前言
本文将讲解node的web服务
通过讲解http请求,node创建web服务等知识点让你更加深入的理解web服务和node创建的web服务
HTTP请求是什么?
HTTP请求是客户端(通常是浏览器或其他应用程序)与服务器之间进行通信的一种方式。
当您在浏览器中输入网址、点击链接或提交表单时,客户端会向服务器发送一个 HTTP 请求,以请求特定的资源或执行特定的操作。
HTTP请求包含以下几个重要部分:
- 请求方法:如 GET(获取资源)、POST(提交数据以创建或更新资源)、PUT(更新资源)、DELETE(删除资源)等。
- 请求 URL:指定要请求的资源的地址。
- 请求头:包含关于请求的各种元数据,如客户端接受的内容类型、语言、用户代理等信息。
- 请求体(对于某些请求方法,如 POST 和 PUT):包含要发送给服务器的数据,例如表单提交的数据。
服务器接收到 HTTP 请求后,会根据请求的内容进行处理,并返回一个相应的 HTTP 响应给客户端。
node创建web服务
首先我们需要初始化一个项目,创建文件夹node_web,使用npm init初始化一个项目并创建一个index.js
接下来我们引入http
const http = require("http");
这样我们就能开始创建web服务了
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const reqUrl = url.parse(req.url);
console.log(reqUrl);
console.log(reqUrl.pathname);
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server is running at http://127.0.0.1:3000");
});
通过这个我们可以看到reqUrl和reqUrl.pathname
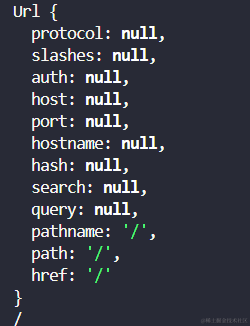
可以知道可以获取到前端给后端发送的请求报文
接下来我们给后端进行响应
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const reqUrl = url.parse(req.url);
console.log(reqUrl);
console.log(reqUrl.pathname);
if (reqUrl.pathname === "/") {
res.end("hello world");
}
});
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("server is running at http://127.0.0.1:3000");
});
可以看到发送请求以后,前端收到了响应
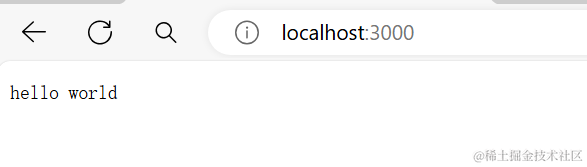
那么如果我想让后端读取html呢?
res.end("<h2>hello world</h2>");
只需要添加请求头参数
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html; charset=utf8",
});
接下来我们就能看到结果为
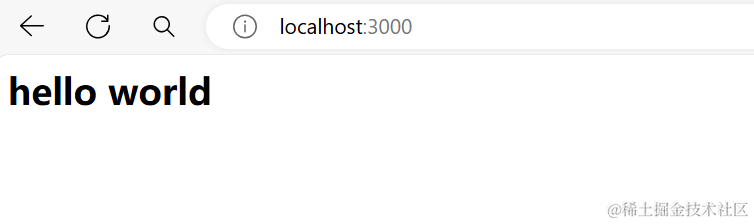
那么我们既然能够获取到请求的路由,我们不就可以编写接口了
修改代码,首先添加一个对象
const data = {
name: "shunyi",
age: 18,
};
然后修改createServer内部代码为
if (reqUrl.pathname === "/") {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html; charset=utf8",
});
res.end("<h2>hello world</h2>");
} else if (reqUrl.pathname === "/user") {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf8",
});
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
}
接下来我们访问http://localhost:3000/user
我们就能看到
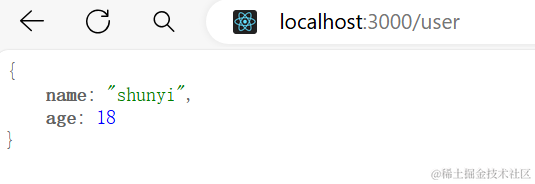
接下来我们继续扩充功能,如果访问的路径不存在,那么我们就需要返回一个404.html
我们首先创建一个404.html
里面放一个简单的404提示
<body>
<h1>404</h1>
<p>你访问的资源不存在哦~</p>
</body>
首先我们就需要改一下createServer内部代码,添加一个else语句块
并在其内部读取文件
首先需要引入fs模块和path模块
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
接下来修改createServer内部代码
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const reqUrl = url.parse(req.url);
console.log(reqUrl);
console.log(reqUrl.pathname);
if (reqUrl.pathname === "/") {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html; charset=utf8",
});
res.end("<h2>hello world</h2>");
} else if (reqUrl.pathname === "/user") {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=utf8",
});
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
} else if (reqUrl.pathname === "/login" && req.method === "POST") {
res.end("login success");
} else {
const pathUrl = path.resolve(__dirname, "./assets/404.html");
const file = fs.readFileSync(pathUrl)
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/html; charset=utf8",
});
res.end(file);
}
});
主要就是添加了下面的代码
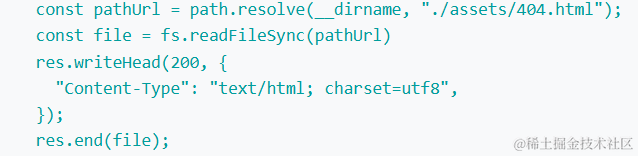
-
path.resolve(__dirname, "./assets/404.html")用于获取当前文件所在目录下assets文件夹中的404.html文件的绝对路径,并将其存储在pathUrl变量中。 -
fs.readFileSync同步读取该文件的内容,并将其存储在file变量中。 -
res.writeHead方法设置响应的状态码为 200(表示成功),并设置响应头的Content-Type为text/html; charset=utf8,表明响应的内容类型是 HTML 文本,且编码为 UTF-8。 -
使用
res.end方法将读取到的文件内容发送给客户端,完成响应的发送。
最后我们访问不存在的url就会出现以下界面
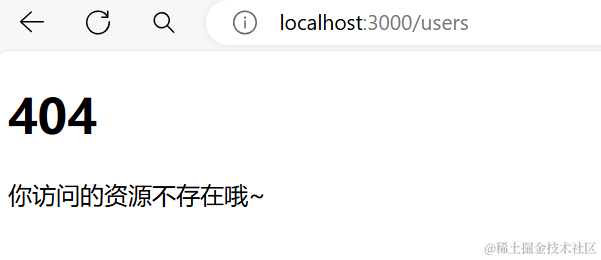
总结
本文介绍了node的web服务,以及什么是http请求
通过实际的例子让你感受一下如何用node去使用web的服务
我们可以体会到,有了node,JavaScript的能力更加的强大了
node的强大远不止于此,大家可以去看看node官网康康,进一步领略一下node的魅力!!