系列文章
本人系列文章-CSDN博客
目录
系列文章
目录
1.简介
1.1 主要步骤
1.2 时序图
2.源码分析
2.1 WindowManagerImpl的addView
2.2 WindowManagerGlobal的addView
2.3 ViewRootImpl
2.4 getWindowSession
2.5 WMS中的openSession
2.6 Session
2.7 class W
2.8 setView
2.9 addToDisplay
2.10 addWindow
2.11 openInputChannel
2.12 Java层openInputChannelPair
2.13 android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair
2.14 openInputChannelPair
2.15 transferTo
2.16 WMS向IMS注册并监听socket
2.17 nativeRegisterInputChannel
2.18 android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel
2.19 android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle
2.20 registerInputChannel
2.21 InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel
2.22 Connection
2.23 android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback
2.24 WindowInputEventReceiver
2.25 InputEventReceiver
2.26 nativeInit
2.27 NativeInputEventReceiver
2.28 initialize
2.29 setFdEvents
2.30 Looper::addFd
1.简介
上一篇中,主要介绍了按键事件中inputdispatcher线程的分发流程,最后会通过sokcet对发送按键消息到应用端,那么这个socket对是什么时候创建的呢?是什么时候和IMS建立连接的呢?本文便主要解答一下这部分内容。
1.1 主要步骤
1.首先当Activity启动后,应用程序端会创建一个空的InputChannel对象。
2.然后应用程序端会通过binder调用到WMS服务,WMS服务会通过openInputChannel 方法会创建一对 InputChannel,一个给到IMS,一个会通过binder调用返回给应用端。
3.然后WMS会将其中一个socket注册到IMS服务中,IMS服务通过epoll机制来监听,是否有来自应用端发送的消息,当应用程序端通过sokcet发送消息时,IMS中的handleReceiveCallback回调函数会执行。
4.然后此时应用端到WMS的binder调用函数返回,返回给应用程序端一个socket,应用程序端会创建一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象,同时应用程序端也会通过epoll机制来监听,是否有来自IMS发送的消息,当存在IMS发送事件到应用程序端时,会调用NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent函数。
1.2 时序图
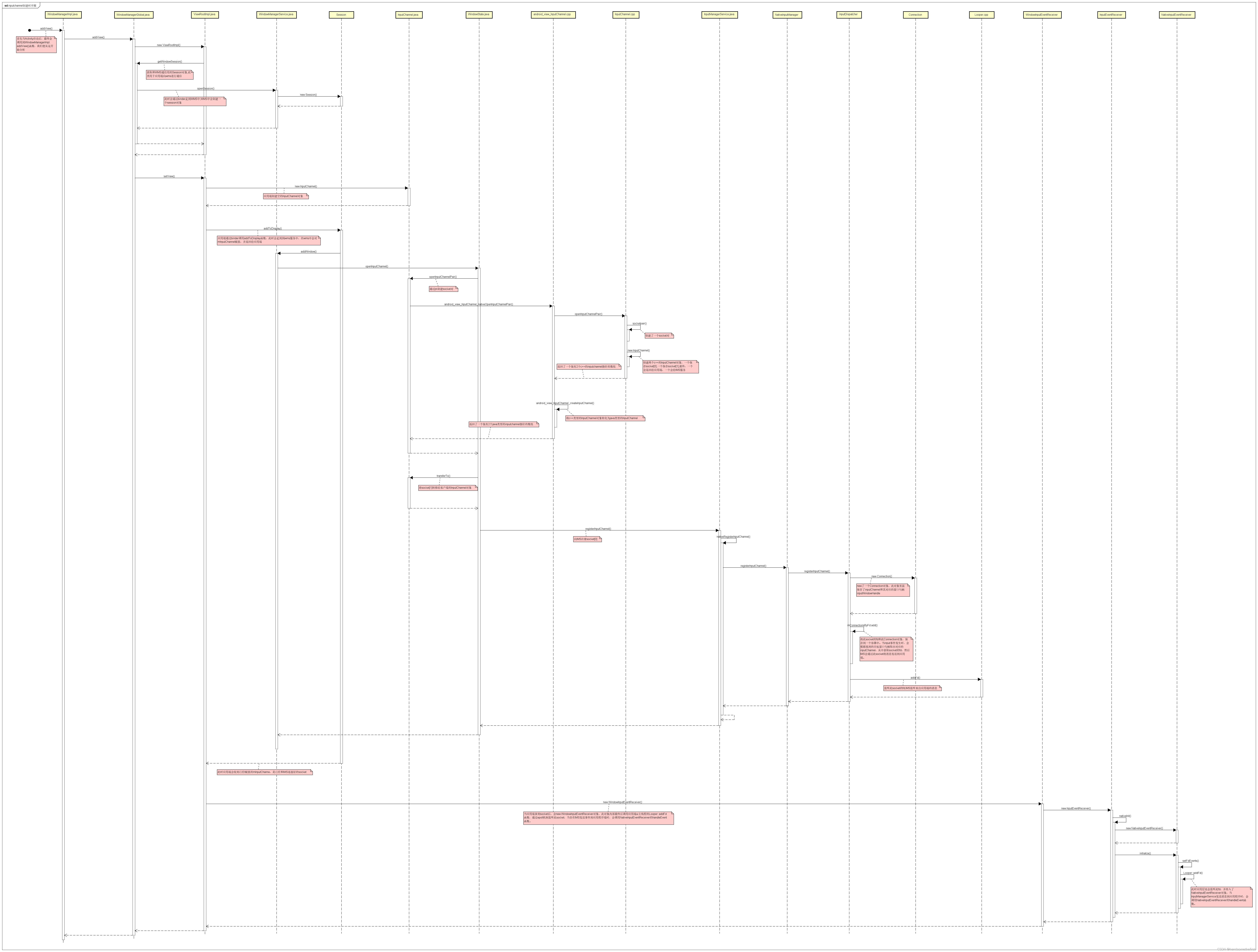
(图片可保存到本地放大观看)
2.源码分析
首先当Activity启动后,最终会调用到WindowManagerImpl.addView()函数,我们便从WindowManagerImpl.addView()函数进行分析。
2.1 WindowManagerImpl的addView
主要作用:
1.调用WindowManagerGlobal对象的addview对象。
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params)
{
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);//mGlobal就是WindowManagerGlobal对象
}2.2 WindowManagerGlobal的addView
主要作用:
1.创建ViewRootImpl对象。
2.调用ViewRootImpl的setView函数,此函数会创建空的InputChannel对象,然后传给WMS,WMS会返回一个和IMS连接好的socket给应用程序端。
此时我们仍然在应用程序进程中。
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
//view代表添加哪个窗口,此时view是DecorView
//params窗口的参数
//display显示到那块屏幕上
//parentWindow父窗口是谁
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
int index = findViewLocked(view, false);//从mViews中查找此view是否已经存在
/*
if (index >= 0) {
if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) {
// Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue.
mRoots.get(index).doDie();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view
+ " has already been added to the window manager.");
}
// The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has.
}*/
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);//将此DecorView保存到mViews容器中
mRoots.add(root); //将此ViewRootImpl保存到容器中
mParams.add(wparams);//保存参数
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}2.3 ViewRootImpl
主要作用:
1.获取IWindowSession代理类,此类用于应用端和wms进行通信。
2.new W(this);W 继承自 IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信。在调用本类的setView时会将此W对象传递给WMS。
//ViewRootImpl.Java
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();//获取IWindowSession代理类,此类用于应用和wms进行通信
mDisplay = display;//显示到那个display中
mDirty = new Rect();
mTempRect = new Rect();
mVisRect = new Rect();
mWinFrame = new Rect();
mWindow = new W(this);//w继承自class W extends IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信
mFirst = true; // true代表此view第一次被添加
mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
mDisplayManager = (DisplayManager)context.getSystemService(Context.DISPLAY_SERVICE);
}2.4 getWindowSession
主要作用:
1.获取和WMS通信用的Session对象。
//WindowManagerGlobal.java
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();//输入法
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();//获取wms的binder代理对象
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {//传入了客户端实现的WindowSessionCallback回调类,用于wms通信到应用程序
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}//aidl接口如下
IWindowSession openSession(in IWindowSessionCallback callback, in IInputMethodClient client,
in IInputContext inputContext);2.5 WMS中的openSession
主要作用:
1.此时会走到WMS中,WMS中会创建一个session对象
//此时会调用到WMS中
public class WindowManagerService extends IWindowManager.Stub
implements Watchdog.Monitor, WindowManagerPolicy.WindowManagerFuncs
{
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext)
{
if (client == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("null client");
if (inputContext == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("null inputContext");
Session session = new Session(this, callback, client, inputContext);
return session;//
}
}2.6 Session
主要作用为:
1.此类内部会保存WindowManagerService对象和客户端实现的IWindowSessionCallback类对象
class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient
{
public Session(WindowManagerService service, IWindowSessionCallback callback,
IInputMethodClient client, IInputContext inputContext) {
mService = service;//此时service是WindowManagerService对象
mCallback = callback;//callback是客户端实现的IWindowSessionCallback类对象,是一个binder对象
mClient = client;//此时是输入法的客户端
mUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
mPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
synchronized (mService.mWindowMap) {
if (mService.mInputMethodManager == null && mService.mHaveInputMethods) {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(
Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
mService.mInputMethodManager = IInputMethodManager.Stub.asInterface(b);//获取输入法的binder代理对象
}
}
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// Note: it is safe to call in to the input method manager
// here because we are not holding our lock.
if (mService.mInputMethodManager != null) {
mService.mInputMethodManager.addClient(client, inputContext,
mUid, mPid);//将此addClient添加到输入法中
} else {
client.setUsingInputMethod(false);
}
client.asBinder().linkToDeath(this, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// The caller has died, so we can just forget about this.
try {
if (mService.mInputMethodManager != null) {
mService.mInputMethodManager.removeClient(client);
}
} catch (RemoteException ee) {
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
}2.7 class W
主要作用:
1.W 继承自 IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信。在调用本类的setView时会将此W对象传递给WMS
static class W extends IWindow.Stub {
private final WeakReference<ViewRootImpl> mViewAncestor;
private final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
W(ViewRootImpl viewAncestor) {
mViewAncestor = new WeakReference<ViewRootImpl>(viewAncestor);
mWindowSession = viewAncestor.mWindowSession;//客户端保存IWindowSession session通信对象
}
}2.8 setView
主要作用为:
1.应用端创建空的InputChannel对象。
2.应用端通过binder调用addToDisplay函数,此时会走到到wms服务中,在wms中会对mInputChannel赋值,并返回。返回的是一个已经和IMS连接的socket。
3.当应用端拿到socket后,会new WindowInputEventReceiver对象,此对象内部最终后调用应用端ui主线程的Looper::addFd函数,通过epoll机制监听此socket,当存在IMS发送事件到应用程序端时,会调用NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent函数。
//frmaework/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
//view是view代表添加哪个窗口,此时view是DecorView
//params窗口的参数
//panelParentView,如果是子窗口,则子窗口存在父窗口,此时是普通窗口,则为null
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs);
if (mWindowAttributes.packageName == null) {
mWindowAttributes.packageName = mBasePackageName;//给mWindowAttributes添加了包名
}
attrs = mWindowAttributes;
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();//客户端创建InputChannel对象,此时的InputChannel是空的对象,并没有赋值的内容
}
try {
//将空的mInputChannel传入其中,应用端通过binder调用到wms中,在wms中会对mInputChannel赋值
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mWinFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel);
//mWindow继承自IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信
//mWindowAttributes窗口属性
//mInputChannel本质是socket,用于应用程序和ims进行输入事件的通信
}
if (mInputChannel != null)
{
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
}
}2.9 addToDisplay
此时会通过binder走到WMS的系统服务中。
主要作用:
1.调用Windowmanagerservice的addWindow函数。
class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets,
Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
//此时mWindow继承自IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信
//outInputChannel本质是socket,用于应用程序和ims进行输入事件的通信
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel);
}
}2.10 addWindow
主要作用:
1.调用WindowState类的openInputChannel函数。
//Windowmanagerservice.java
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel)
//此时client客户端的Window,继承自IWindow.Stub,用于wms服务端向应用端通信
//outInputChannel本质是socket,用于应用程序和ims进行输入事件的通信
{
//仅当窗口的inputFeatures未指定NO_INPUT_CHANNEL选项时才会为此窗口创建InputChannel对
boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null&& (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0);
if (callingUid != SYSTEM_UID)
{
Slog.e(TAG_WM,"App trying to use insecure INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL flag. Ignoring");
openInputChannels = true;
}
if (openInputChannels)
{
win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel);//win1是一个WindowState类对象,调用其类的openInputChannel函数
}
}2.11 openInputChannel
主要作用为:
1.调用openInputChannelPair创建一个InputChannel对
2.将0号inputChannel调用InputManager.registerInputChannel注册到IMS中
3.将1号inputChannel传递给outInputChannel,即传递给应用端。
// frmaework/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java
void openInputChannel(InputChannel outInputChannel)
{
if (mInputChannel != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Window already has an input channel.");
}
String name = getName();
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);//会创建一个sokcet对
mInputChannel = inputChannels[0];
mClientChannel = inputChannels[1];
mInputWindowHandle.inputChannel = inputChannels[0];//其中0号inputChannel交给InputWindowHandle保存
if (outInputChannel != null) {
mClientChannel.transferTo(outInputChannel);//将mClientChannel所持有的1号inputChannel传递给outInputChannel
mClientChannel.dispose();
mClientChannel = null;
}
/*else {
// If the window died visible, we setup a dummy input channel, so that taps
// can still detected by input monitor channel, and we can relaunch the app.
// Create dummy event receiver that simply reports all events as handled.
mDeadWindowEventReceiver = new DeadWindowEventReceiver(mClientChannel);
}*/
mService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mInputChannel, mInputWindowHandle);//将0号的InputChannel向IMS进行注册
//mService定义是com.android.server.wm.WindowManagerService mService
//故mInputManager是构造wms时传入的,mInputManager是InputManagerService对象
}2.12 Java层openInputChannelPair
//路径:frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\InputChannel.java
public static InputChannel[] openInputChannelPair(String name)
{
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name must not be null");
}
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Opening input channel pair '" + name + "'");
}
return nativeOpenInputChannelPair(name);
}2.13 android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair
主要作用为:
1.调用InputChannel::openInputChannelPair创建两个c++类型的InputChannel对象。
2.将c++层的两个InputChannel对象转化为java层的InputChannel对象,并返回到java层。
路径:frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static jobjectArray android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair(JNIEnv* env,
jclass clazz, jstring nameObj) {
const char* nameChars = env->GetStringUTFChars(nameObj, NULL);
std::string name = nameChars;
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(nameObj, nameChars);
sp<InputChannel> serverChannel;
sp<InputChannel> clientChannel;
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);//调用c++层的openInputChannelPair
if (result) {
String8 message;
message.appendFormat("Could not open input channel pair. status=%d", result);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.string());
return NULL;
}
//创建两个存储gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz类型的对象的数组,默认值为null
jobjectArray channelPair = env->NewObjectArray(2, gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, NULL);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
return NULL;
}
//将c++类型的serverChannel对象转化为java类型的serverChannelObj
jobject serverChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(serverChannel));
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
return NULL;
}
jobject clientChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env,
std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(clientChannel));
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
return NULL;
}
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 0, serverChannelObj);//将java类型的serverChannelObj放入数组
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 1, clientChannelObj);
return channelPair;//返回一个存储java类型的ChannelObj数组
}2.14 openInputChannelPair
主要作用为:
1.通过socketpair创建一个socket对。
2.设置socket对的发送缓冲区和接受缓冲区的大小
3.用c++层的InputChannel封装socket对,一个封装给IMS,一个封装最终会通过binder调用返回给应用端。
// frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const std::string& name,sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {//将sockets数组传入,通过socketpair函数创建sockets对,返回值为0代表成功
status_t result = -errno;
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not create socket pair. errno=%d",
name.c_str(), errno);
outServerChannel.clear();
outClientChannel.clear();
return result;
}
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));//设置socket[0]的发送缓冲区大小
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));//设置socket[0]的接收缓冲区大小
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));//设置socket[1]的发送缓冲区大小
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));//设置socket[1]的接收缓冲区大小
std::string serverChannelName = name;
serverChannelName += " (server)";
outServerChannel = new InputChannel(serverChannelName, sockets[0]);//用InputChannel封装sockets[0],给服务端
std::string clientChannelName = name;
clientChannelName += " (client)";
outClientChannel = new InputChannel(clientChannelName, sockets[1]);//用InputChannel封装sockets[1],给客户端
return OK;
}2.15 transferTo
主要作用是:
1.转移socket给输入的参数。
// frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\InputChannel.java
public void transferTo(InputChannel outParameter) {
if (outParameter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("outParameter must not be null");
}
nativeTransferTo(outParameter);
}static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,jobject otherObj) {
if (android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj) != NULL) {
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/IllegalStateException",
"Other object already has a native input channel.");
return;
}
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj, nativeInputChannel);//将调用者mClientChannel对应的NativeInputChannel对象,赋值给outInputChannel
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);//将调用者mClientChannel的置空
}static NativeInputChannel* android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env,jobject inputChannelObj) {
jlong longPtr = env->GetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr);
return reinterpret_cast<NativeInputChannel*>(longPtr);
}2.16 WMS向IMS注册并监听socket
//InputManagerService.java
//注册输入通道,以便将其用作输入事件目标。
//@param inputChannel要注册的输入通道。
//@param inputWindowHandle与输入通道关联的输入窗口句柄,如果没有,则为null。
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel,InputWindowHandle inputWindowHandle) {
if (inputChannel == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null.");
}
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);//mPtr是nativeInit返回的值,是指向NativeInputManager的指针。
//inputChannel输入通道
//inputWindowHandle窗口的句柄
}2.17 nativeRegisterInputChannel
主要作用为:
1.将java层获取的inputChannel对象转化为c++层的inputChannel。
2.将java层的窗口句柄inputWindowHandleObj对象转化为c++层的inputWindowHandle。
3.向IMS注册此inputChannel对象和对应的窗口句柄inputWindowHandle
4.设置一个回调函数handleInputChannelDisposed,此回调函数会在调用java层的InputChannel对象完成或者销毁时触发,其会调用unregisterInputChannel取消IMS中已经保存和监听的socket
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jobject inputWindowHandleObj, jboolean monitor) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);//从java层获取native层的inputChannel对象
if (inputChannel == NULL) {
throwInputChannelNotInitialized(env);
return;
}
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle =
android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(env, inputWindowHandleObj);//获取此窗口在input中的句柄
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(
env, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);//向ims注册监听此socket
if (status) {
std::string message;
message += StringPrintf("Failed to register input channel. status=%d", status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.c_str());
return;
}
if (! monitor) {//此时是false
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);//设置一个回调函数,此回调函数会在调用java层的InputChannel对象完成或者销毁时,触发
//主要是调用unregisterInputChannel取消IMS中已经保存和监听的socket
}
}2.18 android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel
主要作用为:
1.通过java层的InputChannel对象获取指向c++层的InputChannel对象的指针。
sp<InputChannel> android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj)
{
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);
return nativeInputChannel != NULL ? nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel() : NULL;
}
static NativeInputChannel* android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env,
jobject inputChannelObj)
{
jlong longPtr = env->GetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr);
return reinterpret_cast<NativeInputChannel*>(longPtr);
}
inline sp<InputChannel> getInputChannel() { return mInputChannel; }2.19 android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle
主要作用为:
1.获取inputWindowHandle类对象,这是WMS的一个窗口的句柄。
//base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputWindowHandle.cpp
sp<NativeInputWindowHandle> android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle(
JNIEnv* env, jobject inputWindowHandleObj) {//inputWindowHandleObj是java层传入的inputWindowHandle类对象
if (!inputWindowHandleObj) {//如果为空,返回
return NULL;
}
AutoMutex _l(gHandleMutex);
jlong ptr = env->GetLongField(inputWindowHandleObj, gInputWindowHandleClassInfo.ptr);
NativeInputWindowHandle* handle;
if (ptr) {
handle = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputWindowHandle*>(ptr);
} else {
jobject inputApplicationHandleObj = env->GetObjectField(inputWindowHandleObj,
gInputWindowHandleClassInfo.inputApplicationHandle);
sp<InputApplicationHandle> inputApplicationHandle =
android_server_InputApplicationHandle_getHandle(env, inputApplicationHandleObj);
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputApplicationHandleObj);
jweak objWeak = env->NewWeakGlobalRef(inputWindowHandleObj);
handle = new NativeInputWindowHandle(inputApplicationHandle, objWeak);
handle->incStrong((void*)android_server_InputWindowHandle_getHandle);
env->SetLongField(inputWindowHandleObj, gInputWindowHandleClassInfo.ptr,
reinterpret_cast<jlong>(handle));
}
return handle;
}2.20 registerInputChannel
主要作用为:
1.调用InputDispatcher的registerInputChannel函数,将窗口的inputChannel和其对应的窗口句柄inputWindowHandle注册到IMS中保存。
//com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
status_t NativeInputManager::registerInputChannel(JNIEnv* /* env */,
const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
ATRACE_CALL();
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->registerInputChannel(
inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);//mInputManager是InputManager.cpp类的对象,
//所以,mInputManager->getDispatcher()是一个InputDispatcher.cpp类的对象
//inputChannel是IMS服务端的socket,用于接收来自应用端的消息
//inputWindowHandle是对应的窗口的句柄。一个窗口对应一个socket对。
}2.21 InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel
主要作用为:
1.new了一个Connection对象,此对象里面保存了inputChannel和其对应的窗口句柄inputWindowHandle
2.将此socket的fd和此Connection对象,保存到一个容器中。当input事件发生时,会根据找到的目标窗口句柄取出对应的inputChannel,从中获取socket的fd,然后IMS会通过此socket将消息发送到应用端。
3.通过 mLooper->addFd,监听此socket的fd,从上文我们知道,WMS会创建两个已经连接好的shocket对,其中一个给到应用程序端,一个给到IMS,此处的作用便是监听来自应用程序端发送给IMS的消息,当应用程序端通过sokcet发送消息时,IMS中的handleReceiveCallback回调函数会执行。
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) {
#if DEBUG_REGISTRATION
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ registerInputChannel - monitor=%s", inputChannel->getName().c_str(),
toString(monitor));
#endif
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (getConnectionIndexLocked(inputChannel) >= 0) {//调用getConnectionIndexLocked方法,
//根据inputChannel的fd值,查找mConnectionsByFd,看看是否此input channel已经注册
ALOGW("Attempted to register already registered input channel '%s'",
inputChannel->getName().c_str());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);//new了一个Connection对象,
//此对象里面保存了inputChannel和其对应的窗口句柄inputWindowHandle
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);//放入mConnectionsByFd中,表示已经注册过的inputChannel
if (monitor) {//此时是false
mMonitoringChannels.push(inputChannel);
}
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
//监听Inputchannel的可读性。
//mLooper的pollOnce()本质上就是epoll_wait(),因此Looper对象具有监听文件描述符可读性事件的能力,在此注册Inputchannel可读性事件,
//并在事件到来时通过handleReceiveCallback()回调进行处理
} // release lock
// Wake the looper because some connections have changed.
mLooper->wake();//唤醒InputDispatcher线程
return OK;
}ssize_t InputDispatcher::getConnectionIndexLocked(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
ssize_t connectionIndex = mConnectionsByFd.indexOfKey(inputChannel->getFd());
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (connection->inputChannel.get() == inputChannel.get()) {
return connectionIndex;
}
}
return -1;
}2.22 Connection
Connection类描述了从ImputDispatcher到目标窗口中的一个连接,其中保存了向窗口发送的事件的状态信息。
在 Connection中,重要的成员有:
1.mlnputPublisher,InputPublisher类的一个对象,它封装InputChannel并直接对其进行写入和读取。另外,它也负责ImputMessage结构体的封装与解析。
2.outboundQueue,用于保存等待通过此Connection进行发送的事件队列。
3.waitQueue,用于保存已经通过此Connection将事件发送给窗口,正在等待窗口反馈的事件队列。
InputDispatcher::Connection::Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor) :
status(STATUS_NORMAL), inputChannel(inputChannel), inputWindowHandle(inputWindowHandle),
monitor(monitor),
inputPublisher(inputChannel), inputPublisherBlocked(false) {
}class Connection : public RefBase {
protected:
virtual ~Connection();
public:
enum Status {
// 连接状态正常
STATUS_NORMAL,
// 发生了不可恢复的通信错误
STATUS_BROKEN,
// input channel已注销。
STATUS_ZOMBIE
};
Status status;
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel; //永不为空
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle; // 可能为空
bool monitor;
InputPublisher inputPublisher;
InputState inputState;
//如果套接字已满,并且在应用程序使用某些输入之前无法发送其他事件,则为True。
bool inputPublisherBlocked;
// 事件队列需要发送到Connection
Queue<DispatchEntry> outboundQueue;
//已发送到connection但尚未收到应用程序“完成”响应的事件队列。
Queue<DispatchEntry> waitQueue;
explicit Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& inputWindowHandle, bool monitor);
inline const std::string getInputChannelName() const { return inputChannel->getName(); }
const std::string getWindowName() const;
const char* getStatusLabel() const;
DispatchEntry* findWaitQueueEntry(uint32_t seq);
};2.23 android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback
主要作用为:
1.设置一个回调函数,此回调函数会在调用java层的InputChannel对象完成或者销毁时触发,主要是调用unregisterInputChannel取消IMS中已经保存和监听的socket,并清空此InputChannel对象对应的Connection对象的outboundQueue和waitQueue队列。
void android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj,
InputChannelObjDisposeCallback callback, void* data) {
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);//根据java层保存的native层的指针的值,获取nativeInputChannel指针
ALOGW("Cannot set dispose callback because input channel object has not been initialized.");
} else {
nativeInputChannel->setDisposeCallback(callback, data);//此时callback是handleInputChannelDisposed
//data是NativeInputManager
}
}
void NativeInputChannel::setDisposeCallback(InputChannelObjDisposeCallback callback, void* data) {
mDisposeCallback = callback;//此时callback是handleInputChannelDisposed
mDisposeData = data;//data是NativeInputManager
}
handleInputChannelDisposed主要作用是取消注册inputchannel。
static void handleInputChannelDisposed(JNIEnv* env,
jobject /* inputChannelObj */, const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel, void* data) {
NativeInputManager* im = static_cast<NativeInputManager*>(data);
ALOGW("Input channel object '%s' was disposed without first being unregistered with "
"the input manager!", inputChannel->getName().c_str());
im->unregisterInputChannel(env, inputChannel);
}那么这个回调函数什么时候会被调用呢?
在Object类里面,有一个方法finalize()。
当VM的垃圾收集器检测到这个对象不可达的时候,也就是说这个对象为垃圾可以被回收的时候,这个对象的finalize ()方法就会被执行,默认情况下,它不做任何处理,我们可以重写这个方法来进行资源的释放。当回收分配的Object对象的内存之前垃圾收集器会调用对象的finalize()方法。
//InputChannel.java
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
try {
nativeDispose(true);
} finally {
super.finalize();
}
}查看对应关系
{ "nativeDispose", "(Z)V",(void*)android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose },static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jboolean finalized) {
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
if (nativeInputChannel) {
if (finalized) {
ALOGW("Input channel object '%s' was finalized without being disposed!",
nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel()->getName().c_str());
}
nativeInputChannel->invokeAndRemoveDisposeCallback(env, obj);
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);
delete nativeInputChannel;
}
}static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jboolean finalized) {
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);//根据java层的InputChannel获取native层的NativeInputChannel
if (nativeInputChannel) {
if (finalized) {
ALOGW("Input channel object '%s' was finalized without being disposed!",
nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel()->getName().c_str());
}
nativeInputChannel->invokeAndRemoveDisposeCallback(env, obj);
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);//设置Java曾保存的指向native层的NativeInputChannel的指针为空
delete nativeInputChannel;//delete
}
}void NativeInputChannel::invokeAndRemoveDisposeCallback(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
if (mDisposeCallback) {
mDisposeCallback(env, obj, mInputChannel, mDisposeData);//会执行handleInputChannelDisposed回调函数
mDisposeCallback = NULL;
mDisposeData = NULL;
}
}handleInputChannelDisposed主要作用是取消注册inputchannel。
static void handleInputChannelDisposed(JNIEnv* env,
jobject /* inputChannelObj */, const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel, void* data) {
NativeInputManager* im = static_cast<NativeInputManager*>(data);
ALOGW("Input channel object '%s' was disposed without first being unregistered with "
"the input manager!", inputChannel->getName().c_str());
im->unregisterInputChannel(env, inputChannel);
}查看unregisterInputChannel
status_t NativeInputManager::unregisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* /* env */,
const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
ATRACE_CALL();
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->unregisterInputChannel(inputChannel);
}查看InputDispatcher的unregisterInputChannel函数。
status_t InputDispatcher::unregisterInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
status_t status = unregisterInputChannelLocked(inputChannel, false /*notify*/);
if (status) {
return status;
}
} // release lock
// Wake the poll loop because removing the connection may have changed the current
// synchronization state.
mLooper->wake();
return OK;
}主要作用为:
1.从容器中删除此Connection对象
2.从epoll_wait中取消此socket的监听
3.清空此connection的等待发送队列outboundQueue和发送成功等待回应的消息队列
status_t InputDispatcher::unregisterInputChannelLocked(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
bool notify) {
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputChannel);//从保存所有inputChannel的容器中找到当前connection的索引
if (connectionIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Attempted to unregister already unregistered input channel '%s'",
inputChannel->getName().c_str());
return BAD_VALUE;
}
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
mConnectionsByFd.removeItemsAt(connectionIndex);//从容器中删除此Connection对象,Connection中保存了inputChannel和其对应的窗口句柄
if (connection->monitor) {
removeMonitorChannelLocked(inputChannel);
}
mLooper->removeFd(inputChannel->getFd());//mLooper本质是epoll_wait,从epoll_wait中取消此socket的监听,即不再监听来自应用程序端的消息
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, notify);//清空此connection的等待发送队列outboundQueue和发送成功等待回应的消息队列
connection->status = Connection::STATUS_ZOMBIE;
return OK;
}void InputDispatcher::abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, bool notify) {
// Clear the dispatch queues.
drainDispatchQueueLocked(&connection->outboundQueue);
traceOutboundQueueLengthLocked(connection);
drainDispatchQueueLocked(&connection->waitQueue);
traceWaitQueueLengthLocked(connection);
if (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
connection->status = Connection::STATUS_BROKEN;
/*此时是false
if (notify) {
// Notify other system components.
onDispatchCycleBrokenLocked(currentTime, connection);
}*/
}
}2.24 WindowInputEventReceiver
此时我们已经知道了WMS将其中一个sokcet注册给了IMS。我们接下来看看第二个socket,应用端是如何处理的?
在上文的ViewRootImpl的setView最后,应用端会new一个WindowInputEventReceiver,然后会调用InputEventReceiver构造函数。
//ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,Looper.myLooper());//mInputChannel是客户端的socket[1],Looper.myLooper主线程的looper
}
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper);//调用InputEventReceiver的构造方法
}
}
2.25 InputEventReceiver
主要作用:
1.保存java层的inputChannel对象
2.获取UI主线程,此处主要是需要将客户端的socket添加到Looper中监听,其实Looper的底层也是epoll_wait
3.调用nativeInit函数,此函数内部会new一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象,然后调用此对象的初始化函数,初始化函数的内部会将此应用端的socket添加到Looper中监听。当存在IMS发送事件到应用程序端时,会调用NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent函数。
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
mInputChannel = inputChannel;//socket[1]
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();//UI 线程消息队列
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),inputChannel, mMessageQueue);
}2.26 nativeInit
主要作用为:
1.new了一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象。
2.调用NativeInputEventReceiver的initialize函数。初始化函数的内部会将此应用端的socket添加到Looper中监听。当存在IMS发送事件到应用程序端时,会调用NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent函数。
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,inputChannelObj);//获取c++层的inputChannel
if (inputChannel == NULL) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "InputChannel is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);//获取消息队列
if (messageQueue == NULL) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,//new了一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
status_t status = receiver->initialize();//初始化NativeInputEventReceiver对象
/*
if (status) {//如果初始化失败
String8 message;
message.appendFormat("Failed to initialize input event receiver. status=%d", status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.string());
return 0;
}*/
receiver->incStrong(gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz); // retain a reference for the object
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get());
}2.27 NativeInputEventReceiver
里面创建了一个InputConsumer类对象,用来保存c++层的inputChannel
NativeInputEventReceiver::NativeInputEventReceiver(JNIEnv* env,
jobject receiverWeak, const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<MessageQueue>& messageQueue) :
mReceiverWeakGlobal(env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak)),
mInputConsumer(inputChannel), mMessageQueue(messageQueue),//创建了一个InputConsumer类对象,用来保存c++层的inputChannel
mBatchedInputEventPending(false), mFdEvents(0)
{
/*
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {//默认false
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Initializing input event receiver.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}*/
}InputConsumer::InputConsumer(const sp<InputChannel>& channel) :
mResampleTouch(isTouchResamplingEnabled()),//是否触摸重新采样
mChannel(channel), mMsgDeferred(false)
{
}2.28 initialize
主要作用:
1.调用setFdEvents函数。
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize()
{
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);//ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT值是1
return OK;
}2.29 setFdEvents
主要作用:
1.调用了Looper的addfd函数,用于监听此fd,并传入了NativeInputEventReceiver对象,当InputManagerService发送消息到应用程序时,会调用NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent函数。
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {//默认是0,此时为1
mFdEvents = events;//设置为ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT
int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();//获取socket[0]的fd
if (events) {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, NULL);//调用了Looper的addfd函数,用于监听此fd,并传入了NativeInputEventReceiver对象
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
}
}
}2.30 Looper::addFd
主要作用为:
1.调用epoll_ctl监听此应用的socket,即监听来自IMS的输入事件。
int Looper::addFd(int fd, int ident, int events,
const sp<LooperCallback>& callback, void* data) {
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
Request request;
request.fd = fd;
request.ident = ident;
request.events = events;
request.seq = mNextRequestSeq++;
request.callback = callback; // 是指 NativeInputEventReceiver
request.data = data;
if (mNextRequestSeq == -1) mNextRequestSeq = 0;
struct epoll_event eventItem;
request.initEventItem(&eventItem);
ssize_t requestIndex = mRequests.indexOfKey(fd);
if (requestIndex < 0) {
// 通过 epoll 监听 fd
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, & eventItem);
......
mRequests.add(fd, request); // 该fd 的 request 加入到 mRequests 队列
} else {
int epollResult = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd, & eventItem);
......
mRequests.replaceValueAt(requestIndex, request);
}
}
return 1;
}