目录
- 1、Arrays工具类
- 2、排序算法
- 2.1 冒泡排序
- 2.2 选择排序
- 2.3 二分查找(折半查找)
- (1)概念:
- (2)步骤:
- 3、正则表达式
- 3.1 正则表达式的概念:
- 3.2 正则表达式的格式:
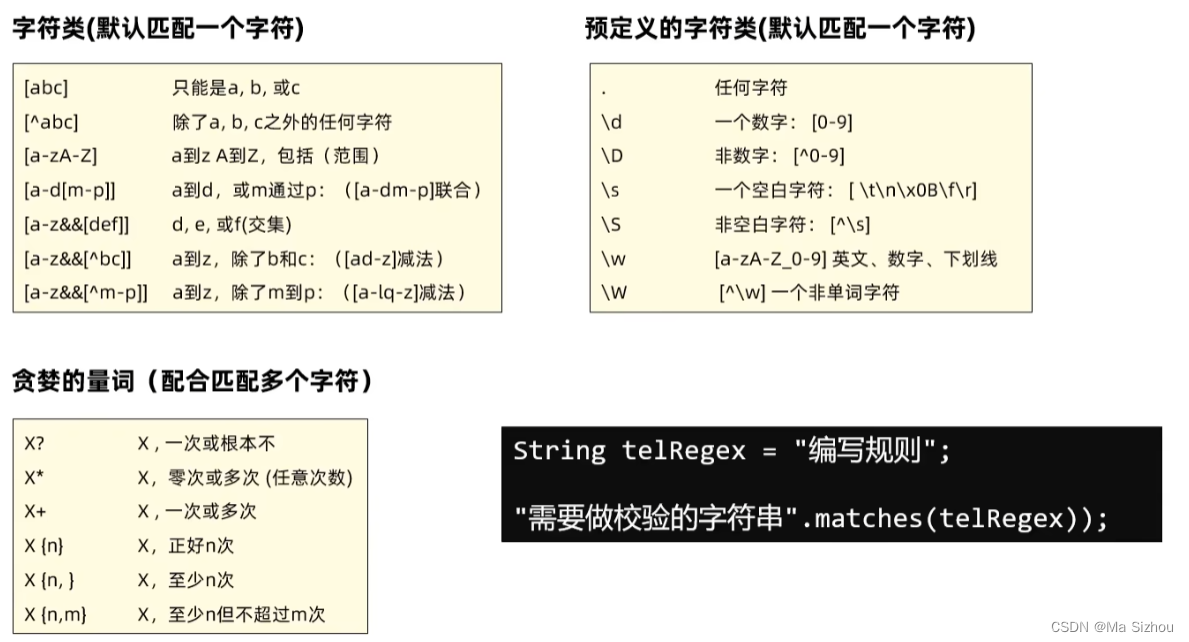
- (1)单个字符类:
- (2)预定义字符类:
- (3)数量:
- 3.3 练习:
- 3.4 String类中与正则有关的常见方法:
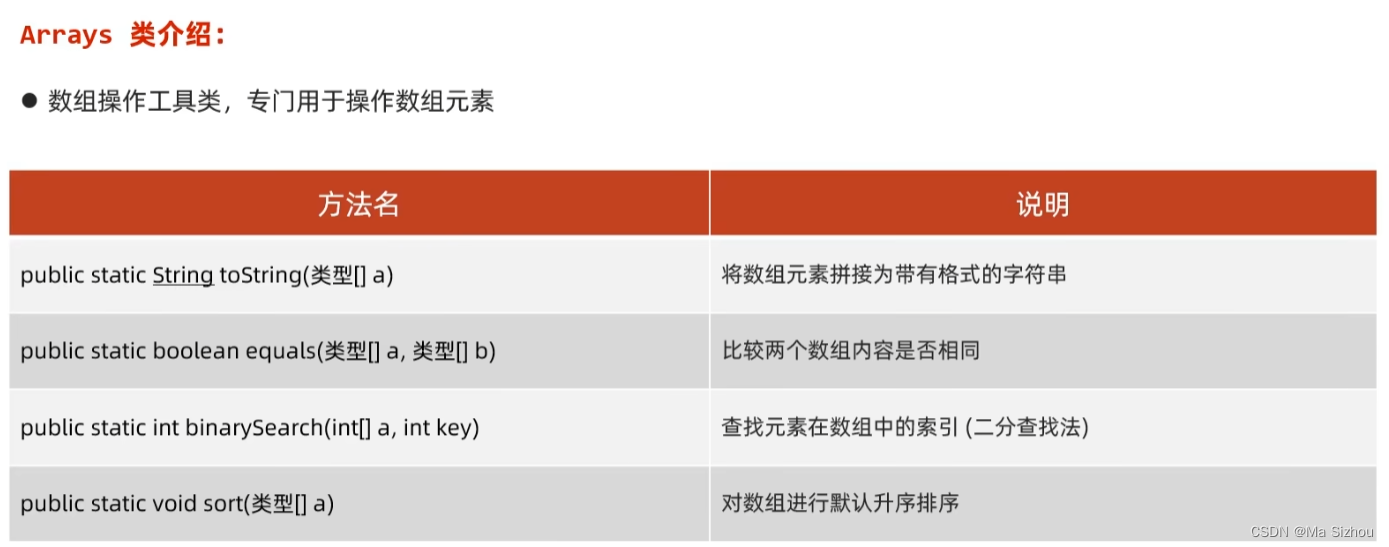
1、Arrays工具类
package it.heima;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraysDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = {11,22, 33,44, 55};
int[] arr2 = {11,22, 33,44, 55};
//1、Arrays.toString():将数组元素拼接为带有格式的字符串
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));//[11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
//2、Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2):比较两个数组内容是否相等
System.out.println(arr1 == arr2);//false
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2));//true
//3、查找元素在数组中的索引(二分查找发:必须是排好序的数组)
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr1, 44));//3
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr1, 66));//-6 查找的元素不存在返回 -(插入点) - 1
//4、对数组进行默认的升序排序。如果降序需要指定比较器,后续介绍 todo
int[] arr3 = {11,77, 33,88, 55};
int[] arr4 = {11,77, 33,88, 55};
Arrays.sort(arr3);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3));
}
}
2、排序算法
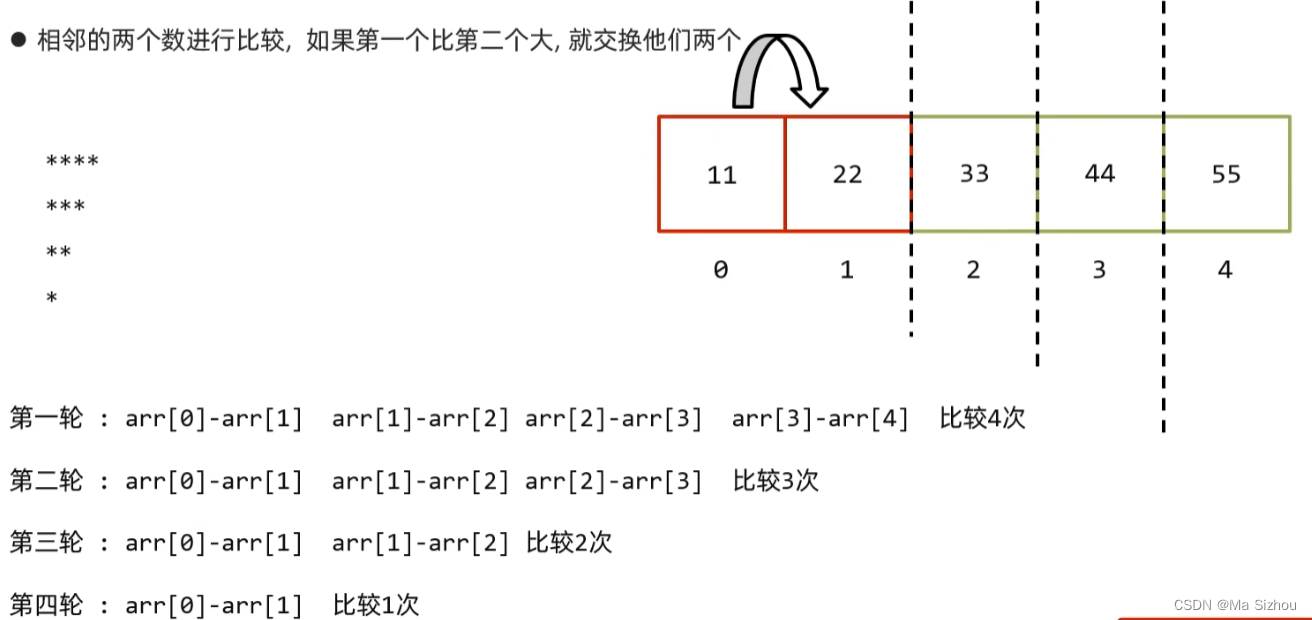
2.1 冒泡排序
package it.heima;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {6, 3, 9, 2, 8, 4};
//外循环:比较轮次
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
//内循环:比较次数
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j + 1]){//从大到小:将最小的冒泡到最上面
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
2.2 选择排序
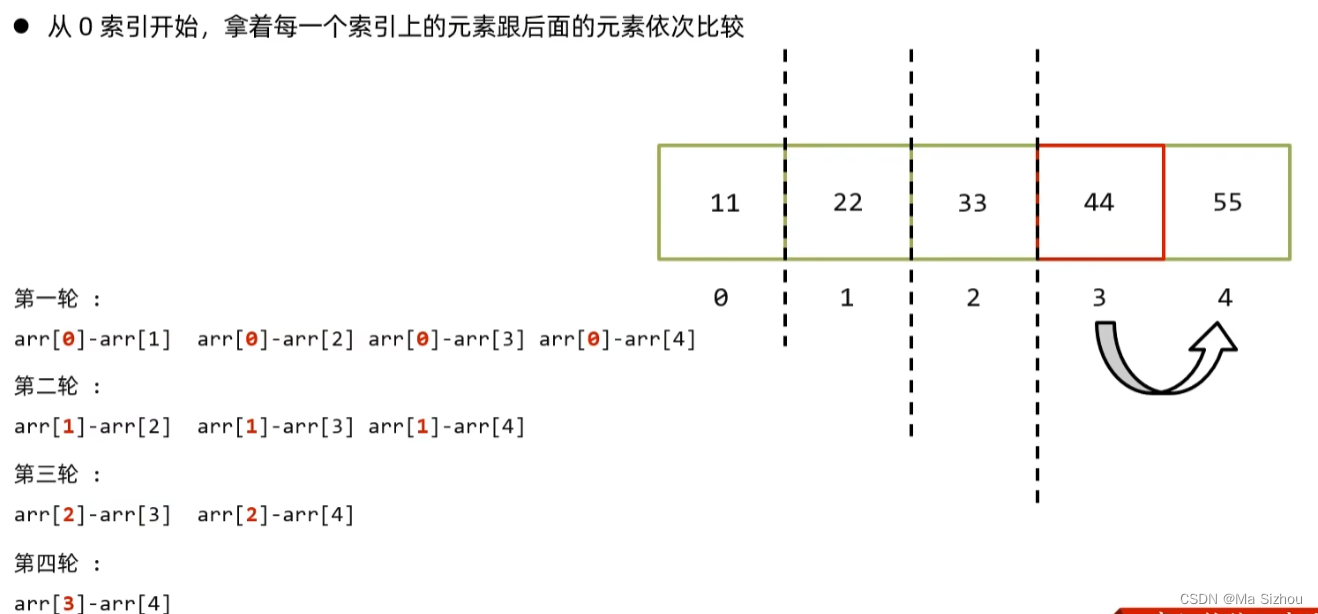
package it.heima;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {6, 3, 9, 2, 8, 4};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]){ //从小到大排序
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//[2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9]
}
}
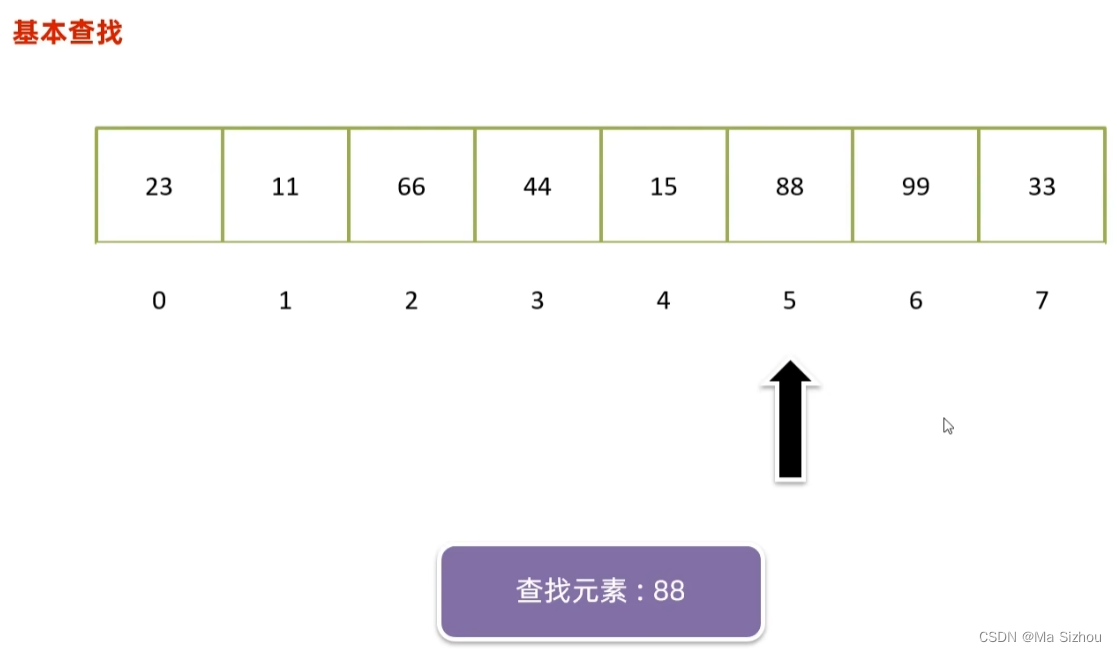
2.3 二分查找(折半查找)
(1)概念:
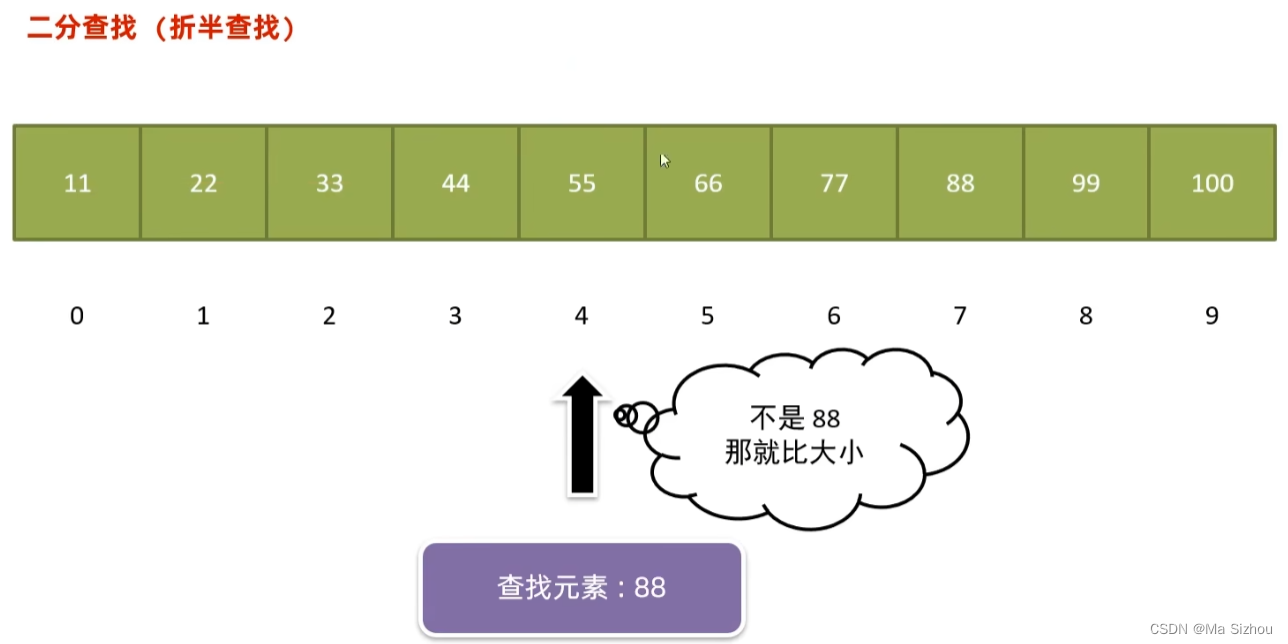
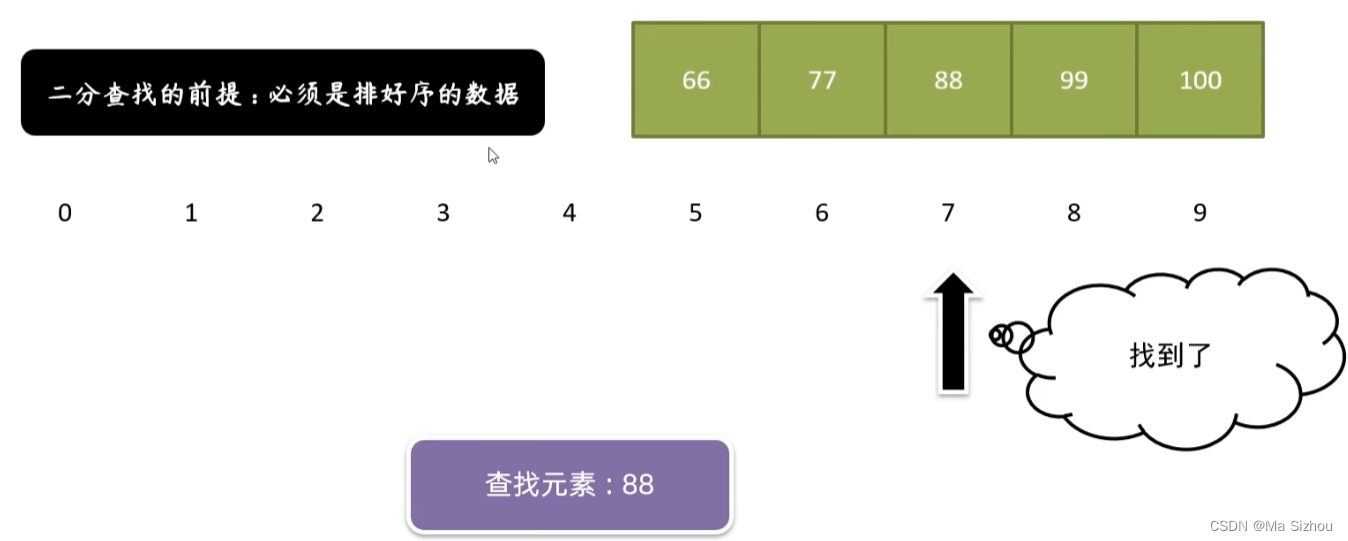
(2)步骤:
第一步:
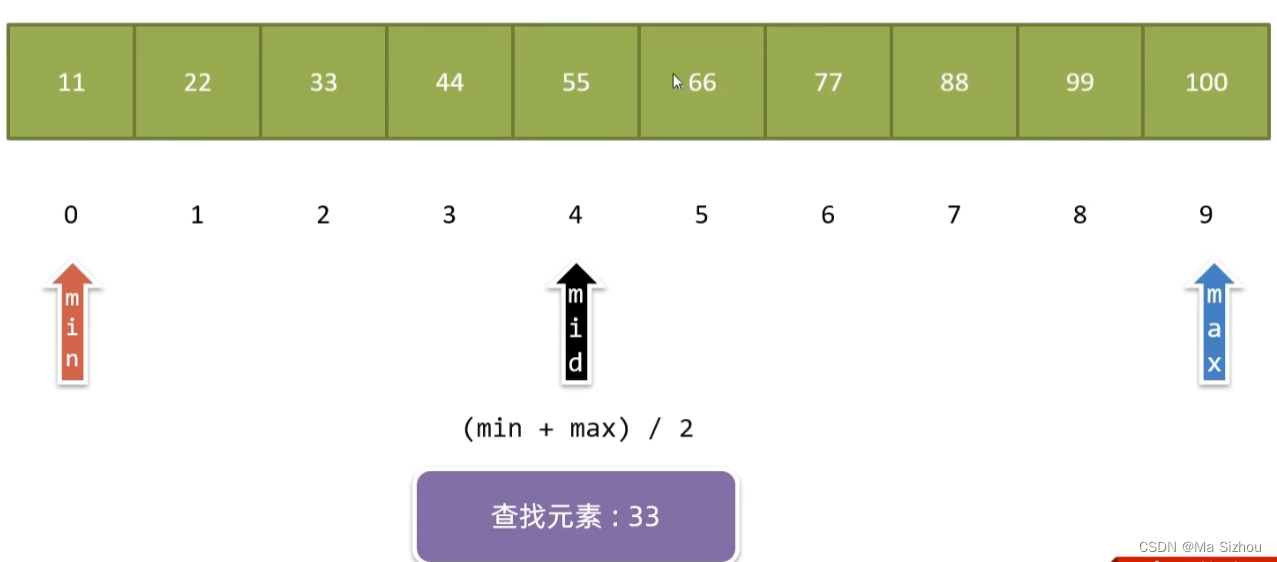
第二步:
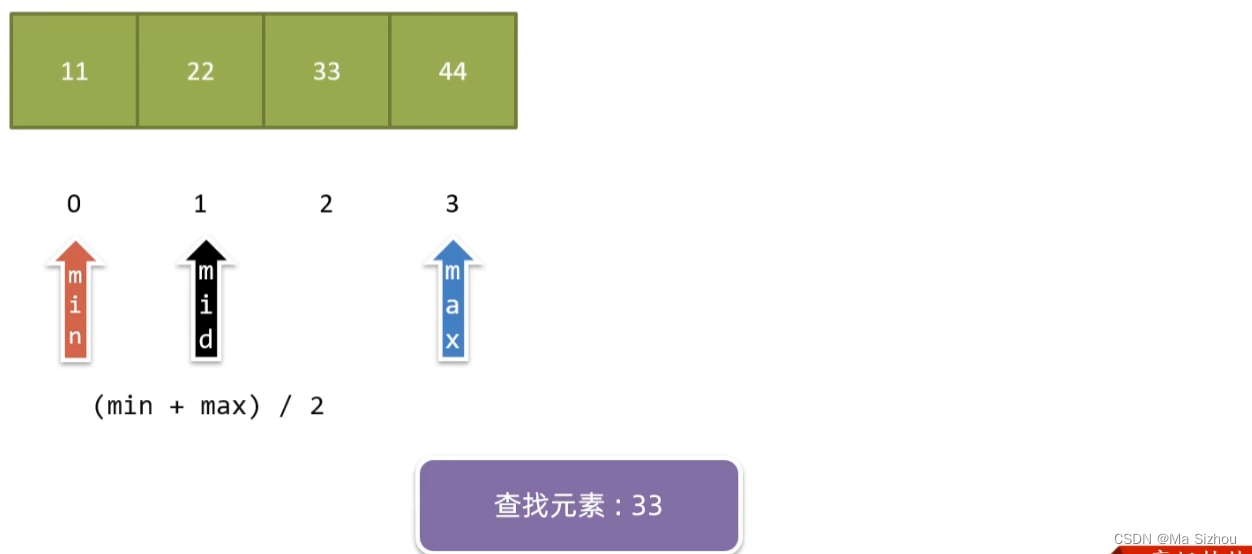
第三步:

总结:

案例:
package it.heima;
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 33;
int[] arr = {11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,100};
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
int mid = -1;
while (left <= right){
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (arr[mid] < num){//说明在右边
left = mid + 1;
}else if (arr[mid] > num){//说明在左边
right = mid - 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
if (mid != -1){
System.out.println("找到了,所在位置为:" + mid);
}
}
}
3、正则表达式
3.1 正则表达式的概念:
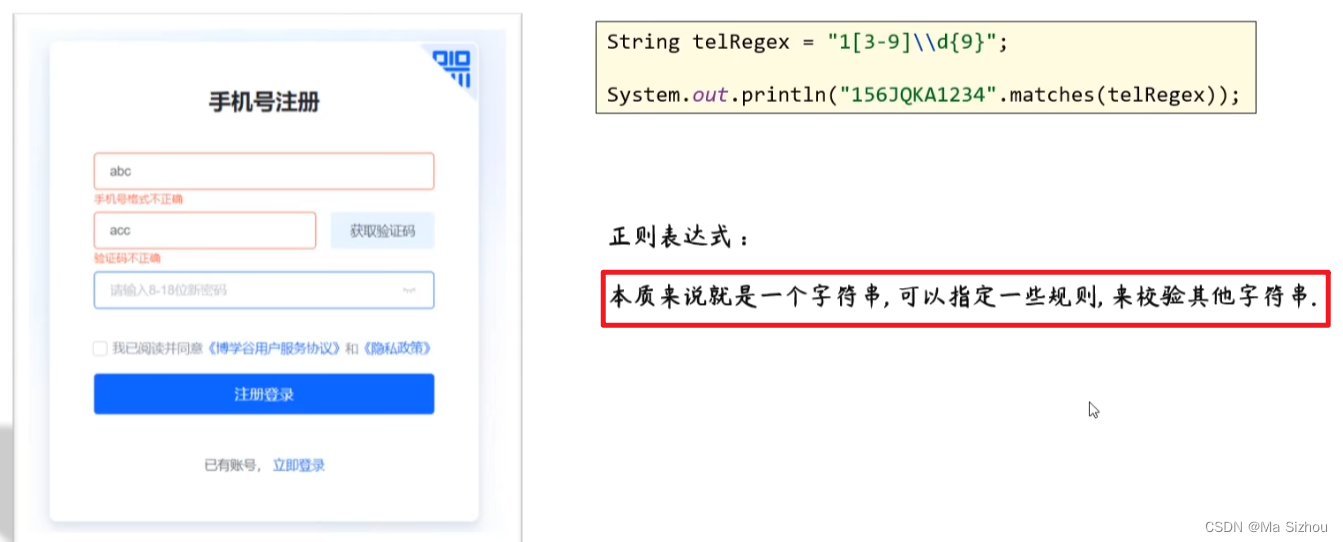
3.2 正则表达式的格式:
(1)单个字符类:
就是这个位置的字符的取值范围,直接看代码理解:
package it.heima.regex;
public class RegexDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 注:
* []:代表单个字符的取值,例如[a]表示这个位置的字符只能是a,[ab]表示这个位置的字符只能为a或b
* ^:代表取反,例如[^a]表示这个位置可以为除了字符a其他任意一个字符,[^ab]表示这个位置可以为除了字符a和b的其他任意一个字符
* -:代表范围,例如[a-z]表示这个位置可以为a到z的任意一个字符,[0-9]表示这个位置可以为0到9的任意一个字符
*/
//(1):[abc]————————》只能是abc中的一个
String s1 = "[abc]";
System.out.println("b".matches(s1));//true
System.out.println("ab".matches(s1));//false
//(2):[^abc]————————》除了abc外的任意一个
String s2 = "[^abc]";
System.out.println("b".matches(s2));//false
System.out.println("x".matches(s2));//true
//(3):[a-zA-Z]————————》a到z,A到Z,包括(范围)
String s3 = "[a-zA-Z]";
System.out.println("0".matches(s3));//false
System.out.println("x".matches(s3));//true
//(4):[a-d[m-p]]————————》a到z,m-p,可以写成[a-dm-p]
String s4 = "[a-d[m-p]]";
System.out.println("e".matches(s4));//false
System.out.println("n".matches(s4));//true
//(5):[a-z&&[def]]————————》a到z中,只有def可以选择,可以写成[def]
String s5 = "[a-z&&[def]]";
System.out.println("e".matches(s5));//true
System.out.println("a".matches(s5));//false
//(6):[a-z&&[^bc]]————————》a到z中,除了bc,其他都可以,可以写成[ad-z]
String s6 = "[a-z&&[^bc]]";
System.out.println("g".matches(s6));//true
System.out.println("c".matches(s6));//false
//(7):[a-z&&[^m-p]]————————》a到z中,除了m-p,其他都可以,可以写成[a-lq-z]
String s7 = "[a-z&&[^m-p]]";
System.out.println("e".matches(s7));//true
System.out.println("n".matches(s7));//false
}
}
(2)预定义字符类:
就是把单个字符的一些常用写法,用别的方式代替了。直接看代码理解:
package it.heima.regex;
public class RegexDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 预定义字符类:
*
* .: 代表任意一个字符
* \d:代表一个数字,和[0-9]一个作用
* \: 代表转义字符,就是把当前字符的含义,转义成另一种含义,例如"\t",表示将当前的t转换成tab健
* \D:代表非数字,和[^0-9]一个作用
* \s:代表一个空白字符
* \S:代表一个非空白字符
* \w:代表英文、数字、下划线,等于[a-zA-Z_0-9]
* \W:代表一个非单词字符,等于[^\w]
*
*/
//(1):.————————》代表任意一个字符
String s1 = ".";
System.out.println("a".matches(s1));//true
System.out.println("*".matches(s1));//true
//(2):/d————————》代表一个数字,和[0-9]一个作用
String s2 = "\\d";//注意:\为转义字符,这里第一个\转义第二个\为字符\
System.out.println("a".matches(s2));//false
System.out.println("4".matches(s2));//true
//(3):\D————————》代表非数字,和[^0-9]一个作用
String s3 = "\\D";
System.out.println("a".matches(s3));//true
System.out.println("4".matches(s3));//false
//(4):\s————————》代表一个空白字符
String s4 = "\\s";
System.out.println(" ".matches(s4));//true
System.out.println("4".matches(s4));//false
//(5):\S————————》代表一个非空白字符
String s5 = "\\S";
System.out.println(" ".matches(s5));//false
System.out.println("4".matches(s5));//true
//(6):\w————————》代表英文、数字、下划线,等于[a-zA-Z_0-9]
String s6 = "\\w";
System.out.println("F".matches(s6));//true
System.out.println("*".matches(s6));//false
//(7):\W————————》代表一个非单词字符,等于[^\w]
String s7 = "\\W";
System.out.println("F".matches(s7));//false
System.out.println("*".matches(s7));//true
}
}
(3)数量:
就是指定出现的次数。
package it.heima.regex;
public class RegexDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 数量:
* ?:代表0次或1次,例如 a?就表示a可以为0次或1次
* *:代表0次或多次,例如 a*就表示a可以为0次或多次(任意次数)
* +:代表1次或多次,例如 a*就表示a可以为1次或多次
* {n}:代表正好n次,例如 a{3}表示a正好3次
* {n,}:代表至少n次,例如 a{3,}表示a至少3次
* {n,m}:代表至少n次,但不超过m次,例如 a{3,6}表示a至少3次但不超过6次
*
*/
//(1):?————————》代表0次或1次
String s1 = "2?";
System.out.println("223".matches(s1));//false
System.out.println("".matches(s1));//true
//(2):?————————》代表0次或多次(任意次数)
String s2 = "2*";
System.out.println("222222".matches(s2));//true
System.out.println("".matches(s2));//true
//(3):+————————》代表1次或多次
String s3 = "2+";
System.out.println("222222".matches(s3));//true
System.out.println("2".matches(s3));//true
System.out.println("".matches(s3));//false
//(4):{n}————————》代表正好n次
String s4 = "2{3}";
System.out.println("222222".matches(s4));//false
System.out.println("222".matches(s4));//true
//(5):{n,}————————》代表至少n次
String s5 = "2{3,}";
System.out.println("222222".matches(s5));//true
System.out.println("22".matches(s5));//false
//(5):{n,m}————————》代表至少n次,但不超过m次
String s6 = "2{3,6}";
System.out.println("22222".matches(s6));//true
System.out.println("22".matches(s6));//false
System.out.println("22222222".matches(s6));//false
}
}
3.3 练习:

package it.heima.regex;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String qqRegex = "[1-9]\\d{4,11}";
System.out.println("1917609089".matches(regex));//true
System.out.println("0917609089".matches(regex));//false
System.out.println("1917609089000".matches(regex));//false
}
}

package it.heima.regex;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String telRegex = "1[3-9]\\d{9}";
System.out.println("16769342819".matches(telRegex));//true
System.out.println("56769342819".matches(telRegex));//false
System.out.println("11769342819".matches(telRegex));//false
System.out.println("167693428190".matches(telRegex));//false
}
}

package it.heima.regex;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String emailRegex = "\\w+[@][\\w&&[^_]]+(\\.[a-z]{2,3})+";
System.out.println("zhangsan@163.com".matches(emailRegex));//true
System.out.println("16769342819@3232qq.com".matches(emailRegex));//true
System.out.println("16769342819".matches(emailRegex));//false
}
}
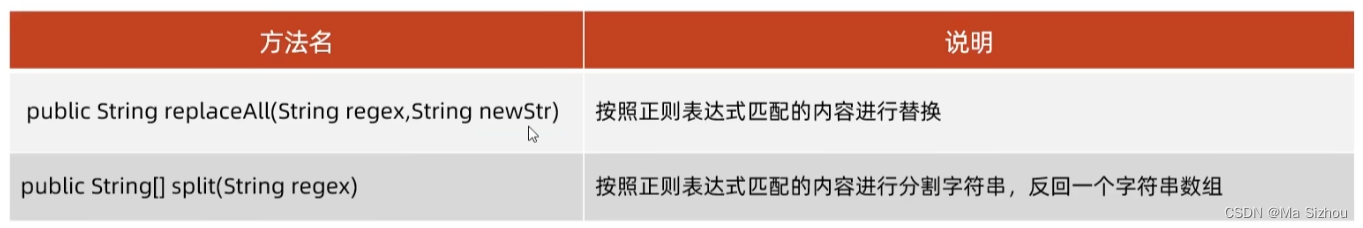
3.4 String类中与正则有关的常见方法:
package it.heima.regex;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "先帝1创业2未半而中道3崩殂4,今5天下三分6,益州疲弊7,此8诚危急存亡之秋也。然9侍卫之臣不懈于内,忠志之士忘身10于外者,盖追先帝之殊遇11,欲报之于陛下也。诚宜12开张圣听13,以光14先帝遗德,恢弘15志士之气,不宜妄自菲薄16,引喻失义17,以塞忠谏之路也18。\n" +
"宫中府中,俱为一体19;陟罚臧否20,不宜异同:若有作奸犯科21及为忠善者22,宜付有司23论其刑赏24,以昭陛下平明之理25;不宜偏私26,使内外异法也27。\n" +
"侍中、侍郎郭攸之、费祎、董允等,此皆良实,志虑忠纯28,是以先帝简拔以遗陛下29:愚以为宫中之事,事无大小,悉以咨之30,然后施行,必能裨补阙漏31,有所广益32。\n" +
"将军向宠,性行淑均33,晓畅34军事,试用35于昔日,先帝称之曰“能”,是以众议举宠为督36:愚以为营37中之事,悉以咨之,必能使行阵38和睦,优劣得所39。";
s = s.replaceAll("[0-9]", " ");//将s中的数字用空格替换
System.out.println(s);
}
}
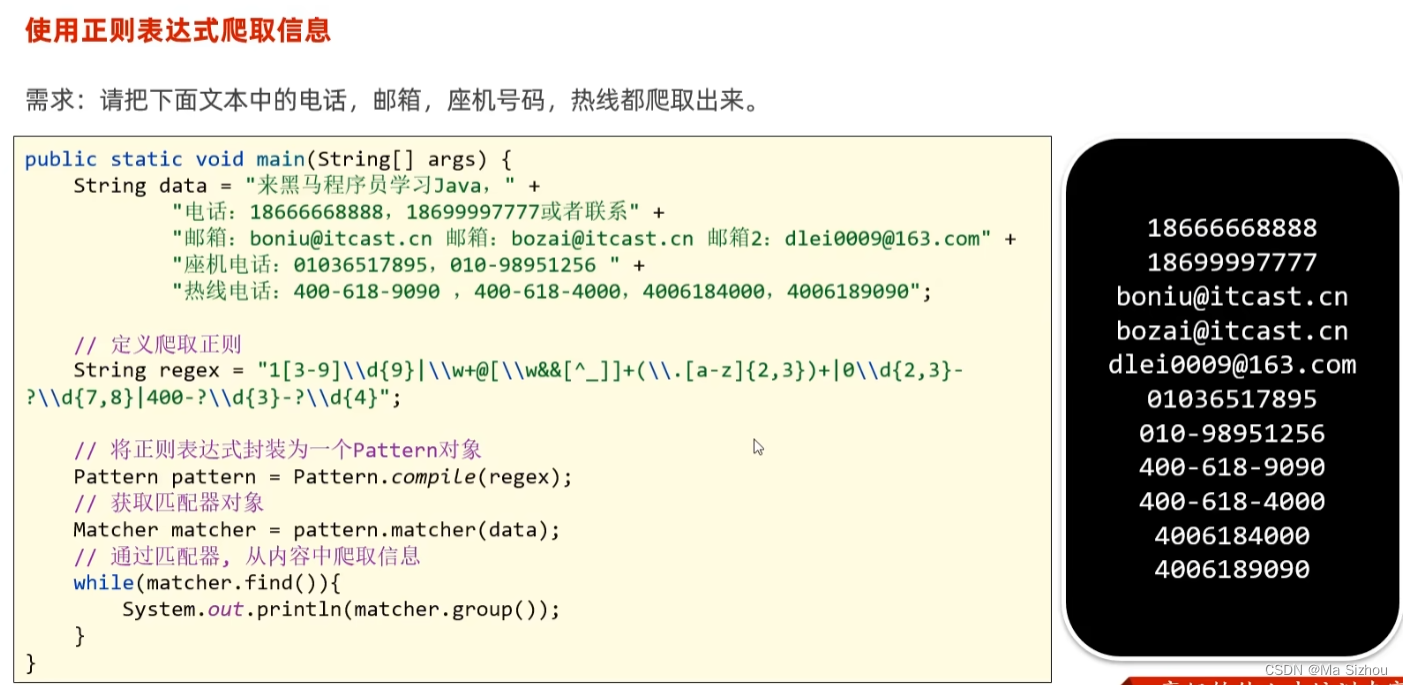
- 代码:
package it.heima.regex;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String data = "来小马课堂学习Java,电话:18666668888,18699998888或者联系" +
"邮箱1:boniu@itcast.cn 邮箱2:bozai@itcast.cn 邮箱3:dlei0009@163.com" +
"座机电话:01036517895,010-98951256" +
"热线电话:400-618-9090,400-618-4000,4006184000,4006189090";
//1、定义爬取正则
String regex = "1[3-9]\\d{9}|\\w+@[\\w&&[^_]]+(\\.[a-z]{2,3})+|0\\d{2,3}-?\\d{7,8}|400-?\\d{3}-?\\d{4}";
//2、将正则表达式封装为 Pattern 对象
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
//3、获取匹配器对象
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(data);
//4、通过匹配器,从内容中爬取信息
while (matcher.find()){
System.out.println(matcher.group());
}
}
}
- 输出:
18666668888
18699998888
boniu@itcast.cn
bozai@itcast.cn
dlei0009@163.com
01036517895
010-98951256
400-618-9090
400-618-4000
4006184000
4006189090
Process finished with exit code 0