第十四天,(ง •_•)ง💪💪,编程语言:C++
目录
226.翻转二叉树
101.对称二叉树
100.相同的树
572.另一个树的子树
104.二叉树的最大深度
559.n叉树的最大深度
111.二叉树的最小深度
总结
226.翻转二叉树
文档讲解:代码随想录翻转二叉树
视频讲解:手撕翻转二叉树
题目:
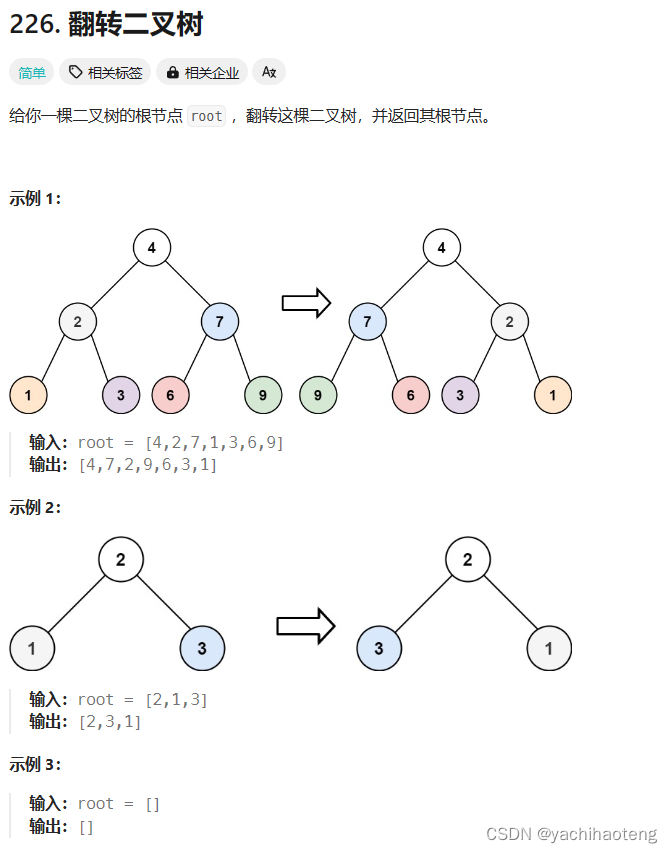
初看:本题翻转二叉树不仅仅是把根节点的左右子树进行了翻转,也把子节点下面的左右子树都进行了翻转。需要对所有中间节点(非叶子节点)进行处理。

代码:前序遍历(递归法)
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
void reverseNode(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr || (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)) return;
TreeNode* tmp = root->left; //中
root->left = root->right;
root->right = tmp;
//swap(root->left, root->right);
reverseNode(root->left); //左
reverseNode(root->right);//右
}
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
reverseNode(root);
return root;
}
};代码: 层次遍历(广度优先遍历)
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};注意:此题能够使用前序遍历和后序遍历,逻辑基本一致,但如果采用中序遍历的方式,要注意把中节点处理后,右子树就变成了左子树,左子树就变成了右子树,因此下次处理的时候仍应处理的是左子树(原右子树)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return root;
invertTree(root->left); // 左
swap(root->left, root->right); // 中
invertTree(root->left); // 注意 这里依然要遍历左孩子,因为中间节点已经翻转了
return root;
}
};101.对称二叉树
文档讲解:代码随想录对称二叉树
视频讲解:手撕对称二叉树
题目:

初看:对称二叉树从根节点开始,往下比较左右节点,之后往下需要分为两条道路,一条左右子树的外层节点,一条比较左右子树的内层节点。因此实际上是比较左右两棵树是否相等。
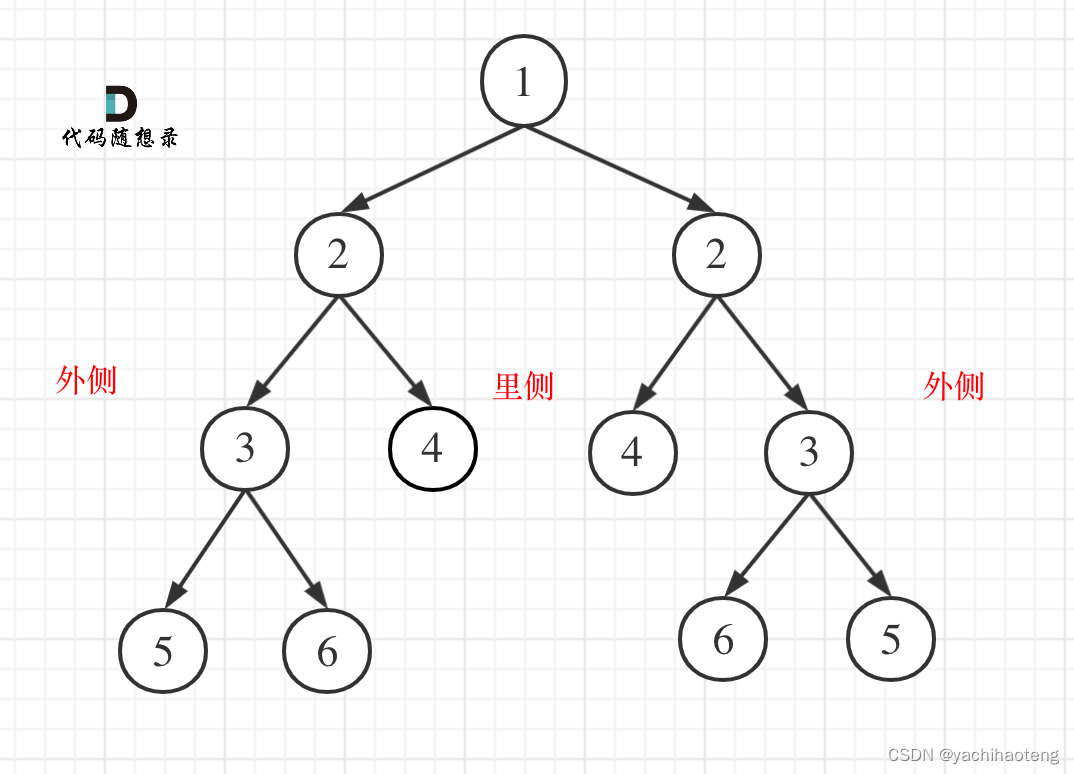
代码:后序遍历(递归法)
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if(left == NULL && right == NULL) return true; //都为空返回true
else if(left == NULL || right == NULL) return false; //有一个为空另一个不为空(都为空前面判断了)返回false
else if(left->val != right->val) return false; //都不为空但是值不相等
else { //都不为空且值相等,向下继续遍历
bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); //外侧比较
bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); //内测比较
return outside && inside; //都为true才返回true;
}
}
//递归法
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return true;
return compare(root->left, root->right);
}
};学习:
- 本题需要遍历两棵树而且要比较内侧和外侧的节点,所以准确的来说是一个树的遍历顺序是左右中,一个树的遍历顺序是右左中。这都可以理解为一种后序遍历,把孩子的信息反馈到父节点身上。
- 本题的递归三部曲:①确定递归函数的参数和返回值:本题需要比较左右子树,因此参数肯定为左子树和右子树的节点,其次本题是判断正确,因此返回bool类型。②确定终止条件:用清楚节点存在的情况:左节点为空,右节点不为空;左不为空,右为空;左右都为空;左右都不为空,比较节点数值。③确定单层递归逻辑:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同时才进入单层递归的逻辑。单层递归的逻辑就是比较:比较二叉树外侧是否对称,传入的是左节点的左孩子,右节点的右孩子;比较内侧是否对称,传入左节点的右孩子,右节点的左孩子;如果左右都对称就返回true ,有一侧不对称就返回false。
代码:迭代法,注意加入节点的顺序即可
class Solution {
public:
//迭代法
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if(root == nullptr) return true;
que.push(root->left);
que.push(root->right);
while(!que.empty()) {
TreeNode* left = que.front();
que.pop();
TreeNode* right = que.front();
que.pop();
if(left == NULL && right == NULL) continue; //都为空进行后序节点比较
else if(left == NULL || right == NULL) return false; //有一个为空另一个不为空(都为空前面判断了)返回false
else if(left->val != right->val) return false; //都不为空但是值不相等
else {
//按顺序加入节点
que.push(left->left); // 加入左节点左孩子
que.push(right->right); // 加入右节点右孩子
que.push(left->right); // 加入左节点右孩子
que.push(right->left); // 加入右节点左孩子
}
}
return true;
}
};注意:迭代法中使用了队列,但实际上并不是层序遍历,而是仅仅通过一个容器来成对的存放我们要比较的元素,知道这一本质之后就发现,用队列,用栈,甚至用数组,都是可以的。
其他题目:
100.相同的树
题目:
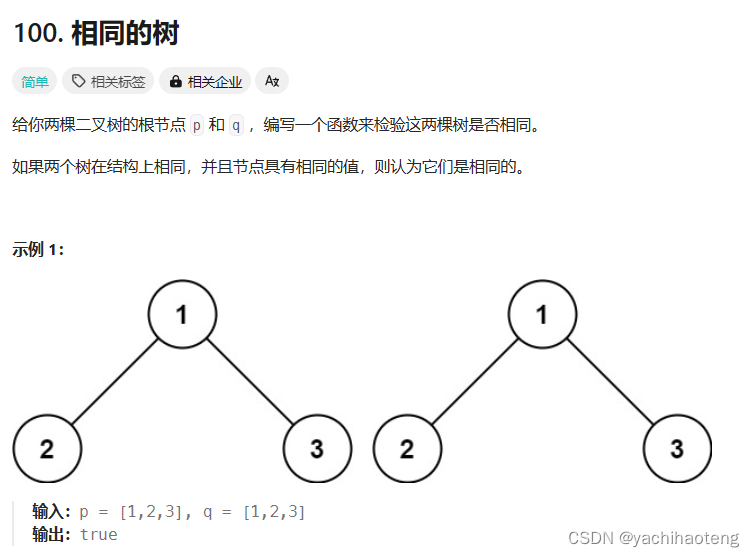
初看:和左右子树对称一样,只不过没有了 根节点,比较的节点也变为了一一对应的关系。
代码:
//时间复杂度O(min(m,n))
//空间复杂度O(min(m,n))
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (!p && !q) return true;
//载入两个节点依次进行判断
que.push(p);
que.push(q);
while(!que.empty()) {
//取出需要比较的节点
TreeNode* node1 = que.front(); que.pop();
TreeNode* node2 = que.front(); que.pop();
if (node1 == nullptr && node2 == nullptr) continue; //都为空进行下一轮判断
else if (node1 == nullptr || node2 == nullptr) return false; //有一个不为空,返回错误
else if (node1->val != node2->val) return false; //都不为空但是值不等
else {
//注意载入节点的顺序
que.push(node1->left);
que.push(node2->left);
que.push(node1->right);
que.push(node2->right);
}
}
return true;
}
};572.另一个树的子树
题目:

初看: 本题事实上与找到相同的树是一样的,只不过它还需要遍历每一个节点。
代码:
//时间复杂度O(n*m)
class Solution {
public:
//暴力匹配==寻找相同的树
bool compare(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
//载入两个节点依次进行判断
que.push(root);
que.push(subRoot);
while(!que.empty()) {
//取出需要比较的节点
TreeNode* node1 = que.front(); que.pop();
TreeNode* node2 = que.front(); que.pop();
if (node1 == nullptr && node2 == nullptr) continue; //都为空进行下一轮判断
else if (node1 == nullptr || node2 == nullptr) return false; //有一个不为空,返回错误
else if (node1->val != node2->val) return false; //都不为空但是值不等
else {
//注意载入节点的顺序
que.push(node1->left);
que.push(node2->left);
que.push(node1->right);
que.push(node2->right);
}
}
return true;
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
//广度优先遍历+暴力匹配
//广度优先遍历
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != nullptr) que.push(root);
if (subRoot == nullptr) return true;
bool result;
while (!que.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = que.front(); que.pop();
if (node->val == subRoot->val) {
result = compare(node, subRoot);
cout << result << endl;
if(result == true) return true;
}
if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
return false;
}
};注意:本题还可以采用KMP算法,和哈希筛选等方法,但过于复杂不利于理解,故没有给出。可前往力扣查看对应例题详解。
104.二叉树的最大深度
文本讲解: 代码随想录二叉树的最大深度
视频讲解:手撕二叉树的最大深度
题目:
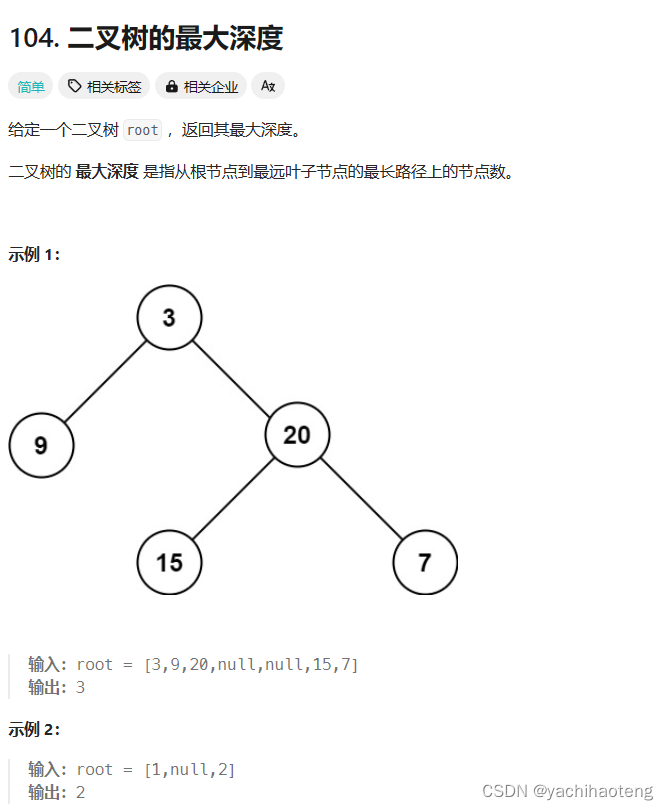
学习:昨天使用了层次遍历的方式求解本题,实际上本题也可以使用深度优先遍历的方式来进行求解。本题是要查找树的最大深度,实际上这与树的高度是一一对应的,根节点的高度就是树的最大深度,因此可以采取前序遍历和后序遍历的方式,来查找根节点的高度。
代码:后序遍历(递归法)
注:相当于每次递归后depth深度+1,之后返回左子树和右子树之中最大的那个深度。
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int getdepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getdepth(root);
}
};代码:前序遍历(递归法)
注:前序遍历相比之下复杂一些,这是因为它需要先处理节点,再进行递归,因此需要一个辅助量result,每次递归前进行赋值判断。实际含义就是先找寻左子树中最大深度,保存最大深度,然后看右子树有没有更大的深度,再进行赋值。
class Solution {
public:
int result;
void getdepth(TreeNode* node, int depth) {
result = depth > result ? depth : result; // 中
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return ;
if (node->left) { // 左
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->left, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
if (node->right) { // 右
depth++; // 深度+1
getdepth(node->right, depth);
depth--; // 回溯,深度-1
}
return ;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
result = 0;
if (root == NULL) return result;
getdepth(root, 1);
return result;
}
};其他题目:
559.n叉树的最大深度
题目:

学习:本题和求二叉树的最大深度逻辑基本相同,只不过是把左右孩子换成了一个数组,增加一个for循环遍历孩子即可。
代码:层次遍历
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
//最大深度就是需要遍历的层数
queue<Node*> que;
int depth = 0; //记入深度
if (root != nullptr) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
//每进行循环深度加1
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
for (auto it = node->children.begin(); it != node->children.end(); it++) {
que.push(*it);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};代码:后序遍历(递归法)
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (root == 0) return 0;
int depth = 0;
//求孩子的最大深度
for (int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++) {
depth = max (depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
//加上根节点
return depth + 1;
}
};111.二叉树的最小深度
文档讲解:代码随想录二叉树的最小深度
视频讲解:手撕二叉树的最小深度
题目:
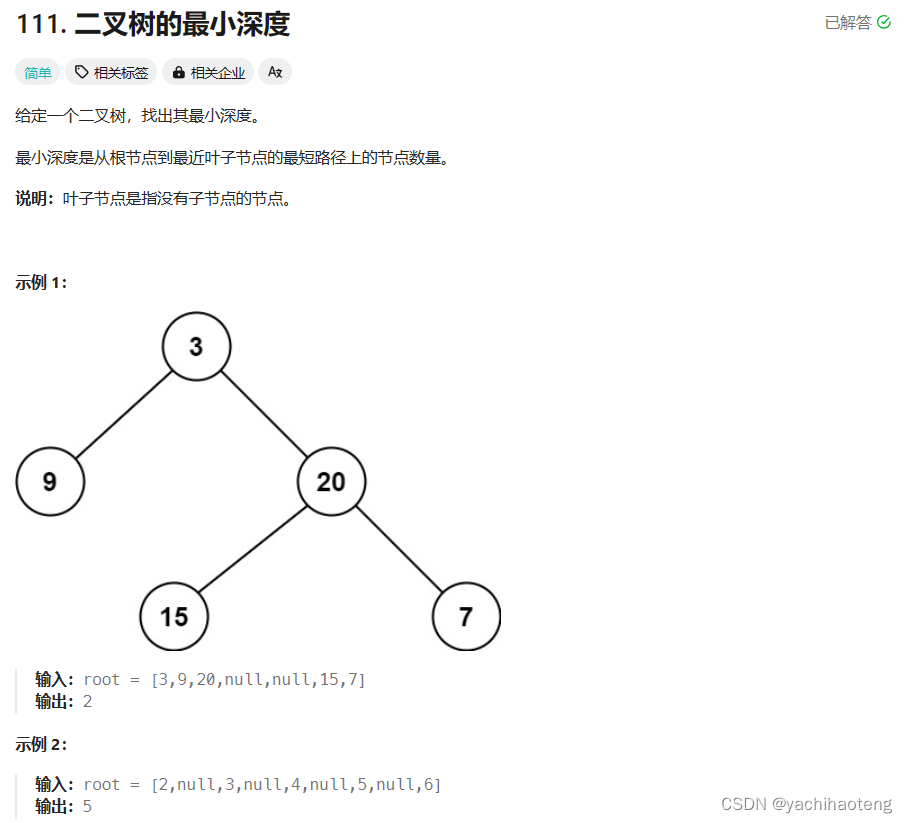
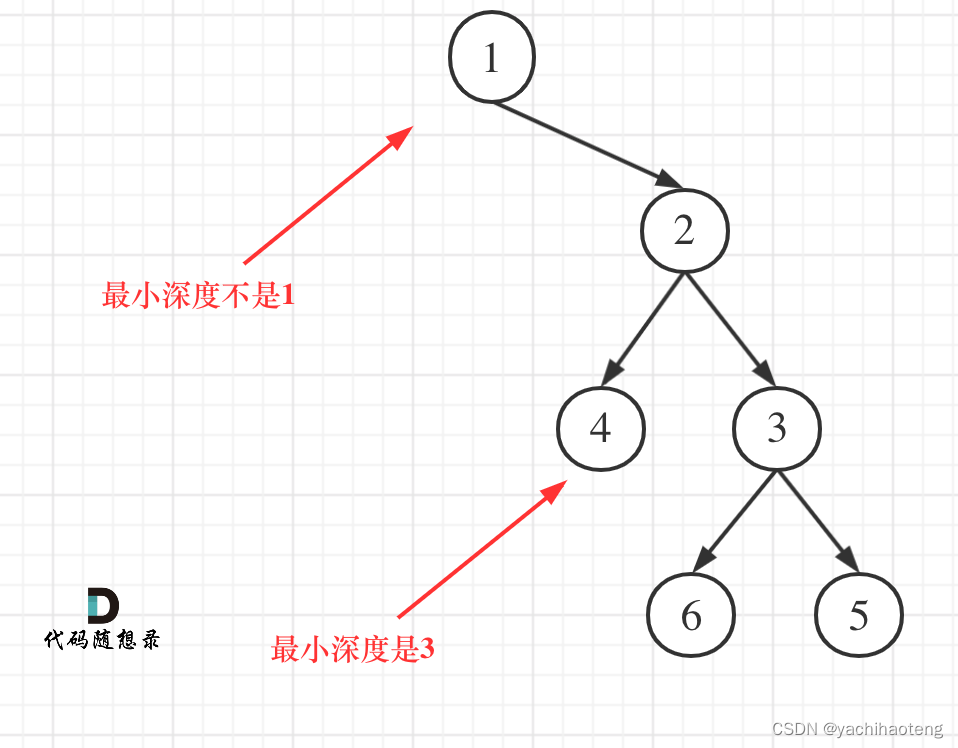
学习: 昨天同样也是用了层次遍历的方法求解本题,本题也能够使用迭代法进行处理,但需要注意的是,只有遍历到叶子节点(左右节点都没有时)才算是遍历到了合法的深度位置。
代码:后序遍历(递归)
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
//只有遍历到一个树的叶子节点(没有孩子)才算是终止
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点,它可能还有孩子
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点,它可能还有孩子
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
//两边都有孩子才取最小的深度
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root);
}
};代码:层次遍历
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
//最小深度,就是在遍历每一层节点的时候,如果发现该节点没有子节点则停下循环。
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int depth = 0; //记入深度
if (root != nullptr) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
//每进行循环深度加1
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
if (node->right == nullptr && node->left == nullptr) {
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
};总结
二叉树遍历有两种方式:广度优先遍历,深度优先遍历。深度优先遍历又分为三种:前序遍历、后序遍历、中序遍历。广度优先遍历就是层次遍历。
二叉树遍历的代码有三种:递归法求前中后序遍历,迭代法使用栈求前中后序遍历,迭代法使用队列求层次遍历。