快速了解@Async注解的用法,包括异步方法无返回值、有返回值,最后总结@Async注解失效的几个坑。
在我们的 SpringBoot 应用中,经常会遇到在一个接口中,同时做事情1,事情2,事情3,如果同步执行的话,则本次接口时间取决于事情1 2 3执行时间之和;
如果三件事同时执行的话,那么本次接口的运行时间取决于事情1 2 3执行时间最长的那个。合理的使用多线程,可以大大缩短接口的运行时间。
下面几个例子简单的介绍了一下多线程如何调用异步方法的例子。
快速使用
1.创建线程池启用异步调用。
@EnableAsync注解,开启异步调用,异步的方法交给特定的线程池去完成。如下:
package com.lch.multithreadingdemo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
/**
* <p>
* 线程池配置
* </p>
*
* @author Lch
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfiguration {
@Bean("myDoSomethingExecutor")
public Executor doSomethingExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 最大线程数:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);
// 缓冲队列:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
executor.setQueueCapacity(500);
// 允许线程的空闲时间60秒:当超过了核心线程之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便我们定位处理任务所在的线程池
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("do-something-");
// 缓冲队列满了之后的拒绝策略:由调用线程处理(一般是主线程)
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
2.使用方法 异步方法无返回值
使用的方式就非常简单了,在需要异步执行的方法上加上@Async注解就可以了。如下:
2.1 Controller:
import com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
/**
* <p>
*
* </p>
*
* @author Lch
*/
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@GetMapping("/open/mySomething")
public String something() {
int count = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
asyncService.doSomething("index = " + i);
}
return "success";
}
}2.2 Service:
package com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.impl;
import com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
/**
* <p>
*
* </p>
*
* @author Lch
*/
@Service
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
@Async("myDoSomethingExecutor")
public void doSomething(String message) {
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 定义日期时间格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
// 格式化当前时间
String formattedNow = now.format(formatter);
// 获取当前线程名
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("时间: "+formattedNow +" 线程: " + threadName + " 执行了方法: " +message);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("do something error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
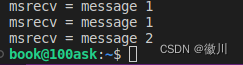
}2.3 执行结果:
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/open/mySomething 结果如下: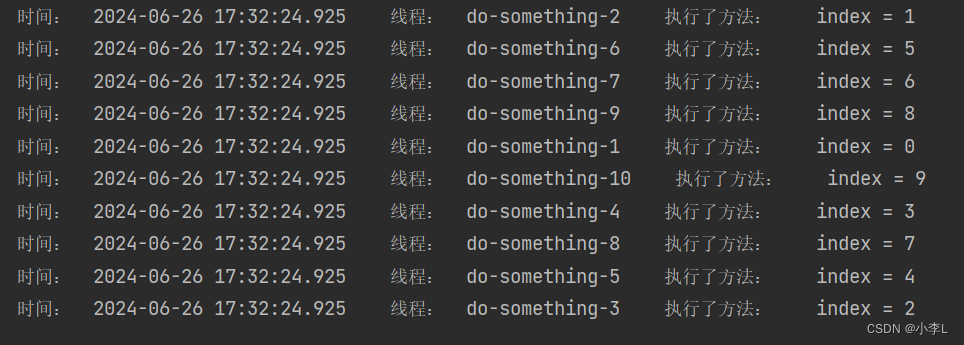
已经达到了异步执行的效果,并且使用到了咱们配置的线程池。
3.使用方法 异步方法有返回值
3.1 Controller:
package com.lch.multithreadingdemo.controller;
import com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
/**
* <p>
*
* </p>
*
* @author Lch
*/
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
/**
* 有返回值
*/
@GetMapping("/open/mySomethings")
public String somethings() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
CompletableFuture<String> doSomething1 = asyncService.doSomething1("第一个方法");
CompletableFuture<String> doSomething2 = asyncService.doSomething2("第二个方法");
CompletableFuture<String> doSomething3 = asyncService.doSomething3("第三个方法");
// 等待所有任务都执行完
CompletableFuture.allOf(doSomething1, doSomething2, doSomething3).join();
// 获取每个任务的返回结果
String result = doSomething1.get() + doSomething2.get() + doSomething3.get();
return result;
}
}
3.2 Service:
package com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.impl;
import com.lch.multithreadingdemo.service.AsyncService;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
/**
* <p>
*
* </p>
*
* @author Lch
*/
@Service
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
@Async("myDoSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 定义日期时间格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
// 格式化当前时间
String formattedNow = now.format(formatter);
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("时间: "+formattedNow +" 线程: " + threadName + " 执行了方法doSomething1: " +message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("方法doSomething1: "+ message);
}
@Override
@Async("myDoSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 定义日期时间格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
// 格式化当前时间
String formattedNow = now.format(formatter);
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("时间: "+formattedNow +" 线程: " + threadName + " 执行了方法doSomething2: " +message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("方法doSomething2: "+ message);
}
@Override
@Async("myDoSomethingExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> doSomething3(String message) throws InterruptedException {
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 定义日期时间格式
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
// 格式化当前时间
String formattedNow = now.format(formatter);
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("时间: "+formattedNow +" 线程: " + threadName + " 执行了方法doSomething1: " +message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("方法doSomething3: "+ message);
}
}
3.3 执行结果:
访问:http://127.0.0.1:8080/open/mySomethings 结果如下:
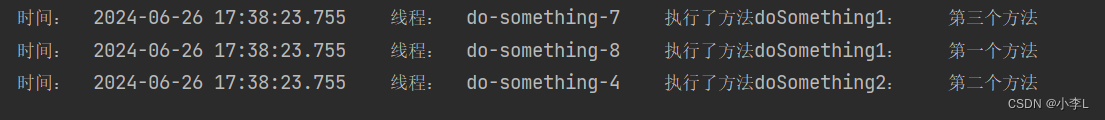
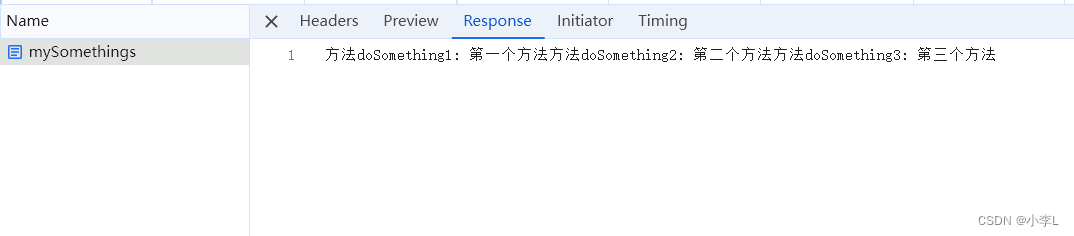
也达到了方法异步执行的效果,并且也拿到了返回值。
注意事项
@Async注解会在以下几个场景失效,也就是说明明使用了注解,但就没有走多线程。1. 异步方法使用static关键词修饰;
2. 异步类不是一个Spring容器的bean(一般使用注解
@Component和@Service,并且能被Spring扫描到);3. SpringBoot应用中没有添加
@EnableAsync注解;4. 在同一个类中,一个方法调用另外一个有@Async注解的方法,注解不会生效。原因是@Async注解的方法,是在代理类中执行的。
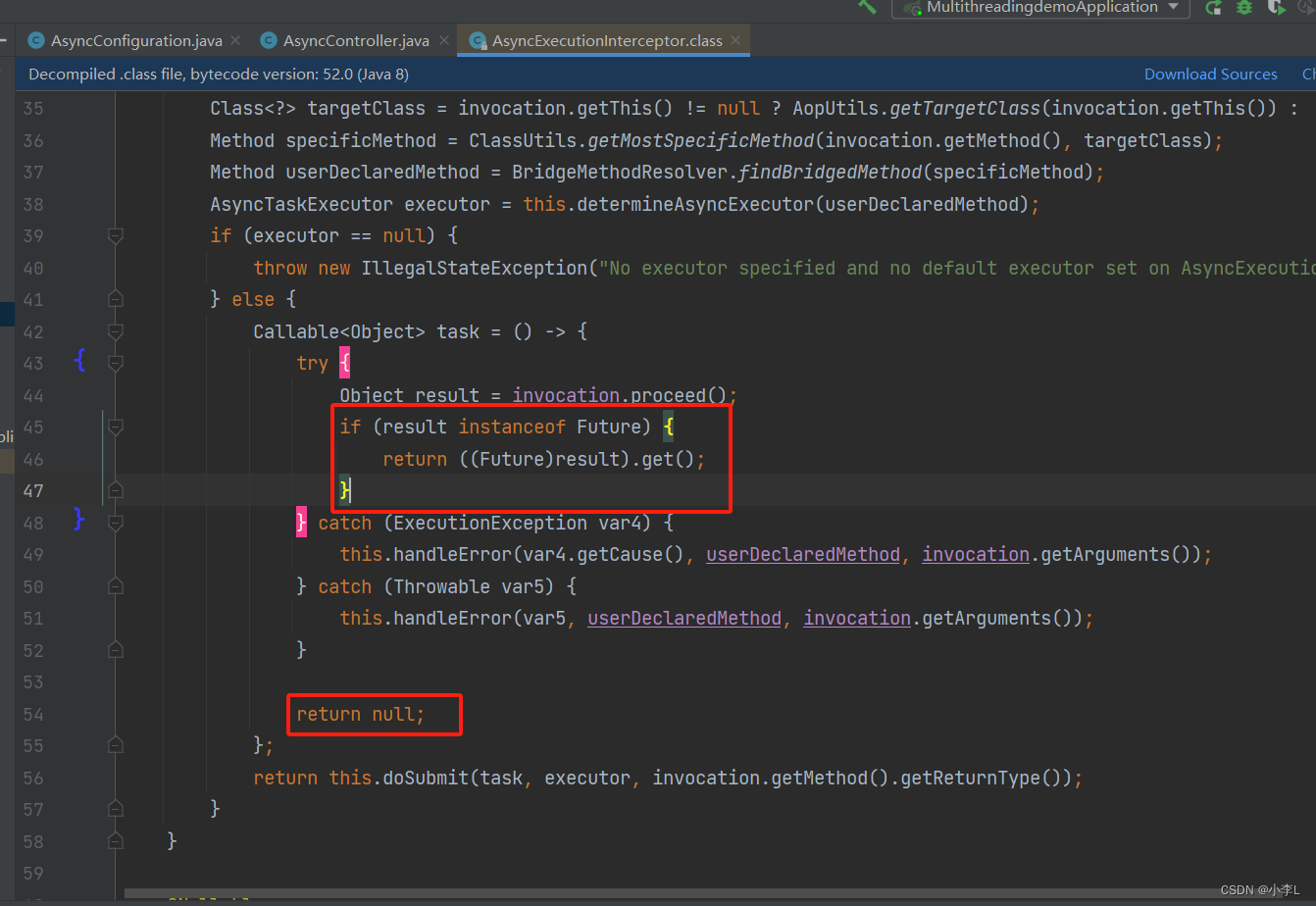
异步方法使用注解@Async的返回值只能为void或者Future及其子类,当返回结果为其他类型时,方法还是会异步执行,但是返回值都是null。