215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
- 1. 题目描述
- 2.详细题解
- 3.代码实现
- 3.1 Python
- 3.2 Java
1. 题目描述
题目中转:215. 数组中的第K个最大元素

2.详细题解
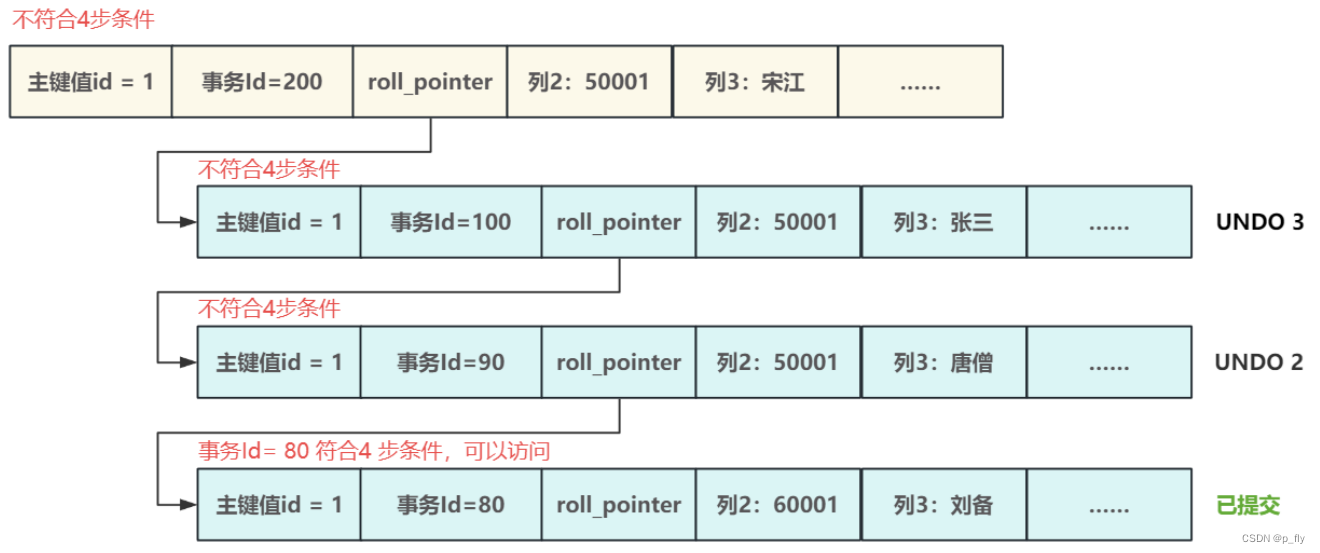
快速排序算法在每一轮排序中,随机选择一个数字
x
x
x,根据与
x
x
x的大小关系将要排序的数据分成独立的两个部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比
x
x
x小(不比
x
x
x大),另外一部分的所有数据比
x
x
x要大(不比
x
x
x小),此时一定可以确定
x
x
x的位置为
m
i
d
mid
mid,若该位置
m
i
d
mid
mid即为要查找的第
k
k
k元素,则已经找到答案,而不用关心左右两个区间中的数字是否有序。
具体的,在实现过程中,若该位置
m
i
d
mid
mid大于
k
k
k,说明
k
k
k在左区间,则递归左区间,否则递归右区间。
该题代码开发工作量略大,主要是边界问题的处理具体。在Python方法一中忽略了子区间仅为两个元素的情况,故造成错误;Python方法二和Java方法一为同一种算法代码实现,提交均为超出时间限制,未通过测试案例均为同一个,根本原因在于数组中存在大量的相同元素时,划分数组时未等分,以致于递归迭代深度太深,例如对于数组
[
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
,
1
]
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],根据;Python方法二和Java方法一,初始化
l
=
0
,
r
=
7
l=0,r=7
l=0,r=7,第一次划分结果为
i
=
7
,
j
=
0
i=7,j=0
i=7,j=0,以
j
=
0
j=0
j=0划分,对于测试未通过的案例,达到10万级的数组长度,且几乎所有数字均为
1
1
1,即为一个极端案例。【该题leetcode的官方题解非常清晰,建议仔细阅读。】
3.代码实现
3.1 Python
Python方法一:
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(nums)
return self.quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k)
def quickSelect(self, nums, l, r, k):
i, j = l+1, r
while i < j:
while i < r and nums[i] <= nums[l]:
i += 1
while j > l and nums[j] >= nums[l]:
j -= 1
if i>=j:
break
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
nums[l], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[l]
if k == j:
return nums[j]
elif k < j:
return self.quickSelect(nums, l, j-1, k)
else:
return self.quickSelect(nums, j+1, r, k)

Python方法二:
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(nums)
return self.quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k)
def quickSelect(self, nums, l, r, k):
i, j = l+1, r
while l < r:
while i < r and nums[i] <= nums[l]:
i += 1
while j > l and nums[j] >= nums[l]:
j -= 1
if i>=j:
break
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
nums[l], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[l]
if k == j:
return nums[j]
elif k < j:
return self.quickSelect(nums, l, j-1, k)
else:
return self.quickSelect(nums, j+1, r, k)

Python方法三:
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(nums)
return self.quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k)
def quickSelect(self, nums, l, r, k):
if l == r:
return nums[k]
i, j, key = l-1, r+1, nums[l]
while i < j:
i += 1
while nums[i] < key:
i += 1
j -= 1
while nums[j] > key:
j -= 1
if i < j:
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
if k <= j:
return self.quickSelect(nums, l, j, k)
else:
return self.quickSelect(nums, j+1, r, k)

3.2 Java
Java方法一:
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
return quickSelect(nums, 0, n-1, n-k);
}
public int quickSelect(int[] nums, int l, int r, int k){
int i = l+1, j = r;
while (l < r){
while (i < r && nums[i] <= nums[l]){i++;}
while (j > l && nums[j] >= nums[l]){j--;}
if (i>=j){break;}
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
if (j==k){return nums[j];}
else if (k < j){return quickSelect(nums, l, j-1, k);}
else{return quickSelect(nums, j+1, r, k);}
}
}

Java方法二:
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
return quickSelect(nums, 0, n - 1, n - k);
}
public int quickSelect(int[] nums, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l == r) return nums[k];
int key = nums[l], i = l - 1, j = r + 1;
while (i < j) {
do i++; while (nums[i] < key);
do j--; while (nums[j] > key);
if (i < j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
if (k <= j) return quickSelect(nums, l, j, k);
else return quickSelect(nums, j + 1, r, k);
}
}

执行用时不必过于纠结,对比可以发现,对于python和java完全相同的编写,java的时间一般是优于python的;至于编写的代码的执行用时击败多少对手,执行用时和网络环境、当前提交代码人数等均有关系,可以尝试完全相同的代码多次执行用时也不是完全相同,只要确保自己代码的算法时间复杂度满足相应要求即可,也可以通过点击分布图查看其它coder的code。