先来了解一下数组对象在堆中的存储形式【数组长度,数组元素类型信息等】+ 【存放元素对象的空间】
Ma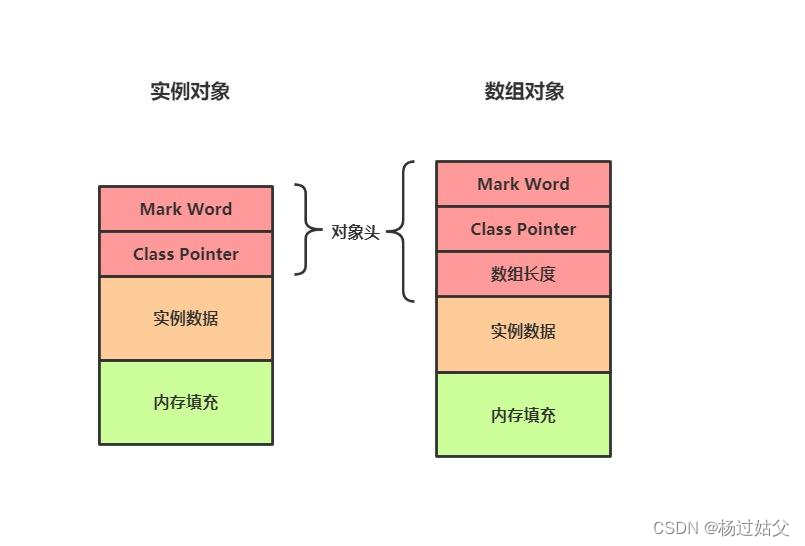
| 基础信息 | 实例数据 | 内存填充 | |
| Mark Word,ClassPointer,数组长度 | 第一个元素 | 第二个元素 | 固定的填充内容 |
所以我们想要获取某个下标的元素首先要获取这个元素的起始位置和每个元素长度
例如我们要取第二个元素的,首先知道第二个元素的起始位置,从其实位置开始按照每个元素的长度取指定的位数,就相当于获取了第二个元素的全部信息。
再来了解一下Java中一个特殊的类sun.misc.Unsafe
sun.misc.Unsafe是JDK提供的用于很底层编程的类,位于sun.misc包中。在有些底层编程的场景,Java语言层面办不到的事情,我们可能需要使用JNI,借助C语言去实现。但是使用JNI并不是唯一的选择,使用JNI会将代码绑定到特定的平台,使用Unsafe类可以保留Java语言代码对平台的独立性,又实现底层编程。
Unsafe类并没有public的构造函数,只提供了一个静态工厂方法,这个静态方法还只提供给JDK标准库自身的类调用,在我们自己随便建的一个普通的类调用这个静态工厂方法还会抛异常。
这个静态工厂方法的代码如下:
@CallerSensitive
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
if (!VM.isSystemDomainLoader(caller.getClassLoader()))
throw new SecurityException("Unsafe");
return theUnsafe;
}可以使用反射的方式
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class TestUnsafe {
private static Unsafe unsafe;
static {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
//
}
}
}Unsafe功能列表
- allocateMemory/freeMemory,分配、释放堆外内存DirectMemory(和c/cpp中的malloc一样)
- CAS操作
- copyMemory
- defineClass(without security checks)
- get/put address 使用堆外内存地址进行数据的读写操作
- get/put volatile 使用堆外内存地址进行数据的读写操作 - volatile版本
- loadFence/storeFence/fullFence 禁止指令重排序
- park/unpark 阻塞/解除阻塞线程
Unsafe的数组操作
unsafe中,有两个关于数组的方法:
public native int arrayBaseOffset(Class<?> arrayClass);
public native int arrayIndexScale(Class<?> arrayClass);
arrayBaseOffset 数组第一个元素相对于数组对象起始地址的偏移量
arrayIndexScale就是指数组中每个元素所占用的空间大小,比如int[] scale就是4,long[] scale就是8,object[] scale就是4(指针大小)
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U;
private static final long SIZECTL;
private static final long TRANSFERINDEX;
private static final long BASECOUNT;
private static final long CELLSBUSY;
private static final long CELLVALUE;
private static final long ABASE;
private static final int ASHIFT;
static {
try {
U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = ConcurrentHashMap.class;
SIZECTL = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("sizeCtl"));
TRANSFERINDEX = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("transferIndex"));
BASECOUNT = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("baseCount"));
CELLSBUSY = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("cellsBusy"));
Class<?> ck = CounterCell.class;
CELLVALUE = U.objectFieldOffset
(ck.getDeclaredField("value"));
Class<?> ak = Node[].class;
ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak);
int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak);
if ((scale & (scale - 1)) != 0)
throw new Error("data type scale not a power of two");
ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}这是CurrentHashMap中的源码我们需要注意的地方有:
Class<?> ak = Node[].class;
ABASE = U.arrayBaseOffset(ak);ABASE:数组第一个元素相对于数组对象起始地址的偏移量 int scale = U.arrayIndexScale(ak);数组中每个元素所占用的空间大小,返回的是所占空间的字节数 scale为2的n次方,2的n次方二进制表示就是某个位置为1其余位置为0 ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale); Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale) 计算int型参数二进制表示数值最高位前面有几个0 由于int一共有32位,出去位1的一位剩下31位,31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale)就表示scale二进制表示最低位有几个连续的0
| 32 | ||
| 32位 | ||
| 000000000000000000000000000(27位) | 1 | 00000(5位) |
| Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros() | 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros() | |
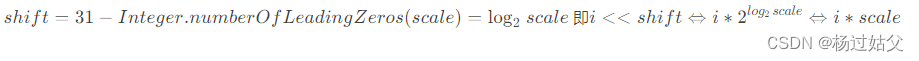
@Test
public void printObjectArrayScale() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Field theUnsafeInstance = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafeInstance.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe U = (Unsafe) theUnsafeInstance.get(Unsafe.class);
Class<?> objectArr = Object[].class;
Class<?> intArr = int[].class;
Class<?> longArr = long[].class;
Class<?> byteArr = byte[].class;
int objectScale = U.arrayIndexScale(objectArr);
int intScale = U.arrayIndexScale(intArr);
int longScale = U.arrayIndexScale(longArr);
int byteScale = U.arrayIndexScale(byteArr);
System.out.println("Object[]的sacle=" + objectScale);
System.out.println("int[]的sacle=" + intScale);
System.out.println("long[]的sacle=" + longScale);
System.out.println("byte[]的sacle=" + byteScale);
}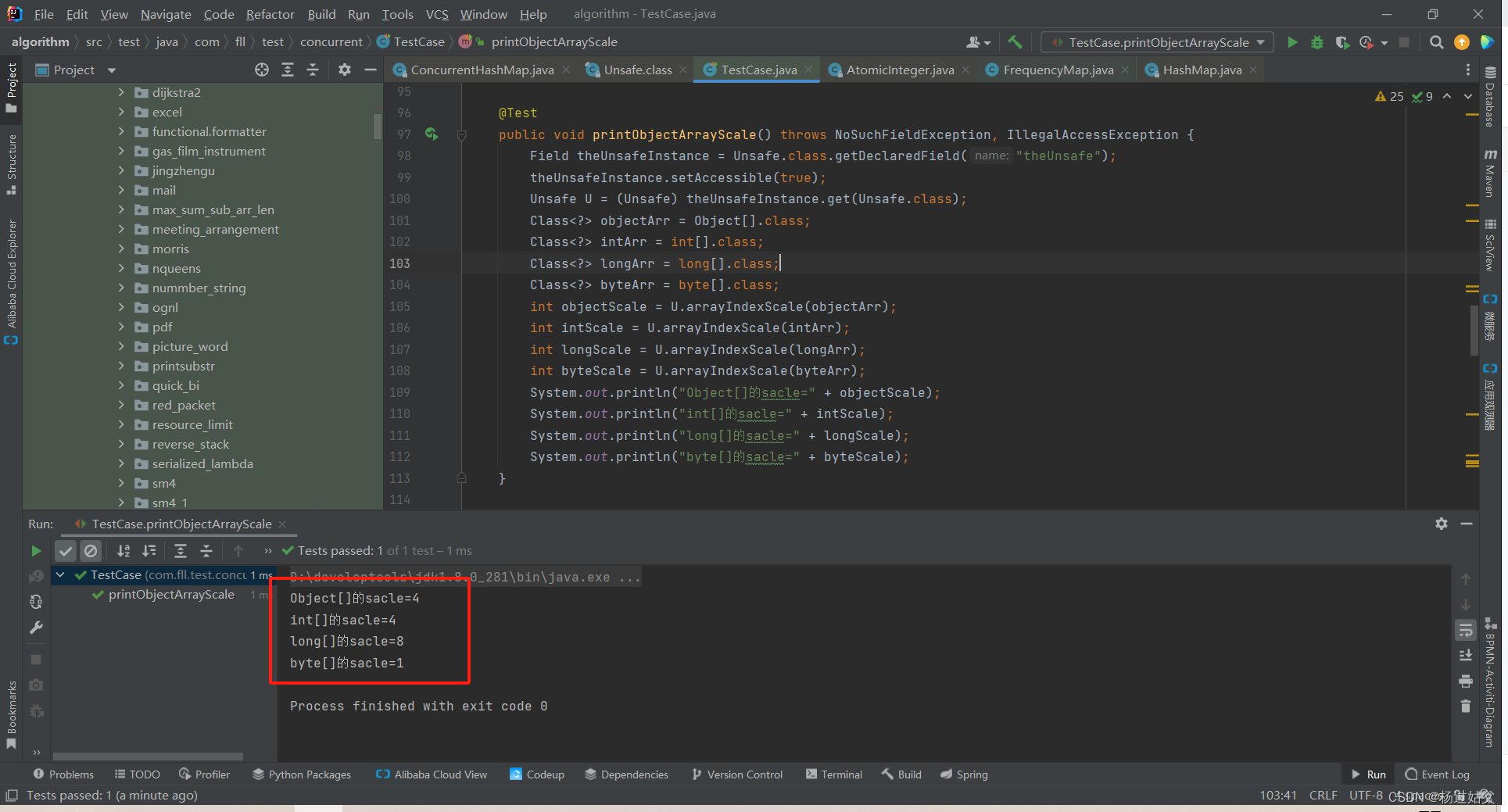
可以通过上面的方法测试,引用类型的数组的scale是4,因为虽然不同对象占用内存大小不一,但是对象数组每个元素是指向对应对象的引用,即内存地址
常规的想法是通过 scale * index 来计算某个元素相对于起始位置的偏移量
@Test
public void findArrayByBaseAndScale() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<Unsafe> clazz = Unsafe.class;
Field unsafeField = clazz.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
unsafeField.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe)unsafeField.get(null);
int[] temp = {1, 2, 3 , 4};
int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class);
System.out.println(unsafe.getInt(temp , base + 0 * scale));
System.out.println(unsafe.getInt(temp , base + 1 * scale));
System.out.println(unsafe.getInt(temp , base + 2 * scale));
System.out.println(unsafe.getInt(temp , base + 3 * scale));
}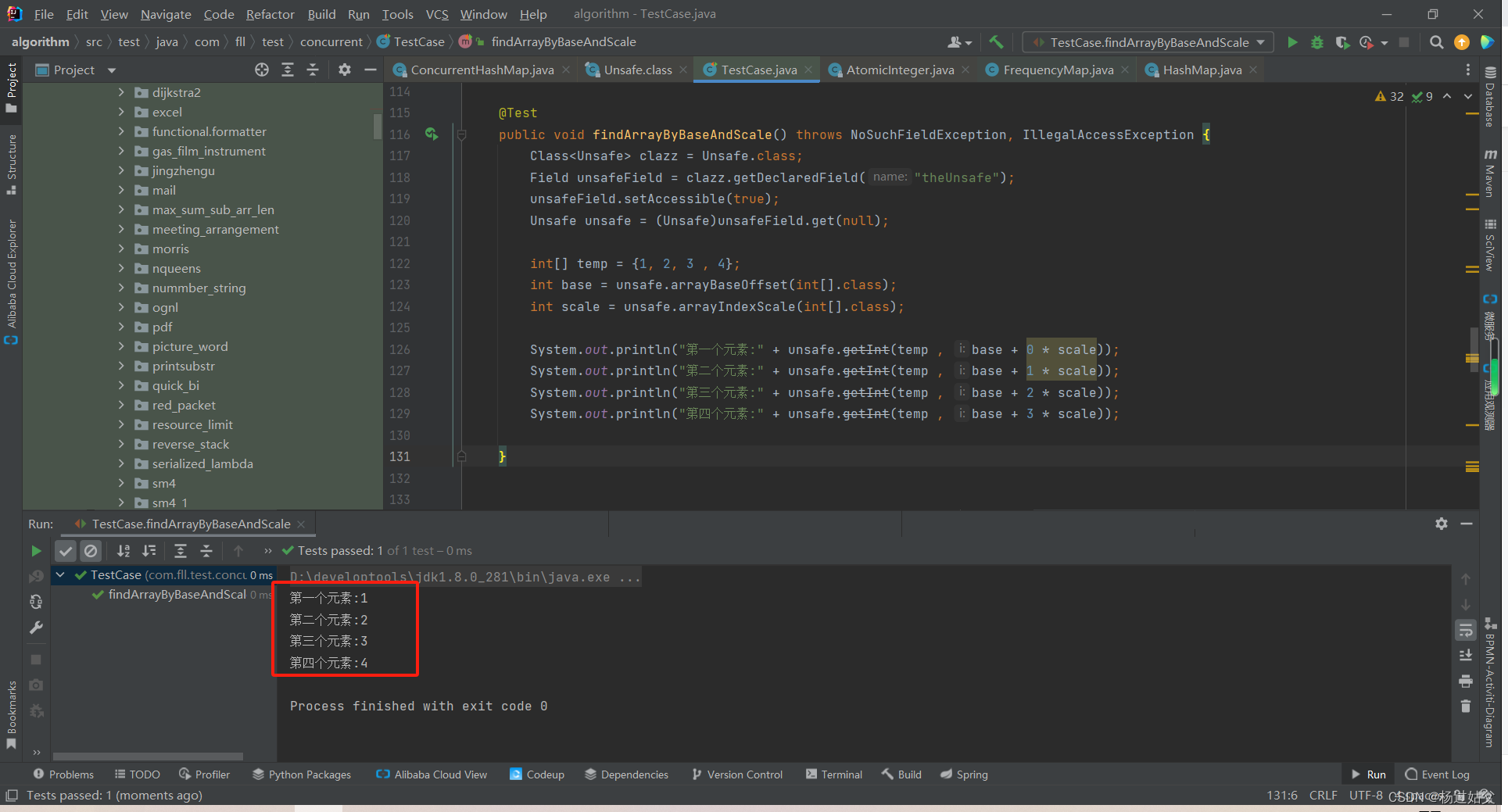
可以看到顺利取到了数组元素
这里看看CurrentHashMap是怎么计算元素的偏移量的
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}这里测试一下它的这种方法
@Test
public void findArrayByBaseAndScale1() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<Unsafe> clazz = Unsafe.class;
Field unsafeField = clazz.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
unsafeField.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe)unsafeField.get(null);
int[] temp = {1, 2, 3 , 4};
int base = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(int[].class);
int scale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(int[].class);
int ASHIFT = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(scale);
System.out.println("第一个元素:" + unsafe.getInt(temp , base + (0 << ASHIFT) ));
System.out.println("第二个元素:" + unsafe.getInt(temp , base + (1 << ASHIFT) ));
System.out.println("第三个元素:" + unsafe.getInt(temp , base + (2 << ASHIFT) ));
System.out.println("第四个元素:" + unsafe.getInt(temp , base + (3 << ASHIFT) ));
}
可以看到也顺利取到了数组的元素
熟悉位运算的很容易理解,其实这就是利用了一个位运算的技巧,通过向左移来实现扩大为2的n次方倍,而scale正好是2的n次方,所以可以这样计算