目录
一、IOU
二、GIOU
三、DIOU
四、DIOU_Loss实战
在前面两章里面训练模型时,损失函数都是选择L1Loss(平均绝对值误差(MAE))损失函数,L1Loss损失函数公式如下:
由公式可知,L1Loss损失函数是线性函数,其梯度是恒定的,即无论预测值与真实值之间的误差大小,其梯度都是常数(+1或-1)。虽然避免了梯度爆炸的问题,但在误差很小时,梯度仍然较大,不利于梯度在接近最优解时的精细调整。同时L1Loss并不直接优化我们最关心的目标——即预测框和真实框的之间的重叠程度。L1Loss通常是分别计算预测框和真实框各个坐标点之间的L1距离,这种方法假设了坐标点之间是相互独立的,没有考虑它们之间的相关性。
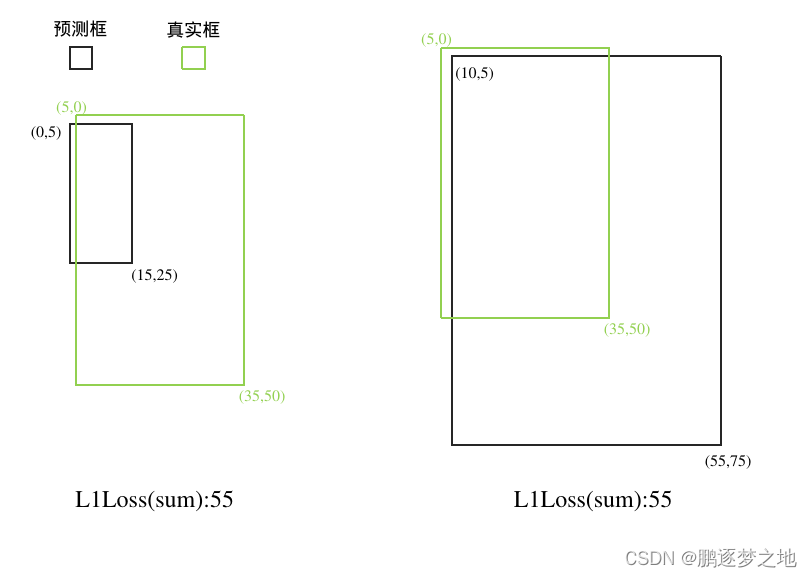
上图中的绿框代表真实框,黑框为模型的预测框,两个预测框的大小不一,与真实框之间的重叠面积也不一致,但得到的L1Loss损失值却是一样的。说明L1Loss损失不能准确反应两个目标边界框重合的程度,因此诞生了IOU损失函数。
一、IOU
论文原文:《UnitBox: An Advanced Object Detection Network》![]() http://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01471
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.01471
IOU(Intersection over Union)损失函数是目标检测中常用的一种损失韩式,主要用于评估预测边界框(Bounding Box)与真实框(Ground Truth Box)之间的重叠程度,并作为优化目标来指导模型训练。
IOU即交并比,适用于衡量两个边界框的之间的重叠程度的度量指标。其计算公式为:
即两个框的相交的面积除以两个框相并的面积。
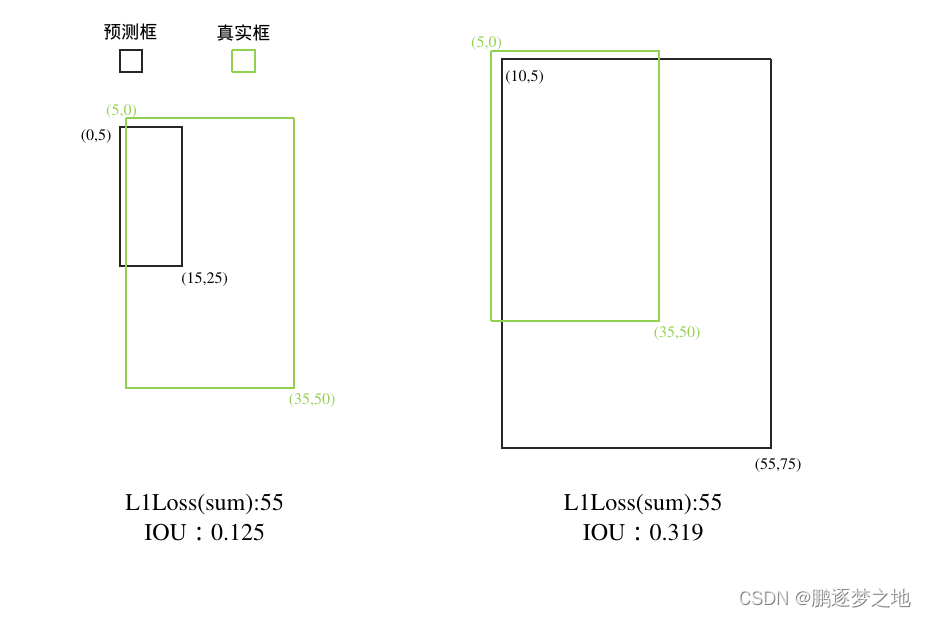
如上图所示,第一个预测框与真实框的相交的面积为(25-5)*(15-5)=200,相并的面积为15*(25-5)+(35-5)*50-200=1600,最终IOU=200/1600=0.125。而第二个预测框的IOU则为0.319。相对于两个预测框计算L1损失的结果相同,可以看出IOU能直接反映出预测框与真实框之间的重叠程度。
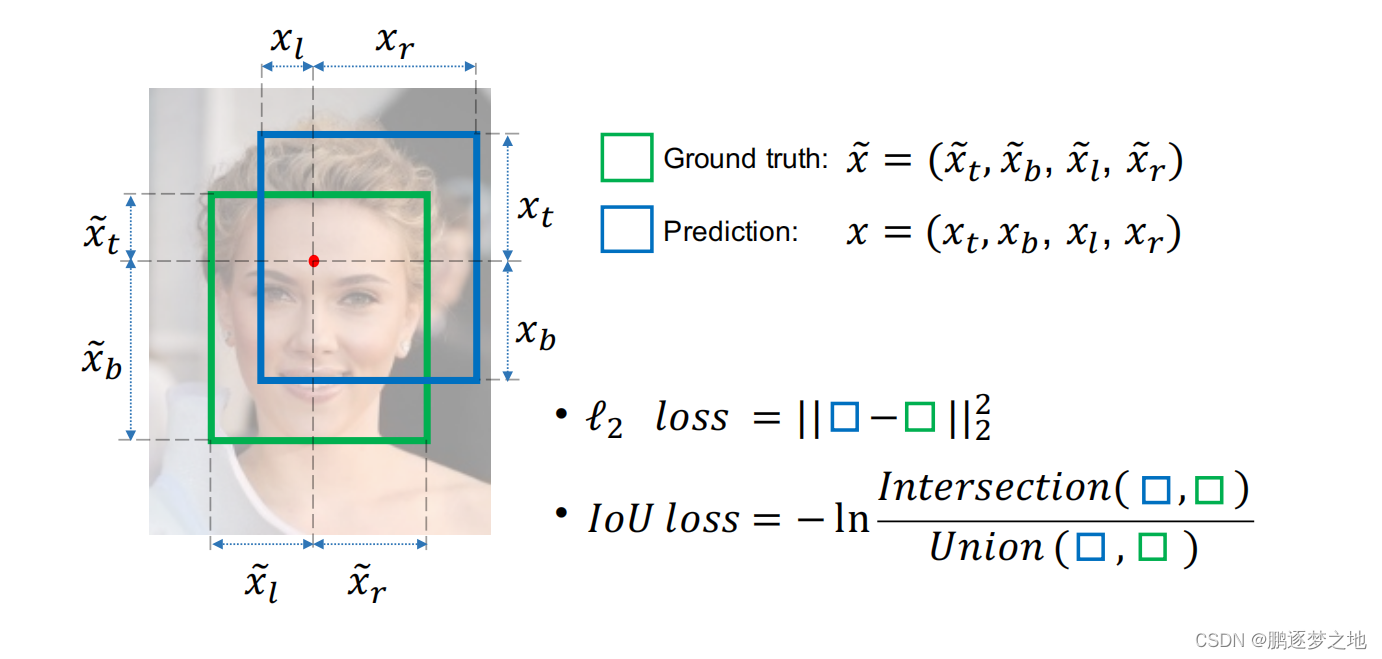
IOU损失计算方式如下:
简单代码实现如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def IOU(RecA, RecB):
x1 = max(RecA[0], RecB[0])
y1 = max(RecA[1], RecB[1])
x2 = min(RecA[2], RecB[2])
y2 = min(RecA[3], RecB[3])
# 计算交集部分面积
interArea = max(0, x2 - x1 + 1) * max(0, y2 - y1 + 1)
# 计算预测值和真实值的面积
RecA_Area = (RecA[2] - RecA[0] + 1) * (RecA[3] - RecA[1] + 1)
RecB_Area = (RecB[2] - RecB[0] + 1) * (RecB[3] - RecB[1] + 1)
#计算并集部分面积
UnionArea=float(RecA_Area + RecB_Area - interArea)
# 计算IOU
iou = interArea / UnionArea
return iou
img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8)
img.fill(255)
RecA = [50, 50, 300, 300] #方框的左上角坐标和右上角坐标
RecB = [60, 60, 320, 320]
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecA[0], RecA[1]), (RecA[2], RecA[3]), (0, 255, 0), 5)
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecB[0], RecB[1]), (RecB[2], RecB[3]), (255, 0, 0), 5)
iou =IOU(RecA, RecB)
font = cv2.FONT_ITALIC
#展示IOU结果
cv2.putText(img, "IOU = %.2f" % iou, (130, 190), font, 0.6, (0, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(img, "IOU_Loss = %.2f" % (1-iou), (80, 350), font, 0.6, (0, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("IOU",img )
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
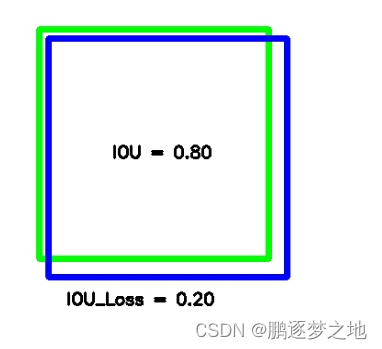
最终结果如上图所示,IOU_Loss相对与L1Loss更能反映预测框与真实框之间的重叠程度。
如上图所示,IOU最大的缺点是当预测框与真实框不相交的时候,其IOU都为0,此时模型的梯度消失,导致无法进一步优化,各位可以试一下将IOU_Loss替换前两章小黄人目标检测任务中的L1_Loss,会发现模型无法收敛。
二、GIOU
原文论文:《Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression》![]() http://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630GIOU(Generalized Intersection over Union),即广义交并比,这是一种在目标检测领域中用来评估预测框与真实框之间重叠度的指标,传统IOU在两个框无重叠时无法反映他们之间的远近关系,在模型训练时会出现梯度消失的情况。为了解决这个问题,GIOU被提出。公式如下:
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630GIOU(Generalized Intersection over Union),即广义交并比,这是一种在目标检测领域中用来评估预测框与真实框之间重叠度的指标,传统IOU在两个框无重叠时无法反映他们之间的远近关系,在模型训练时会出现梯度消失的情况。为了解决这个问题,GIOU被提出。公式如下:
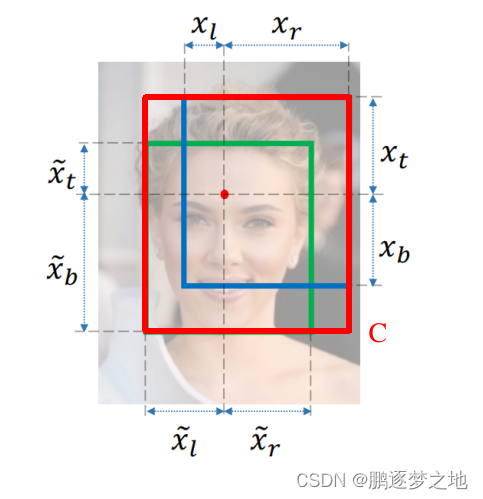
GIOU引入了一个最小闭包区域(即能同事包含预测框与真实框的最小矩形框),如上图中的红框C,并引入了一个额外的惩罚项来反映两个框的远近程度。
代码实现如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
def GIOU(RecA, RecB):
x1 = max(RecA[0], RecB[0])
y1 = max(RecA[1], RecB[1])
x2 = min(RecA[2], RecB[2])
y2 = min(RecA[3], RecB[3])
# 计算交集部分面积
interArea = max(0, x2 - x1 + 1) * max(0, y2 - y1 + 1)
# 计算预测值和真实值的面积
RecA_Area = (RecA[2] - RecA[0] + 1) * (RecA[3] - RecA[1] + 1)
RecB_Area = (RecB[2] - RecB[0] + 1) * (RecB[3] - RecB[1] + 1)
#计算并集部分面积
UnionArea=float(RecA_Area + RecB_Area - interArea)
# 计算IOU
iou = interArea / UnionArea
C_x1 = min(RecA[0], RecB[0])
C_y1 = min(RecA[1], RecB[1])
C_x2 = max(RecA[2], RecB[2])
C_y2 = max(RecA[3], RecB[3])
#计算最小闭包矩形面积
C_area = (C_x2 - C_x1) * (C_y2 - C_y1)
IOU = interArea / UnionArea
GIOU = IOU - abs((C_area - UnionArea) / C_area)
return GIOU
img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8)
img.fill(255)
RecA = [50, 50, 80,80] #方框的左上角坐标和右上角坐标
RecB = [100, 160, 320, 320]
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecA[0], RecA[1]), (RecA[2], RecA[3]), (0, 255, 0), 5)
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecB[0], RecB[1]), (RecB[2], RecB[3]), (255, 0, 0), 5)
iou =GIOU(RecA, RecB)
font = cv2.FONT_ITALIC
#展示IOU结果
cv2.putText(img, "GIOU = %.2f" % iou, (200, 450), font, 0.6, (0, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("IOU",img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
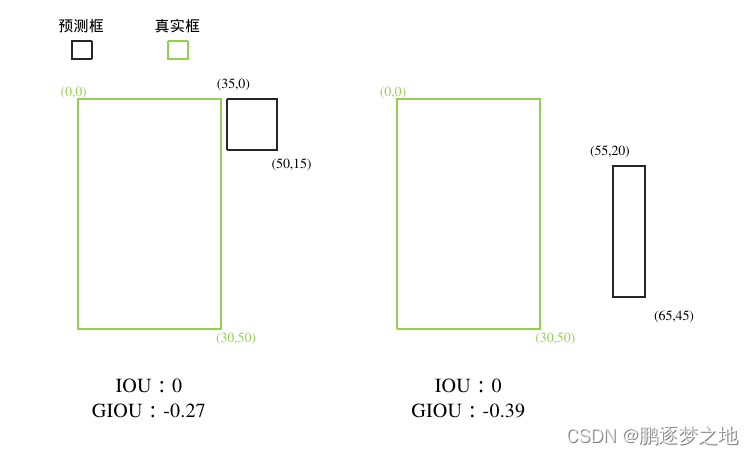
GIOU在计算预测框与真实框之间的重叠程度时,即使两框之间无重叠区域,其结果也不会为0,有效的解决了模型在预测框也真实框之间无交集时出现的梯度消失问题。
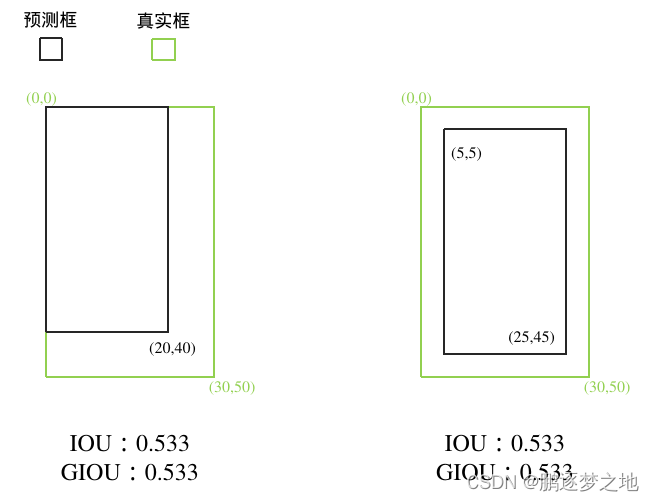
当真实框内含预测框时,如上图所示,IOU和GIOU的值相同,无法反映出哪个预测框更好。
三、DIOU
论文原文:《Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression》![]() http://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287
DIOU(Distance Intersection over Union)是一种改进的交并比,DIOU既考虑到了IOU的缺点,又考虑到了GIOU的缺点。DIOU也是增加了最小闭包区域(即能同事包含预测框与真实框的最小矩形框),但不再计算闭包区域与预测框真实框之间的交并比,而是计算它们之间的欧氏距离。公式如下:
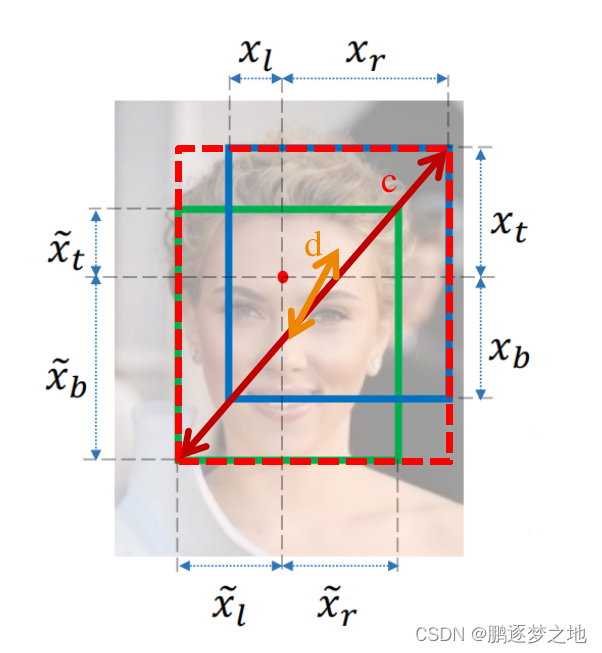
其中c代表最小闭包区域矩形的对角线距离,d代表预测框中心点和真实框中心点距离。DIOU等于d的平方除以c的平方。
代码实现如下
import cv2
import numpy as np
def DIOU(RecA, RecB):
x1 = max(RecA[0], RecB[0])
y1 = max(RecA[1], RecB[1])
x2 = min(RecA[2], RecB[2])
y2 = min(RecA[3], RecB[3])
# 计算交集部分面积
interArea = max(0, x2 - x1 + 1) * max(0, y2 - y1 + 1)
# 计算预测值和真实值的面积
RecA_Area = (RecA[2] - RecA[0] + 1) * (RecA[3] - RecA[1] + 1)
RecB_Area = (RecB[2] - RecB[0] + 1) * (RecB[3] - RecB[1] + 1)
#计算并集部分面积
UnionArea=float(RecA_Area + RecB_Area - interArea)
# 计算IOU
iou = interArea / UnionArea
# DISTANCE
C_x1 = min(RecA[0], RecB[0])
C_y1 = min(RecA[1], RecB[1])
C_x2 = max(RecA[2], RecB[2])
C_y2 = max(RecA[3], RecB[3])
center_x1 = (RecA[0]+RecA[2]) / 2
center_y1 = (RecA[1]+RecA[3]) / 2
center_x2 = (RecB[0] + RecB[2]) / 2
center_y2 = (RecB[1] + RecB[3]) / 2
center_distance = (center_x2 - center_x1) ** 2 + (center_y2 - center_y1) ** 2
c_distance = (C_x2 - C_x1) ** 2 + (C_y2 - C_y1) ** 2
DIOU = iou - center_distance / c_distance
return DIOU
img = np.zeros((512, 512, 3), np.uint8)
img.fill(255)
RecA = [0, 0, 30,50] #方框的左上角坐标和右上角坐标
RecB = [5, 5, 25, 45]
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecA[0], RecA[1]), (RecA[2], RecA[3]), (0, 255, 0), 5)
cv2.rectangle(img, (RecB[0], RecB[1]), (RecB[2], RecB[3]), (255, 0, 0), 5)
iou =DIOU(RecA, RecB)
font = cv2.FONT_ITALIC
#展示IOU结果
cv2.putText(img, "DIOU = %.2f" % iou, (200, 450), font, 0.6, (0, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("IOU",img)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
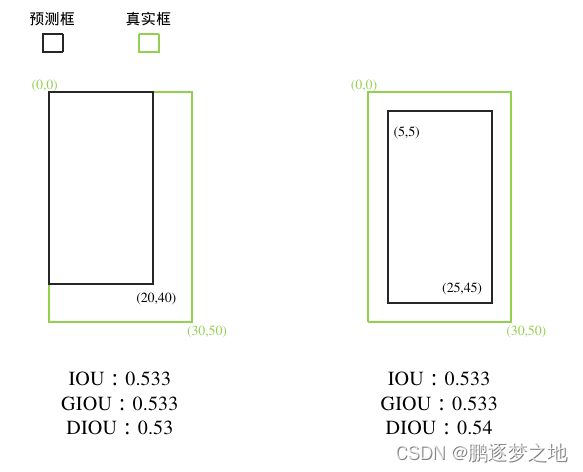
当真实框内含预测框时,DIOU也能反映出不同的预测框之间的差距,有效的解决了GIOU的缺点。
现在还有各种改进的交并比,如CIOU、EIOU、Focal-EIOU、SIOU、WIOU等,如果大家有兴趣可以去学习一下这些改进的IOU。
四、DIOU_Loss实战
在这一节我们用学习到的DIOU替换前两章中的小黄人目标检测的L1Loss损失函数。
DIOU_Loss代码如下
class DIou_Loss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(DIou_Loss, self).__init__()
def box_iou(self, b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch,[x1,y1,x2,y2]) x1,y1 左上角坐标,x2,y2右下角坐标
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, [x1,y1,x2,y2])
返回为:
-------
iou: tensor, shape=(batch, 1)
"""
b1_wh = b1[:, 2:4] - b1[:, :2]
b2_wh = b2[:, 2:4] - b2[:, :2]
inter_x1 = torch.max(b1[:, 0], b2[:, 0])
inter_y1 = torch.max(b1[:, 1], b2[:, 1])
inter_x2 = torch.min(b1[:, 2], b2[:, 2])
inter_y2 = torch.min(b1[:, 3], b2[:, 3])
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
# ----------------------------------------------------#
intersect_area = (torch.clamp(inter_x2 - inter_x1, min=0)+1) * (torch.clamp(inter_y2 - inter_y1, min=0)+1)
b1_area = (b1_wh[:, 0]+1) * (b1_wh[:, 1]+1)
b2_area = (b2_wh[:, 0]+1) * (b2_wh[:, 1]+1)
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / union_area
# DISTANCE
C_x1 = torch.min(b1[...,0], b2[...,0])
C_y1 = torch.min(b1[...,1], b2[...,1])
C_x2 = torch.max(b1[...,2], b2[...,2])
C_y2 = torch.max(b1[...,3], b2[...,3])
center_x1 = (b1[...,0] + b1[...,2]) / 2
center_y1 = (b1[...,1] + b1[...,3]) / 2
center_x2 = (b2[...,0] + b2[...,2]) / 2
center_y2 = (b2[...,1] + b2[...,3]) / 2
center_distance = (center_x2 - center_x1) ** 2 + (center_y2 - center_y1) ** 2
c_distance = (C_x2 - C_x1) ** 2 + (C_y2 - C_y1) ** 2
DIOU = iou - center_distance / c_distance
return DIOU
def forward(self, input, targets=None):
iou = self.box_iou(input, targets) # 计算交互比
loss = torch.mean((1 - iou))
return loss其余代码可以去github下载
GitHub - 1578630119/Single_Object_Detection
再将损失函数换成DIOU_Loss,同时我们还可以利用IOU计算模型的准确率,设置一个阈值,即交并比值,当大于这个值,则这个预测框是正确的,小于则是错误的,最终可以得到模型准确率。代码如下
def iou(b1, b2):
b1_wh = b1[:, 2:4] - b1[:, :2]
b2_wh = b2[:, 2:4] - b2[:, :2]
inter_x1 = torch.max(b1[:, 0], b2[:, 0])
inter_y1 = torch.max(b1[:, 1], b2[:, 1])
inter_x2 = torch.min(b1[:, 2], b2[:, 2])
inter_y2 = torch.min(b1[:, 3], b2[:, 3])
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
# ----------------------------------------------------#
intersect_area = (torch.clamp(inter_x2 - inter_x1, min=0) + 1) * (torch.clamp(inter_y2 - inter_y1, min=0) + 1)
b1_area = (b1_wh[:, 0] + 1) * (b1_wh[:, 1] + 1)
b2_area = (b2_wh[:, 0] + 1) * (b2_wh[:, 1] + 1)
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / union_area
return iou
def test():
#如果已经训练好了权重,模型直接加载权重文件进行测试#
model_test=Net_res()
model_test.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth',map_location=device))
model_test.eval()
model_test=model_test.to(device)
test_loss = 0
correct=0
with torch.no_grad(): # 仅测试模型,禁用梯度计算
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(eval_loader):
data = data.to(device)
target = target.to(device)
output = model_test(data)
test_loss += criterion(output, target).item()
result = iou(output, target)
result = torch.where(result > 0.3, 1, 0)
correct = correct + result.sum()
print('Accuracy:{:.2f}%'.format((correct / ((batch_idx+1)*test_batch_size)).to('cpu').detach().numpy()*100))
print('Test Loss:',test_loss/(batch_idx+1))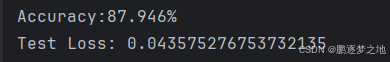




![[单master节点部署]14.deamonSet和配置管理中心](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d788318764314c65b1c6a4ed66303f6d.png)