目录
一、二叉树的定义
编辑
二、二叉树的创建
三、二叉树的遍历
1、前序遍历
2、中序遍历
3、后序遍历
4、层序遍历
四、二叉树遍历方法的使用
五、二叉树的操作
1、节点的个数
2、叶子节点的个数
3、第k层节点的个数
4、二叉树的高度
5、检查值为value的元素是否存在
一、二叉树的定义
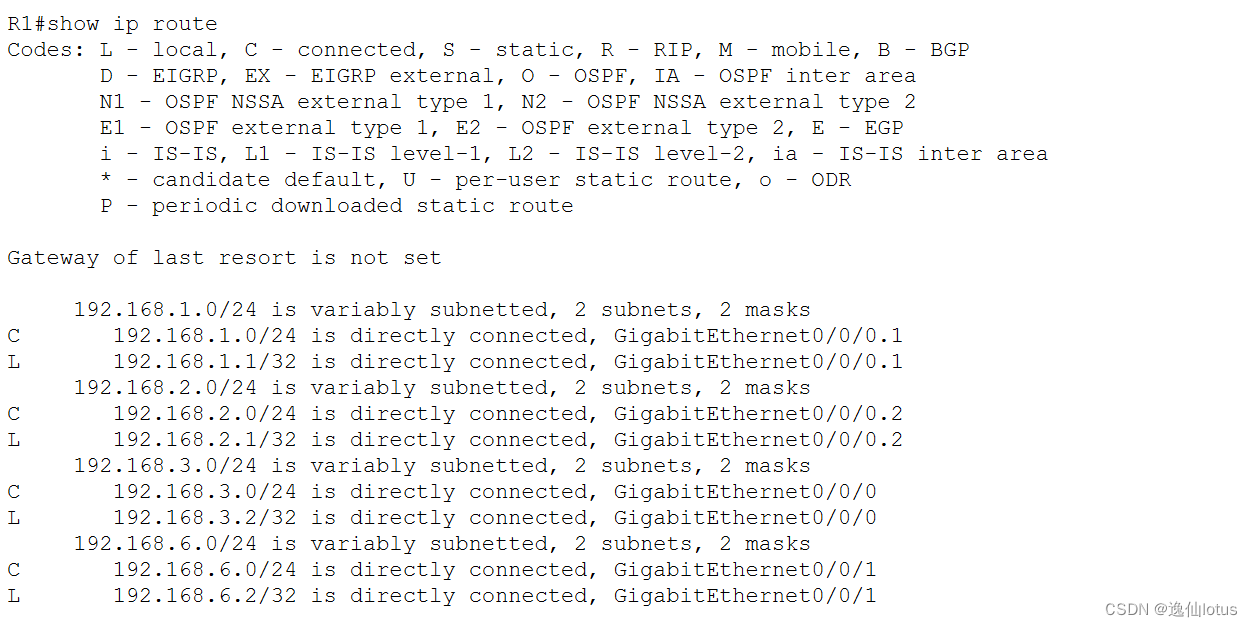
二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。二叉树特点是每个节点最多只能有两棵子树,且有左右之分。
二叉树是n个有限元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者由一个称为根(root)的元素及两个不相交的、被分别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成,是有序树。当集合为空时,称该二叉树为空二叉树。在二叉树中,一个元素也称作一个节点。
二、二叉树的创建
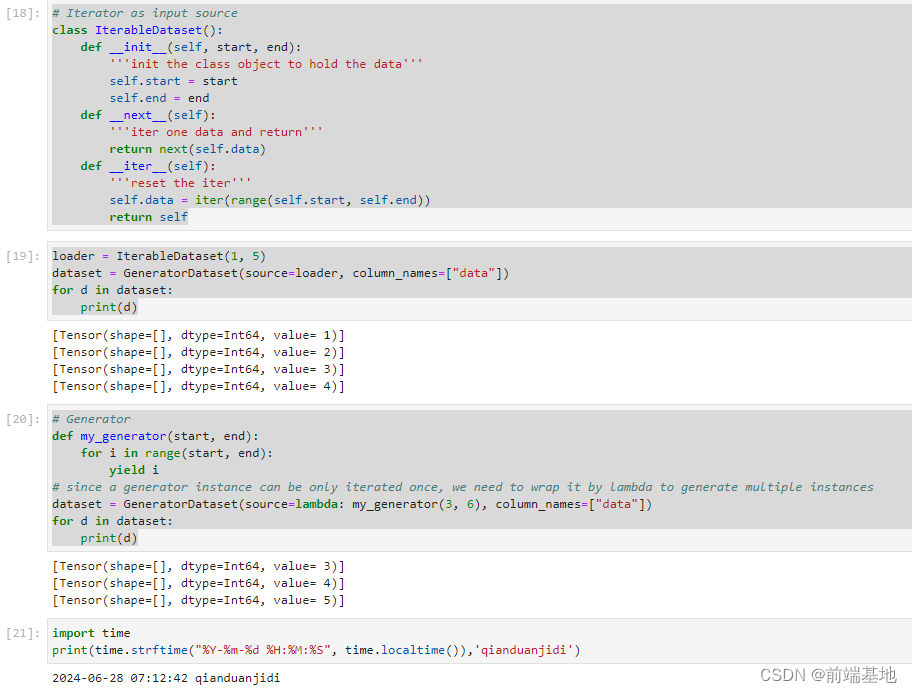
二叉树每个节点有自己的元素和左右孩子节点的地址,定义一个内部类来定义每个节点。
public class BinaryTree {
static class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
public TreeNode creatTree(){
TreeNode A=new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode B=new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode C=new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode D=new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode E=new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode F=new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode G=new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode H=new TreeNode('H');
A.left=B;
A.right=C;
B.left=D;
B.right=E;
C.left=F;
C.right=G;
E.right=H;
return A;
}
}三、二叉树的遍历
1、前序遍历
前序遍历:根-->根的左子树-->根的右子树
void preorder(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}2、中序遍历
中序遍历:根的左子树-->根-->根的右子树
void inorder(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return;
}
preorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val);
preorder(root.right);
}3、后序遍历
后序遍历:根的左子树-->根的右子树-->根
void postorder(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return;
}
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val);
}4、层序遍历
将节点的值放入队列中,然后出队列。
void levelorder(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode>queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur=queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
if (cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}四、二叉树遍历方法的使用
定义一个Main方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree=new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.TreeNode root=binaryTree.creatTree();
//前序遍历
binaryTree.preorder(root);
System.out.println();
//中序遍历
binaryTree.inorder(root);
System.out.println();
//后序遍历
binaryTree.postorder(root);
System.out.println();
//层序遍历
binaryTree.levelorder(root);
System.out.println();
}
}执行结果:
A B D E H C F G
D B E H A F C G
D H E B F G C A
A B C D E F G H
五、二叉树的操作
1、节点的个数
遍历求节点个数
public int usedSize;
int getSize(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
usedSize++;
getSize(root.left);
getSize(root.right);
return usedSize;
}子问题求节点个数
int getSize1(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
return getSize1(root.left)+getSize1(root.right)+1;
}2、叶子节点的个数
当节点的左右子节点为空时,则该节点就是叶子节点。
遍历求叶子节点
public int leafSize;
int getLeafNodeCount(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
leafSize++;
}
getLeafNodeCount(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
return leafSize;
}子问题求叶子节点
int getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
if (root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount1(root.left)+getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);
}3、第k层节点的个数
int getKUsedSize(TreeNode root,int k){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
if (k==1){
return 1;
}
return getKUsedSize(root.left,k-1)+getKUsedSize(root.right,k-1);
}4、二叉树的高度
int getHight(TreeNode root){
if (root==null){
return 0;
}
int getleftHight=getHight(root.left);
int getrightHight=getHight(root.right);
return getleftHight > getrightHight ? getleftHight+1 : getrightHight+1;
}5、检查值为value的元素是否存在
TreeNode findValue(TreeNode root,char value){
if (root==null){
return null;
}
if (root.val==value){
return root;
}
TreeNode ret1=findValue(root.left,value);
if (ret1!=null){
return ret1;
}
TreeNode ret2=findValue(root.right,value);
if (ret2!=null){
return ret2;
}
return null;
}







![Qt项目实战[MP3音乐播放器搜索引擎]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/83e89d5c664c4e889601f1ee0571cbb5.png)