系列文章目录
一、MySQL的函数(重点)
二、MySQL的窗口函数(重点)
三、MySQL的视图(熟悉)
四、MySQL的事务(熟悉)
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 一、MySQL的函数
- 1. 聚合函数
- 2. group_concat
- 3. 数学函数
- 4. 字符串函数
- 5. 日期函数
- 7. MySQl的if语句
- 8. MySQL的Case When
- 二、MySQL的窗口函数
- 1. 概述
- 2. 窗口函数的分类
- 3.分组排序函数
- 4.聚合开窗函数
- 5.lag和lead函数
- 6.首尾聚合函数
- 三、MySQL的视图
- 1. 概念
- 2. 作用
- 3. 代码详解
- 四、MySQL的事务
- 1.介绍
- 2. 事务的特性-ACID
- 3. 事务的操作
- 3.1 操作步骤
- 3.2 操作模型
- 3.3 案例解析
- 4.隔离级别的演示
- 4.1 脏读
- 4.2 不可重复读
- 4.3 幻读
- 4.4 串行化
前言
本文主要详解了MySQL的函数,事务,视图。
一、MySQL的函数
1. 聚合函数
2. group_concat
-
语法
group_concat()函数首先根据group by指定的列进行分组,并且用分隔符分隔,将同一个分组中的值连接起来,返回一个字符串结果。 -
概念
group_concat([distinct] 字段名 [order by 排序字段 asc/desc] [separator '分隔符']) # 分隔符默认是逗号 -
代码
create database mydb4; use mydb4; create table emp( emp_id int primary key auto_increment comment '编号', emp_name char(20) not null default '' comment '姓名', salary decimal(10,2) not null default 0 comment '工资', department char(20) not null default '' comment '部门' ); insert into emp(emp_name,salary,department) values('张晶晶',5000,'财务部'),('王飞飞',5800,'财务部'),('赵刚',6200,'财务部'),('刘小贝',5700,'人事部'), ('王大鹏',6700,'人事部'),('张小斐',5200,'人事部'),('刘云云',7500,'销售部'),('刘云鹏',7200,'销售部'), ('刘云鹏',7800,'销售部'); -- 将所有员工的名字合成一行 # 将整张表当做是一组,将emp_name这一列的值进行拼接 select group_concat(emp_name) from emp; # 按照department进行分组,将同一组的emp_name按照_进行拼接 select department,group_concat(emp_name separator '_') from emp group by department ; -- 13、查询和"01"号的同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学的信息 # 查询学号为01的学生学习的科目,对科目进行拼接 select Sid,group_concat(CId order by CId separator '_') as c1 from SC where Sid = '01' group by Sid ; # 查询所有的学生学习的科目,对科目进行拼接 select Sid,group_concat(CId order by CId separator '_') as c2 from SC group by Sid ; # 将拼接后的结果进行对比 select t2.SId from (select Sid,group_concat(CId order by CId separator '_') as c1 from SC where Sid = '01' group by Sid ) t1 join (select Sid,group_concat(CId order by CId separator '_') as c2 from SC group by Sid ) t2 on t1.c1 = t2.c2 where t2.SId != '01';
3. 数学函数
-- 1、求绝对值 abs
select abs(-5);
-- 查询财务部最低工资和人事部最低工资之间的差值
select abs((select min(salary) from emp where department = '财务部') - (select min(salary) from emp where department = '人事部'));
-- 2、向上取整 ceil
select ceil(5.1); -- 6
-- 3、向下取整 floor
select floor(5.9); -- 5
-- 4、求列表的最大值
select greatest(1,2,3); -- 3
-- 5、求列表的最小值
select least(1,2,3); -- 1
-- 6、求余数
select mod(10,3); -- 取10 除以 3的余数
-- 7、返回圆周率
select pi();
-- 8、求x的y次方
select pow(2,3); -- 2的3次方 8
select pow(2,10); -- 2的10次方 1024
-- 9、获取随机数
-- 获取0-1之间的随机数 ,包含0,不包含1
select rand();
-- 获取1-100之间的随机数
-- [0,1) * 100 ---> [0,99.99] + 1 ----> [1,100.99] -->向下取整 --->[1,100]
select floor(rand() * 100 + 1);
-- 10、四舍五入函数 - 取整
select round(5.49999); # 5
select round(5.50000); # 6
-- 11、四舍五入函数 - 带小数
select round(5.44999,2); # 5.45
select round(5.444,2); # 5.44
-- 12、截取指定的数字,不会四舍五入
select truncate(5.44999,2);
4. 字符串函数
#----------字符串函数------------
-- 1、获取字符串长度
select char_length('我爱你中国'); # 5
select character_length('我爱你中国'); # 5 同上
-- 2、字符串拼接
select concat('我爱你','中国','广州');
select concat(emp_name,'_',department) from emp;
select concat('2023','-','12','-','23');
-- 3、字符串拼接,指定固定的分隔符,第一个参数就是分隔符
select concat_ws('-','2023','12','23');
-- 4、去除空格
select trim(' 中国 '); # 去除两端空格
select ltrim(' 中国 '); # 去除左边空格
select rtrim(' 中国 '); # 去除右边边空格
-- 5、replace替换
select replace('我爱你中国and中国','中国','广州'); -- 将字符串中的中国全部替换为广州
-- 6、字符串翻转
select reverse('我爱你中国');
-- 7、获取字符串的后几个字符
select right('17812345678',4); # 获取手机号的后四位
select left('17812345678',3); # 获取手机号的前四位
-- 8、字符串截取
# 第一个数字表示从哪个字符(从1开始)开始,第二个数字表示截取的长度
select substr('2023-12-23',1,4); # 2023
select substring('2023-12-23',1,4); # 2023
# 如果只填写一个数字,表示从这个字符开始,截取到最后
select substr('2023-12-23',2); # 023-12-23
select substr('2023-12-23',6,2); # 12
-- 统计emp表中,每一种姓氏的人数
select substr(emp_name,1,1),count(*) from emp group by substr(emp_name,1,1)
# 9、将字母转为大写
select upper('hello');
# 10、将字母转为小写
select lower('HeLLo');
# 应用场景:不区分大小写来进行字符串比较 ,则可以把字符串都转为小写或者大写,再来比较
5. 日期函数
#-------------日期函数-----------------
-- 1、获取当前时间
select current_time(); # 16:35:52
select curtime(); # 16:36:07
select current_timestamp(); # 2024-04-05 16:36:17
select curdate() # 2024-04-05
select now(); # 2024-04-05 16:36:27
-- 2、获取从1970年到此时此刻的秒值
-- 这个毫秒值可以用来做时间计算
-- select UNIX_TIMESTAMP() - UNIX_TIMESTAMP() / 3600 / 24;
select UNIX_TIMESTAMP() ;
-- 3、将一个日期转为毫秒值
select UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2008-08-08'); # 1218124800 --->1970年到2008年一共过了1218124800秒
-- 需求假如一个商品的的下单日期是:2023-12-23, 我想统计最近3个月的下单量
select * from emp where (UNIX_TIMESTAMP() - UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2023-12-23'))/3600/24/30 <= 3;
select (UNIX_TIMESTAMP() - UNIX_TIMESTAMP('2000-01-05'))/3600/24;
-- 4、从一个日期中获取年月日
select date('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取年月日 2000-10-12
select year('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取年 2000
select month('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取月 10
select day('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取日 12
select hour('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取时 12
select minute('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取分 34
select second('2000-10-12 12:34:56'); # 获取秒 56
select WEEK('2024-04-05 12:34:56'); # 13 获取今年的第几周
# 0 表示星期一, 1 表示星期二 2 表示星期三 3表示星期四.... 6表示星期日
select weekday('2024-04-07 12:34:56'); # 4 获取今天是周几,从0开始
# 获取季度
select quarter('2024-04-07 12:34:56'); -- # 2 第二季度
# 日期的格式化 2024-1-1 1:1:1 ----> 2024-01-01 01:01:01
select date_format('2024-1-1 1:1:1','%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s');
-- 2024-01-01 01:01:01
select date_format('2024-1-1 1:1:1','%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s');
-- 2024-01-01 01:01:01 ->2024/01/01
select date_format('2024-1-1 1:1:1','%Y/%m/%d');
-- 2024-01-01 01:01:01 ->2024年01月01日
select date_format('2024-1-1 1:1:1','%Y年%m月%d日');
select date_format('2024-1-1 1:1:1','%m月%d日');
#----------------------------方式1------------------------------------
# 计算两个时间之间的差值,相差了多少天
select datediff('2024-04-05', '2024-04-01');
select datediff(curdate(), '2000-01-05');
select abs(datediff('2000-01-05',curdate()));
#----------------------------方式2------------------------------------
# 计算两个时间之间相差多少天
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR, '2020-01-01', '2023-01-01') AS years_difference;
# 计算两个时间之间相差多少月
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(MONTH , '2020-01-01', '2023-01-01') AS years_difference;
# 计算两个时间之间相差多少天
SELECT TIMESTAMPDIFF(DAY , '2020-01-01', '2023-01-01') AS years_difference;
#日期向前或者向后推几天
SELECT date_add('2017-06-15', INTERVAL 10 DAY); -- 2017-06-25 向后推10天
SELECT date_add('2017-06-15', INTERVAL -10 DAY); -- 2017-06-05 向前推10天
select date_sub('2017-06-15', INTERVAL 10 DAY); -- 2017-06-05 向前推10天 作用同上
SELECT date_add('2017-06-15 09:34:21', INTERVAL 15 MINUTE); -- 时间向后推15分钟
SELECT date_add('2017-06-15 09:34:21', INTERVAL -3 HOUR); -- 时间向前推3个小时
SELECT date_add('2017-06-15 09:34:21', INTERVAL -3 year); -- 时间向前推3年
7. MySQl的if语句
-
概念

-
代码
-- if(表达式,值1,值2) -- 如果表达式为真,则返回值1,否则返回值2 select *,if(score >= 60,'及格','不及格') as flag from SC; -- IFNULL(v1,v2) -- 如果 v1 的值不为 NULL,则返回 v1,否则返回 v2。 select empno,ename,job,mgr,hiredate,sal,ifnull(comm,0) as comm ,deptno from mydb4.emp;
8. MySQL的Case When
-
概念

-
代码
#---------------------方式1-case后边不加内容-------------------------------------- # 如果when的后边是一个条件,则case后边不需要加字段 # [0-60] 不及格,[60-70]及格 [70-80] 良好 [80-100]优秀 select *, CASE WHEN score >= 60 and score <= 70 THEN '及格' WHEN score > 70 and score <= 80 THEN '良好' WHEN score > 80 and score <= 100 THEN '优秀' ELSE '不及格' END as 'flag' from SC; #---------------------方式2-case后边加内容-------------------------------------- # 如果when的后边是一个单值,则case后边需要加字段 select *, CASE Ssex WHEN '男' THEN '靓仔' WHEN '女' THEN '靓女' ELSE '人妖' END from Student; #---------------------方式3-if和case when外层可以加函数------------------ -- 统计学生表男同学有多少位 select count(*) from Student where Ssex = '男'; select count(if(Ssex = '男',1,null)) from Student; select sum(if(Ssex = '男',1,0)) from Student; select sum(case Ssex when '男' then 1 else 0 end) from Student;
二、MySQL的窗口函数
1. 概述
1、窗口函数可以在对分组数据进行聚合或者操作时,既能对组整体进行操作,又能保留组内数据的明细数据
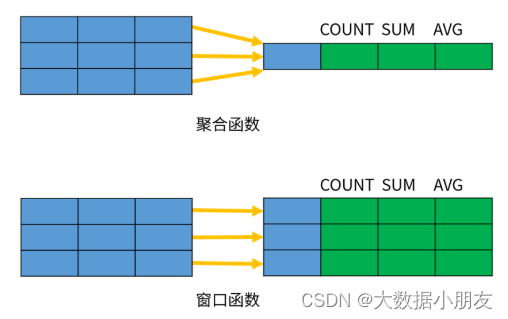
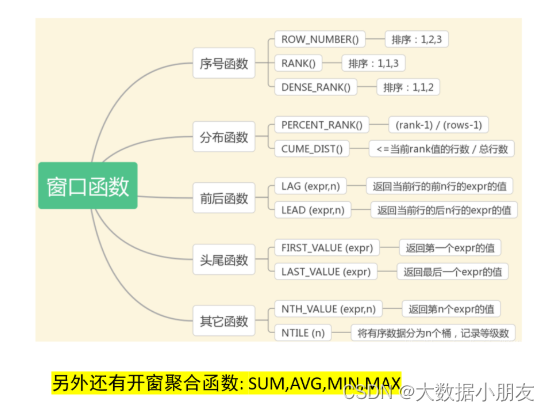
2. 窗口函数的分类
语法
窗口函数名 ( [参数] ) OVER (
[PARTITION BY] ... # 分区/分组
ORDER BY ... #组内排序
[窗口范围]
)
3.分组排序函数
-
介绍
row_number排名标记: 1 2 3 4 5 6 rank排名标记: 1 1 3 4 5 6 dense_rank排名标记: 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 -
特点
分组排序函数会对数据按照自定自定进行分组,并在组内排序,还可以最排序后的数据打编号(名次标记) -
代码
use mydb4; create table employee( dname varchar(20), -- 部门名 eid varchar(20), ename varchar(20), hiredate date, -- 入职日期 salary double -- 薪资 ); truncate table employee; insert into employee values('研发部','1001','刘备','2021-11-01',3000); insert into employee values('研发部','1002','关羽','2021-11-02',5000); insert into employee values('研发部','1003','张飞','2021-11-03',7000); insert into employee values('研发部','1004','赵云','2021-11-04',7000); insert into employee values('研发部','1005','马超','2021-11-05',4000); insert into employee values('研发部','1006','黄忠','2021-11-06',4000); insert into employee values('销售部','1007','曹操','2021-12-01',2000); insert into employee values('销售部','1008','许褚','2021-12-02',3000); insert into employee values('销售部','1009','典韦','2021-12-03',5000); insert into employee values('销售部','1010','张辽','2021-12-04',6000); insert into employee values('销售部','1011','徐晃','2021-12-05',9000); insert into employee values('销售部','1012','曹洪','2021-12-06',6000); insert into employee values('人事部','1013','孙权','2022-11-01',1000); insert into employee values('人事部','1014','周瑜','2022-11-02',3000); insert into employee values('人事部','1015','鲁肃','2022-11-03',5000); insert into employee values('人事部','1016','黄盖','2022-11-04',8000); insert into employee values('人事部','1017','陆逊','2021-11-05',9000); insert into employee values('人事部','1018','吕蒙','2022-11-06',7000); select * from employee order by salary desc ; #-------------------基本用法------------------------------ -- 对每个部门的员工按照薪资排序,并给出排名 #partition by dname 按照dname进行分组 #order by salary desc 按照salar进行组内降序排序 # row_number排名标记: 1 2 3 4 5 6 select *, row_number() over (partition by dname order by salary desc ) as rk from employee; #rank排名标记: 1 1 3 4 5 6 select *, rank() over (partition by dname order by salary desc ) as rk from employee; #dense_rank排名标记: 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 select *, dense_rank() over (partition by dname order by salary desc ) as rk from employee; #-------------------应用场景------------------------------ -- 查询每个部门的薪资最高的前三位员工信息,分组Top3 #dense_rank排名标记: 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 with t1 as( select *, dense_rank() over (partition by dname order by salary desc ) as rk from employee ) select * from t1 where rk <= 3;
4.聚合开窗函数
-
sum聚合开窗
#----------------------------------- # 默认从开头累加到当前行 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) rk from employee; # 指定从开头累加到当前行 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) rk from employee; # 指定从上三行累加到当前行,一共累加了4行 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between 3 preceding and current row ) rk from employee; # 指定从上三行累加到下1行,一共累加了5行 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between 3 preceding and 1 following ) rk from employee; # 指定当前行累加到最后一行 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between current row and unbounded following ) rk from employee; # 从开头累加到最后 select *, sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following ) rk from employee; # 如果去掉partition by,则整张表当做是一组 select *, sum(salary) over(order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following ) rk from employee; -
其他聚合开窗
# 查询当目前为止,薪资最高的值 select *, max(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) rk from employee; # 查询当目前为止,薪资最低的值 select *, min(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) rk from employee; # 查询当目前为止,平均薪资 select *, avg(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) rk from employee; # 查询当目前为止,非空的薪资数量 select *, count(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) rk from employee;
5.lag和lead函数
-
介绍
返回位于当前行的前n行(LAG(expr,n))或后n行(LEAD(expr,n))的expr的值 -
代码
#--------------------lead函数-------------------- # 将下1行的hiredate值放在当前行,如果没有下1行,则使用默认值'1000-01-01' select *, lead(hiredate,1,'1000-01-01') over(partition by dname order by hiredate ) rk from employee; # 将下2行的hiredate值放在当前行,如果没有下2行,则使用默认值'1000-01-01' select *, lag(hiredate,2,'1000-01-01') over(partition by dname order by hiredate ) rk from employee;
6.首尾聚合函数
-
介绍
FIRST_VALUE: 返回组内第一个值 LAST_VALUE : 返回最后一个值 -
代码
select dname, ename, hiredate, salary, first_value(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as first, last_value(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last from employee;
三、MySQL的视图
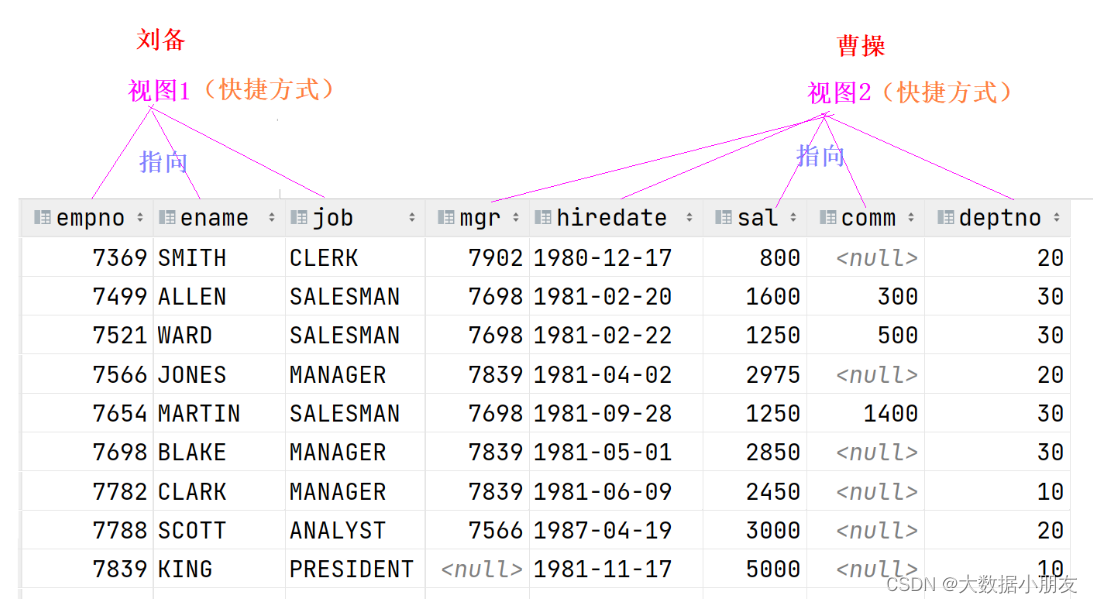
1. 概念
1、视图可以理解为一个临时表,但是这个表中没有实际数据,你可以任务视图只是保存一段sql语句
2、视图中不保存表真实数据,每次使用视图时,会从原表重新获取数据,视图的数据是随着原表变化的
3、视图可以理解为一个快捷方式,里边保存的是一条sql语句,指向原表
4、视图是用来查询的,不用对视图使用update、insert、delete来修改原表数据
语法
create or replace
view 视图的名字 #视图名字需要在同一个数据库中唯一
as 查询语句
2. 作用
1、简化sql书写、类似with,但是with只能一条sql中用一次,而视图可以永久当做一张表使用
2、权限控制,在公司中我们可以每个人的权限将原表一部分封装成视图,让不同人操作不同的视图
3. 代码详解
- 创建视图
-
代码1
#------------------创建视图---------------------- create or replace view my_view1 as select * from mydb3.dept where dname = 'ACCOUNTING' or dname = 'RESEARCH'; select * from my_view1; #-------查询财务部和研发部薪资小于5000的员工信息 with t1 as ( select * from mydb3.emp where sal < 5000 ) select * from my_view1 v join t1 on v.deptno = t1.deptno; #------------------对视图重命名---------------------- -- rename table 视图名 to 新视图名; rename table my_view1 to my_view11 #------------------删除视图---------------------- -- drop view 视图名[,视图名…]; drop view if exists my_view11; -
代码2
-
不用视图的写法
select dname from dept a , (select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by avg(sal) desc limit 1) b where a.deptno = b.deptno; -
用视图的写法
# 创建视图 create or replace view my_view_avg_sal as select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno order by avg(sal) desc limit 1; #使用视图 select dname from dept a , my_view_avg_sal b where a.deptno = b.deptno;
-
四、MySQL的事务
1.介绍
1、只有MySQL的引擎是InnoDB时,才支持事务,MyISAM和其他引擎不支持事务操作
2、事务是将一组SQL语句当做是一个整体,这组SQL只有全部执行成功,结果才算成功,只要有一条失败,则结果就失败
3、只有增删改才涉及到事务操作,而查询不涉及到事务操作,因为增删改是会修改表数据的
2. 事务的特性-ACID
1、原子性(Atomicity)。事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的所有操作要么全部执行,要么全部不执行,不会出现部分执行的情况。
2、一致性(Consistency)。比如转账之前和转账之后总金额是一致的
3、隔离性(Isolation)。事务的执行不会被其他事务干扰。你在存款,你的家人在从同一账号取款
4、持久性(Durability)。一旦事务提交,其对数据库的更改就是永久性的,不可更改
3. 事务的操作
3.1 操作步骤
-
开启事务
begin 或 START TRANSACTION #一旦开启事务,则会将开启事务之后的sql看做是一个整体 -
提交事务
commit #如果所有sql都执行成功,则将之前的所有的sql操作生效 -
回滚事务
rollback # 如果之前的sql执行失败,则所有的历史记录全部清空,回到事务之前的状态
3.2 操作模型
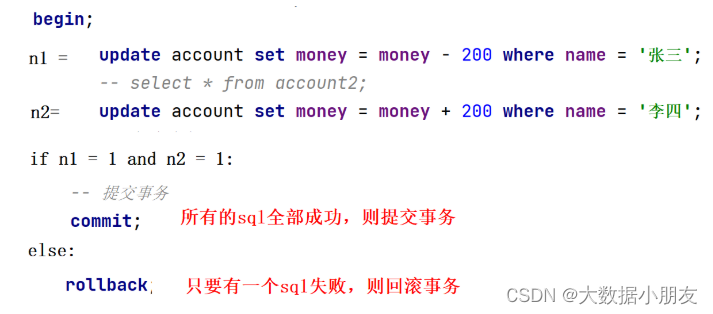
-- 转账
#---------------以下模型有问题----------------
-- 自动开启事务
update account set money = money - 200 where name = '张三';
-- 自动提交事务
-- 自动开启事务
update account set money = money + 200 where name = '李四';
-- 自动提交事务
#---------------要改为以下模型----------------
-- 手动开启事务
update account set money = money - 200 where name = '张三';
update account set money = money + 200 where name = '李四';
-- 手动提交事务
3.3 案例解析
#-----------------------------------
set autocommit=0; #禁止自动提交 set autocommit=1; #开启自动提交
-- 模拟账户转账
-- 开启事务 : 将两个update看做是一个整体,不可分割
begin;
update account set money = money - 200 where name = '张三';
-- select * from account2;
update account set money = money + 200 where name = '李四';
-- 提交事务
commit;
-- 如果转账中的任何一条出现问题,则回滚事务
rollback;
4.隔离级别的演示

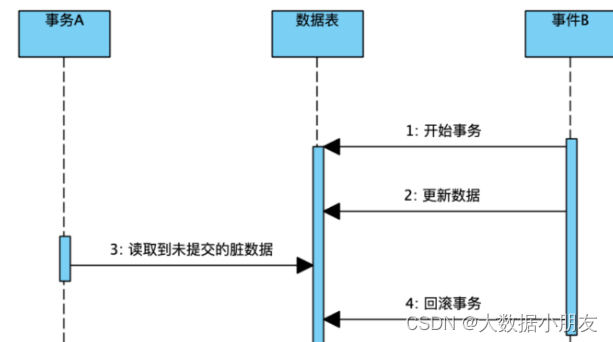
4.1 脏读
mysql -h192.168.88.100 -uroot -p #通过cmd进入mysql
#设置隔离级别为读未提交
set session transaction isolation level read uncommitted;
# 查看隔离级别
show variables like '%isolation%';
# 在一个事务中读取到另一个事务未提交的数据
4.2 不可重复读
#设置隔离级别为读已提交
set session transaction isolation level read committed;
# 在一个A事务中,A事务在未提交,读取到B事务提交前和提交后数据不一致
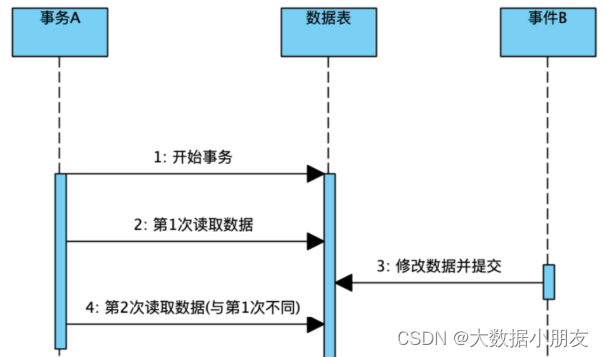
4.3 幻读
##设置隔离级别为可重复读
set session transaction isolation level repeatable read;
# 在一个A事务中,A事务在提交前和提交后,读取到B事务数据不一致
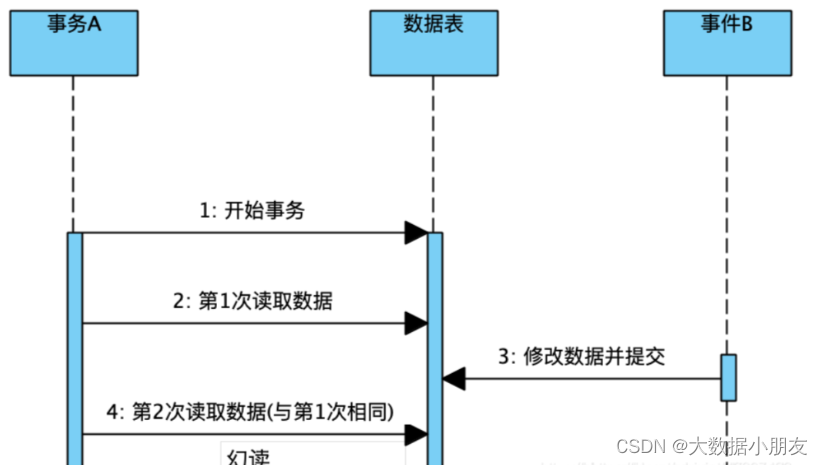
4.4 串行化
##设置隔离级别为串行化
set session transaction isolation level serializable;
#多个事务同时操作一张表时,会将表进行加锁,同一时刻只有一个事务能够操作这张表,其他事务只能等待,直到上一个事务提交