目录
1、Redisson lock 方法原理解析
1. 如果指定了过期时间
2. 如果没有指定过期时间
3. lock 方法的主要步骤
Redisson lock 方法完整代码
分步骤解释
步骤 1:尝试获取锁
步骤 2:获取锁失败,发起订阅
步骤 3:循环等待锁释放和尝试获取锁
小结
2、Redisson tryLock 方法原理解析
1. 如果指定了过期时间
2. 如果没有指定过期时间
3. tryLock 方法的主要步骤
Redisson tryLock 方法完整代码
分步骤解释
步骤 1:尝试获取锁
步骤 2:获取锁失败,计算剩余时间并发起订阅
步骤 3:循环等待锁释放和尝试获取锁
小结
3、Redisson unlock 方法原理解析
unlock 方法的主要步骤
Redisson unlock 方法完整代码
分步骤解释
步骤 1:调用 unlock 方法
步骤 2:异步解锁操作
步骤 3:等待异步操作完成
小结
1、Redisson lock 方法原理解析
1. 如果指定了过期时间
- 异步续命机制(Watchdog 机制)不再生效,锁会在指定的时间过期并自动释放。
2. 如果没有指定过期时间
- 启动 Watchdog 机制,自动续命锁,直到显式调用
unlock()方法释放锁为止。
3. lock 方法的主要步骤
以下是 Redisson lock 方法的完整代码及其详细分步骤解释。
Redisson lock 方法完整代码
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); // 获取当前线程ID
Long ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId); // 尝试获取锁,等待时间为-1,表示无限等待
if (ttl == null) { // 如果成功获取到锁,直接返回
return;
}
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId); // 订阅锁释放通知
pubSub.timeout(future); // 设置超时回调
RedissonLockEntry entry;
if (interruptibly) {
entry = commandExecutor.getInterrupted(future); // 获取可中断的锁条目
} else {
entry = commandExecutor.get(future); // 获取锁条目
}
try {
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId); // 尝试重新获取锁
if (ttl == null) { // 如果成功获取到锁,退出循环
break;
}
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 等待锁释放通知
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 再次等待锁释放通知
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
entry.getLatch().acquire(); // 等待锁释放通知
} else {
entry.getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly(); // 等待锁释放通知,不可中断
}
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(entry, threadId); // 取消订阅
}
}
分步骤解释
步骤 1:尝试获取锁
- 方法调用:
tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId) - 解释:
- 使用 Lua 脚本尝试原子性地获取锁。
- 如果锁不存在,创建新锁并设置过期时间。
- 如果锁存在并且由当前线程持有,增加锁的重入计数并重新设置过期时间。
- 如果成功获取到锁,返回
null,否则返回锁的剩余存活时间。
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
return evalWrite(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
}
-
Lua 脚本原理
-
检查锁是否存在:
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;- 如果锁不存在(
exists返回 0),则创建一个新的锁,并将其设置为当前线程持有,同时设置过期时间。
- 如果锁不存在(
-
检查锁是否由当前线程持有:
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;- 如果锁已经存在并且由当前线程持有(
hexists返回 1),则增加锁的重入计数,并重新设置过期时间。
- 如果锁已经存在并且由当前线程持有(
-
返回锁的剩余存活时间:
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);- 如果锁存在且不由当前线程持有,则返回锁的剩余存活时间。
-
步骤 2:获取锁失败,发起订阅
如果初次尝试获取锁失败,Redisson 会订阅锁的释放通知。
- 方法调用:
subscribe(threadId) - 解释:
- 如果初次尝试获取锁失败,Redisson 会订阅锁的释放通知。
- 通过
subscribe方法订阅锁的释放通知,以便在锁被释放时能够及时收到通知。 pubSub.timeout(future)设置超时回调,以防订阅过程中出现问题。- 使用
commandExecutor.get或commandExecutor.getInterrupted获取订阅结果,根据是否可中断进行选择。
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
pubSub.timeout(future);
RedissonLockEntry entry;
if (interruptibly) {
entry = commandExecutor.getInterrupted(future);
} else {
entry = commandExecutor.get(future);
}
步骤 3:循环等待锁释放和尝试获取锁
在等待锁释放期间,Redisson 会进入一个循环,不断尝试重新获取锁。
- 代码块:
try {
while (true) {
ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
entry.getLatch().acquire();
} else {
entry.getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(entry, threadId);
}
- 解释:
-
尝试获取锁:
- 在循环中,Redisson 不断调用
tryAcquire方法尝试获取锁。 - 如果成功获取到锁,退出循环。
- 在循环中,Redisson 不断调用
-
等待锁释放通知:
- 如果获取锁失败且锁的剩余存活时间大于 0,Redisson 会等待锁释放通知。
- 使用
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)方法在指定时间内等待锁的释放。
-
重复尝试获取锁:
- 在锁释放或等待超时后,Redisson 会继续尝试获取锁,直到成功或显式中断。
-
取消订阅:
- 在获取锁成功或最终失败后,调用
unsubscribe(entry, threadId)取消订阅锁的释放通知。
- 在获取锁成功或最终失败后,调用
-
小结
-
指定过期时间:
- 锁会在指定的时间过期并自动释放,异步续命机制不再生效。
-
未指定过期时间:
- 启动 Watchdog 机制,自动续命锁,确保锁在持有期间不会被自动释放,直到显式调用
unlock()方法释放锁为止。
- 启动 Watchdog 机制,自动续命锁,确保锁在持有期间不会被自动释放,直到显式调用
2、Redisson tryLock 方法原理解析
tryLock 方法与 lock 方法不同的是,tryLock 方法在获取锁失败时不会一直阻塞,而是根据指定的等待时间和租约时间进行尝试,并返回是否成功获取锁。
1. 如果指定了过期时间
- 异步续命机制(Watchdog 机制)不再生效,锁会在指定的时间过期并自动释放。
2. 如果没有指定过期时间
- 启动 Watchdog 机制,自动续命锁,直到显式调用
unlock()方法释放锁为止。
3. tryLock 方法的主要步骤
以下是 Redisson tryLock 方法的完整代码及其详细分步骤解释。
Redisson tryLock 方法完整代码
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true; // 成功获取到锁
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
try {
subscribeFuture.get(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
if (!subscribeFuture.completeExceptionally(new RedisTimeoutException(
"Unable to acquire subscription lock after " + time + "ms. " +
"Try to increase 'subscriptionsPerConnection' and/or 'subscriptionConnectionPoolSize' parameters."))) {
subscribeFuture.whenComplete((res, ex) -> {
if (ex == null) {
unsubscribe(res, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true; // 成功获取到锁
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture), threadId);
}
}
分步骤解释
步骤 1:尝试获取锁
- 方法调用:
tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId) - 解释:
- 使用 Lua 脚本尝试原子性地获取锁。
- 如果锁不存在,创建新锁并设置过期时间。
- 如果锁存在并且由当前线程持有,增加锁的重入计数并重新设置过期时间。
- 如果成功获取到锁,返回
null,否则返回锁的剩余存活时间。
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture;
if (leaseTime > 0) {
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, internalLockLeaseTime,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
CompletionStage<Long> f = ttlRemainingFuture.thenApply(ttlRemaining -> {
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
if (leaseTime > 0) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
return ttlRemaining;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper<>(f);
}
-
Lua 脚本原理
-
检查锁是否存在:
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;- 如果锁不存在(
exists返回 0),则创建一个新的锁,并将其设置为当前线程持有,同时设置过期时间。
- 如果锁不存在(
-
检查锁是否由当前线程持有:
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); return nil; end;- 如果锁已经存在并且由当前线程持有(
hexists返回 1),则增加锁的重入计数,并重新设置过期时间。
- 如果锁已经存在并且由当前线程持有(
-
返回锁的剩余存活时间:
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);- 如果锁存在且不由当前线程持有,则返回锁的剩余存活时间。
-
步骤 2:获取锁失败,计算剩余时间并发起订阅
如果初次尝试获取锁失败,Redisson 会订阅锁的释放通知。
- 方法调用:
subscribe(threadId) - 解释:
- 如果初次尝试获取锁失败,Redisson 会订阅锁的释放通知。
- 通过
subscribe方法订阅锁的释放通知,以便在锁被释放时能够及时收到通知。 pubSub.timeout(future)设置超时回调,以防订阅过程中出现问题。- 使用
commandExecutor.get或commandExecutor.getInterrupted获取订阅结果,根据是否可中断进行选择。
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId);
try {
subscribeFuture.get(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
if (!subscribeFuture.completeExceptionally(new RedisTimeoutException(
"Unable to acquire subscription lock after " + time + "ms. " +
"Try to increase 'subscriptionsPerConnection' and/or 'subscriptionConnectionPoolSize' parameters."))) {
subscribeFuture.whenComplete((res, ex) -> {
if (ex == null) {
unsubscribe(res, threadId);
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
步骤 3:循环等待锁释放和尝试获取锁
在等待锁释放期间,Redisson 会进入一个循环,不断尝试重新获取锁。
- 代码块:
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
return true; // 成功获取到锁
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) {
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
}
} finally {
unsubscribe(commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture), threadId);
}
- 解释:
- 尝试获取锁:
- 在循环中,Redisson 不断调用
tryAcquire方法尝试获取锁。 - 如果成功获取到锁,退出循环
- 在循环中,Redisson 不断调用
- 尝试获取锁:
并返回 true。
-
等待锁释放通知:
- 如果获取锁失败且锁的剩余存活时间大于 0,Redisson 会等待锁释放通知。
- 使用
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)方法在指定时间内等待锁的释放。
-
重复尝试获取锁:
- 在锁释放或等待超时后,Redisson 会继续尝试获取锁,直到成功或显式中断。
-
取消订阅:
- 在获取锁成功或最终失败后,调用
unsubscribe(entry, threadId)取消订阅锁的释放通知。
- 在获取锁成功或最终失败后,调用
小结
Redisson 的 tryLock 方法提供了一种非阻塞的分布式锁机制,通过以下几个步骤实现:
-
尝试获取锁:
- 通过 Lua 脚本进行原子性操作,确保获取锁的过程是线程安全的。
- 如果成功获取到锁,返回
true。
-
获取锁失败,计算剩余时间并发起订阅:
- 如果初次获取锁失败,Redisson 会订阅锁的释放通知,并等待一定时间。
-
循环等待锁释放和尝试获取锁:
- 在等待锁释放期间,Redisson 进入循环,不断尝试重新获取锁。
- 使用
entry.getLatch().tryAcquire方法在指定时间内等待锁的释放。 - 如果成功获取到锁,退出循环并返回
true,否则在时间用尽后返回false。
3、Redisson unlock 方法原理解析
unlock 方法用于释放已经持有的锁,确保其他线程可以获取锁。Redisson 通过 Lua 脚本原子性地执行解锁操作,以保证解锁过程的安全性和一致性。
unlock 方法的主要步骤
以下是 Redisson unlock 方法的完整代码及其详细分步骤解释。
Redisson unlock 方法完整代码
@Override
public void unlock() {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockAsync(threadId);
commandExecutor.get(future);
}
private <T> RFuture<T> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getRawName(), getChannelName()),
LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
分步骤解释
步骤 1:调用 unlock 方法
- 方法调用:
unlock() - 解释:
- 获取当前线程的 ID。
- 调用
unlockAsync方法进行异步解锁操作。 - 使用
commandExecutor.get(future)等待异步操作完成。
@Override
public void unlock() {
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockAsync(threadId);
commandExecutor.get(future);
}
步骤 2:异步解锁操作
- 方法调用:
unlockAsync(threadId) - 解释:
- 使用 Lua 脚本原子性地执行解锁操作。
- 如果锁由当前线程持有,减少锁的重入计数。
- 如果重入计数减到 0,删除锁并发布解锁消息。
private <T> RFuture<T> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
"if (counter > 0) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
"return 0; " +
"else " +
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; "+
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getRawName(), getChannelName()),
LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
-
Lua 脚本原理
-
检查锁是否由当前线程持有:
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then return nil; end;- 如果锁不由当前线程持有(
hexists返回 0),返回nil,表示解锁失败。
- 如果锁不由当前线程持有(
-
减少锁的重入计数:
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); if (counter > 0) then redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); return 0; else redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); return 1; end;- 如果锁由当前线程持有,减少锁的重入计数(
hincrby)。 - 如果重入计数大于 0,重新设置锁的过期时间,并返回
0,表示锁仍然被持有。 - 如果重入计数减到 0,删除锁(
del),并发布解锁消息(publish),返回1,表示锁已释放。
- 如果锁由当前线程持有,减少锁的重入计数(
-
步骤 3:等待异步操作完成
- 方法调用:
commandExecutor.get(future) - 解释:
- 等待异步解锁操作完成。
- 如果解锁操作失败,抛出异常。
commandExecutor.get(future);
小结
Redisson 的 unlock 方法通过以下几个步骤实现安全可靠的解锁操作:
-
调用
unlock方法:- 获取当前线程的 ID。
- 调用
unlockAsync方法进行异步解锁操作。 - 使用
commandExecutor.get(future)等待异步操作完成。
-
异步解锁操作:
- 使用 Lua 脚本原子性地执行解锁操作,确保操作的安全性和一致性。
- 如果锁由当前线程持有,减少锁的重入计数。
- 如果重入计数减到 0,删除锁并发布解锁消息。
-
等待异步操作完成:
- 等待异步解锁操作完成,如果解锁操作失败,抛出异常。
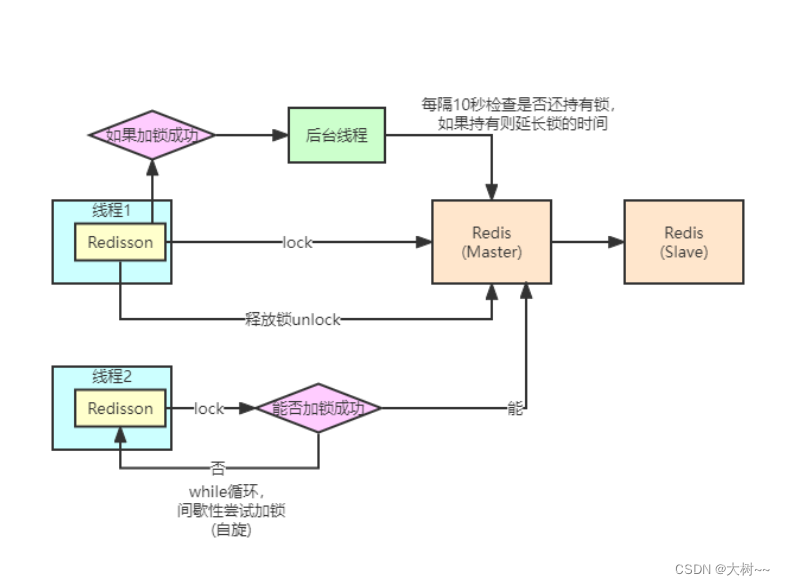
4、流程图