接着上篇文章说到(上篇文章地址:http://t.csdnimg.cn/udpsT![]() http://t.csdnimg.cn/udpsT)我们在代码中发现重写了equals方法后还需要重写hashcode方法,为什么呢?
http://t.csdnimg.cn/udpsT)我们在代码中发现重写了equals方法后还需要重写hashcode方法,为什么呢?
对于set这种数据类型,里面的值是不允许有重复的,所以这个时候肯定会用到equals和hashcode进行比较
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class Userinfo implements Serializable {
private String username;
private int password;
public Userinfo() {
}
public Userinfo(String username, int password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Userinfo userinfo = (Userinfo) o;
return password == userinfo.password && Objects.equals(username, userinfo.username);
}
//
// @Override
// public int hashCode() {
// return Objects.hash(username, password);
// }
} @Test
void testHashCode(){
Userinfo user1=new Userinfo("yinan",123);
Userinfo user2=new Userinfo("yinan",123);
Set<Userinfo> set=new HashSet<>();
set.add(user1);
set.add(user2);
set.forEach(System.out::println);
}在以上代码中,我重写了equals方法,这个时候我把user1和user2同时放入set中
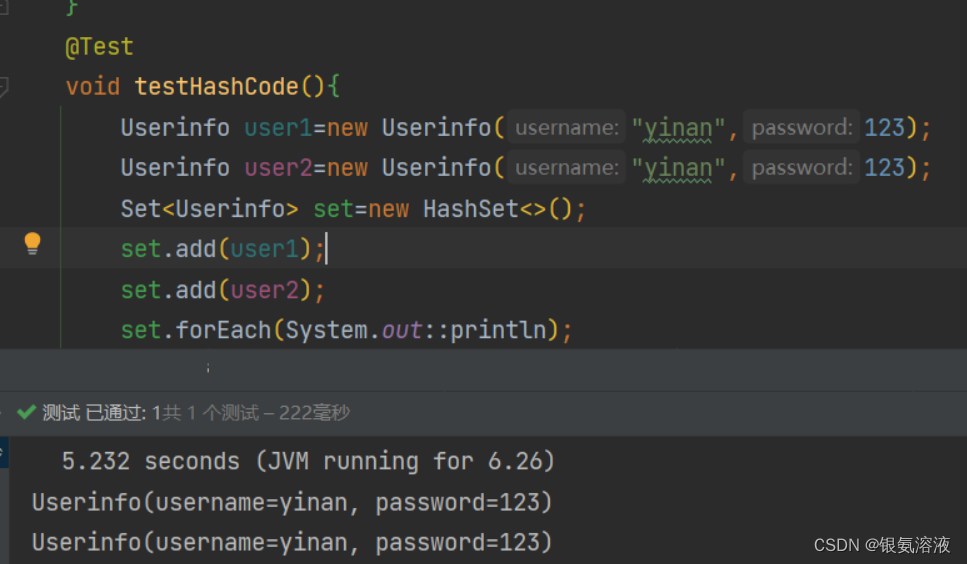
我们发现在最后的结果中set并没有合并这两个相同的对象,而是分别进行了输出,那就说明set误把这两个相同的对象看成了是不相同的对象,那我们再重写hashcode方法
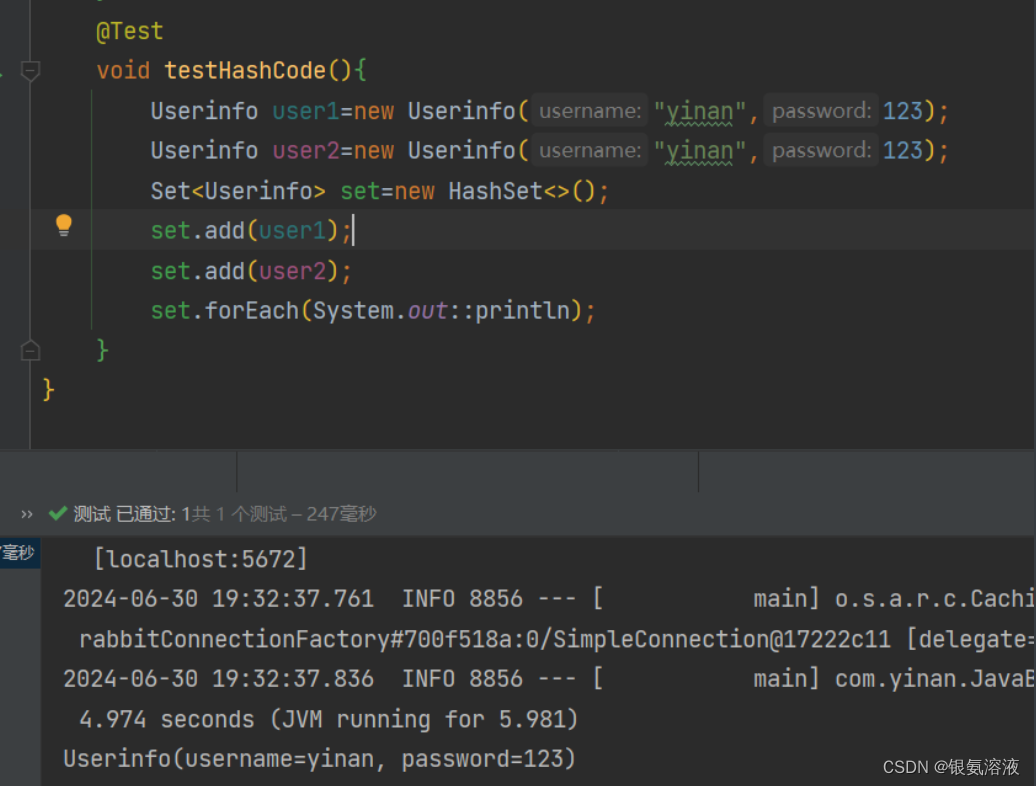
重写了hashcode方法后,我们的输出结果就只有一条数据了
为什么呢?
这是因为set在新增数据进行比较数据是否相同的时候,首先会先去调用hashcode比较这两个对象的hashcode值是否相同,在我们还没有重写hashcode方法之前,两个对象的hashcode的值是不同的,所以这个时候就直接返回;后来,我们重写了hashcode方法,让两个对象返回相同的hashcode值,这个时候再用重写的equals去比较两个对象的值是否相同,如果都相同就会只存放一个值进入set中。
这就是为什么要在重写equals方法后还要重写hashcode方法。




![[HBM] HBM TSV (Through Silicon Via) 结构与工艺](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8d31fad7a28745eb81e253606f226423.png#pic_center)