目录
- imuPreintegration.cpp
- 1. TransformFusion 类
- 1.1. lidarOdometryHandler
- 1.2. imuOdometryHandler
- 2. IMUPreintegration 类
- 2.1. imuHandler
- 2.2. odometryHandler⭐
- 2.2.1. 初始化系统, 把初始的lidar位姿,速度,零偏加入到因子图中
- 2.2.2. 将两帧之间的imu做预积分
- 2.2.2.1. imuIntegratorOpt_->integrateMeasurement
- 2.2.3. 优化之后,根据最新的imu状态进行传播
- 参考
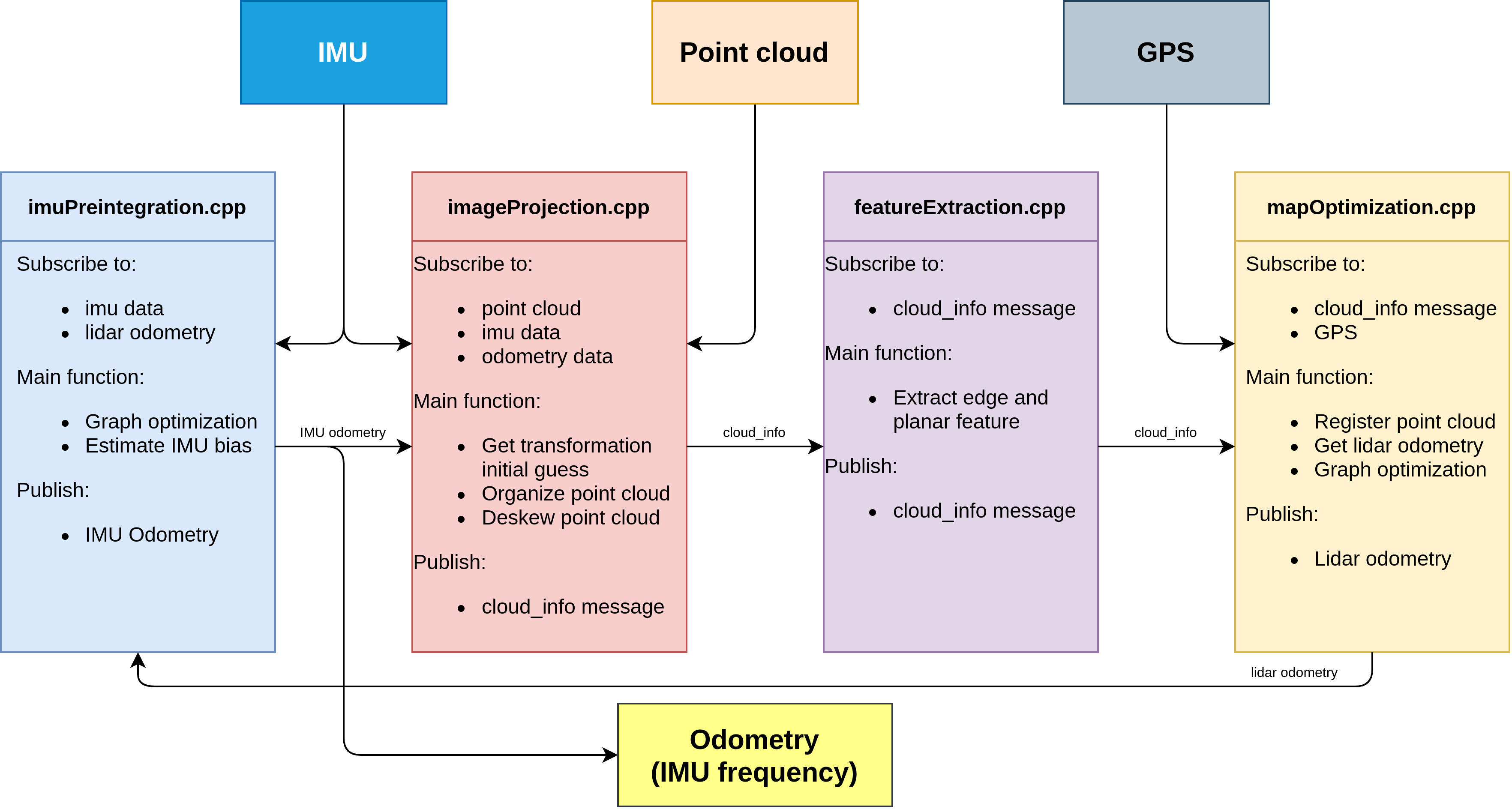 传感器输入: IMU,Point Cloud, GPS(可选)
传感器输入: IMU,Point Cloud, GPS(可选)
输出 : IMU 频率的odometry
imageProjection.cpp: 接受IMU,PointCloud以及IMU预积分输出的IMU odometry(系统刚初始化时没有IMU odometry)。
- 主要功能:
- 基于IMU odometry得到系统的初始位姿
- 将点云投影到cv::mat中,做相应的预处理
- 对原始点云数据做运动补偿(点云的去畸变补偿在代码中只应用于旋转部分,注释掉了平移部分)
featureExtraction.cpp :
- 主要功能:
- 提取点云边缘特征和面特征
mapOptimization.cpp:
- 主要功能:
- 将提取到点云特征与地图中的边缘特征和面特征进行配准
- 配准后得到当前帧在地图中的位姿
- 图优化: 将lidar的帧间约束,回环的约束,(GPS因子)添加到因子图中
imuPreintegration.cpp:一开始并没有工作,只有收到lidar odometry后才会工作
- 主要功能:
- 图优化:lidar odometry和IMU的帧间约束添加到因子图中
- 估计IMU零偏
imuPreintegration.cpp
主函数主要存在两个类IMUPreintegration ImuP和TransformFusion TF。
其中TransformFusion 负责订阅lidar odometry和IMU数据,根据前一时刻激光里程计,和当前时刻的IMU里程计变换增量,计算当前时刻IMU里程计
IMUPreintegration 负责1. 基于激光里程计,两帧激光里程计之间的IMU预积分量构建因子图,优化当前帧的状态(包括位姿,速度,偏置)。2. 以优化后的状态为基础,施加IMU预积分量,得到每一时刻的IMU里程计。
1. TransformFusion 类
TransformFusion()
{
// 如果lidar帧和baselink不是同一个坐标系 // 通常baselink指车体系
// ros 官方推荐使用try catch查找tf的变换
if(lidarFrame != baselinkFrame)
{
try
{ // 查询一下lidar和baselink之间的tf变换,赋值给lidar2Baselink // ros::Time(0): 表示最新时刻
tfListener.waitForTransform(lidarFrame, baselinkFrame, ros::Time(0), ros::Duration(3.0));
tfListener.lookupTransform(lidarFrame, baselinkFrame, ros::Time(0), lidar2Baselink);
}
catch (tf::TransformException ex)
{
ROS_ERROR("%s",ex.what());
}
}
// 订阅地图优化节点的全局位姿和预积分节点的增量位姿
subLaserOdometry = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>("lio_sam/mapping/odometry", 5, &TransformFusion::lidarOdometryHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
subImuOdometry = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>(odomTopic+"_incremental", 2000, &TransformFusion::imuOdometryHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
pubImuOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>(odomTopic, 2000);
pubImuPath = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path> ("lio_sam/imu/path", 1);
}
1.1. lidarOdometryHandler
主要负责保存全局位姿
void lidarOdometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odomMsg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
lidarOdomAffine = odom2affine(*odomMsg);
lidarOdomTime = odomMsg->header.stamp.toSec();
}
1.2. imuOdometryHandler
为该node的主要函数
- 基于最新lidar帧之后的IMU里程计数据计算出IMU的增量,补偿到lidar的位姿即可得到最新的预测位姿:
以IMU的频率向外发布位姿:

基于90s是估计出的最佳位姿与之后还未处理的IMU位姿做积分推算,推算出当前IMU意义上的位姿的结果。
// 弹出时间戳小于最新lidar位姿时刻之前的imu里程计数据
while (!imuOdomQueue.empty())
{
if (imuOdomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() <= lidarOdomTime)
imuOdomQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
// 计算最新队列里imu里程计的增量
Eigen::Affine3f imuOdomAffineFront = odom2affine(imuOdomQueue.front());
Eigen::Affine3f imuOdomAffineBack = odom2affine(imuOdomQueue.back());
Eigen::Affine3f imuOdomAffineIncre = imuOdomAffineFront.inverse() * imuOdomAffineBack;
// 增量补偿到lidar的位姿上去,就得到了最新的预测的位姿
Eigen::Affine3f imuOdomAffineLast = lidarOdomAffine * imuOdomAffineIncre;
- 发送全局一致位姿的最新位姿
float x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw;
// 分解成平移+欧拉角的形式
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(imuOdomAffineLast, x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw);
// publish latest odometry
nav_msgs::Odometry laserOdometry = imuOdomQueue.back();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.x = x;
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.y = y;
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.z = z;
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation = tf::createQuaternionMsgFromRollPitchYaw(roll, pitch, yaw);
pubImuOdometry.publish(laserOdometry);
- 更新tf
static tf::TransformBroadcaster tfOdom2BaseLink;
tf::Transform tCur;
tf::poseMsgToTF(laserOdometry.pose.pose, tCur);
if(lidarFrame != baselinkFrame)
tCur = tCur * lidar2Baselink;
// 更新odom到baselink的tf
tf::StampedTransform odom_2_baselink = tf::StampedTransform(tCur, odomMsg->header.stamp, odometryFrame, baselinkFrame);
// 发送tf
tfOdom2BaseLink.sendTransform(odom_2_baselink);
- 发送imu里程计的轨迹
if (imuTime - last_path_time > 0.1)
{
last_path_time = imuTime;
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose_stamped;
pose_stamped.header.stamp = imuOdomQueue.back().header.stamp;
pose_stamped.header.frame_id = odometryFrame;
pose_stamped.pose = laserOdometry.pose.pose;
// 把最新的位姿放入轨迹中
imuPath.poses.push_back(pose_stamped);
// 把lidar时间戳之前的轨迹全部擦除(只显示当前lidar帧到最新imu帧的轨迹)
while(!imuPath.poses.empty() && imuPath.poses.front().header.stamp.toSec() < lidarOdomTime - 1.0)
imuPath.poses.erase(imuPath.poses.begin());
// 发布轨迹,这个轨迹实际上是可视化imu预积分节点输出的预测值
if (pubImuPath.getNumSubscribers() != 0)
{
imuPath.header.stamp = imuOdomQueue.back().header.stamp;
imuPath.header.frame_id = odometryFrame;
pubImuPath.publish(imuPath);
}
}
2. IMUPreintegration 类
IMUPreintegration()
{
// 订阅IMU信息,接受到IMU信息执行imuHandler,预测每一时刻(imu频率)的imu里程计
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu> (imuTopic, 2000, &IMUPreintegration::imuHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 订阅地图优化节点的增量里程计消息,并执行odometryHandler,用两帧之间的imu预计分量构建因子图,优化当前帧位姿(这个位姿仅用于更新每时刻的imu里程计,以及下一次因子图优化)
subOdometry = nh.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>("lio_sam/mapping/odometry_incremental",5, &IMUPreintegration::odometryHandler, this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
// 发布imu里程计
pubImuOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry> (odomTopic+"_incremental", 2000);
- 2个订阅:
高频率的IMU数据;
低频率的lidar里程计; - 1个发布:
高频率的IMU里程计,随imuHandler()发布。
然后设置IMU预积分的噪声方差:
// gtsam::PreintegrationParams: 预积分相关参数,我们对imu数据进行预积分之前通常需要实现直到imu的噪声,重力方向等参数
boost::shared_ptr<gtsam::PreintegrationParams> p = gtsam::PreintegrationParams::MakeSharedU(imuGravity);
p->accelerometerCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3,3) * pow(imuAccNoise, 2); // acc white noise in continuous
p->gyroscopeCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3,3) * pow(imuGyrNoise, 2); // gyro white noise in continuous
// 速度积分得到位置时的噪声
p->integrationCovariance = gtsam::Matrix33::Identity(3,3) * pow(1e-4, 2); // error committed in integrating position from velocities
gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias prior_imu_bias((gtsam::Vector(6) << 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0).finished());; // assume zero initial bias
分别是重力加速度大小,线加速度噪声协方差,角速度噪声协方差,积分速度到位移的协方差和bias,后两个是拍脑袋写的,头三个都是在utility.h从配置文件中读取的。
接下来设置的是状态量:位移,速度和bias的先验噪声,
// 初始位姿置信度设置比较高 三维姿态+三维位置
priorPoseNoise = gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas((gtsam::Vector(6) << 1e-2, 1e-2, 1e-2, 1e-2, 1e-2, 1e-2).finished()); // rad,rad,rad,m, m, m
// 初始速度之置信度就设置差一点
priorVelNoise = gtsam::noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(3, 1e4); // m/s ,方差设置为10的四次方,认为置信度很低
// 零偏的置信度也设置高一点
priorBiasNoise = gtsam::noiseModel::Isotropic::Sigma(6, 1e-3); // 1e-2 ~ 1e-3 seems to be good
然后是两帧之间pose的噪声和bias的噪声:
// 正常情况下lidar odom的协方差矩阵
correctionNoise = gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas((gtsam::Vector(6) << 0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1).finished()); // rad,rad,rad,m, m, m
// lidar odom退化后的协方差矩阵
correctionNoise2 = gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas((gtsam::Vector(6) << 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1).finished()); // rad,rad,rad,m, m, m
// 两帧bias的协方差矩阵
noiseModelBetweenBias = (gtsam::Vector(6) << imuAccBiasN, imuAccBiasN, imuAccBiasN, imuGyrBiasN, imuGyrBiasN, imuGyrBiasN).finished();
如果输入的lidar里程计有较大的误差,那么pose噪声就使用correctionNoise2,一般情况用correctionNoise。
最后是2个预积分器,分别用于图优化中使用和输出IMU里程计时使用:
// gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements: 跟预积分相关的计算就在这个类中实现
// imu预积分器,用于预测每一时刻(imu频率)的IMU里程计(转到lidar系了,与激光里程计同一个系)
imuIntegratorImu_ = new gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements(p, prior_imu_bias); // setting up the IMU integration for IMU message thread
// imu预积分器,用于因子图优化
imuIntegratorOpt_ = new gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements(p, prior_imu_bias); // setting up the IMU integration for optimization
2.1. imuHandler
这个函数是发布IMU里程计的,由于预积分器在odometry()中被更新了,相关的信息都在里面,那么就可以根据输入的高频IMU数据发布同样高频的IMU里程计信息。(被imageProjection和tranformFusion订阅)
- 当来了IMU数据的时候,首先对IMU数据进行坐标转换,转化到lidar系下:
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imu_raw)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
// imu原始测量数据转换到lidar系,加速度、角速度、RPY
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImu = imuConverter(*imu_raw);
注意了,由于IMU数据不包括位移,所以这个坐标变换只涉及到旋转。
在odometryHandler()里,我们可以看到gtsam::Pose3 curPose = lidarPose.compose(lidar2Imu),他说把lidarpose转换到IMU系,但是这里又是把IMU数据转到lidar系,岂不是冲突了吗?我们再看看lidar2Imu:
gtsam::Pose3 lidar2Imu = gtsam::Pose3(gtsam::Rot3(1, 0, 0, 0), gtsam::Point3(extTrans.x(), extTrans.y(), extTrans.z()));只涉及到平移的变换,不涉及旋转变换。所以说,整个类,是在lidar坐标系下进行的,原点却是body坐标系的原点。
- 把来的最新一个imu数据加到预积分器里:
imuIntegratorImu_->integrateMeasurement(gtsam::Vector3(thisImu.linear_acceleration.x, thisImu.linear_acceleration.y, thisImu.linear_acceleration.z),
gtsam::Vector3(thisImu.angular_velocity.x, thisImu.angular_velocity.y, thisImu.angular_velocity.z), dt);
- 用当前已经收到的最新的激光里程计时刻对应的状态、偏置,施加从该时刻开始到当前时刻的imu预计分量,得到当前时刻的状态:
// predict odometry
// 根据这个值预测最新的状态
// predict: 预积分量可以计算出两帧之间的相对位置,速度,姿态的变化量,结合上一帧状态量就可以计算出下一关键帧的推算值
gtsam::NavState currentState = imuIntegratorImu_->predict(prevStateOdom, prevBiasOdom);
- 发布odometry
最后,把当前预测的imu里程计包装成message发布出去就大功告成了,注意这次是在lidar坐标系下,不光是旋转,平移也是lidar系下的:
nav_msgs::Odometry odometry;
odometry.header.stamp = thisImu.header.stamp;
odometry.header.frame_id = odometryFrame;
odometry.child_frame_id = "odom_imu";
// transform imu pose to ldiar
// 将这个状态转到lidar坐标系下发送出去
gtsam::Pose3 imuPose = gtsam::Pose3(currentState.quaternion(), currentState.position());
gtsam::Pose3 lidarPose = imuPose.compose(imu2Lidar);
odometry.pose.pose.position.x = lidarPose.translation().x();
odometry.pose.pose.position.y = lidarPose.translation().y();
odometry.pose.pose.position.z = lidarPose.translation().z();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.x = lidarPose.rotation().toQuaternion().x();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.y = lidarPose.rotation().toQuaternion().y();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.z = lidarPose.rotation().toQuaternion().z();
odometry.pose.pose.orientation.w = lidarPose.rotation().toQuaternion().w();
odometry.twist.twist.linear.x = currentState.velocity().x();
odometry.twist.twist.linear.y = currentState.velocity().y();
odometry.twist.twist.linear.z = currentState.velocity().z();
odometry.twist.twist.angular.x = thisImu.angular_velocity.x + prevBiasOdom.gyroscope().x();
odometry.twist.twist.angular.y = thisImu.angular_velocity.y + prevBiasOdom.gyroscope().y();
odometry.twist.twist.angular.z = thisImu.angular_velocity.z + prevBiasOdom.gyroscope().z();
pubImuOdometry.publish(odometry);
2.2. odometryHandler⭐
订阅地图优化节点的增量里程计消息odometry_incremental
主要执行:
- 初始化系统, 把初始的lidar位姿,速度,零偏加入到因子图中
- 将两帧之间的imu做预积分
- 图优化之后,获得一个最合理的状态量估计值,包括PVQ,各种noise,bias。根据最新的imu状态进行传播
2.2.1. 初始化系统, 把初始的lidar位姿,速度,零偏加入到因子图中
- 首先是把优化器相关内容重置一下,
// 1. initialize system
if (systemInitialized == false)
{ // 优化问题进行复位
resetOptimization();
void resetOptimization()
{
gtsam::ISAM2Params optParameters;
optParameters.relinearizeThreshold = 0.1;
optParameters.relinearizeSkip = 1;
optimizer = gtsam::ISAM2(optParameters);
gtsam::NonlinearFactorGraph newGraphFactors;
graphFactors = newGraphFactors;
gtsam::Values NewGraphValues;
graphValues = NewGraphValues;
}
可以发现他把优化器optimizer,因子graphFactors和属性值graphValues干脆都换成新的了。注意了,在GTSAM图优化里,optimizer,graphFactors和graphValues是三个重要的工具对象。
- 然后从imu优化队列中删除当前帧激光里程计时刻之前的imu数据:
while (!imuQueOpt.empty())
{
if (ROS_TIME(&imuQueOpt.front()) < currentCorrectionTime - delta_t)
{
lastImuT_opt = ROS_TIME(&imuQueOpt.front());
imuQueOpt.pop_front();
}
else
break;
}
- 接下来开始正菜了,往因子图里添加里程计位姿先验因子:
// 将lidar的位姿转移到imu坐标系下
prevPose_ = lidarPose.compose(lidar2Imu);
// 设置其初始位姿和置信度
// gtsam::Pose3: 表示六自由度位姿 // model:置信度
// gtsam::PriorFactor<T> : 先验因子,表示对某个状态量T的一个先验估计,约束某个状态变量的状态不会离该先验值过远
// X(0): 表示第一个位姿
gtsam::PriorFactor<gtsam::Pose3> priorPose(X(0), prevPose_, priorPoseNoise);
// 约束加入到因子中
graphFactors.add(priorPose);
lidarpose是lidar->world的变换,首先当然得转化为IMU->world的形式,prevPose_是因子priorPose的数值,然后把这个因子加到因子图graphFactors里。
- 类似的,添加速度先验因子:
// 初始化速度,这里就直接赋0了
// gtsam::Vector3:表示三自由度速度
prevVel_ = gtsam::Vector3(0, 0, 0);
gtsam::PriorFactor<gtsam::Vector3> priorVel(V(0), prevVel_, priorVelNoise);
// 将对速度的约束也加入到因子图中
graphFactors.add(priorVel);
- 添加imu偏置先验因子:
// 初始化零偏
// gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias : 表示imu零偏
prevBias_ = gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias();
gtsam::PriorFactor<gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias> priorBias(B(0), prevBias_, priorBiasNoise);
// 零偏加入到因子图中
graphFactors.add(priorBias);
- 以上把约束加入完毕,下面开始添加状态量
// 将各种状态量赋值为初始值
graphValues.insert(X(0), prevPose_);
graphValues.insert(V(0), prevVel_);
graphValues.insert(B(0), prevBias_);
- 开始优化:虽然我不知道它是怎么做到的,但是我知道它做完了。
// 约束和状态量更新isam优化器
optimizer.update(graphFactors, graphValues);
- 清空优化器
// 进优化器之后保存约束和状态量的变量就清零,方便下一次添加因子
graphFactors.resize(0);
graphValues.clear();
- 把优化后的prevBias_给到预积分器:
imuIntegratorImu_->resetIntegrationAndSetBias(prevBias_);
imuIntegratorOpt_->resetIntegrationAndSetBias(prevBias_);
- 初始化完成,key是循环的计数。初始化后直接return掉,进入下次循环。
key = 1;
systemInitialized = true;
return;
2.2.2. 将两帧之间的imu做预积分
正常情况下的图优化 :基于最新帧和上一帧lidar里程计信息和两帧之间的IMU信息,利用图优化得到准确的位姿状态量(PVQ)和IMU状态量(noise,bias)
- 首先把IMU数据导入到用于优化的IMU预积分器中:
// 2. integrate imu data and optimize
while (!imuQueOpt.empty())
{
// pop and integrate imu data that is between two optimizations
// 将imu信息取出来
sensor_msgs::Imu *thisImu = &imuQueOpt.front();
double imuTime = ROS_TIME(thisImu);
// 时间上小于当前lidar位姿的都取出来(构造帧间约束)
if (imuTime < currentCorrectionTime - delta_t)
{
// 计算两个imu量之间的时间差
double dt = (lastImuT_opt < 0) ? (1.0 / 500.0) : (imuTime - lastImuT_opt);
// 调用预积分接口将imu数据送进入处理
// integrateMeasurement : 输入IMU的测量值,其内部会自动实现预积分量的更新以及协方差矩阵的更新
imuIntegratorOpt_->integrateMeasurement(
gtsam::Vector3(thisImu->linear_acceleration.x, thisImu->linear_acceleration.y, thisImu->linear_acceleration.z),
gtsam::Vector3(thisImu->angular_velocity.x, thisImu->angular_velocity.y, thisImu->angular_velocity.z), dt);
// 记录当前imu时间
lastImuT_opt = imuTime;
imuQueOpt.pop_front();
}
else
break;
}
- 添加IMU预积分因子:
// 两帧间imu预积分完成之后,就将其转换成预积分约束
const gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements& preint_imu = dynamic_cast<const gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements&>(*imuIntegratorOpt_);
// 预积分约束对相邻两帧之间的位姿(X) 速度(V) 零偏(B)形成约束
// gtsam::ImuFactor: IMU因子,通过IMU预积分量构造出IMU因子,即IMU约束
gtsam::ImuFactor imu_factor(X(key - 1), V(key - 1), X(key), V(key), B(key - 1), preint_imu);
// 加入因子图
graphFactors.add(imu_factor);
- 添加imu bias因子,前一帧bias,当前帧bias,观测值,噪声协方差;deltaTij()是积分段的时间:
// 零偏的约束,两帧间零偏相差不会太大,因此使用常量约束
// deltaTij : 预计分量跨越的时间长度
// gtsam::BetweenFactor : 状态量间的约束,约束相邻两状态量之间的差值不会距离该约束过远
graphFactors.add(gtsam::BetweenFactor<gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias>(B(key - 1), B(key), gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias(),
gtsam::noiseModel::Diagonal::Sigmas(sqrt(imuIntegratorOpt_->deltaTij()) * noiseModelBetweenBias)));
- 添加位姿因子:看到了吗,根据位姿准不准,它添加的协方差是不一样的,
// 将lidar的位姿转移到imu坐标系下
gtsam::Pose3 curPose = lidarPose.compose(lidar2Imu);
// lidar位姿补偿到imu坐标系下,同时根据是否退化选择不同的置信度,作为这一帧的先验估计
gtsam::PriorFactor<gtsam::Pose3> pose_factor(X(key), curPose, degenerate ? correctionNoise2 : correctionNoise);
// 加入因子图
graphFactors.add(pose_factor);
- 现在呢,从上一帧到当前帧之间的IMU有了,上一帧状态量也有,当前帧输入的里程计也有,那么就可以获取图优化之后当前帧的一个初始预测值了
// gtsam::PreintegratedImuMeasurements predict: 预积分量可以计算出两帧之间的相对位置,速度,姿态的变化量,结合上一帧状态量就可以计算出下一关键帧的推算值
// 根据上一时刻的状态,结合预积分结果,对当前状态进行预测
gtsam::NavState propState_ = imuIntegratorOpt_->predict(prevState_, prevBias_);
- 以上内容是完成graphFactors的配置,接下来配置graphValues:
由于key-1帧的graphValues已经有了,所以只用配置key帧的数据。
// 预测量作为初始值插入因子图中
graphValues.insert(X(key), propState_.pose());// propState_.pose() :预积分出的位置
graphValues.insert(V(key), propState_.v()); // propState_.v() :预积分出的速度
graphValues.insert(B(key), prevBias_);
- 优化:
optimizer.update(graphFactors, graphValues);
// 两次优化,让结果更好
optimizer.update();
graphFactors.resize(0);
graphValues.clear();
// Overwrite the beginning of the preintegration for the next step.
- 拿到结果:
gtsam::Values result = optimizer.calculateEstimate();
- 把当前帧得到的结果给到prev帧,留给下个循环用:
// 获取优化后的当前状态作为当前帧的最佳估计
prevPose_ = result.at<gtsam::Pose3>(X(key));
prevVel_ = result.at<gtsam::Vector3>(V(key));
prevState_ = gtsam::NavState(prevPose_, prevVel_);
prevBias_ = result.at<gtsam::imuBias::ConstantBias>(B(key));
// Reset the optimization preintegration object.
// 当前约束任务已经完成,预积分约束复位,同时需要设置一下零偏作为下一次积分的先决条件
imuIntegratorOpt_->resetIntegrationAndSetBias(prevBias_);
- imu因子图优化结果,速度或者偏置过大,认为失败:
// 一个简单的失败检测
if (failureDetection(prevVel_, prevBias_))
{
// 状态异常就直接复位
resetParams();
return;
}
2.2.2.1. imuIntegratorOpt_->integrateMeasurement
/**
* 将单个IMU测量值添加到预积分中。
* @param measuredAcc 测量的加速度(body frame,由传感器给出)
* @param measuredOmega 测量的角速度(由传感器给出)
* @param dt 与上一次IMU测量之间的间隔
*/
void PreintegratedCombinedMeasurements::integrateMeasurement(
const Vector3& measuredAcc, const Vector3& measuredOmega, double dt) {
// Update preintegrated measurements.
Matrix9 A; // overall Jacobian wrt preintegrated measurements (df/dx)
Matrix93 B, C;
PreintegrationType::update(measuredAcc, measuredOmega, dt, &A, &B, &C);
// 更新预积分测量协方差:如[2]所示,我们考虑一阶传播,该传播可以被视为EKF框架中的预测阶段。
// 在这种实现中,与[2]相反,我们考虑了偏差选择的不确定性,并保持了偏差和预积分测量之间的相关性
// Single Jacobians to propagate covariance
// TODO(frank): should we not also account for bias on position?
Matrix3 theta_H_biasOmega = -C.topRows<3>();
Matrix3 vel_H_biasAcc = -B.bottomRows<3>();
// overall Jacobian wrt preintegrated measurements (df/dx)
Eigen::Matrix<double, 15, 15> F;
F.setZero();
F.block<9, 9>(0, 0) = A;
F.block<3, 3>(0, 12) = theta_H_biasOmega;
F.block<3, 3>(6, 9) = vel_H_biasAcc;
F.block<6, 6>(9, 9) = I_6x6;
// propagate uncertainty
// TODO(frank): use noiseModel routine so we can have arbitrary noise models.
const Matrix3& aCov = p().accelerometerCovariance;
const Matrix3& wCov = p().gyroscopeCovariance;
const Matrix3& iCov = p().integrationCovariance;
// first order uncertainty propagation
// Optimized matrix multiplication (1/dt) * G * measurementCovariance * G.transpose()
Eigen::Matrix<double, 15, 15> G_measCov_Gt;
G_measCov_Gt.setZero(15, 15);
// BLOCK DIAGONAL TERMS
D_t_t(&G_measCov_Gt) = dt * iCov;
D_v_v(&G_measCov_Gt) = (1 / dt) * vel_H_biasAcc
* (aCov + p().biasAccOmegaInt.block<3, 3>(0, 0))
* (vel_H_biasAcc.transpose());
D_R_R(&G_measCov_Gt) = (1 / dt) * theta_H_biasOmega
* (wCov + p().biasAccOmegaInt.block<3, 3>(3, 3))
* (theta_H_biasOmega.transpose());
D_a_a(&G_measCov_Gt) = dt * p().biasAccCovariance;
D_g_g(&G_measCov_Gt) = dt * p().biasOmegaCovariance;
// OFF BLOCK DIAGONAL TERMS
Matrix3 temp = vel_H_biasAcc * p().biasAccOmegaInt.block<3, 3>(3, 0)
* theta_H_biasOmega.transpose();
D_v_R(&G_measCov_Gt) = temp;
D_R_v(&G_measCov_Gt) = temp.transpose();
preintMeasCov_ = F * preintMeasCov_ * F.transpose() + G_measCov_Gt;
}
void TangentPreintegration::update(const Vector3& measuredAcc,
const Vector3& measuredOmega, const double dt, Matrix9* A, Matrix93* B,
Matrix93* C) {
// Correct for bias in the sensor frame
Vector3 acc = biasHat_.correctAccelerometer(measuredAcc);
Vector3 omega = biasHat_.correctGyroscope(measuredOmega);
// Possibly correct for sensor pose by converting to body frame
Matrix3 D_correctedAcc_acc, D_correctedAcc_omega, D_correctedOmega_omega;
if (p().body_P_sensor)
boost::tie(acc, omega) = correctMeasurementsBySensorPose(acc, omega,
D_correctedAcc_acc, D_correctedAcc_omega, D_correctedOmega_omega);
// Do update
deltaTij_ += dt;
preintegrated_ = UpdatePreintegrated(acc, omega, dt, preintegrated_, A, B, C);
if (p().body_P_sensor) {
// More complicated derivatives in case of non-trivial sensor pose
*C *= D_correctedOmega_omega;
if (!p().body_P_sensor->translation().isZero())
*C += *B * D_correctedAcc_omega;
*B *= D_correctedAcc_acc; // NOTE(frank): needs to be last
}
// new_H_biasAcc = new_H_old * old_H_biasAcc + new_H_acc * acc_H_biasAcc
// where acc_H_biasAcc = -I_3x3, hence
// new_H_biasAcc = new_H_old * old_H_biasAcc - new_H_acc
preintegrated_H_biasAcc_ = (*A) * preintegrated_H_biasAcc_ - (*B);
// new_H_biasOmega = new_H_old * old_H_biasOmega + new_H_omega * omega_H_biasOmega
// where omega_H_biasOmega = -I_3x3, hence
// new_H_biasOmega = new_H_old * old_H_biasOmega - new_H_omega
preintegrated_H_biasOmega_ = (*A) * preintegrated_H_biasOmega_ - (*C);
}
2.2.3. 优化之后,根据最新的imu状态进行传播
对最新lidar帧之后的IMU信息做预积分
- 首先更新最新一帧lidarpose的位姿,速度,bias:
// 3. after optiization, re-propagate imu odometry preintegration
prevStateOdom = prevState_;
prevBiasOdom = prevBias_;
- 从imu队列中删除当前激光里程计时刻之前的imu数据:
// 首先把lidar帧之前的imu状态全部弹出去,只基于最新odom帧之后的imu信息做位姿推算
while (!imuQueImu.empty() && ROS_TIME(&imuQueImu.front()) < currentCorrectionTime - delta_t)
{
lastImuQT = ROS_TIME(&imuQueImu.front());
imuQueImu.pop_front();
}
这里要特别注意一下,这个IMU的buffer和之前的不一样,imuQueImu是用于发布IMU里程计的buffer,而之前的imuQueOpt是用于优化的buffer。
- 如果现在IMU buffer还有数据,那么就加到用于发布IMU里程计的IMU预积分器里,会在imuHandler()中被用到:
// 如果有新于lidar状态时刻的imu
if (!imuQueImu.empty())
{
// reset bias use the newly optimized bias
// 这个预积分变量复位(使用最新推断出的零偏)
imuIntegratorImu_->resetIntegrationAndSetBias(prevBiasOdom);
// integrate imu message from the beginning of this optimization
// 然后把剩下的imu状态重新积分
for (int i = 0; i < (int)imuQueImu.size(); ++i)
{
sensor_msgs::Imu *thisImu = &imuQueImu[i];
double imuTime = ROS_TIME(thisImu);
double dt = (lastImuQT < 0) ? (1.0 / 500.0) :(imuTime - lastImuQT);
// integrateMeasurement : 输入IMU的测量值,其内部会自动实现预积分量的更新以及协方差矩阵的更新
imuIntegratorImu_->integrateMeasurement(gtsam::Vector3(thisImu->linear_acceleration.x, thisImu->linear_acceleration.y, thisImu->linear_acceleration.z),
gtsam::Vector3(thisImu->angular_velocity.x, thisImu->angular_velocity.y, thisImu->angular_velocity.z), dt);
lastImuQT = imuTime;
}
}
- 更新帧号key,同时告诉imuHandler()我可以的:
// 每做一次优化,key+1
++key;
doneFirstOpt = true;
每来一帧lidar帧,map_optimazation节点会输出两种位姿:一种带回环的好的位姿,一种不带回环的增量性质的位姿

为了得到全局最优的位姿估计,把最新的位姿估计结果与lidar帧的 Δ T \Delta T ΔT求出补偿,再传递给带回环的odom位姿,即可得到全局一致的位姿状态。
为什么不直接对带回环的odom位姿做IMU积分?在回环的位姿中,可能存在位姿的跳变,不能做IMU的紧耦合操作
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/iwanderu/article/details/123167888?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502