文章目录
- 一、曲线方程
- 1. 问题描述
- 2. 实现方案
一、曲线方程
1. 问题描述
现有数学模型为 f ( x ) = A e x + B s i n ( x ) + C x D f(x)=Ae^x+Bsin(x)+Cx^D f(x)=Aex+Bsin(x)+CxD ,但不知道 A A A 、 B B B 、 C C C 、 D D D 各参数系数,实验数据中含有噪声即 f ( x ) = A e x + B s i n ( x ) + C x D + n o i s e f(x)=Ae^x+Bsin(x)+Cx^D+noise f(x)=Aex+Bsin(x)+CxD+noise ,此时用ceres进行拟合。
2. 实现方案
2.1 含噪声的数据生成
以
A
=
0.02
A=0.02
A=0.02 、
B
=
3.2
B=3.2
B=3.2 、
C
=
1.1
C=1.1
C=1.1 、
D
=
3
D=3
D=3 为例进行实验数据生成。
// 生成曲线对应真值数据
double function(double x){
return 0.02*exp(x)+3.2*sin(x)+1.1*pow(x,3);
}
// 真值数据添加噪声
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> measurement_data_generation(double begin,double end,double stride,double (*fun)(double)){
std::vector<std::pair<double,double>> out;
//创建一个 std::mt19937 类型的随机数生成器 mt,并使用当前时间的微秒数作为种子,以确保每次运行时生成的随机数序列不同
std::mt19937 mt;
mt.seed(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
for(double i=begin;i<end;i=i+stride){
// 使用 std::uniform_real_distribution<double>(0, 20) 生成一个在 0 到 20 之间的随机 double 值
double y_=std::uniform_real_distribution<double>(0,20)(mt);
// 将随机值 y_ 与通过调用 fun(i) 得到的值相加
y_=y_+fun(i);
out.push_back(std::make_pair(i,y_));
}
return out;
}
2.2 自定义残差计算模型
根据数学模型搭建ceres残差计算模型:
struct my_ceres_test{
public:
my_ceres_test(double x,double y):x_(x),y_(y){}
template<typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const A,
const T* const B,
const T* const C,
const T* const D,
T* residual)const{
residual[0]=y_-A[0]*exp(x_)-B[0]*sin(x_)-C[0]*pow(x_,D[0]);
return true;
}
private:
double x_;
double y_;
};
2.3 完整代码
完整程序如下:
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "glog/logging.h"
#include <random>
#include <chrono>
#include <cmath>
// #define MATPLOT
#ifdef MATPLOT
#include "matplotlibcpp.h"
#endif
// 生成曲线对应真值数据
double function(double x){
return 0.02*exp(x)+3.2*sin(x)+1.1*pow(x,3);
}
/**
* @description: 真值数据添加噪声
* @date: 2024/06/23
* @param[i]: begin:数据生成的起始值
* @param[i]: end:数据生成的结束值(不包含在内)
* @param[i]: stride:每次迭代的步长
* @param[i]: fun:一个函数指针,指向一个接受一个 double 类型参数并返回一个 double 类型值的函数
* @return: std::vector<std::pair<double, double>>
**/
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> measurement_data_generation(double begin,double end,double stride,double (*fun)(double)){
std::vector<std::pair<double,double>> out;
//创建一个 std::mt19937 类型的随机数生成器 mt,并使用当前时间的微秒数作为种子,以确保每次运行时生成的随机数序列不同
std::mt19937 mt;
mt.seed(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count());
for(double i=begin;i<end;i=i+stride){
// 使用 std::uniform_real_distribution<double>(0, 20) 生成一个在 0 到 20 之间的随机 double 值
double y_=std::uniform_real_distribution<double>(0,20)(mt);
// 将随机值 y_ 与通过调用 fun(i) 得到的值相加
y_=y_+fun(i);
out.push_back(std::make_pair(i,y_));
}
return out;
}
//y=A*exp(x)+B*sinx+C*x^3, A=0.02,B=3.2,C=1.1,D=3
struct my_ceres_test{
public:
my_ceres_test(double x,double y):x_(x),y_(y){}
template<typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const A,
const T* const B,
const T* const C,
const T* const D,
T* residual)const{
residual[0]=y_-A[0]*exp(x_)-B[0]*sin(x_)-C[0]*pow(x_,D[0]);
return true;
}
private:
double x_;
double y_;
};
int main(int argc,char** argv){
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
ceres::Problem problem;
double A=0.0, B=0.0, C=0.0, D=1.0;
double begin=1.0, end=10.0, stride=0.02;
std::vector<std::pair<double,double>> datas = measurement_data_generation(begin, end, stride, function);
std::cout << "\n test data sum: " << datas.size() <<" \n" << std::endl;
for(auto data_:datas){
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function=new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<my_ceres_test,1,1,1,1,1>(new my_ceres_test(data_.first,data_.second));
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function,nullptr,&A,&B,&C,&D);
}
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout=true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
// std::cout<<summary.FullReport()<<std::endl;
std::cout << summary.BriefReport() << "\n";
std::cout<<" A = "<<A<<"\n B = "<<B<<"\n C = "<<C<<"\n D = "<<D<<std::endl;
#ifdef MATPLOT
std::vector<double> x,y,y_;
for(auto data_:datas){
x.push_back(data_.first);
y.push_back(data_.second);
y_.push_back(A*exp(data_.first)+B*sin(data_.first)+C*pow(data_.first,D));
}
matplotlibcpp::figure_size(1200,800);
matplotlibcpp::named_plot("$y=Ae^x+Bsinx+Cx^3+n$",x,y,"bx--");
matplotlibcpp::named_plot("fitied,$y=\\hat{A}e^x+\\hat{B}sinx+\\hat{C}x^3$",x,y_,"r-");
matplotlibcpp::legend();
matplotlibcpp::grid(true);
matplotlibcpp::title("my_ceres_test plot");
matplotlibcpp::show();
#endif
return 0;
}
注意:取消上述代码 #define MATPLOT 注释,可使用 matplotlibcpp 工具进行数据可视化
matplotlibcpp 的源码安装:# 先下载上述链接 matplotlibcpp源码 sudo apt-get install python3.8-dev sudo apt-get install python3-dev mkdir matplotlib-cpp-master/build && cd matplotlib-cpp-master/build cmake .. make -j4 sudo make install
CMakeLists.txt 如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.16)
project(my_test)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
# Ceres库
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
include_directories(${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# matplotcpp 依赖
find_package(PythonLibs REQUIRED)
include_directories(
${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_executable(my_test_matplot my_test_matplot.cpp)
target_link_libraries(my_test_matplot ${CERES_LIBRARIES} ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES})
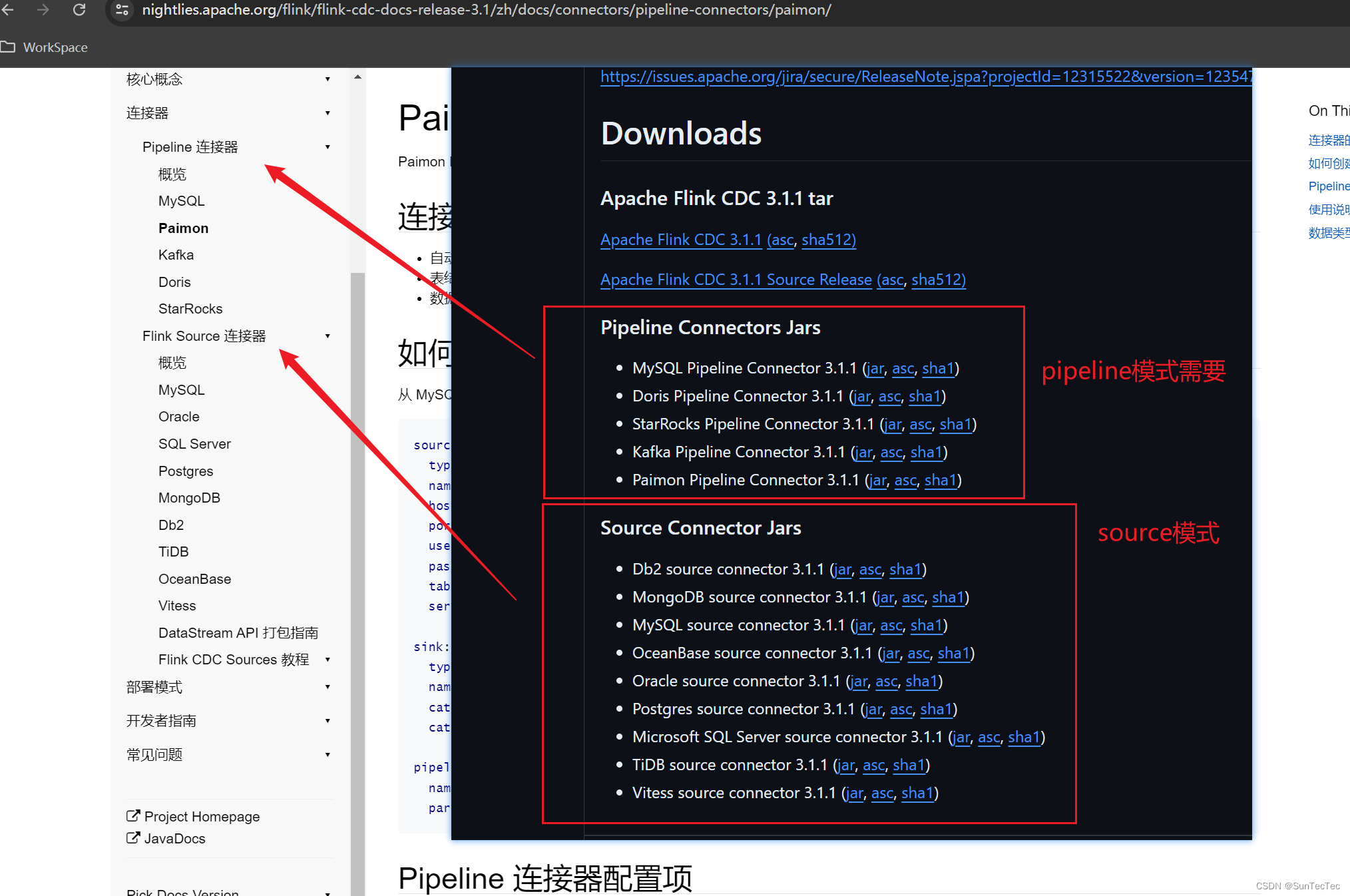
2.4 优化过程及结果
由图可知,测试数据共451组;Ceres最终找到的解决方案:
A
=
0.0239231
,
B
=
8.34126
,
C
=
1.70188
,
D
=
2.78483
A=0.0239231, B=8.34126, C=1.70188, D=2.78483
A=0.0239231,B=8.34126,C=1.70188,D=2.78483 目标函数值为
8832.095
8832.095
8832.095 (优化前目标函数值为
66298520
66298520
66298520)。

如下所示,使用 matplotlibcpp 进行数据可视化: