1. 简介
接口响应慢会直接影响用户体验和降低业务效率。为了有效应对这一问题,合理使用多线程技术成为了一种高效的解决方案。通过将独立的任务分配给不同的线程进行并行处理,我们可以充分利用系统资源,避免单一任务阻塞整个系统,从而显著提高业务整体效率。先来看看如下的业务接口:
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
// 获取积分信息
Map<String, Object> score = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/scores/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
// 获取订单信息
Map<String, Object> order = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/orders/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
// 获取交易信息
Map<String, Object> trade = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
return Map.of("score", score, "order", order, "trade", trade) ;
}上面代码中调用的3个接口如下:
// 积分接口
@GetMapping("/scores/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> index(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
// 模拟耗时操作
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1) ;
return Map.of("data", String.format("获取用户【%d】积分成功", id)) ;
}
// 订单接口
@GetMapping("/orders/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> index(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
// 模拟耗时操作
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2) ;
return Map.of("data", String.format("获取用户【%d】订单成功", id)) ;
}
// 交易接口
@GetMapping("/trades/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> index(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
// 模拟耗时操作
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2) ;
return Map.of("data", String.format("获取用户【%d】交易成功", id)) ;
}请求接口结果如下
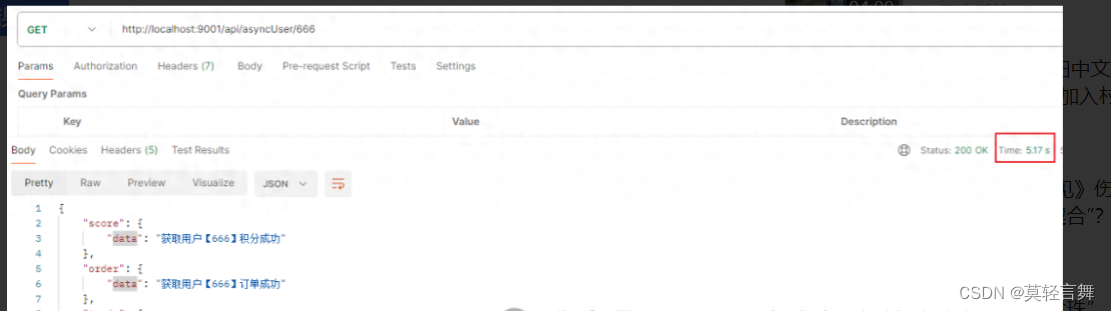
接口查询成功,但是总耗时达到了5秒,这对于大多数用户来说是无法接受的。在现代的互联网应用中,用户对响应速度的要求越来越高,一个快速的响应可以大大提升用户体验和满意度。当接口查询耗时过长时,用户可能会面临等待时间过长、页面无响应等问题,这不仅影响了用户的正常使用,还可能导致用户流失。接下来通过异步的方式优化上面的代码。
2. 接口优化
上面代码优化如下
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>() ;
// 获取积分信息
CompletableFuture<Void> scoreTask = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.printf("执行线程: %s%n", Thread.currentThread().getName()) ;
Map<String, Object> score = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/scores/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
result.put("score", score) ;
}) ;
// 获取订单信息
CompletableFuture<Void> orderTask = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.printf("执行线程: %s%n", Thread.currentThread().getName()) ;
Map<String, Object> order = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/orders/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
result.put("order", order) ;
}) ;
// 获取交易信息
CompletableFuture<Void> tradeTask = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.printf("执行线程: %s%n", Thread.currentThread().getName()) ;
Map<String, Object> trade = this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
result.put("trade", trade) ;
}) ;
scoreTask.join() ;
orderTask.join() ;
tradeTask.join() ;
return result ;
}查询结果

时间缩短到2s,控制台输出如下:

分别在不同线程中执行。
2.1 异步优化①
上面的代码还可以进行优化,有以下原因:
- 线程安全问题:多个线程修改共享变量result,result是在主线程中创建的,并且是在多个子线程中直接修改的,这可能会导致线程安全问题(虽然这里不会)。
- 返回值问题:CompletableFuture<Void>类型并不适合这里,因为我们实际上需要获取结果。应该使用CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>>来存储和返回每个请求的结果。
- 合并结果:我们应该在所有任务完成后合并结果,而不是直接修改主线程中的result对象。
根据上面的问题,代码优化如下:
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
// 使用CompletableFuture.supplyAsync来返回结果
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> scoreFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/scores/{id}", Map.class, id));
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> orderFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/orders/{id}", Map.class, id));
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> tradeFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id));
// 使用CompletableFuture.allOf等待所有任务完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(scoreFuture, orderFuture, tradeFuture).join();
// 合并结果
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("score", scoreFuture.get());
result.put("order", orderFuture.get());
result.put("trade", tradeFuture.get());
return result;
}这里代码其实还有问题,继续往下看。
2.2 异步优化②
上面代码中,如果有任何一个接口发生异常,那么将会导致该业务接口返回异常。如下示例
CompletableFuture<Map<String, Object>> tradeFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(1 / 0) ;
return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id) ;
});上面代码人为制造异常,最终接口调用如下结果:
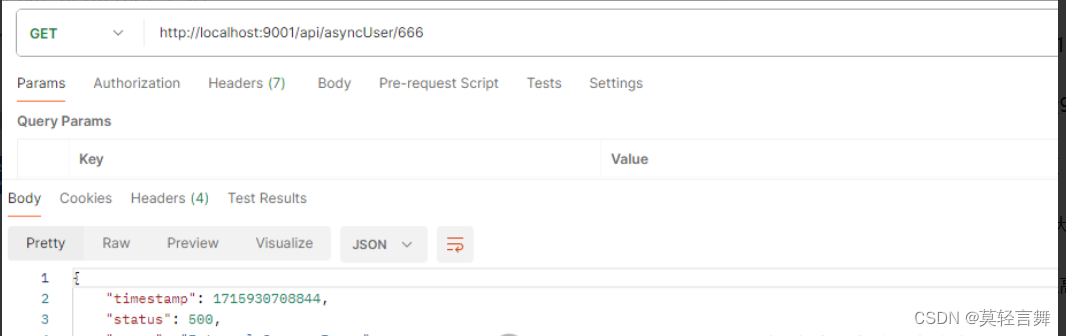
为了优化这段代码,使其能够优雅地处理异常,并且当任何接口发生异常时不会影响到其他接口的调用结果,将代码做如下调整:
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Map<String, Object> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Map> scoreFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/scores/{id}", Map.class, id))
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
CompletableFuture<Map> orderFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/orders/{id}", Map.class, id))
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
CompletableFuture<Map> tradeFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(1 / 0) ;
return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id);
})
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
// 使用CompletableFuture.allOf等待所有任务完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(scoreFuture, orderFuture, tradeFuture).join() ;
return Map.of("score", scoreFuture.get(), "order", orderFuture.get(), "trade", tradeFuture.get()) ;
}请求结果如下

不会因某一个接口出现问题而影响到整个业务接口。
2.3 异步优化③
在上面的代码中通过join操作来获取最终执行的结果,它会阻塞当前主线程(Tomcat线程)直到所有任务完成。如果有很多这样的请求同时到达,它会直接影响tomcat整体的吞吐量,我们可以通过接口异步处理的方式来进异步的优化,代码调整如下:
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Callable<Map> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
System.out.printf("请求开始: %d%n", System.currentTimeMillis()) ;
CompletableFuture<Map> scoreFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/scores/{id}", Map.class, id))
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
CompletableFuture<Map> orderFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/orders/{id}", Map.class, id))
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
CompletableFuture<Map> tradeFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:9001/api/trades/{id}", Map.class, id))
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
Callable<Map> cb = () -> {
CompletableFuture.allOf(scoreFuture, orderFuture, tradeFuture).join() ;
return Map.of("score", scoreFuture.get(), "order", orderFuture.get(), "trade", tradeFuture.get()) ;
} ;
System.out.printf("请求结束: %d%n", System.currentTimeMillis()) ;
return cb ;
}测试结果,控制台输出

通过输出结果看出,tomcat线程仅仅执行了3ms就返回。这样一来,tomcat整体的吞吐量将会明显的提高。
3. 注意事项
在上面的代码中CompletableFuture#supplyAsync方法调用默认情况下使用的是ForkJoinPool.commonPool()。在实际的生产环境我们应该指定自己的线程池。自定义线程池更好地控制并发级别、线程数、队列深度等参数,以确保系统资源的有效利用和避免资源耗尽。使用方法如下:
private static final ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(18, 18, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1000)) ;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Callable<Map> allInfo(@PathVariable("id") Long id) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Map> scoreFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://xxx", Map.class, id), pool)
.exceptionally(ex -> Map.of("data", String.format("接口发生异常: %s", ex.getMessage()))) ;
// ...
}
![[渗透测试] 任意文件读取漏洞](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/440dc721b9004c80b6b3d3fade0ce0ad.png#pic_center)