一、runAsync
1、runAsync(Runnable)
2、runAsync(Runnable, Executor)
二、supplyAsync
1、supplyAsync(Supplier)
2、supplyAsync(Supplier , Executor)
三、CompletableFuture中 get 与 join的区别
四、thenApply方法
1、thenApply(Function)
五、handle方法
1、handle(BiFunction fn),>
2、handleAsync(BiFunction fn,Executor),>
3、thenCombine
4、thenCombineAsync
六、thenCompose方法
1、thenCompose
七、allOf / anyOf
普通情况下,我们的接口逻辑都是串行化的,有时候在我们方法中可能存在着非常耗时的操作这样就会造成代码阻塞,但是呢,为了用户的体验,我们可能需要将一些复杂的数据开启线程进行异步处理。
所谓异步,其实就是实现一个可无需等待被调用函数的返回值而让操作继续运行的方法,简单的讲就是另启一个线程来完成调用中的部分计算,使调用继续运行或返回,而不需要等待计算结果。
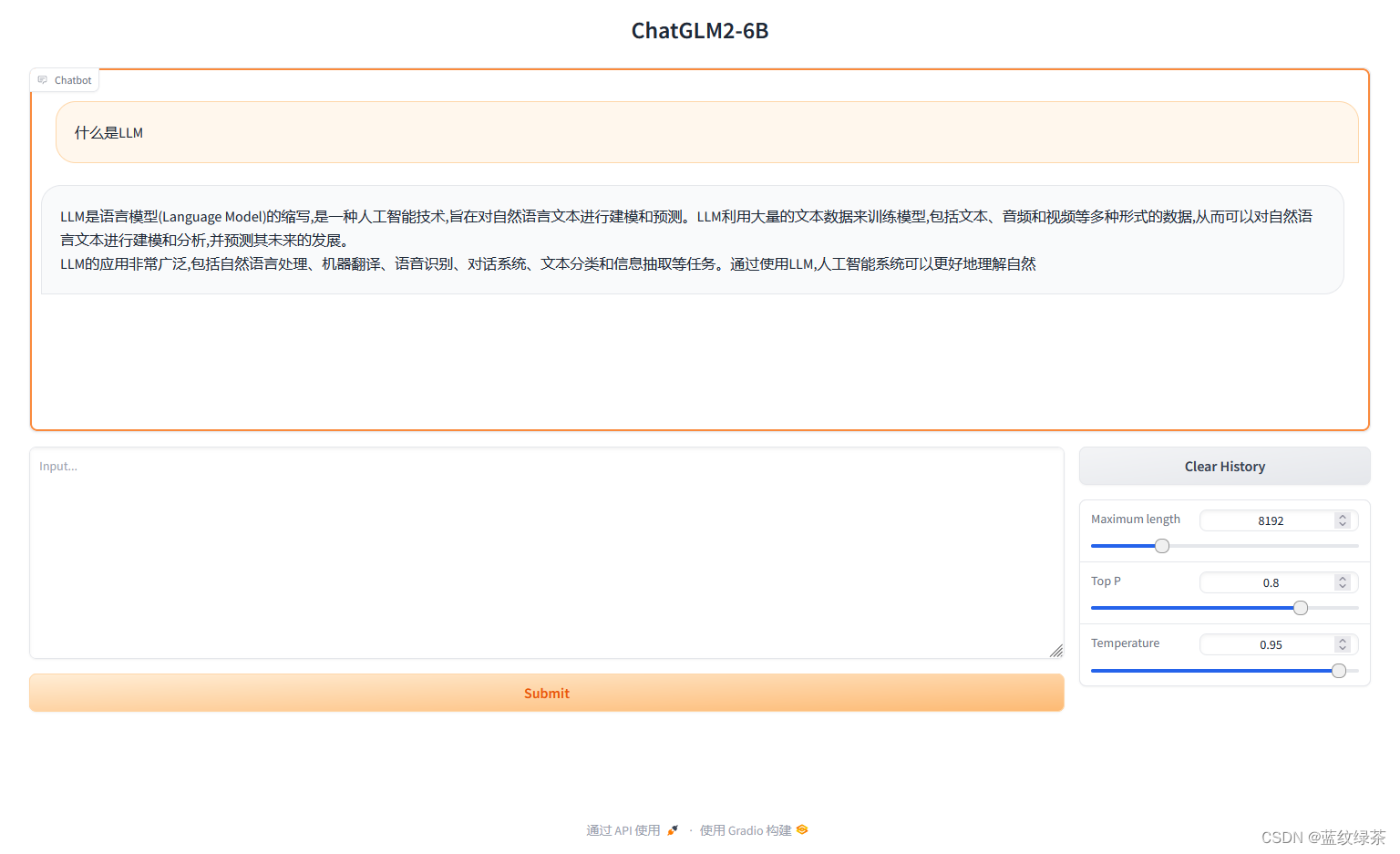
Java8 提供的CompletableFuture 可以自定义线程池或使用默认线程池对数据进行异步处理,且可以根据需求选择是否返回异步结果!灵活的使用CompletableFuture可以让我们感受java8的异步编程之美!
以下,便是CompletableFuture 的异步操作创建方式示例。
CompletableFuture的思想是,当被调用时,它们会立即被安排启动开始执行异步任务(与流式操作中的延迟计算有着明显区别)。
一、runAsync
1、runAsync(Runnable)
使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码,
public class AsyncDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当前调用者线程为:main
System.out.println("当前调用者线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 异步方法内当前执行线程为:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
System.out.println("异步方法内当前执行线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(111);
});
}
}
2、runAsync(Runnable, Executor)
使用指定的线程池执行异步代码。此异步方法无法返回值。
public class AsyncDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//当前调用者线程为:main
System.out.println("当前调用者线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// fixme 根据阿里规约 建议真实开发时使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 定义线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 异步方法内当前执行线程为:pool-1-thread-1
System.out.println("异步方法内当前执行线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(111);
}, threadPool);
// 演示代码,所以选择执行完后关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
二、supplyAsync
1、supplyAsync(Supplier)
使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码,异步操作有返回值
public class SupplyDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 异步方法内当前执行线程为:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
System.out.println("异步方法内当前执行线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 模拟返回值
return "hello,world";
});
// 获取异步线程执行结果
System.out.println(supplyAsync.join());
}
}
2、supplyAsync(Supplier , Executor)
使用指定线程池 来执行可获取返回值的异步任务
public class SupplyDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// fixme 根据阿里规约 建议真实开发时使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 定义线程池
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 异步方法内当前执行线程为:pool-1-thread-1
System.out.println("异步方法内当前执行线程为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 模拟耗时与返回结果
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello,world";
},threadPool);
// 获取异步线程执行结果
System.out.println(supplyAsync.join());
}
}
三、CompletableFuture中 get 与 join的区别
CompletableFuture 使用 supplyAsync 来执行异步任务的话,可通过调用 get 或 join方法便可获取异步线程的执行结果。
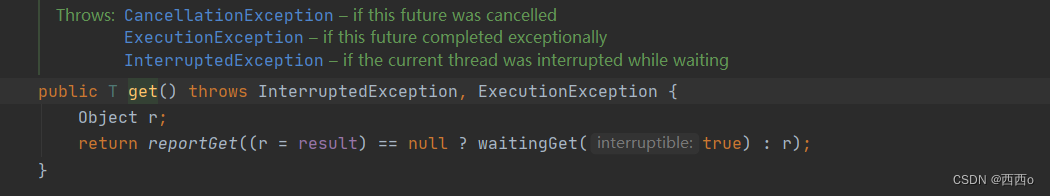
不同:get方法返回结果,抛出的是检查异常,必须用户throw或者try/catch处理,join返回结果,抛出未检查异常。
相同:join和get方法都是依赖于完成信号并返回结果T的阻塞方法。(阻塞调用者线程,等待异步线程返回结果)。
join:
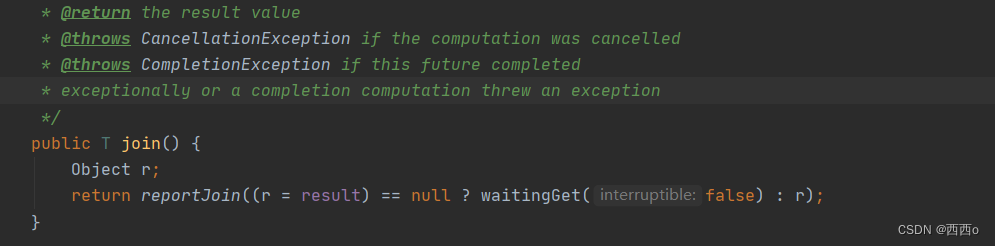
get:
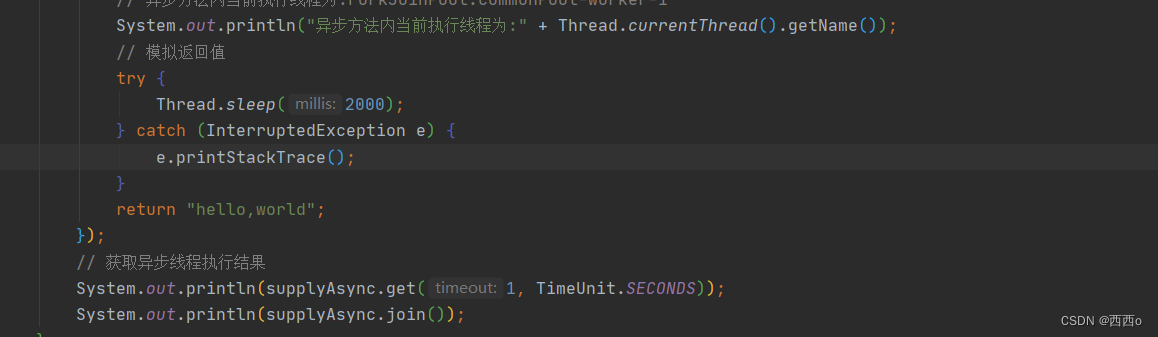
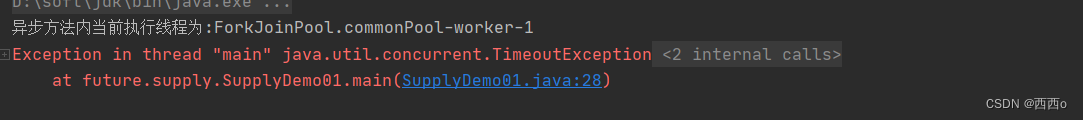
需要注意的是, completableFuture 的get 方法 有重载,还有一个可传入获取结果等待时间的get方法
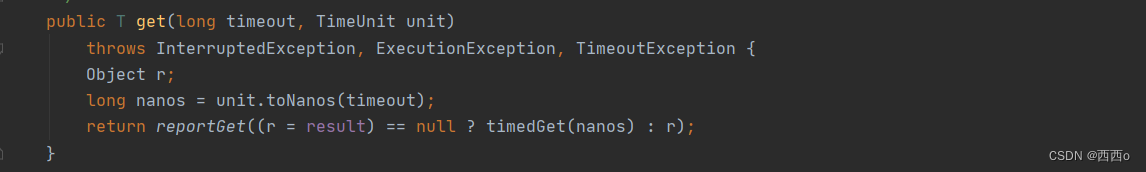
如果超过等待时间,异步线程还未返回结果,那么get 调用者线程则会抛出TimeoutException 异常
四、thenApply方法
当我们第二个任务依赖第一个任务的结果的时候,可以使用 thenApply相关方法来把这两个线程串行化,参数是一个Function(代表着我们需要传入一个转换的函数 具体可参考JAVA8 函数式接口)thenApply 只可以执行正常的任务,任务出现异常则不会执行 thenApply 方法;如果当第一个任务出现异常时仍要执行第二个任务,可以使用下方的Handle方法
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
T:上一个异步任务返回值
U: 当前执行最后返回值
1、thenApply(Function)
thenApply:thenApply中的线程为调用者线程,与CompletableFuture 底层默认所用的 ForkJoin无关!
示例:
public class SupplyDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "hello";
}).thenApply(e -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return e + ",";
}).thenApply(e -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return (e + "world").toUpperCase();
});
System.out.println(future.join());
}
}
程序执行情况:
最后JOIN 获取结果为 HELLO,WORLD
三个线程分别是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1,main,main(2)thenApplyAsync(Function)
thenApplyAsync:当我们第二个任务依赖第一个任务的结果的时候,且第二个任务也想采用异步的方式,则可以使用 thenApplyAsync(Function)
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "hello";
}).thenApplyAsync(e -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return e + ",";
}).thenApplyAsync(e -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
return (e + "world").toUpperCase();
});
System.out.println(future.join());
}
程序执行情况:
最后JOIN 获取结果为 HELLO,WORLD
三个线程均是 是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-xxxx
当然,我们也可以使用 thenApplyAsync(Function, Executor) 来使用自定义线程池执行我们的异步任务
五、handle方法
handle 是执行任务完成时对结果的处理, handle 方法和 thenApply 方法处理方式大致一样,不同的是 handle 是在任务完成后再执行且Handle可以根据可以根据任务是否有异常来进行做相应的后续处理操作。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn,Executor executor);
1、handle(BiFunction<T, Throwable, U> fn)
使用Handler方法 预估异常情况 进行逻辑处理 默认handle中使用的线程为调用者线程
public class HandleDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前supplyAsync 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 模拟异常
int a = 1 / 0;
return "hello";
}).handle((x, t) -> {
System.out.println("当前handle 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (t != null) {
// 出现异常 打印异常信息 或者doSomething
System.out.println("发现上一个异步任务出异常了" + t.getMessage());
} else {
// 未出异常 doSomething
return x;
}
// 设置默认结果
return "error";
});
System.out.println(future.join());
}
}
程序执行情况:
当前supplyAsync 执行线程:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
当前handle 执行线程:main
发现上一个异步任务出异常了java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
error
2、handleAsync(BiFunction<T, Throwable, U> fn,Executor)
使用自定义的线程 (或者使用默认的ForkJoin)进行异步处理第二个线程的任务
public class HandleDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前supplyAsync 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 模拟异常
int a = 1 / 0;
return "hello";
},threadPool).handleAsync((x, t) -> {
System.out.println("当前handle 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (t != null) {
// 出现异常 打印异常信息 或者doSomething
System.out.println("发现上一个异步任务出异常了" + t.getMessage());
} else {
// 未出异常 doSomething
return x;
}
// 设置默认结果
return "error";
},threadPool);
System.out.println(future.join());
}
}
程序执行情况:
当前supplyAsync 执行线程:pool-1-thread-1
当前handle 执行线程:pool-1-thread-2
发现上一个异步任务出异常了java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
error
七、thenCombine方法
thenCombine 会在两个CompletableFuture任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果一块处理。
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
3、thenCombine
thenCombine 会在两个CompletableFuture任务都执行完成后,调用者线程会把两个异步任务的结果一块处理
public class ThenCombineDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> helloAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("hello 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> worldAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("world 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture<String> result = worldAsync.thenCombine(helloAsync, (hello, world) -> {
System.out.println("result 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return (hello + "," + world).toUpperCase();
});
System.out.println("获取结果 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("两个异步任务合并结果:" + result.join());
}
}
程序执行结果:
hello 执行线程:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
world 执行线程:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
result 执行线程:main
获取结果 执行线程:main
两个异步任务合并结果:WORLD,HELLO
4、thenCombineAsync
thenCombineAsync 会在两个CompletableFuture任务都执行完成后,再用一个异步线程把两个任务的结果一块处理
六、thenCompose方法
thenCompose 方法允许你对两个CompletableFuture任务进行流水线操作,当第一个异步任务操作完成时,会将其结果作为参数传递给第二个任务。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor) ;
1、thenCompose
thenCompose当第一个异步任务操作完成时,会将其结果作为参数传递给第二个任务(第二个任务为串行化操作,由调用者线程执行)
public class ThenComposeDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<String> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("hello 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "hello";
}).thenCompose((hello -> {
System.out.println("thenCompose 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((hello + "world")::toUpperCase);
}));
System.out.println("获取结果 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("两个异步任务流水线执行结果:" + result.join());
}
}
程序执行情况:
hello 执行线程:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
thenCompose 执行线程:main
获取结果 执行线程:main
两个异步任务流水线执行结果: HELLOWORLD(2)thenComposeAsync
thenComposeAsync当第一个异步任务操作完成时,会将其结果作为参数传递给第二个任务(第二个任务仍为异步线程执行操作,可由默认ForkJoin线程池执行,也可使用自定义线程池)
public class ThenComposeDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<String> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("hello 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "hello";
},threadPool).thenComposeAsync((hello -> {
System.out.println("thenCompose 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((hello + "world")::toUpperCase);
}),threadPool);
System.out.println("获取结果 执行线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("两个异步任务流水线执行结果:" + result.join());
}
}
程序执行情况:
hello 执行线程:pool-1-thread-1
获取结果 执行线程:main
thenCompose 执行线程:pool-1-thread-2
两个异步任务流水线执行结果: HELLOWORLD
七、allOf / anyOf
allOf:CompletableFuture是多个任务都执行完成后才会执行,只有有一个任务执行异常,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回null。
anyOf :CompletableFuture是多个任务只要有一个任务执行完成,则返回的CompletableFuture执行get方法时会抛出异常,如果都是正常执行,则get返回执行完成任务的结果。
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");
return "cf3 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> cfAll = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1 任务完成");
return "cf1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2 任务完成");
return "cf2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3 任务完成");
return "cf3 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> cfAll = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll结果->" + cfAll.get());
}