上一篇博客从源码层面解释了appium-inspector工具实现原理,这篇博客将介绍如何从0构建一款简单的类似appium-inspector的工具。如果要实现一款类似appium-inspector的demo工具,大致需要完成如下六个模块内容
- 启动 Appium 服务器
- 连接到移动设备或模拟器
- 启动应用并获取页面源代码
- 解析页面源代码
- 展示 UI 元素
- 生成 Locator
启动appium服务
安装appium,因为要启动android的模拟器,后续需要连接到appium server上,所以这里还需要安装driver,这里需要安装uiautomater2的driver。
npm install -g appium
appium -v
appium
//安装driver
appium driver install uiautomator2
appium driver list
//启动appium服务
appium成功启动appium服务后,该服务默认监听在4723端口上,启动结果如下图所示

连接到移动设备或模拟器
在编写代码连接到移动设备前,需要安装android以及一些SDK,然后通过Android studio启动一个android的手机模拟器,这部分内容这里不再详细展开,启动模拟器后,再编写代码让client端连接下appium服务端。
下面代码通过调用webdriverio这个lib中提供remote对象来连接到appium服务器上。另外,下面的代码中还封装了ensureClient()方法,连接appium服务后,会有一个session,这个sessionId超时后会过期,所以,这里增加ensureClient()方法来判断是否需要client端重新连接appium,获取新的sessionId信息。
import { remote } from 'webdriverio';
import fs from 'fs';
import xml2js from 'xml2js';
import express from 'express';
import cors from 'cors';
import path from 'path';
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url';
// 获取当前文件的目录名
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename);
// 加载配置文件
const config = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('./src/config.json', 'utf-8'));
// 配置连接参数
const opts = {
path: '/',
port: 4723,
capabilities: {
'appium:platformName': config.platformName,
'appium:platformVersion': config.platformVersion,
'appium:deviceName': config.deviceName,
'appium:app': config.app,
'appium:automationName': config.automationName,
'appium:appWaitActivity':config.appActivity
},
};
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
let client;
const initializeAppiumClient = async () => {
try {
client = await remote(opts);
console.log('Connected to Appium server');
} catch (err) {
console.error('Failed to connect to Appium server:', err);
}
};
//解决session过期的问题
const ensureClient = async () => {
if (!client) {
await initializeAppiumClient();
} else {
try {
await client.status();
} catch (err) {
if (err.message.includes('invalid session id')) {
console.log('Session expired, reinitializing Appium client');
await initializeAppiumClient();
} else {
throw err;
}
}
}
};启动应用并获取页面信息
当client端连接到appium server后,获取当前模拟器上应用页面信息是非常简单的,这里需要提前在模拟器上安装一个app,并开启app。代码的代码中将获取page source信息,获取screenshot信息,点击tap信息都封装成了api接口,并通过express,在9096端口上启动了一个后端服务。
app.get('/page-source', async (req, res) => {
try {
await ensureClient();
// 获取页面源代码
const pageSource = await client.getPageSource();
const parser = new xml2js.Parser();
const result = await parser.parseStringPromise(pageSource);
res.json(result);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error occurred:', err);
res.status(500).send('Error occurred');
}
});
app.get('/screenshot', async (req, res) => {
try {
await ensureClient();
// 获取截图
const screenshot = await client.takeScreenshot();
res.send(screenshot);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error occurred:', err);
res.status(500).send('Error occurred');
}
});
app.post('/tap', async (req, res) => {
try {
await ensureClient();
const { x, y } = req.body;
await client.touchAction({
action: 'tap',
x,
y
});
res.send({ status: 'success', x, y });
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error occurred while tapping element:', err);
res.status(500).send('Error occurred');
}
});
app.listen(9096, async() => {
await initializeAppiumClient();
console.log('Appium Inspector server running at http://localhost:9096');
});
process.on('exit', async () => {
if (client) {
await client.deleteSession();
console.log('Appium client session closed');
}
});下图就是上述服务启动后,调用接口,获取到的页面page source信息,这里把xml格式的page source转换成了json格式存储。结果如下图所示:

显示appUI以及解析获取element信息
下面的代码是使用react编写,所以,可以通过react提供的命令,先初始化一个react项目,再编写下面的代码。对于在react编写的应用上显示mobile app的ui非常简单,调用上面后端服务封装的api获取page source,使用<imag src=screenshot>就可以在web UI上显示mobile app的UI。
另外,除了显示UI外,当点击某个页面元素时,期望能获取到该元素的相关信息,这样才能结合元素信息生成locator,这里封装了findElementAtCoordinates方法来从pageSource中查找match的元素,查找的逻辑是根据坐标信息,也就是pagesource中bounds字段信息进行匹配match的。
import React, {useState, useEffect, useRef} from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const App = () => {
const [pageSource, setPageSource] = useState('');
const [screenshot, setScreenshot] = useState('');
const [elementInfo, setElementInfo] = useState(null);
const [highlightBounds, setHighlightBounds] = useState(null);
const imageRef = useRef(null);
const ERROR_MARGIN = 5; // 可以调整误差范围
const getPageSource = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('http://localhost:9096/page-source');
setPageSource(response.data);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error fetching page source:', err);
}
};
const getScreenshot = async () => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('http://localhost:9096/screenshot');
setScreenshot(`data:image/png;base64,${response.data}`);
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error fetching screenshot:', err);
}
};
useEffect( () => {
getPageSource();
getScreenshot()
}, []);
const handleImageClick = (event) => {
if (imageRef.current && pageSource) {
const rect = imageRef.current.getBoundingClientRect();
const x = event.clientX - rect.left;
const y = event.clientY - rect.top;
// 检索页面源数据中的元素
pageSource.hierarchy.$.bounds="[0,0][1080,2208]";
const element = findElementAtCoordinates(pageSource.hierarchy, x, y);
if (element) {
setElementInfo(element.$);
const bounds = parseBounds(element.$.bounds);
setHighlightBounds(bounds);
} else {
setElementInfo(null);
setHighlightBounds(null);
}
}
};
const parseBounds = (boundsStr) => {
const bounds = boundsStr.match(/\d+/g).map(Number);
return {
left: bounds[0],
top: bounds[1],
right: bounds[2],
bottom: bounds[3],
centerX: (bounds[0] + bounds[2]) / 2,
centerY: (bounds[1] + bounds[3]) / 2,
};
};
const findElementAtCoordinates = (node, x, y) => {
if (!node || !node.$ || !node.$.bounds) {
return null;
}
const bounds = parseBounds(node.$.bounds);
const withinBounds = (x, y, bounds) => {
return (
x >= bounds.left &&
x <= bounds.right &&
y >= bounds.top &&
y <= bounds.bottom
);
};
if (withinBounds(x, y, bounds)) {
for (const child of Object.values(node)) {
if (Array.isArray(child)) {
for (const grandChild of child) {
const foundElement = findElementAtCoordinates(grandChild, x, y);
if (foundElement) {
return foundElement;
}
}
}
}
return node;
}
return null;
};
return (
<div>
{screenshot && (
<div style={{ position: 'relative' }}>
<img
ref={imageRef}
src={screenshot}
alt="Mobile App Screenshot"
onClick={handleImageClick}
style={{ cursor: 'pointer', width: '1080px', height: '2208px' }} // 根据 page source 调整大小
/>
{highlightBounds && (
<div
style={{
position: 'absolute',
left: highlightBounds.left,
top: highlightBounds.top,
width: highlightBounds.right - highlightBounds.left,
height: highlightBounds.bottom - highlightBounds.top,
border: '2px solid red',
pointerEvents: 'none',
}}
/>
)}
</div>
)}
{elementInfo && (
<div>
<h3>Element Info</h3>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(elementInfo, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
};
export default App;
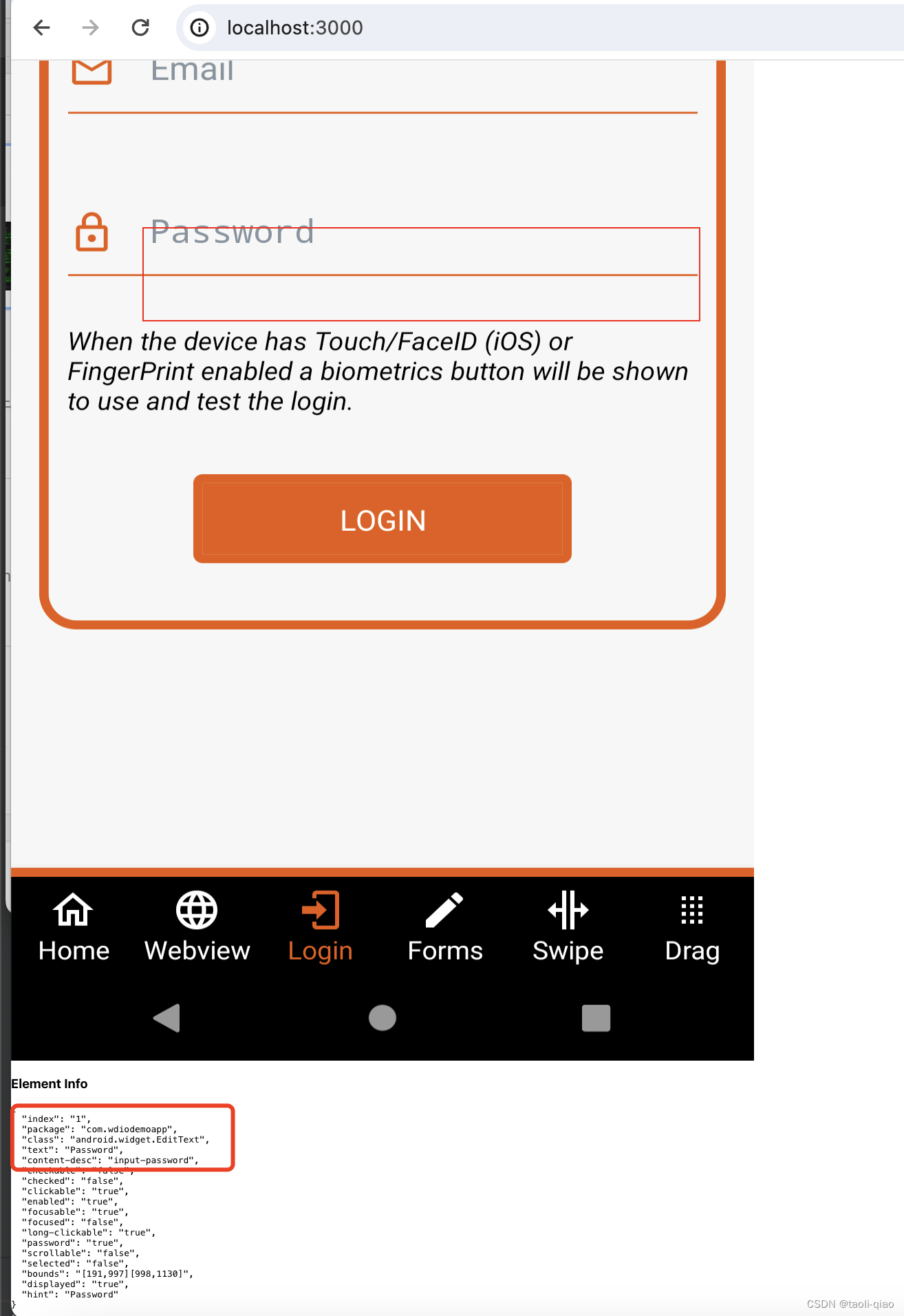
下图图一是android模拟器上启动了一个mobile app页面。

下图是启动react编写的前端应用,可以看到,在该应用上显示了模拟器上的mobile app ui,当点击某个元素时,会显示被点击元素的相关信息,说明整个逻辑已经打通。当点击password这个输入框元素时,下面显示了element info,可以看到成功查找到了对应的element。当然,这个工具只是一个显示核心过程的demo code。例如higlight的红框,不是以目标元素为中心画的。
关于生成locator部分,这里并没有提供code,当获取到element信息后,还需要获取该element的parent element,根据locator的一些规则,编写方法实现,更多的细节可以参考appium-server 源代码。
整个工具的demo code 详见这里,关于如果启动应用部分,可以看readme信息。




![[C/C++] -- gdb调试与coredump](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4c3cb2973d4a462987217acd8d660dfd.png)


![[激光原理与应用-97]:激光焊接焊中检测系统系列介绍 - 1 - 什么是焊接以及传统的焊接方法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cfd98a4394514dfb8780ae4eb290775b.png)