers in one task.
It is for avoiding OutOfMemory error in tasks. Work with Parquet 1.6.0 and above.
This config parameter is defined in Parquet, so that it does not start with 'hive.'.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.parquet.timestamp.skip.conversion</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Current Hive implementation of parquet stores timestamps to UTC, this flag allows skipping of the conversionon reading parquet files from other tools</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.int.timestamp.conversion.in.seconds</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Boolean/tinyint/smallint/int/bigint value is interpreted as milliseconds during the timestamp conversion.
Set this flag to true to interpret the value as seconds to be consistent with float/double.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.memory.pool</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>Maximum fraction of heap that can be used by ORC file writers</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.write.format</name>
<value/>
<description>
Define the version of the file to write. Possible values are 0.11 and 0.12.
If this parameter is not defined, ORC will use the run length encoding (RLE)
introduced in Hive 0.12. Any value other than 0.11 results in the 0.12 encoding.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.stripe.size</name>
<value>67108864</value>
<description>Define the default ORC stripe size, in bytes.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.block.size</name>
<value>268435456</value>
<description>Define the default file system block size for ORC files.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.dictionary.key.size.threshold</name>
<value>0.8</value>
<description>
If the number of keys in a dictionary is greater than this fraction of the total number of
non-null rows, turn off dictionary encoding. Use 1 to always use dictionary encoding.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.row.index.stride</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>
Define the default ORC index stride in number of rows. (Stride is the number of rows
an index entry represents.)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.row.index.stride.dictionary.check</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If enabled dictionary check will happen after first row index stride (default 10000 rows)
else dictionary check will happen before writing first stripe. In both cases, the decision
to use dictionary or not will be retained thereafter.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.buffer.size</name>
<value>262144</value>
<description>Define the default ORC buffer size, in bytes.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.base.delta.ratio</name>
<value>8</value>
<description>
The ratio of base writer and
delta writer in terms of STRIPE_SIZE and BUFFER_SIZE.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.block.padding</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Define the default block padding, which pads stripes to the HDFS block boundaries.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.block.padding.tolerance</name>
<value>0.05</value>
<description>
Define the tolerance for block padding as a decimal fraction of stripe size (for
example, the default value 0.05 is 5% of the stripe size). For the defaults of 64Mb
ORC stripe and 256Mb HDFS blocks, the default block padding tolerance of 5% will
reserve a maximum of 3.2Mb for padding within the 256Mb block. In that case, if the
available size within the block is more than 3.2Mb, a new smaller stripe will be
inserted to fit within that space. This will make sure that no stripe written will
cross block boundaries and cause remote reads within a node local task.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.default.compress</name>
<value>ZLIB</value>
<description>Define the default compression codec for ORC file</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.encoding.strategy</name>
<value>SPEED</value>
<description>
Expects one of [speed, compression].
Define the encoding strategy to use while writing data. Changing this will
only affect the light weight encoding for integers. This flag will not
change the compression level of higher level compression codec (like ZLIB).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.compression.strategy</name>
<value>SPEED</value>
<description>
Expects one of [speed, compression].
Define the compression strategy to use while writing data.
This changes the compression level of higher level compression codec (like ZLIB).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.split.strategy</name>
<value>HYBRID</value>
<description>
Expects one of [hybrid, bi, etl].
This is not a user level config. BI strategy is used when the requirement is to spend less time in split generation as opposed to query execution (split generation does not read or cache file footers). ETL strategy is used when spending little more time in split generation is acceptable (split generation reads and caches file footers). HYBRID chooses between the above strategies based on heuristics.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.ms.footer.cache.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable using file metadata cache in metastore for ORC file footers.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.ms.footer.cache.ppd.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to enable file footer cache PPD (hive.orc.splits.ms.footer.cache.enabled
must also be set to true for this to work).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.include.file.footer</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If turned on splits generated by orc will include metadata about the stripes in the file. This
data is read remotely (from the client or HS2 machine) and sent to all the tasks.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.directory.batch.ms</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
How long, in ms, to wait to batch input directories for processing during ORC split
generation. 0 means process directories individually. This can increase the number of
metastore calls if metastore metadata cache is used.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.include.fileid</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Include file ID in splits on file systems that support it.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.splits.allow.synthetic.fileid</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Allow synthetic file ID in splits on file systems that don't have a native one.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.cache.stripe.details.size</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Max cache size for keeping meta info about orc splits cached in the client.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.compute.splits.num.threads</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>How many threads orc should use to create splits in parallel.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.orc.cache.use.soft.references</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
By default, the cache that ORC input format uses to store orc file footer use hard
references for the cached object. Setting this to true can help avoid out of memory
issues under memory pressure (in some cases) at the cost of slight unpredictability in
overall query performance.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.skip.corrupt.data</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If ORC reader encounters corrupt data, this value will be used to determine
whether to skip the corrupt data or throw exception. The default behavior is to throw exception.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.orc.zerocopy</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Use zerocopy reads with ORC. (This requires Hadoop 2.3 or later.)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lazysimple.extended_boolean_literal</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
LazySimpleSerde uses this property to determine if it treats 'T', 't', 'F', 'f',
'1', and '0' as extened, legal boolean literal, in addition to 'TRUE' and 'FALSE'.
The default is false, which means only 'TRUE' and 'FALSE' are treated as legal
boolean literal.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.skewjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to enable skew join optimization.
The algorithm is as follows: At runtime, detect the keys with a large skew. Instead of
processing those keys, store them temporarily in an HDFS directory. In a follow-up map-reduce
job, process those skewed keys. The same key need not be skewed for all the tables, and so,
the follow-up map-reduce job (for the skewed keys) would be much faster, since it would be a
map-join.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.dynamic.partition.hashjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to enable dynamically partitioned hash join optimization.
This setting is also dependent on enabling hive.auto.convert.join
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.join</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether Hive enables the optimization about converting common join into mapjoin based on the input file size</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether Hive enables the optimization about converting common join into mapjoin based on the input file size.
If this parameter is on, and the sum of size for n-1 of the tables/partitions for a n-way join is smaller than the
specified size, the join is directly converted to a mapjoin (there is no conditional task).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask.size</name>
<value>10000000</value>
<description>
If hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask is off, this parameter does not take affect.
However, if it is on, and the sum of size for n-1 of the tables/partitions for a n-way join is smaller than this size,
the join is directly converted to a mapjoin(there is no conditional task). The default is 10MB
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.join.use.nonstaged</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
For conditional joins, if input stream from a small alias can be directly applied to join operator without
filtering or projection, the alias need not to be pre-staged in distributed cache via mapred local task.
Currently, this is not working with vectorization or tez execution engine.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.skewjoin.key</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>
Determine if we get a skew key in join. If we see more than the specified number of rows with the same key in join operator,
we think the key as a skew join key.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.skewjoin.mapjoin.map.tasks</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>
Determine the number of map task used in the follow up map join job for a skew join.
It should be used together with hive.skewjoin.mapjoin.min.split to perform a fine grained control.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.skewjoin.mapjoin.min.split</name>
<value>33554432</value>
<description>
Determine the number of map task at most used in the follow up map join job for a skew join by specifying
the minimum split size. It should be used together with hive.skewjoin.mapjoin.map.tasks to perform a fine grained control.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.heartbeat.interval</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Send a heartbeat after this interval - used by mapjoin and filter operators</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.row.max.size</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>When trying a smaller subset of data for simple LIMIT, how much size we need to guarantee each row to have at least.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.optimize.limit.file</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>When trying a smaller subset of data for simple LIMIT, maximum number of files we can sample.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.optimize.enable</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable to optimization to trying a smaller subset of data for simple LIMIT first.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.optimize.fetch.max</name>
<value>50000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of rows allowed for a smaller subset of data for simple LIMIT, if it is a fetch query.
Insert queries are not restricted by this limit.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.pushdown.memory.usage</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>
Expects value between 0.0f and 1.0f.
The fraction of available memory to be used for buffering rows in Reducesink operator for limit pushdown optimization.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.limit.query.max.table.partition</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
This controls how many partitions can be scanned for each partitioned table.
The default value "-1" means no limit.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.join.hashtable.max.entries</name>
<value>4194304</value>
<description>
If hive.auto.convert.join.noconditionaltask is off, this parameter does not take affect.
However, if it is on, and the predicated number of entries in hashtable for a given join
input is larger than this number, the join will not be converted to a mapjoin.
The value "-1" means no limit.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hashtable.key.count.adjustment</name>
<value>1.0</value>
<description>Adjustment to mapjoin hashtable size derived from table and column statistics; the estimate of the number of keys is divided by this value. If the value is 0, statistics are not usedand hive.hashtable.initialCapacity is used instead.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hashtable.initialCapacity</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>Initial capacity of mapjoin hashtable if statistics are absent, or if hive.hashtable.key.count.adjustment is set to 0</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hashtable.loadfactor</name>
<value>0.75</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.followby.gby.localtask.max.memory.usage</name>
<value>0.55</value>
<description>
This number means how much memory the local task can take to hold the key/value into an in-memory hash table
when this map join is followed by a group by. If the local task's memory usage is more than this number,
the local task will abort by itself. It means the data of the small table is too large to be held in memory.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.localtask.max.memory.usage</name>
<value>0.9</value>
<description>
This number means how much memory the local task can take to hold the key/value into an in-memory hash table.
If the local task's memory usage is more than this number, the local task will abort by itself.
It means the data of the small table is too large to be held in memory.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapjoin.check.memory.rows</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>The number means after how many rows processed it needs to check the memory usage</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.debug.localtask</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.input.format</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.CombineHiveInputFormat</value>
<description>The default input format. Set this to HiveInputFormat if you encounter problems with CombineHiveInputFormat.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.input.format</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveInputFormat</value>
<description>The default input format for tez. Tez groups splits in the AM.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.container.size</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>By default Tez will spawn containers of the size of a mapper. This can be used to overwrite.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.cpu.vcores</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
By default Tez will ask for however many cpus map-reduce is configured to use per container.
This can be used to overwrite.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.java.opts</name>
<value/>
<description>By default Tez will use the Java options from map tasks. This can be used to overwrite.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.log.level</name>
<value>INFO</value>
<description>
The log level to use for tasks executing as part of the DAG.
Used only if hive.tez.java.opts is used to configure Java options.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.hs2.user.access</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to grant access to the hs2/hive user for queries</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.query.name</name>
<value/>
<description>
This named is used by Tez to set the dag name. This name in turn will appear on
the Tez UI representing the work that was done.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.bucketingsorting</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Don't create a reducer for enforcing
bucketing/sorting for queries of the form:
insert overwrite table T2 select * from T1;
where T1 and T2 are bucketed/sorted by the same keys into the same number of buckets.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapred.partitioner</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.DefaultHivePartitioner</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.enforce.sortmergebucketmapjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If the user asked for sort-merge bucketed map-side join, and it cannot be performed, should the query fail or not ?</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.enforce.bucketmapjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If the user asked for bucketed map-side join, and it cannot be performed,
should the query fail or not ? For example, if the buckets in the tables being joined are
not a multiple of each other, bucketed map-side join cannot be performed, and the
query will fail if hive.enforce.bucketmapjoin is set to true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Will the join be automatically converted to a sort-merge join, if the joined tables pass the criteria for sort-merge join.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join.reduce.side</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join (if enabled) should be applied to reduce side.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join.bigtable.selection.policy</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.optimizer.AvgPartitionSizeBasedBigTableSelectorForAutoSMJ</value>
<description>
The policy to choose the big table for automatic conversion to sort-merge join.
By default, the table with the largest partitions is assigned the big table. All policies are:
. based on position of the table - the leftmost table is selected
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.optimizer.LeftmostBigTableSMJ.
. based on total size (all the partitions selected in the query) of the table
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.optimizer.TableSizeBasedBigTableSelectorForAutoSMJ.
. based on average size (all the partitions selected in the query) of the table
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.optimizer.AvgPartitionSizeBasedBigTableSelectorForAutoSMJ.
New policies can be added in future.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join.to.mapjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If hive.auto.convert.sortmerge.join is set to true, and a join was converted to a sort-merge join,
this parameter decides whether each table should be tried as a big table, and effectively a map-join should be
tried. That would create a conditional task with n+1 children for a n-way join (1 child for each table as the
big table), and the backup task will be the sort-merge join. In some cases, a map-join would be faster than a
sort-merge join, if there is no advantage of having the output bucketed and sorted. For example, if a very big sorted
and bucketed table with few files (say 10 files) are being joined with a very small sorter and bucketed table
with few files (10 files), the sort-merge join will only use 10 mappers, and a simple map-only join might be faster
if the complete small table can fit in memory, and a map-join can be performed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.script.trust</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.rowoffset</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to provide the row offset virtual column</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.index.filter</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable automatic use of indexes</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.index.autoupdate</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to update stale indexes automatically</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.ppd</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable predicate pushdown</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.ppd.windowing</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable predicate pushdown through windowing</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ppd.recognizetransivity</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to transitively replicate predicate filters over equijoin conditions.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ppd.remove.duplicatefilters</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
During query optimization, filters may be pushed down in the operator tree.
If this config is true only pushed down filters remain in the operator tree,
and the original filter is removed. If this config is false, the original filter
is also left in the operator tree at the original place.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.point.lookup</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to transform OR clauses in Filter operators into IN clauses</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.point.lookup.min</name>
<value>31</value>
<description>Minimum number of OR clauses needed to transform into IN clauses</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.partition.columns.separate</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Extract partition columns from IN clauses</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.constant.propagation</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable constant propagation optimizer</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.remove.identity.project</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Removes identity project from operator tree</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.metadataonly</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to eliminate scans of the tables from which no columns are selected. Note
that, when selecting from empty tables with data files, this can produce incorrect
results, so it's disabled by default. It works correctly for normal tables.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.null.scan</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Dont scan relations which are guaranteed to not generate any rows</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.ppd.storage</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to push predicates down to storage handlers</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.groupby</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable the bucketed group by from bucketed partitions/tables.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to try bucket mapjoin</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin.sortedmerge</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to try sorted bucket merge map join</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.reducededuplication</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Remove extra map-reduce jobs if the data is already clustered by the same key which needs to be used again.
This should always be set to true. Since it is a new feature, it has been made configurable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.reducededuplication.min.reducer</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>
Reduce deduplication merges two RSs by moving key/parts/reducer-num of the child RS to parent RS.
That means if reducer-num of the child RS is fixed (order by or forced bucketing) and small, it can make very slow, single MR.
The optimization will be automatically disabled if number of reducers would be less than specified value.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.sort.dynamic.partition</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When enabled dynamic partitioning column will be globally sorted.
This way we can keep only one record writer open for each partition value
in the reducer thereby reducing the memory pressure on reducers.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.sampling.orderby</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Uses sampling on order-by clause for parallel execution.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.sampling.orderby.number</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Total number of samples to be obtained.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.sampling.orderby.percent</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>
Expects value between 0.0f and 1.0f.
Probability with which a row will be chosen.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.distinct.rewrite</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>When applicable this optimization rewrites distinct aggregates from a single stage to multi-stage aggregation. This may not be optimal in all cases. Ideally, whether to trigger it or not should be cost based decision. Until Hive formalizes cost model for this, this is config driven.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.union.remove</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to remove the union and push the operators between union and the filesink above union.
This avoids an extra scan of the output by union. This is independently useful for union
queries, and specially useful when hive.optimize.skewjoin.compiletime is set to true, since an
extra union is inserted.
The merge is triggered if either of hive.merge.mapfiles or hive.merge.mapredfiles is set to true.
If the user has set hive.merge.mapfiles to true and hive.merge.mapredfiles to false, the idea was the
number of reducers are few, so the number of files anyway are small. However, with this optimization,
we are increasing the number of files possibly by a big margin. So, we merge aggressively.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.correlation</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>exploit intra-query correlations.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.limittranspose</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to push a limit through left/right outer join or union. If the value is true and the size of the outer
input is reduced enough (as specified in hive.optimize.limittranspose.reduction), the limit is pushed
to the outer input or union; to remain semantically correct, the limit is kept on top of the join or the union too.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.limittranspose.reductionpercentage</name>
<value>1.0</value>
<description>
When hive.optimize.limittranspose is true, this variable specifies the minimal reduction of the
size of the outer input of the join or input of the union that we should get in order to apply the rule.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.limittranspose.reductiontuples</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
When hive.optimize.limittranspose is true, this variable specifies the minimal reduction in the
number of tuples of the outer input of the join or the input of the union that you should get in order to apply the rule.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.filter.stats.reduction</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to simplify comparison
expressions in filter operators using column stats
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.skewjoin.compiletime</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to create a separate plan for skewed keys for the tables in the join.
This is based on the skewed keys stored in the metadata. At compile time, the plan is broken
into different joins: one for the skewed keys, and the other for the remaining keys. And then,
a union is performed for the 2 joins generated above. So unless the same skewed key is present
in both the joined tables, the join for the skewed key will be performed as a map-side join.
The main difference between this parameter and hive.optimize.skewjoin is that this parameter
uses the skew information stored in the metastore to optimize the plan at compile time itself.
If there is no skew information in the metadata, this parameter will not have any affect.
Both hive.optimize.skewjoin.compiletime and hive.optimize.skewjoin should be set to true.
Ideally, hive.optimize.skewjoin should be renamed as hive.optimize.skewjoin.runtime, but not doing
so for backward compatibility.
If the skew information is correctly stored in the metadata, hive.optimize.skewjoin.compiletime
would change the query plan to take care of it, and hive.optimize.skewjoin will be a no-op.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.cte.materialize.threshold</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
If the number of references to a CTE clause exceeds this threshold, Hive will materialize it
before executing the main query block. -1 will disable this feature.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.index.filter.compact.minsize</name>
<value>5368709120</value>
<description>Minimum size (in bytes) of the inputs on which a compact index is automatically used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.index.filter.compact.maxsize</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>Maximum size (in bytes) of the inputs on which a compact index is automatically used. A negative number is equivalent to infinity.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.compact.query.max.entries</name>
<value>10000000</value>
<description>The maximum number of index entries to read during a query that uses the compact index. Negative value is equivalent to infinity.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.compact.query.max.size</name>
<value>10737418240</value>
<description>The maximum number of bytes that a query using the compact index can read. Negative value is equivalent to infinity.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.compact.binary.search</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether or not to use a binary search to find the entries in an index table that match the filter, where possible</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.autogather</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>A flag to gather statistics (only basic) automatically during the INSERT OVERWRITE command.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.column.autogather</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>A flag to gather column statistics automatically.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.dbclass</name>
<value>fs</value>
<description>
Expects one of the pattern in [custom, fs].
The storage that stores temporary Hive statistics. In filesystem based statistics collection ('fs'),
each task writes statistics it has collected in a file on the filesystem, which will be aggregated
after the job has finished. Supported values are fs (filesystem) and custom as defined in StatsSetupConst.java.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.default.publisher</name>
<value/>
<description>The Java class (implementing the StatsPublisher interface) that is used by default if hive.stats.dbclass is custom type.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.default.aggregator</name>
<value/>
<description>The Java class (implementing the StatsAggregator interface) that is used by default if hive.stats.dbclass is custom type.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.atomic</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>whether to update metastore stats only if all stats are available</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.client.stats.counters</name>
<value/>
<description>
Subset of counters that should be of interest for hive.client.stats.publishers (when one wants to limit their publishing).
Non-display names should be used
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.reliable</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether queries will fail because stats cannot be collected completely accurately.
If this is set to true, reading/writing from/into a partition may fail because the stats
could not be computed accurately.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.analyze.stmt.collect.partlevel.stats</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>analyze table T compute statistics for columns. Queries like these should compute partitionlevel stats for partitioned table even when no part spec is specified.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.gather.num.threads</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>
Number of threads used by partialscan/noscan analyze command for partitioned tables.
This is applicable only for file formats that implement StatsProvidingRecordReader (like ORC).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.collect.tablekeys</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether join and group by keys on tables are derived and maintained in the QueryPlan.
This is useful to identify how tables are accessed and to determine if they should be bucketed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.collect.scancols</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether column accesses are tracked in the QueryPlan.
This is useful to identify how tables are accessed and to determine if there are wasted columns that can be trimmed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.ndv.error</name>
<value>20.0</value>
<description>
Standard error expressed in percentage. Provides a tradeoff between accuracy and compute cost.
A lower value for error indicates higher accuracy and a higher compute cost.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.stats.ndv.densityfunction</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to use density function to estimate the NDV for the whole table based on the NDV of partitions</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.max.variable.length</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>
To estimate the size of data flowing through operators in Hive/Tez(for reducer estimation etc.),
average row size is multiplied with the total number of rows coming out of each operator.
Average row size is computed from average column size of all columns in the row. In the absence
of column statistics, for variable length columns (like string, bytes etc.), this value will be
used. For fixed length columns their corresponding Java equivalent sizes are used
(float - 4 bytes, double - 8 bytes etc.).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.list.num.entries</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>
To estimate the size of data flowing through operators in Hive/Tez(for reducer estimation etc.),
average row size is multiplied with the total number of rows coming out of each operator.
Average row size is computed from average column size of all columns in the row. In the absence
of column statistics and for variable length complex columns like list, the average number of
entries/values can be specified using this config.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.map.num.entries</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>
To estimate the size of data flowing through operators in Hive/Tez(for reducer estimation etc.),
average row size is multiplied with the total number of rows coming out of each operator.
Average row size is computed from average column size of all columns in the row. In the absence
of column statistics and for variable length complex columns like map, the average number of
entries/values can be specified using this config.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.fetch.partition.stats</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Annotation of operator tree with statistics information requires partition level basic
statistics like number of rows, data size and file size. Partition statistics are fetched from
metastore. Fetching partition statistics for each needed partition can be expensive when the
number of partitions is high. This flag can be used to disable fetching of partition statistics
from metastore. When this flag is disabled, Hive will make calls to filesystem to get file sizes
and will estimate the number of rows from row schema.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.fetch.column.stats</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Annotation of operator tree with statistics information requires column statistics.
Column statistics are fetched from metastore. Fetching column statistics for each needed column
can be expensive when the number of columns is high. This flag can be used to disable fetching
of column statistics from metastore.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.join.factor</name>
<value>1.1</value>
<description>
Hive/Tez optimizer estimates the data size flowing through each of the operators. JOIN operator
uses column statistics to estimate the number of rows flowing out of it and hence the data size.
In the absence of column statistics, this factor determines the amount of rows that flows out
of JOIN operator.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.deserialization.factor</name>
<value>1.0</value>
<description>
Hive/Tez optimizer estimates the data size flowing through each of the operators. In the absence
of basic statistics like number of rows and data size, file size is used to estimate the number
of rows and data size. Since files in tables/partitions are serialized (and optionally
compressed) the estimates of number of rows and data size cannot be reliably determined.
This factor is multiplied with the file size to account for serialization and compression.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stats.filter.in.factor</name>
<value>1.0</value>
<description>
Currently column distribution is assumed to be uniform. This can lead to overestimation/underestimation
in the number of rows filtered by a certain operator, which in turn might lead to overprovision or
underprovision of resources. This factor is applied to the cardinality estimation of IN clauses in
filter operators.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.support.concurrency</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether Hive supports concurrency control or not.
A ZooKeeper instance must be up and running when using zookeeper Hive lock manager
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lock.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.zookeeper.ZooKeeperHiveLockManager</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lock.numretries</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>The number of times you want to try to get all the locks</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.unlock.numretries</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>The number of times you want to retry to do one unlock</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lock.sleep.between.retries</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
The time should be in between 0 sec (exclusive) and 9223372036854775807 sec (exclusive).
The maximum sleep time between various retries
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.lock.mapred.only.operation</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This param is to control whether or not only do lock on queries
that need to execute at least one mapred job.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>node01,node02,node03</value>
<description>
List of ZooKeeper servers to talk to. This is needed for:
1. Read/write locks - when hive.lock.manager is set to
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.zookeeper.ZooKeeperHiveLockManager,
2. When HiveServer2 supports service discovery via Zookeeper.
3. For delegation token storage if zookeeper store is used, if
hive.cluster.delegation.token.store.zookeeper.connectString is not set
4. LLAP daemon registry service
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.client.port</name>
<value>2181</value>
<description>
The port of ZooKeeper servers to talk to.
If the list of Zookeeper servers specified in hive.zookeeper.quorum
does not contain port numbers, this value is used.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.session.timeout</name>
<value>1200000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
ZooKeeper client's session timeout (in milliseconds). The client is disconnected, and as a result, all locks released,
if a heartbeat is not sent in the timeout.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.namespace</name>
<value>hive_zookeeper_namespace</value>
<description>The parent node under which all ZooKeeper nodes are created.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.clean.extra.nodes</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Clean extra nodes at the end of the session.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.connection.max.retries</name>
<value>3</value>
<description>Max number of times to retry when connecting to the ZooKeeper server.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.connection.basesleeptime</name>
<value>1000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Initial amount of time (in milliseconds) to wait between retries
when connecting to the ZooKeeper server when using ExponentialBackoffRetry policy.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DummyTxnManager</value>
<description>
Set to org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.lockmgr.DbTxnManager as part of turning on Hive
transactions, which also requires appropriate settings for hive.compactor.initiator.on,
hive.compactor.worker.threads, hive.support.concurrency (true), hive.enforce.bucketing
(true), and hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode (nonstrict).
The default DummyTxnManager replicates pre-Hive-0.13 behavior and provides
no transactions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.strict.locking.mode</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
In strict mode non-ACID
resources use standard R/W lock semantics, e.g. INSERT will acquire exclusive lock.
In nonstrict mode, for non-ACID resources, INSERT will only acquire shared lock, which
allows two concurrent writes to the same partition but still lets lock manager prevent
DROP TABLE etc. when the table is being written to
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.timeout</name>
<value>300s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
time after which transactions are declared aborted if the client has not sent a heartbeat.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.heartbeat.threadpool.size</name>
<value>5</value>
<description>The number of threads to use for heartbeating. For Hive CLI, 1 is enough. For HiveServer2, we need a few</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.manager.dump.lock.state.on.acquire.timeout</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Set this to true so that when attempt to acquire a lock on resource times out, the current state of the lock manager is dumped to log file. This is for debugging. See also hive.lock.numretries and hive.lock.sleep.between.retries.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.max.open.txns</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of open transactions. If
current open transactions reach this limit, future open transaction requests will be
rejected, until this number goes below the limit.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.count.open.txns.interval</name>
<value>1s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Time in seconds between checks to count open transactions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.max.open.batch</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>
Maximum number of transactions that can be fetched in one call to open_txns().
This controls how many transactions streaming agents such as Flume or Storm open
simultaneously. The streaming agent then writes that number of entries into a single
file (per Flume agent or Storm bolt). Thus increasing this value decreases the number
of delta files created by streaming agents. But it also increases the number of open
transactions that Hive has to track at any given time, which may negatively affect
read performance.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.txn.retryable.sqlex.regex</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma separated list
of regular expression patterns for SQL state, error code, and error message of
retryable SQLExceptions, that's suitable for the metastore DB.
For example: Can't serialize.*,40001$,^Deadlock,.*ORA-08176.*
The string that the regex will be matched against is of the following form, where ex is a SQLException:
ex.getMessage() + " (SQLState=" + ex.getSQLState() + ", ErrorCode=" + ex.getErrorCode() + ")"
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.initiator.on</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to run the initiator and cleaner threads on this metastore instance or not.
Set this to true on one instance of the Thrift metastore service as part of turning
on Hive transactions. For a complete list of parameters required for turning on
transactions, see hive.txn.manager.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.worker.threads</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
How many compactor worker threads to run on this metastore instance. Set this to a
positive number on one or more instances of the Thrift metastore service as part of
turning on Hive transactions. For a complete list of parameters required for turning
on transactions, see hive.txn.manager.
Worker threads spawn MapReduce jobs to do compactions. They do not do the compactions
themselves. Increasing the number of worker threads will decrease the time it takes
tables or partitions to be compacted once they are determined to need compaction.
It will also increase the background load on the Hadoop cluster as more MapReduce jobs
will be running in the background.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.worker.timeout</name>
<value>86400s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Time in seconds after which a compaction job will be declared failed and the
compaction re-queued.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.check.interval</name>
<value>300s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Time in seconds between checks to see if any tables or partitions need to be
compacted. This should be kept high because each check for compaction requires
many calls against the NameNode.
Decreasing this value will reduce the time it takes for compaction to be started
for a table or partition that requires compaction. However, checking if compaction
is needed requires several calls to the NameNode for each table or partition that
has had a transaction done on it since the last major compaction. So decreasing this
value will increase the load on the NameNode.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.delta.num.threshold</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>
Number of delta directories in a table or partition that will trigger a minor
compaction.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.delta.pct.threshold</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>
Percentage (fractional) size of the delta files relative to the base that will trigger
a major compaction. (1.0 = 100%, so the default 0.1 = 10%.)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.max.num.delta</name>
<value>500</value>
<description>Maximum number of delta files that the compactor will attempt to handle in a single job.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.abortedtxn.threshold</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>
Number of aborted transactions involving a given table or partition that will trigger
a major compaction.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.initiator.failed.compacts.threshold</name>
<value>2</value>
<description>
Expects value between 1 and 20.
Number of consecutive compaction failures (per table/partition) after which automatic compactions will not be scheduled any more. Note that this must be less than hive.compactor.history.retention.failed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.cleaner.run.interval</name>
<value>5000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Time between runs of the cleaner thread
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.job.queue</name>
<value/>
<description>
Used to specify name of Hadoop queue to which
Compaction jobs will be submitted. Set to empty string to let Hadoop choose the queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.history.retention.succeeded</name>
<value>3</value>
<description>
Expects value between 0 and 100.
Determines how many successful compaction records will be retained in compaction history for a given table/partition.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.history.retention.failed</name>
<value>3</value>
<description>
Expects value between 0 and 100.
Determines how many failed compaction records will be retained in compaction history for a given table/partition.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.history.retention.attempted</name>
<value>2</value>
<description>
Expects value between 0 and 100.
Determines how many attempted compaction records will be retained in compaction history for a given table/partition.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compactor.history.reaper.interval</name>
<value>2m</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Determines how often compaction history reaper runs
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.timedout.txn.reaper.start</name>
<value>100s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Time delay of 1st reaper run after metastore start
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.timedout.txn.reaper.interval</name>
<value>180s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Time interval describing how often the reaper runs
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.writeset.reaper.interval</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Frequency of WriteSet reaper runs
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.cardinality.check</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Set to true to ensure that each SQL Merge statement ensures that for each row in the target
table there is at most 1 matching row in the source table per SQL Specification.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.indexer.segments.granularity</name>
<value>DAY</value>
<description>
Expects one of the pattern in [YEAR, MONTH, WEEK, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND].
Granularity for the segments created by the Druid storage handler
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.indexer.partition.size.max</name>
<value>5000000</value>
<description>Maximum number of records per segment partition</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.indexer.memory.rownum.max</name>
<value>75000</value>
<description>Maximum number of records in memory while storing data in Druid</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.broker.address.default</name>
<value>localhost:8082</value>
<description>
Address of the Druid broker. If we are querying Druid from Hive, this address needs to be
declared
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.coordinator.address.default</name>
<value>localhost:8081</value>
<description>Address of the Druid coordinator. It is used to check the load status of newly created segments</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.select.threshold</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>
When we can split a Select query, this is the maximum number of rows that we try to retrieve
per query. In order to do that, we obtain the estimated size for the complete result. If the
number of records of the query results is larger than this threshold, we split the query in
total number of rows/threshold parts across the time dimension. Note that we assume the
records to be split uniformly across the time dimension
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.http.numConnection</name>
<value>20</value>
<description>
Number of connections used by
the HTTP client.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.http.read.timeout</name>
<value>PT1M</value>
<description>
Read timeout period for the HTTP
client in ISO8601 format (for example P2W, P3M, PT1H30M, PT0.750S), default is period of 1 minute.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.sleep.time</name>
<value>PT10S</value>
<description>Sleep time between retries in ISO8601 format (for example P2W, P3M, PT1H30M, PT0.750S), default is period of 10 seconds.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.basePersistDirectory</name>
<value>/tmp</value>
<description>Local temporary directory used to persist intermediate indexing state.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.storage.storageDirectory</name>
<value>/druid/segments</value>
<description>druid deep storage location.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.metadata.base</name>
<value>druid</value>
<description>Default prefix for metadata tables</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.metadata.db.type</name>
<value>mysql</value>
<description>
Expects one of the pattern in [mysql, postgres].
Type of the metadata database.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.metadata.username</name>
<value/>
<description>Username to connect to Type of the metadata DB.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.metadata.password</name>
<value/>
<description>Password to connect to Type of the metadata DB.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.metadata.uri</name>
<value/>
<description>URI to connect to the database (for example jdbc:mysql://hostname:port/DBName).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.working.directory</name>
<value>/tmp/workingDirectory</value>
<description>Default hdfs working directory used to store some intermediate metadata</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.maxTries</name>
<value>5</value>
<description>Maximum number of retries before giving up</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.druid.passiveWaitTimeMs</name>
<value>30000</value>
<description>Wait time in ms default to 30 seconds.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hbase.wal.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether writes to HBase should be forced to the write-ahead log.
Disabling this improves HBase write performance at the risk of lost writes in case of a crash.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hbase.generatehfiles</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>True when HBaseStorageHandler should generate hfiles instead of operate against the online table.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hbase.snapshot.name</name>
<value/>
<description>The HBase table snapshot name to use.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hbase.snapshot.restoredir</name>
<value>/tmp</value>
<description>The directory in which to restore the HBase table snapshot.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.archive.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether archiving operations are permitted</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.index.groupby</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable optimization of group-by queries using Aggregate indexes.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.outerjoin.supports.filters</name>
<value>true</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.fetch.task.conversion</name>
<value>more</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, minimal, more].
Some select queries can be converted to single FETCH task minimizing latency.
Currently the query should be single sourced not having any subquery and should not have
any aggregations or distincts (which incurs RS), lateral views and joins.
0. none : disable hive.fetch.task.conversion
1. minimal : SELECT STAR, FILTER on partition columns, LIMIT only
2. more : SELECT, FILTER, LIMIT only (support TABLESAMPLE and virtual columns)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.fetch.task.conversion.threshold</name>
<value>1073741824</value>
<description>
Input threshold for applying hive.fetch.task.conversion. If target table is native, input length
is calculated by summation of file lengths. If it's not native, storage handler for the table
can optionally implement org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.metadata.InputEstimator interface.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.fetch.task.aggr</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Aggregation queries with no group-by clause (for example, select count(*) from src) execute
final aggregations in single reduce task. If this is set true, Hive delegates final aggregation
stage to fetch task, possibly decreasing the query time.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compute.query.using.stats</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When set to true Hive will answer a few queries like count(1) purely using stats
stored in metastore. For basic stats collection turn on the config hive.stats.autogather to true.
For more advanced stats collection need to run analyze table queries.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.fetch.output.serde</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.DelimitedJSONSerDe</value>
<description>The SerDe used by FetchTask to serialize the fetch output.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cache.expr.evaluation</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If true, the evaluation result of a deterministic expression referenced twice or more
will be cached.
For example, in a filter condition like '.. where key + 10 = 100 or key + 10 = 0'
the expression 'key + 10' will be evaluated/cached once and reused for the following
expression ('key + 10 = 0'). Currently, this is applied only to expressions in select
or filter operators.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.variable.substitute</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>This enables substitution using syntax like ${var} ${system:var} and ${env:var}.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.variable.substitute.depth</name>
<value>40</value>
<description>The maximum replacements the substitution engine will do.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.conf.validation</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enables type checking for registered Hive configurations</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.semantic.analyzer.hook</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>enable or disable the Hive client authorization</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.authorization.plugin.sqlstd.SQLStdHiveAuthorizerFactory</value>
<description>
The Hive client authorization manager class name. The user defined authorization class should implement
interface org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.authorization.HiveAuthorizationProvider.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authenticator.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.HadoopDefaultAuthenticator</value>
<description>
hive client authenticator manager class name. The user defined authenticator should implement
interface org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.HiveAuthenticationProvider.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.metastore.authorization.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.authorization.DefaultHiveMetastoreAuthorizationProvider</value>
<description>
Names of authorization manager classes (comma separated) to be used in the metastore
for authorization. The user defined authorization class should implement interface
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.authorization.HiveMetastoreAuthorizationProvider.
All authorization manager classes have to successfully authorize the metastore API
call for the command execution to be allowed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.metastore.authorization.auth.reads</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>If this is true, metastore authorizer authorizes read actions on database, table</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.metastore.authenticator.manager</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.HadoopDefaultMetastoreAuthenticator</value>
<description>
authenticator manager class name to be used in the metastore for authentication.
The user defined authenticator should implement interface org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.security.HiveAuthenticationProvider.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.createtable.user.grants</name>
<value/>
<description>
the privileges automatically granted to some users whenever a table gets created.
An example like "userX,userY:select;userZ:create" will grant select privilege to userX and userY,
and grant create privilege to userZ whenever a new table created.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.createtable.group.grants</name>
<value/>
<description>
the privileges automatically granted to some groups whenever a table gets created.
An example like "groupX,groupY:select;groupZ:create" will grant select privilege to groupX and groupY,
and grant create privilege to groupZ whenever a new table created.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.createtable.role.grants</name>
<value/>
<description>
the privileges automatically granted to some roles whenever a table gets created.
An example like "roleX,roleY:select;roleZ:create" will grant select privilege to roleX and roleY,
and grant create privilege to roleZ whenever a new table created.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.createtable.owner.grants</name>
<value/>
<description>
The privileges automatically granted to the owner whenever a table gets created.
An example like "select,drop" will grant select and drop privilege to the owner
of the table. Note that the default gives the creator of a table no access to the
table (but see HIVE-8067).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.task.factory</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.parse.authorization.HiveAuthorizationTaskFactoryImpl</value>
<description>Authorization DDL task factory implementation</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.sqlstd.confwhitelist</name>
<value/>
<description>
List of comma separated Java regexes. Configurations parameters that match these
regexes can be modified by user when SQL standard authorization is enabled.
To get the default value, use the 'set <param>' command.
Note that the hive.conf.restricted.list checks are still enforced after the white list
check
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.authorization.sqlstd.confwhitelist.append</name>
<value/>
<description>
List of comma separated Java regexes, to be appended to list set in
hive.security.authorization.sqlstd.confwhitelist. Using this list instead
of updating the original list means that you can append to the defaults
set by SQL standard authorization instead of replacing it entirely.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.print.header</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to print the names of the columns in query output.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.cli.tez.session.async</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to start Tez
session in background when running CLI with Tez, allowing CLI to be available earlier.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.error.on.empty.partition</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to throw an exception if dynamic partition insert generates empty results.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.compact.file</name>
<value/>
<description>internal variable</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.blockfilter.file</name>
<value/>
<description>internal variable</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.index.compact.file.ignore.hdfs</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When true the HDFS location stored in the index file will be ignored at runtime.
If the data got moved or the name of the cluster got changed, the index data should still be usable.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exim.uri.scheme.whitelist</name>
<value>hdfs,pfile,file</value>
<description>A comma separated list of acceptable URI schemes for import and export.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exim.strict.repl.tables</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Parameter that determines if 'regular' (non-replication) export dumps can be
imported on to tables that are the target of replication. If this parameter is
set, regular imports will check if the destination table(if it exists) has a 'repl.last.id' set on it. If so, it will fail.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.repl.task.factory</name>
<value>org.apache.hive.hcatalog.api.repl.exim.EximReplicationTaskFactory</value>
<description>
Parameter that can be used to override which ReplicationTaskFactory will be
used to instantiate ReplicationTask events. Override for third party repl plugins
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mapper.cannot.span.multiple.partitions</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.rework.mapredwork</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
should rework the mapred work or not.
This is first introduced by SymlinkTextInputFormat to replace symlink files with real paths at compile time.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.concatenate.check.index</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If this is set to true, Hive will throw error when doing
'alter table tbl_name [partSpec] concatenate' on a table/partition
that has indexes on it. The reason the user want to set this to true
is because it can help user to avoid handling all index drop, recreation,
rebuild work. This is very helpful for tables with thousands of partitions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.io.exception.handlers</name>
<value/>
<description>
A list of io exception handler class names. This is used
to construct a list exception handlers to handle exceptions thrown
by record readers
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.log4j.file</name>
<value/>
<description>
Hive log4j configuration file.
If the property is not set, then logging will be initialized using hive-log4j2.properties found on the classpath.
If the property is set, the value must be a valid URI (java.net.URI, e.g. "file:///tmp/my-logging.xml"),
which you can then extract a URL from and pass to PropertyConfigurator.configure(URL).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.log4j.file</name>
<value/>
<description>
Hive log4j configuration file for execution mode(sub command).
If the property is not set, then logging will be initialized using hive-exec-log4j2.properties found on the classpath.
If the property is set, the value must be a valid URI (java.net.URI, e.g. "file:///tmp/my-logging.xml"),
which you can then extract a URL from and pass to PropertyConfigurator.configure(URL).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.async.log.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to enable Log4j2's asynchronous logging. Asynchronous logging can give
significant performance improvement as logging will be handled in separate thread
that uses LMAX disruptor queue for buffering log messages.
Refer https://logging.apache.org/log4j/2.x/manual/async.html for benefits and
drawbacks.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.log.explain.output</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to log explain output for every query.
When enabled, will log EXPLAIN EXTENDED output for the query at INFO log4j log level.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.explain.user</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to show explain result at user level.
When enabled, will log EXPLAIN output for the query at user level.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.autogen.columnalias.prefix.label</name>
<value>_c</value>
<description>
String used as a prefix when auto generating column alias.
By default the prefix label will be appended with a column position number to form the column alias.
Auto generation would happen if an aggregate function is used in a select clause without an explicit alias.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.autogen.columnalias.prefix.includefuncname</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to include function name in the column alias auto generated by Hive.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.class</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.CodahaleMetrics</value>
<description>
Expects one of [org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.codahalemetrics, org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.legacymetrics].
Hive metrics subsystem implementation class.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.reporter</name>
<value>JSON_FILE, JMX</value>
<description>Reporter type for metric class org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.CodahaleMetrics, comma separated list of JMX, CONSOLE, JSON_FILE, HADOOP2</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.file.location</name>
<value>/tmp/report.json</value>
<description>For metric class org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.CodahaleMetrics JSON_FILE reporter, the location of local JSON metrics file. This file will get overwritten at every interval.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.file.frequency</name>
<value>5s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
For metric class org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.CodahaleMetrics JSON_FILE reporter, the frequency of updating JSON metrics file.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.hadoop2.frequency</name>
<value>30s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
For metric class org.apache.hadoop.hive.common.metrics.metrics2.CodahaleMetrics HADOOP2 reporter, the frequency of updating the HADOOP2 metrics system.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.service.metrics.hadoop2.component</name>
<value>hive</value>
<description>Component name to provide to Hadoop2 Metrics system. Ideally 'hivemetastore' for the MetaStore and and 'hiveserver2' for HiveServer2.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.perf.logger</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.log.PerfLogger</value>
<description>
The class responsible for logging client side performance metrics.
Must be a subclass of org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.log.PerfLogger
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.start.cleanup.scratchdir</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>To cleanup the Hive scratchdir when starting the Hive Server</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.scratchdir.lock</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>To hold a lock file in scratchdir to prevent to be removed by cleardanglingscratchdir</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.insert.into.multilevel.dirs</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Where to insert into multilevel directories like
"insert directory '/HIVEFT25686/chinna/' from table"
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.warehouse.subdir.inherit.perms</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Set this to false if the table directories should be created
with the permissions derived from dfs umask instead of
inheriting the permission of the warehouse or database directory.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.insert.into.external.tables</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>whether insert into external tables is allowed</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.temporary.table.storage</name>
<value>default</value>
<description>
Expects one of [memory, ssd, default].
Define the storage policy for temporary tables.Choices between memory, ssd and default
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.driver.run.hooks</name>
<value/>
<description>A comma separated list of hooks which implement HiveDriverRunHook. Will be run at the beginning and end of Driver.run, these will be run in the order specified.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ddl.output.format</name>
<value/>
<description>
The data format to use for DDL output. One of "text" (for human
readable text) or "json" (for a json object).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.entity.separator</name>
<value>@</value>
<description>Separator used to construct names of tables and partitions. For example, dbname@tablename@partitionname</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.entity.capture.transform</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Compiler to capture transform URI referred in the query</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.display.partition.cols.separately</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
In older Hive version (0.10 and earlier) no distinction was made between
partition columns or non-partition columns while displaying columns in describe
table. From 0.12 onwards, they are displayed separately. This flag will let you
get old behavior, if desired. See, test-case in patch for HIVE-6689.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.ssl.protocol.blacklist</name>
<value>SSLv2,SSLv3</value>
<description>SSL Versions to disable for all Hive Servers</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.clear.dangling.scratchdir</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Clear dangling scratch dir periodically in HS2</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.clear.dangling.scratchdir.interval</name>
<value>1800s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Interval to clear dangling scratch dir periodically in HS2
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.sleep.interval.between.start.attempts</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
The time should be in between 0 msec (inclusive) and 9223372036854775807 msec (inclusive).
Amount of time to sleep between HiveServer2 start attempts. Primarily meant for tests
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.max.start.attempts</name>
<value>30</value>
<description>
Expects value bigger than 0.
Number of times HiveServer2 will attempt to start before exiting, sleeping 60 seconds between retries.
The default of 30 will keep trying for 30 minutes.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.support.dynamic.service.discovery</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether HiveServer2 supports dynamic service discovery for its clients. To support this, each instance of HiveServer2 currently uses ZooKeeper to register itself, when it is brought up. JDBC/ODBC clients should use the ZooKeeper ensemble: hive.zookeeper.quorum in their connection string.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.zookeeper.namespace</name>
<value>hiveserver2</value>
<description>The parent node in ZooKeeper used by HiveServer2 when supporting dynamic service discovery.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.zookeeper.publish.configs</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether we should publish HiveServer2's configs to ZooKeeper.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.global.init.file.location</name>
<value>${env:HIVE_CONF_DIR}</value>
<description>
Either the location of a HS2 global init file or a directory containing a .hiverc file. If the
property is set, the value must be a valid path to an init file or directory where the init file is located.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.transport.mode</name>
<value>binary</value>
<description>
Expects one of [binary, http].
Transport mode of HiveServer2.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.bind.host</name>
<value/>
<description>Bind host on which to run the HiveServer2 Thrift service.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.driver.parallel.compilation</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to
enable parallel compilation of the queries between sessions and within the same session on HiveServer2. The default is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.compile.lock.timeout</name>
<value>0s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds a request will wait to acquire the compile lock before giving up. Setting it to 0s disables the timeout.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.parallel.ops.in.session</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to allow several parallel operations (such as SQL statements) in one session.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.host</name>
<value>0.0.0.0</value>
<description>The host address the HiveServer2 WebUI will listen on</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.port</name>
<value>10002</value>
<description>The port the HiveServer2 WebUI will listen on. This can beset to 0 or a negative integer to disable the web UI</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.max.threads</name>
<value>50</value>
<description>The max HiveServer2 WebUI threads</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.use.ssl</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Set this to true for using SSL encryption for HiveServer2 WebUI.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.keystore.path</name>
<value/>
<description>SSL certificate keystore location for HiveServer2 WebUI.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.keystore.password</name>
<value/>
<description>SSL certificate keystore password for HiveServer2 WebUI.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.use.spnego</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If true, the HiveServer2 WebUI will be secured with SPNEGO. Clients must authenticate with Kerberos.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.spnego.keytab</name>
<value/>
<description>The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the HiveServer2 WebUI SPNEGO service principal.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.spnego.principal</name>
<value>HTTP/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM</value>
<description>
The HiveServer2 WebUI SPNEGO service principal.
The special string _HOST will be replaced automatically with
the value of hive.server2.webui.host or the correct host name.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.webui.max.historic.queries</name>
<value>25</value>
<description>The maximum number of past queries to show in HiverSever2 WebUI.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.default.queues</name>
<value/>
<description>
A list of comma separated values corresponding to YARN queues of the same name.
When HiveServer2 is launched in Tez mode, this configuration needs to be set
for multiple Tez sessions to run in parallel on the cluster.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.sessions.per.default.queue</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>
A positive integer that determines the number of Tez sessions that should be
launched on each of the queues specified by "hive.server2.tez.default.queues".
Determines the parallelism on each queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.initialize.default.sessions</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag is used in HiveServer2 to enable a user to use HiveServer2 without
turning on Tez for HiveServer2. The user could potentially want to run queries
over Tez without the pool of sessions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.session.lifetime</name>
<value>162h</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is hour if not specified.
The lifetime of the Tez sessions launched by HS2 when default sessions are enabled.
Set to 0 to disable session expiration.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.session.lifetime.jitter</name>
<value>3h</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is hour if not specified.
The jitter for Tez session lifetime; prevents all the sessions from restarting at once.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.sessions.init.threads</name>
<value>16</value>
<description>
If hive.server2.tez.initialize.default.sessions is enabled, the maximum number of
threads to use to initialize the default sessions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.sessions.restricted.configs</name>
<value/>
<description>
The configuration settings that cannot be set when submitting jobs to HiveServer2. If
any of these are set to values different from those in the server configuration, an
exception will be thrown.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.tez.sessions.custom.queue.allowed</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Expects one of [true, false, ignore].
Whether Tez session pool should allow submitting queries to custom queues. The options
are true, false (error out), ignore (accept the query but ignore the queue setting).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.logging.operation.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>When true, HS2 will save operation logs and make them available for clients</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.logging.operation.log.location</name>
<value>/opt/module/hive/apache-hive-2.2.0-bin/tmp/${user.name}/operation_logs</value>
<description>Top level directory where operation logs are stored if logging functionality is enabled</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.logging.operation.level</name>
<value>EXECUTION</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, execution, performance, verbose].
HS2 operation logging mode available to clients to be set at session level.
For this to work, hive.server2.logging.operation.enabled should be set to true.
NONE: Ignore any logging
EXECUTION: Log completion of tasks
PERFORMANCE: Execution + Performance logs
VERBOSE: All logs
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.metrics.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Enable metrics on the HiveServer2.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.port</name>
<value>10001</value>
<description>Port number of HiveServer2 Thrift interface when hive.server2.transport.mode is 'http'.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.path</name>
<value>cliservice</value>
<description>Path component of URL endpoint when in HTTP mode.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.max.message.size</name>
<value>104857600</value>
<description>Maximum message size in bytes a HS2 server will accept.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.max.idle.time</name>
<value>1800s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Maximum idle time for a connection on the server when in HTTP mode.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.worker.keepalive.time</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Keepalive time for an idle http worker thread. When the number of workers exceeds min workers, excessive threads are killed after this time interval.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.request.header.size</name>
<value>6144</value>
<description>Request header size in bytes, when using HTTP transport mode. Jetty defaults used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.response.header.size</name>
<value>6144</value>
<description>Response header size in bytes, when using HTTP transport mode. Jetty defaults used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.auth.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>When true, HiveServer2 in HTTP transport mode, will use cookie based authentication mechanism.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.max.age</name>
<value>86400s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Maximum age in seconds for server side cookie used by HS2 in HTTP mode.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.domain</name>
<value/>
<description>Domain for the HS2 generated cookies</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.path</name>
<value/>
<description>Path for the HS2 generated cookies</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.is.secure</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Deprecated: Secure attribute of the HS2 generated cookie (this is automatically enabled for SSL enabled HiveServer2).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.http.cookie.is.httponly</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>HttpOnly attribute of the HS2 generated cookie.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.port</name>
<value>10000</value>
<description>Port number of HiveServer2 Thrift interface when hive.server2.transport.mode is 'binary'.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.sasl.qop</name>
<value>auth</value>
<description>
Expects one of [auth, auth-int, auth-conf].
Sasl QOP value; set it to one of following values to enable higher levels of
protection for HiveServer2 communication with clients.
Setting hadoop.rpc.protection to a higher level than HiveServer2 does not
make sense in most situations. HiveServer2 ignores hadoop.rpc.protection in favor
of hive.server2.thrift.sasl.qop.
"auth" - authentication only (default)
"auth-int" - authentication plus integrity protection
"auth-conf" - authentication plus integrity and confidentiality protection
This is applicable only if HiveServer2 is configured to use Kerberos authentication.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.min.worker.threads</name>
<value>5</value>
<description>Minimum number of Thrift worker threads</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.max.worker.threads</name>
<value>500</value>
<description>Maximum number of Thrift worker threads</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.exponential.backoff.slot.length</name>
<value>100ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Binary exponential backoff slot time for Thrift clients during login to HiveServer2,
for retries until hitting Thrift client timeout
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.login.timeout</name>
<value>20s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Timeout for Thrift clients during login to HiveServer2
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.worker.keepalive.time</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Keepalive time (in seconds) for an idle worker thread. When the number of workers exceeds min workers, excessive threads are killed after this time interval.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.async.exec.threads</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>Number of threads in the async thread pool for HiveServer2</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.async.exec.shutdown.timeout</name>
<value>10s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
How long HiveServer2 shutdown will wait for async threads to terminate.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.async.exec.wait.queue.size</name>
<value>100</value>
<description>
Size of the wait queue for async thread pool in HiveServer2.
After hitting this limit, the async thread pool will reject new requests.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.async.exec.keepalive.time</name>
<value>10s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Time that an idle HiveServer2 async thread (from the thread pool) will wait for a new task
to arrive before terminating
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.async.exec.async.compile</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to enable compiling async query asynchronously. If enabled, it is unknown if the query will have any resultset before compilation completed.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.long.polling.timeout</name>
<value>5000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Time that HiveServer2 will wait before responding to asynchronous calls that use long polling
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.session.impl.classname</name>
<value/>
<description>Classname for custom implementation of hive session</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.session.impl.withugi.classname</name>
<value/>
<description>Classname for custom implementation of hive session with UGI</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication</name>
<value>NONE</value>
<description>
Expects one of [nosasl, none, ldap, kerberos, pam, custom].
Client authentication types.
NONE: no authentication check
LDAP: LDAP/AD based authentication
KERBEROS: Kerberos/GSSAPI authentication
CUSTOM: Custom authentication provider
(Use with property hive.server2.custom.authentication.class)
PAM: Pluggable authentication module
NOSASL: Raw transport
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.allow.user.substitution</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Allow alternate user to be specified as part of HiveServer2 open connection request.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.kerberos.keytab</name>
<value/>
<description>Kerberos keytab file for server principal</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.kerberos.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>Kerberos server principal</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.spnego.keytab</name>
<value/>
<description>
keytab file for SPNego principal, optional,
typical value would look like /etc/security/keytabs/spnego.service.keytab,
This keytab would be used by HiveServer2 when Kerberos security is enabled and
HTTP transport mode is used.
This needs to be set only if SPNEGO is to be used in authentication.
SPNego authentication would be honored only if valid
hive.server2.authentication.spnego.principal
and
hive.server2.authentication.spnego.keytab
are specified.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.spnego.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>
SPNego service principal, optional,
typical value would look like HTTP/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM
SPNego service principal would be used by HiveServer2 when Kerberos security is enabled
and HTTP transport mode is used.
This needs to be set only if SPNEGO is to be used in authentication.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.url</name>
<value/>
<description>
LDAP connection URL(s),
this value could contain URLs to mutiple LDAP servers instances for HA,
each LDAP URL is separated by a SPACE character. URLs are used in the
order specified until a connection is successful.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.baseDN</name>
<value/>
<description>LDAP base DN</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.Domain</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.groupDNPattern</name>
<value/>
<description>
COLON-separated list of patterns to use to find DNs for group entities in this directory.
Use %s where the actual group name is to be substituted for.
For example: CN=%s,CN=Groups,DC=subdomain,DC=domain,DC=com.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.groupFilter</name>
<value/>
<description>
COMMA-separated list of LDAP Group names (short name not full DNs).
For example: HiveAdmins,HadoopAdmins,Administrators
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.userDNPattern</name>
<value/>
<description>
COLON-separated list of patterns to use to find DNs for users in this directory.
Use %s where the actual group name is to be substituted for.
For example: CN=%s,CN=Users,DC=subdomain,DC=domain,DC=com.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.userFilter</name>
<value/>
<description>
COMMA-separated list of LDAP usernames (just short names, not full DNs).
For example: hiveuser,impalauser,hiveadmin,hadoopadmin
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.guidKey</name>
<value>uid</value>
<description>
LDAP attribute name whose values are unique in this LDAP server.
For example: uid or CN.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.groupMembershipKey</name>
<value>member</value>
<description>
LDAP attribute name on the user entry that references a group, the user belongs to.
For example: member, uniqueMember or memberUid
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.groupClassKey</name>
<value>groupOfNames</value>
<description>
LDAP attribute name on the group entry that is to be used in LDAP group searches.
For example: group, groupOfNames or groupOfUniqueNames.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.customLDAPQuery</name>
<value/>
<description>
A full LDAP query that LDAP Atn provider uses to execute against LDAP Server.
If this query returns a null resultset, the LDAP Provider fails the Authentication
request, succeeds if the user is part of the resultset.For example: (&(objectClass=group)(objectClass=top)(instanceType=4)(cn=Domain*))
(&(objectClass=person)(|(sAMAccountName=admin)(|(memberOf=CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=domain,DC=com)(memberOf=CN=Administrators,CN=Builtin,DC=domain,DC=com))))
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.custom.authentication.class</name>
<value/>
<description>
Custom authentication class. Used when property
'hive.server2.authentication' is set to 'CUSTOM'. Provided class
must be a proper implementation of the interface
org.apache.hive.service.auth.PasswdAuthenticationProvider. HiveServer2
will call its Authenticate(user, passed) method to authenticate requests.
The implementation may optionally implement Hadoop's
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configurable class to grab Hive's Configuration object.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication.pam.services</name>
<value/>
<description>
List of the underlying pam services that should be used when auth type is PAM
A file with the same name must exist in /etc/pam.d
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.enable.doAs</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Setting this property to true will have HiveServer2 execute
Hive operations as the user making the calls to it.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.table.type.mapping</name>
<value>CLASSIC</value>
<description>
Expects one of [classic, hive].
This setting reflects how HiveServer2 will report the table types for JDBC and other
client implementations that retrieve the available tables and supported table types
HIVE : Exposes Hive's native table types like MANAGED_TABLE, EXTERNAL_TABLE, VIRTUAL_VIEW
CLASSIC : More generic types like TABLE and VIEW
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.session.hook</name>
<value/>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.use.SSL</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Set this to true for using SSL encryption in HiveServer2.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.keystore.path</name>
<value/>
<description>SSL certificate keystore location.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.keystore.password</name>
<value/>
<description>SSL certificate keystore password.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.map.fair.scheduler.queue</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
If the YARN fair scheduler is configured and HiveServer2 is running in non-impersonation mode,
this setting determines the user for fair scheduler queue mapping.
If set to true (default), the logged-in user determines the fair scheduler queue
for submitted jobs, so that map reduce resource usage can be tracked by user.
If set to false, all Hive jobs go to the 'hive' user's queue.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.builtin.udf.whitelist</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma separated list of builtin udf names allowed in queries.
An empty whitelist allows all builtin udfs to be executed. The udf black list takes precedence over udf white list
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.builtin.udf.blacklist</name>
<value/>
<description>Comma separated list of udfs names. These udfs will not be allowed in queries. The udf black list takes precedence over udf white list</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.allow.udf.load.on.demand</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether enable loading UDFs from metastore on demand; this is mostly relevant for
HS2 and was the default behavior before Hive 1.2. Off by default.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.session.check.interval</name>
<value>6h</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
The time should be bigger than or equal to 3000 msec.
The check interval for session/operation timeout, which can be disabled by setting to zero or negative value.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.close.session.on.disconnect</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Session will be closed when connection is closed. Set this to false to have session outlive its parent connection.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.idle.session.timeout</name>
<value>7d</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Session will be closed when it's not accessed for this duration, which can be disabled by setting to zero or negative value.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.idle.operation.timeout</name>
<value>5d</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Operation will be closed when it's not accessed for this duration of time, which can be disabled by setting to zero value.
With positive value, it's checked for operations in terminal state only (FINISHED, CANCELED, CLOSED, ERROR).
With negative value, it's checked for all of the operations regardless of state.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.idle.session.check.operation</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Session will be considered to be idle only if there is no activity, and there is no pending operation.
This setting takes effect only if session idle timeout (hive.server2.idle.session.timeout) and checking
(hive.server2.session.check.interval) are enabled.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.retry.limit</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Number of retries upon failure of Thrift HiveServer2 calls</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.connect.retry.limit</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Number of retries while opening a connection to HiveServe2</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.retry.delay.seconds</name>
<value>1s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Number of seconds for the HiveServer2 thrift client to wait between consecutive connection attempts. Also specifies the time to wait between retrying thrift calls upon failures
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.user</name>
<value>anonymous</value>
<description>Username to use against thrift client</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.password</name>
<value>anonymous</value>
<description>Password to use against thrift client</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.resultset.serialize.in.tasks</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether we should serialize the Thrift structures used in JDBC ResultSet RPC in task nodes.
We use SequenceFile and ThriftJDBCBinarySerDe to read and write the final results if this is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.resultset.max.fetch.size</name>
<value>1000</value>
<description>Max number of rows sent in one Fetch RPC call by the server to the client.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.xsrf.filter.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>If enabled, HiveServer2 will block any requests made to it over http if an X-XSRF-HEADER header is not present</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.security.command.whitelist</name>
<value>set,reset,dfs,add,list,delete,reload,compile</value>
<description>Comma separated list of non-SQL Hive commands users are authorized to execute</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.mv.files.thread</name>
<value>15</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
The size should be in between 0Pb (inclusive) and 1Kb (inclusive).
Number of threads used to move files in move task. Set it to 0 to disable multi-threaded file moves. This parameter is also used by MSCK to check tables.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.load.dynamic.partitions.thread</name>
<value>15</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
The size should be in between 1 bytes (inclusive) and 1Kb (inclusive).
Number of threads used to load dynamic partitions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.multi.insert.move.tasks.share.dependencies</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If this is set all move tasks for tables/partitions (not directories) at the end of a
multi-insert query will only begin once the dependencies for all these move tasks have been
met.
Advantages: If concurrency is enabled, the locks will only be released once the query has
finished, so with this config enabled, the time when the table/partition is
generated will be much closer to when the lock on it is released.
Disadvantages: If concurrency is not enabled, with this disabled, the tables/partitions which
are produced by this query and finish earlier will be available for querying
much earlier. Since the locks are only released once the query finishes, this
does not apply if concurrency is enabled.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.infer.bucket.sort</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If this is set, when writing partitions, the metadata will include the bucketing/sorting
properties with which the data was written if any (this will not overwrite the metadata
inherited from the table if the table is bucketed/sorted)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.infer.bucket.sort.num.buckets.power.two</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
If this is set, when setting the number of reducers for the map reduce task which writes the
final output files, it will choose a number which is a power of two, unless the user specifies
the number of reducers to use using mapred.reduce.tasks. The number of reducers
may be set to a power of two, only to be followed by a merge task meaning preventing
anything from being inferred.
With hive.exec.infer.bucket.sort set to true:
Advantages: If this is not set, the number of buckets for partitions will seem arbitrary,
which means that the number of mappers used for optimized joins, for example, will
be very low. With this set, since the number of buckets used for any partition is
a power of two, the number of mappers used for optimized joins will be the least
number of buckets used by any partition being joined.
Disadvantages: This may mean a much larger or much smaller number of reducers being used in the
final map reduce job, e.g. if a job was originally going to take 257 reducers,
it will now take 512 reducers, similarly if the max number of reducers is 511,
and a job was going to use this many, it will now use 256 reducers.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.optimize.listbucketing</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Enable list bucketing optimizer. Default value is false so that we disable it by default.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server.read.socket.timeout</name>
<value>10s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Timeout for the HiveServer to close the connection if no response from the client. By default, 10 seconds.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server.tcp.keepalive</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable TCP keepalive for the Hive Server. Keepalive will prevent accumulation of half-open connections.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.decode.partition.name</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to show the unquoted partition names in query results.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.execution.engine</name>
<value>mr</value>
<description>
Expects one of [mr, tez, spark].
Chooses execution engine. Options are: mr (Map reduce, default), tez, spark. While MR
remains the default engine for historical reasons, it is itself a historical engine
and is deprecated in Hive 2 line. It may be removed without further warning.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.execution.mode</name>
<value>container</value>
<description>
Expects one of [container, llap].
Chooses whether query fragments will run in container or in llap
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.jar.directory</name>
<value/>
<description>
This is the location hive in tez mode will look for to find a site wide
installed hive instance.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.user.install.directory</name>
<value>/user/</value>
<description>
If hive (in tez mode only) cannot find a usable hive jar in "hive.jar.directory",
it will upload the hive jar to "hive.user.install.directory/user.name"
and use it to run queries.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorized mode of query execution.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.reduce.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorized mode of the reduce-side of query execution.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.reduce.groupby.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorized mode of the reduce-side GROUP BY query execution.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.mapjoin.native.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable native (i.e. non-pass through) vectorization
of queries using MapJoin.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.mapjoin.native.multikey.only.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to restrict use of native vector map join hash tables to
the MultiKey in queries using MapJoin.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.mapjoin.minmax.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vector map join hash tables to
use max / max filtering for integer join queries using MapJoin.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.mapjoin.overflow.repeated.threshold</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>
The number of small table rows for a match in vector map join hash tables
where we use the repeated field optimization in overflow vectorized row batch for join queries using MapJoin.
A value of -1 means do use the join result optimization. Otherwise, threshold value can be 0 to maximum integer.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.mapjoin.native.fast.hashtable.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable use of native fast vector map join hash tables in
queries using MapJoin.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.groupby.checkinterval</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>Number of entries added to the group by aggregation hash before a recomputation of average entry size is performed.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.groupby.maxentries</name>
<value>1000000</value>
<description>
Max number of entries in the vector group by aggregation hashtables.
Exceeding this will trigger a flush irrelevant of memory pressure condition.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.groupby.flush.percent</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>Percent of entries in the group by aggregation hash flushed when the memory threshold is exceeded.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.execution.reducesink.new.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable the new vectorization
of queries using ReduceSink.
iThe default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.use.vectorized.input.format</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorizing with vectorized input file format capable SerDe.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.use.vector.serde.deserialize</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorizing rows using vector deserialize.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.use.row.serde.deserialize</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable vectorizing using row deserialize.
The default value is false.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.vectorized.adaptor.usage.mode</name>
<value>all</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, chosen, all].
Specifies the extent to which the VectorUDFAdaptor will be used for UDFs that do not have a cooresponding vectorized class.
0. none : disable any usage of VectorUDFAdaptor
1. chosen : use VectorUDFAdaptor for a small set of UDFs that were choosen for good performance
2. all : use VectorUDFAdaptor for all UDFs
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.typecheck.on.insert</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>This property has been extended to control whether to check, convert, and normalize partition value to conform to its column type in partition operations including but not limited to insert, such as alter, describe etc.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hadoop.classpath</name>
<value/>
<description>
For Windows OS, we need to pass HIVE_HADOOP_CLASSPATH Java parameter while starting HiveServer2
using "-hiveconf hive.hadoop.classpath=%HIVE_LIB%".
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.rpc.query.plan</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to send the query plan via local resource or RPC</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compute.splits.in.am</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to generate the splits locally or in the AM (tez only)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.input.generate.consistent.splits</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to generate consistent split locations when generating splits in the AM</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.prewarm.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Enables container prewarm for Tez/Spark (Hadoop 2 only)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.prewarm.numcontainers</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>Controls the number of containers to prewarm for Tez/Spark (Hadoop 2 only)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.stageid.rearrange</name>
<value>none</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, idonly, traverse, execution].
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.explain.dependency.append.tasktype</name>
<value>false</value>
<description/>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.counters.group.name</name>
<value>HIVE</value>
<description>The name of counter group for internal Hive variables (CREATED_FILE, FATAL_ERROR, etc.)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.support.quoted.identifiers</name>
<value>column</value>
<description>
Expects one of [none, column].
Whether to use quoted identifier. 'none' or 'column' can be used.
none: default(past) behavior. Implies only alphaNumeric and underscore are valid characters in identifiers.
column: implies column names can contain any character.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.support.sql11.reserved.keywords</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable support for SQL2011 reserved keywords.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.support.special.characters.tablename</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
This flag should be set to true to enable support for special characters in table names.
When it is set to false, only [a-zA-Z_0-9]+ are supported.
The only supported special character right now is '/'. This flag applies only to quoted table names.
The default value is true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.users.in.admin.role</name>
<value/>
<description>
Comma separated list of users who are in admin role for bootstrapping.
More users can be added in ADMIN role later.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.compat</name>
<value>0.12</value>
<description>
Enable (configurable) deprecated behaviors by setting desired level of backward compatibility.
Setting to 0.12:
Maintains division behavior: int / int = double
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.convert.join.bucket.mapjoin.tez</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether joins can be automatically converted to bucket map joins in hive
when tez is used as the execution engine.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.exec.check.crossproducts</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Check if a plan contains a Cross Product. If there is one, output a warning to the Session's console.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.localize.resource.wait.interval</name>
<value>5000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Time to wait for another thread to localize the same resource for hive-tez.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.localize.resource.num.wait.attempts</name>
<value>5</value>
<description>The number of attempts waiting for localizing a resource in hive-tez.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.auto.reducer.parallelism</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Turn on Tez' auto reducer parallelism feature. When enabled, Hive will still estimate data sizes
and set parallelism estimates. Tez will sample source vertices' output sizes and adjust the estimates at runtime as
necessary.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.max.partition.factor</name>
<value>2.0</value>
<description>When auto reducer parallelism is enabled this factor will be used to over-partition data in shuffle edges.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.min.partition.factor</name>
<value>0.25</value>
<description>
When auto reducer parallelism is enabled this factor will be used to put a lower limit to the number
of reducers that tez specifies.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.bucket.pruning</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When pruning is enabled, filters on bucket columns will be processed by
filtering the splits against a bitset of included buckets. This needs predicates
produced by hive.optimize.ppd and hive.optimize.index.filters.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.bucket.pruning.compat</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
When pruning is enabled, handle possibly broken inserts due to negative hashcodes.
This occasionally doubles the data scan cost, but is default enabled for safety
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.dynamic.partition.pruning</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
When dynamic pruning is enabled, joins on partition keys will be processed by sending
events from the processing vertices to the Tez application master. These events will be
used to prune unnecessary partitions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.dynamic.partition.pruning.max.event.size</name>
<value>1048576</value>
<description>Maximum size of events sent by processors in dynamic pruning. If this size is crossed no pruning will take place.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.dynamic.partition.pruning.max.data.size</name>
<value>104857600</value>
<description>Maximum total data size of events in dynamic pruning.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.dynamic.semijoin.reduction</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>When dynamic semijoin is enabled, shuffle joins will perform a leaky semijoin before shuffle. This requires hive.tez.dynamic.partition.pruning to be enabled.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.max.bloom.filter.entries</name>
<value>100000000</value>
<description>Bloom filter should be of at max certain size to be effective</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.smb.number.waves</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>The number of waves in which to run the SMB join. Account for cluster being occupied. Ideally should be 1 wave.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.exec.print.summary</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Display breakdown of execution steps, for every query executed by the shell.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.exec.inplace.progress</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Updates tez job execution progress in-place in the terminal when hive-cli is used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.in.place.progress</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Allows hive server 2 to send progress bar update information. This is currently available only if the execution engine is tez.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.exec.inplace.progress</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Updates spark job execution progress in-place in the terminal.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.container.max.java.heap.fraction</name>
<value>0.8</value>
<description>This is to override the tez setting with the same name</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.task.scale.memory.reserve-fraction.min</name>
<value>0.3</value>
<description>This is to override the tez setting tez.task.scale.memory.reserve-fraction</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.task.scale.memory.reserve.fraction.max</name>
<value>0.5</value>
<description>The maximum fraction of JVM memory which Tez will reserve for the processor</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.task.scale.memory.reserve.fraction</name>
<value>-1.0</value>
<description>The customized fraction of JVM memory which Tez will reserve for the processor</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.enabled</name>
<value/>
<description>Whether the LLAP IO layer is enabled.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.nonvector.wrapper.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether the LLAP IO layer is enabled for non-vectorized queries that read inputs
that can be vectorized
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.memory.mode</name>
<value>cache</value>
<description>
Expects one of [cache, none].
LLAP IO memory usage; 'cache' (the default) uses data and metadata cache with a
custom off-heap allocator, 'none' doesn't use either (this mode may result in
significant performance degradation)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.alloc.min</name>
<value>256Kb</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
Minimum allocation possible from LLAP buddy allocator. Allocations below that are
padded to minimum allocation. For ORC, should generally be the same as the expected
compression buffer size, or next lowest power of 2. Must be a power of 2.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.alloc.max</name>
<value>16Mb</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
Maximum allocation possible from LLAP buddy allocator. For ORC, should be as large as
the largest expected ORC compression buffer size. Must be a power of 2.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.metadata.fraction</name>
<value>0.1</value>
<description>
Temporary setting for on-heap metadata cache fraction of xmx, set to avoid potential
heap problems on very large datasets when on-heap metadata cache takes over
everything. -1 managed metadata and data together (which is more flexible). This
setting will be removed (in effect become -1) once ORC metadata cache is moved off-heap.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.arena.count</name>
<value>8</value>
<description>
Arena count for LLAP low-level cache; cache will be allocated in the steps of
(size/arena_count) bytes. This size must be <= 1Gb and >= max allocation; if it is
not the case, an adjusted size will be used. Using powers of 2 is recommended.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.memory.size</name>
<value>1Gb</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
Maximum size for IO allocator or ORC low-level cache.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.direct</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether ORC low-level cache should use direct allocation.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.mmap</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether ORC low-level cache should use memory mapped allocation (direct I/O).
This is recommended to be used along-side NVDIMM (DAX) or NVMe flash storage.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.allocator.mmap.path</name>
<value>/tmp</value>
<description>
Expects a writable directory on the local filesystem.
The directory location for mapping NVDIMM/NVMe flash storage into the ORC low-level cache.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.use.lrfu</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether ORC low-level cache should use LRFU cache policy instead of default (FIFO).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.lrfu.lambda</name>
<value>0.01</value>
<description>
Lambda for ORC low-level cache LRFU cache policy. Must be in [0, 1]. 0 makes LRFU
behave like LFU, 1 makes it behave like LRU, values in between balance accordingly.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.cache.allow.synthetic.fileid</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether LLAP cache should use synthetic file ID if real one is not available. Systems
like HDFS, Isilon, etc. provide a unique file/inode ID. On other FSes (e.g. local
FS), the cache would not work by default because LLAP is unable to uniquely track the
files; enabling this setting allows LLAP to generate file ID from the path, size and
modification time, which is almost certain to identify file uniquely. However, if you
use a FS without file IDs and rewrite files a lot (or are paranoid), you might want
to avoid this setting.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.orc.gap.cache</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether LLAP cache for ORC should remember gaps in ORC compression buffer read
estimates, to avoid re-reading the data that was read once and discarded because it
is unneeded. This is only necessary for ORC files written before HIVE-9660.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.use.fileid.path</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether LLAP should use fileId (inode)-based path to ensure better consistency for the
cases of file overwrites. This is supported on HDFS.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether LLAP should try to re-encode and cache data for non-ORC formats. This is used
on LLAP Server side to determine if the infrastructure for that is initialized.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.formats</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat,</value>
<description>
The table input formats for which LLAP IO should re-encode and cache data.
Comma-separated list.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.alloc.size</name>
<value>256Kb</value>
<description>
Expects a byte size value with unit (blank for bytes, kb, mb, gb, tb, pb).
Allocation size for the buffers used to cache encoded data from non-ORC files. Must
be a power of two between hive.llap.io.allocator.alloc.min and
hive.llap.io.allocator.alloc.max.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.vector.serde.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether LLAP should use vectorized SerDe reader to read text data when re-encoding.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.vector.serde.async.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether LLAP should use async mode in vectorized SerDe reader to read text data.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.slice.row.count</name>
<value>100000</value>
<description>
Row count to use to separate cache slices when reading encoded data from row-based
inputs into LLAP cache, if this feature is enabled.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.encode.slice.lrr</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to separate cache slices when reading encoded data from text inputs via MR
MR LineRecordRedader into LLAP cache, if this feature is enabled. Safety flag.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.orc.time.counters</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether to enable time counters for LLAP IO layer (time spent in HDFS, etc.)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.allow.uber</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether or not to allow the planner to run vertices in the AM.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.enforce.tree</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enforce that all parents are in llap, before considering vertex</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.enforce.vectorized</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enforce that inputs are vectorized, before considering vertex</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.enforce.stats</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enforce that col stats are available, before considering vertex</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.max.input.size</name>
<value>10737418240</value>
<description>Check input size, before considering vertex (-1 disables check)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.max.output.size</name>
<value>1073741824</value>
<description>Check output size, before considering vertex (-1 disables check)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.skip.compile.udf.check</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
Whether to skip the compile-time check for non-built-in UDFs when deciding whether to
execute tasks in LLAP. Skipping the check allows executing UDFs from pre-localized
jars in LLAP; if the jars are not pre-localized, the UDFs will simply fail to load.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.allow.permanent.fns</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Whether LLAP decider should allow permanent UDFs.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.execution.mode</name>
<value>none</value>
<description>
Expects one of [auto, none, all, map, only].
Chooses whether query fragments will run in container or in llap
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.object.cache.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Cache objects (plans, hashtables, etc) in llap</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.decoding.metrics.percentiles.intervals</name>
<value>30</value>
<description>
Comma-delimited set of integers denoting the desired rollover intervals (in seconds)
for percentile latency metrics on the LLAP daemon IO decoding time.
hive.llap.queue.metrics.percentiles.intervals
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.io.threadpool.size</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>Specify the number of threads to use for low-level IO thread pool.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.service.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>The name of the LLAP daemon's service principal.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.keytab.file</name>
<value/>
<description>The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the LLAP daemon's service principal.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.zk.sm.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>The name of the principal to use to talk to ZooKeeper for ZooKeeper SecretManager.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.zk.sm.keytab.file</name>
<value/>
<description>
The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the principal to use to talk to
ZooKeeper for ZooKeeper SecretManager.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.webui.spnego.keytab</name>
<value/>
<description>
The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the LLAP WebUI SPNEGO principal.
Typical value would look like /etc/security/keytabs/spnego.service.keytab.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.webui.spnego.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>
The LLAP WebUI SPNEGO service principal. Configured similarly to
hive.server2.webui.spnego.principal
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.principal</name>
<value/>
<description>
The name of the principal to use to run tasks. By default, the clients are required
to provide tokens to access HDFS/etc.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.keytab.file</name>
<value/>
<description>
The path to the Kerberos Keytab file containing the principal to use to run tasks.
By default, the clients are required to provide tokens to access HDFS/etc.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.zk.sm.connectionString</name>
<value/>
<description>ZooKeeper connection string for ZooKeeper SecretManager.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.zk.registry.user</name>
<value/>
<description>
In the LLAP ZooKeeper-based registry, specifies the username in the Zookeeper path.
This should be the hive user or whichever user is running the LLAP daemon.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.zk.registry.namespace</name>
<value/>
<description>
In the LLAP ZooKeeper-based registry, overrides the ZK path namespace. Note that
using this makes the path management (e.g. setting correct ACLs) your responsibility.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.acl</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>The ACL for LLAP daemon.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.acl.blocked</name>
<value/>
<description>The deny ACL for LLAP daemon.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.management.acl</name>
<value>*</value>
<description>The ACL for LLAP daemon management.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.management.acl.blocked</name>
<value/>
<description>The deny ACL for LLAP daemon management.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.remote.token.requires.signing</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Expects one of [false, except_llap_owner, true].
Whether the token returned from LLAP management API should require fragment signing.
True by default; can be disabled to allow CLI to get tokens from LLAP in a secure
cluster by setting it to true or 'except_llap_owner' (the latter returns such tokens
to everyone except the user LLAP cluster is authenticating under).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.delegation.token.lifetime</name>
<value>14d</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
LLAP delegation token lifetime, in seconds if specified without a unit.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.management.rpc.port</name>
<value>15004</value>
<description>RPC port for LLAP daemon management service.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.auto.auth</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether or not to set Hadoop configs to enable auth in LLAP web app.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.rpc.num.handlers</name>
<value>5</value>
<description>Number of RPC handlers for LLAP daemon.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.work.dirs</name>
<value/>
<description>
Working directories for the daemon. This should not be set if running as a YARN
application via Slider. It must be set when not running via Slider on YARN. If the value
is set when running as a Slider YARN application, the specified value will be used.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.yarn.shuffle.port</name>
<value>15551</value>
<description>YARN shuffle port for LLAP-daemon-hosted shuffle.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.yarn.container.mb</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>llap server yarn container size in MB. Used in LlapServiceDriver and package.py</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.queue.name</name>
<value/>
<description>Queue name within which the llap slider application will run. Used in LlapServiceDriver and package.py</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.container.id</name>
<value/>
<description>ContainerId of a running LlapDaemon. Used to publish to the registry</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.shuffle.dir.watcher.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>TODO doc</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.am.liveness.heartbeat.interval.ms</name>
<value>10000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Tez AM-LLAP heartbeat interval (milliseconds). This needs to be below the task timeout
interval, but otherwise as high as possible to avoid unnecessary traffic.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.am.liveness.connection.timeout.ms</name>
<value>10000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Amount of time to wait on connection failures to the AM from an LLAP daemon before
considering the AM to be dead.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.am.use.fqdn</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to use FQDN of the AM machine when submitting work to LLAP.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.am.liveness.connection.sleep.between.retries.ms</name>
<value>2000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Sleep duration while waiting to retry connection failures to the AM from the daemon for
the general keep-alive thread (milliseconds).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.timeout.seconds</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Amount of time to wait before failing the query when there are no llap daemons running
(alive) in the cluster.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.num.executors</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>
Number of executors to use in LLAP daemon; essentially, the number of tasks that can be
executed in parallel.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.am-reporter.max.threads</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>
Maximum number of threads to be used for AM reporter. If this is lower than number of
executors in llap daemon, it would be set to number of executors at runtime.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.rpc.port</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>The LLAP daemon RPC port.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.memory.per.instance.mb</name>
<value>4096</value>
<description>The total amount of memory to use for the executors inside LLAP (in megabytes).</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.xmx.headroom</name>
<value>5%</value>
<description>
The total amount of heap memory set aside by LLAP and not used by the executors. Can
be specified as size (e.g. '512Mb'), or percentage (e.g. '5%'). Note that the latter is
derived from the total daemon XMX, which can be different from the total executor
memory if the cache is on-heap; although that's not the default configuration.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.vcpus.per.instance</name>
<value>4</value>
<description>The total number of vcpus to use for the executors inside LLAP.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.num.file.cleaner.threads</name>
<value>1</value>
<description>Number of file cleaner threads in LLAP.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.file.cleanup.delay.seconds</name>
<value>300s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
How long to delay before cleaning up query files in LLAP (in seconds, for debugging).
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.service.hosts</name>
<value/>
<description>
Explicitly specified hosts to use for LLAP scheduling. Useful for testing. By default,
YARN registry is used.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.service.refresh.interval.sec</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
LLAP YARN registry service list refresh delay, in seconds.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.communicator.num.threads</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>Number of threads to use in LLAP task communicator in Tez AM.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.download.permanent.fns</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether LLAP daemon should localize the resources for permanent UDFs.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.node.reenable.min.timeout.ms</name>
<value>200ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Minimum time after which a previously disabled node will be re-enabled for scheduling,
in milliseconds. This may be modified by an exponential back-off if failures persist.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.node.reenable.max.timeout.ms</name>
<value>10000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Maximum time after which a previously disabled node will be re-enabled for scheduling,
in milliseconds. This may be modified by an exponential back-off if failures persist.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.node.disable.backoff.factor</name>
<value>1.5</value>
<description>
Backoff factor on successive blacklists of a node due to some failures. Blacklist times
start at the min timeout and go up to the max timeout based on this backoff factor.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.num.schedulable.tasks.per.node</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
The number of tasks the AM TaskScheduler will try allocating per node. 0 indicates that
this should be picked up from the Registry. -1 indicates unlimited capacity; positive
values indicate a specific bound.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.scheduler.locality.delay</name>
<value>0ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
The time should be in between -1 msec (inclusive) and 9223372036854775807 msec (inclusive).
Amount of time to wait before allocating a request which contains location information, to a location other than the ones requested. Set to -1 for an infinite delay, 0for no delay.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.task.preemption.metrics.intervals</name>
<value>30,60,300</value>
<description>
Comma-delimited set of integers denoting the desired rollover intervals (in seconds)
for percentile latency metrics. Used by LLAP daemon task scheduler metrics for
time taken to kill task (due to pre-emption) and useful time wasted by the task that
is about to be preempted.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.task.scheduler.wait.queue.size</name>
<value>10</value>
<description>LLAP scheduler maximum queue size.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.wait.queue.comparator.class.name</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hive.llap.daemon.impl.comparator.ShortestJobFirstComparator</value>
<description>
The priority comparator to use for LLAP scheduler prioroty queue. The built-in options
are org.apache.hadoop.hive.llap.daemon.impl.comparator.ShortestJobFirstComparator and
.....FirstInFirstOutComparator
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.task.scheduler.enable.preemption</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether non-finishable running tasks (e.g. a reducer waiting for inputs) should be
preempted by finishable tasks inside LLAP scheduler.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.communicator.connection.timeout.ms</name>
<value>16000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Connection timeout (in milliseconds) before a failure to an LLAP daemon from Tez AM.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.communicator.listener.thread-count</name>
<value>30</value>
<description>The number of task communicator listener threads.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.task.communicator.connection.sleep.between.retries.ms</name>
<value>2000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Sleep duration (in milliseconds) to wait before retrying on error when obtaining a
connection to LLAP daemon from Tez AM.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.web.port</name>
<value>15002</value>
<description>LLAP daemon web UI port.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.web.ssl</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether LLAP daemon web UI should use SSL.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.client.consistent.splits</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Whether to setup split locations to match nodes on which llap daemons are running, instead of using the locations provided by the split itself</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.validate.acls</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether LLAP should reject permissive ACLs in some cases (e.g. its own management
protocol or ZK paths), similar to how ssh refuses a key with bad access permissions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.output.service.port</name>
<value>15003</value>
<description>LLAP daemon output service port</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.output.stream.timeout</name>
<value>120s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
The timeout for the client to connect to LLAP output service and start the fragment
output after sending the fragment. The fragment will fail if its output is not claimed.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.output.service.send.buffer.size</name>
<value>131072</value>
<description>Send buffer size to be used by LLAP daemon output service</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.output.service.max.pending.writes</name>
<value>8</value>
<description>
Maximum number of queued writes allowed per connection when sending data
via the LLAP output service to external clients.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.enable.grace.join.in.llap</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>Override if grace join should be allowed to run in llap.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.hs2.coordinator.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>
Whether to create the LLAP coordinator; since execution engine and container vs llap
settings are both coming from job configs, we don't know at start whether this should
be created. Default true.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.llap.daemon.logger</name>
<value>query-routing</value>
<description>
Expects one of [query-routing, rfa, console].
logger used for llap-daemons.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.future.timeout</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Timeout for requests from Hive client to remote Spark driver.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.job.monitor.timeout</name>
<value>60s</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is sec if not specified.
Timeout for job monitor to get Spark job state.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.connect.timeout</name>
<value>1000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Timeout for remote Spark driver in connecting back to Hive client.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.server.connect.timeout</name>
<value>90000ms</value>
<description>
Expects a time value with unit (d/day, h/hour, m/min, s/sec, ms/msec, us/usec, ns/nsec), which is msec if not specified.
Timeout for handshake between Hive client and remote Spark driver. Checked by both processes.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.secret.bits</name>
<value>256</value>
<description>Number of bits of randomness in the generated secret for communication between Hive client and remote Spark driver. Rounded down to the nearest multiple of 8.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.rpc.threads</name>
<value>8</value>
<description>Maximum number of threads for remote Spark driver's RPC event loop.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.rpc.max.size</name>
<value>52428800</value>
<description>Maximum message size in bytes for communication between Hive client and remote Spark driver. Default is 50MB.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.channel.log.level</name>
<value/>
<description>Channel logging level for remote Spark driver. One of {DEBUG, ERROR, INFO, TRACE, WARN}.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.rpc.sasl.mechanisms</name>
<value>DIGEST-MD5</value>
<description>Name of the SASL mechanism to use for authentication.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.client.rpc.server.address</name>
<value/>
<description>The server address of HiverServer2 host to be used for communication between Hive client and remote Spark driver. Default is empty, which means the address will be determined in the same way as for hive.server2.thrift.bind.host.This is only necessary if the host has mutiple network addresses and if a different network address other than hive.server2.thrift.bind.host is to be used.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.dynamic.partition.pruning</name>
<value>false</value>
<description>
When dynamic pruning is enabled, joins on partition keys will be processed by writing
to a temporary HDFS file, and read later for removing unnecessary partitions.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.spark.dynamic.partition.pruning.max.data.size</name>
<value>104857600</value>
<description>Maximum total data size in dynamic pruning.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.reorder.nway.joins</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Runs reordering of tables within single n-way join (i.e.: picks streamtable)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.merge.nway.joins</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Merge adjacent joins into a single n-way join</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.log.every.n.records</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>
Expects value bigger than 0.
If value is greater than 0 logs in fixed intervals of size n rather than exponentially.
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.msck.path.validation</name>
<value>throw</value>
<description>
Expects one of [throw, skip, ignore].
The approach msck should take with HDFS directories that are partition-like but contain unsupported characters. 'throw' (an exception) is the default; 'skip' will skip the invalid directories and still repair the others; 'ignore' will skip the validation (legacy behavior, causes bugs in many cases)
</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.msck.repair.batch.size</name>
<value>0</value>
<description>Batch size for the msck repair command. If the value is greater than zero, it will execute batch wise with the configured batch size. The default value is zero. Zero means it will execute directly (Not batch wise)</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.llap.concurrent.queries</name>
<value>-1</value>
<description>The number of queries allowed in parallel via llap. Negative number implies 'infinite'.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.tez.enable.memory.manager</name>
<value>true</value>
<description>Enable memory manager for tez</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.hash.table.inflation.factor</name>
<value>2.0</value>
<description>Expected inflation factor between disk/in memory representation of hash tables</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.log.trace.id</name>
<value/>
<description>Log tracing id that can be used by upstream clients for tracking respective logs. Truncated to 64 characters. Defaults to use auto-generated session id.</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.conf.restricted.list</name>
<value>hive.security.authenticator.manager,hive.security.authorization.manager,hive.users.in.admin.role,hive.server2.xsrf.filter.enabled</value>
<description>Comma separated list of configuration options which are immutable at runtime</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.conf.hidden.list</name>
<value>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword,hive.server2.keystore.password</value>
<description>Comma separated list of configuration options which should not be read by normal user like passwords</description>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.conf.internal.variable.list</name>
<value>hive.added.files.path,hive.added.jars.path,hive.added.archives.path</value>
<description>Comma separated list of variables which are used internally and should not be configurable.</description>
</property>
</configuration>