本文基于上一篇http://t.csdnimg.cn/0qm2R 的基础上添加OpenFeign的使用。
微服务通信
在微服务架构中,微服务之间的通信通常有两种方式:RPC 和 HTTP。在 Spring Cloud 中,默认使用 HTTP 进行微服务的通信,最常用的实现形式有两种:RestTemplate OpenFeign
HTTP 通信
RestTemplate
RestTemplate是 Spring 提供的用于同步 HTTP 请求的客户端工具,可以方便地与其他微服务进行 HTTP 调用。
OpenFeign
OpenFeign是一个声明式的 HTTP 客户端,使得编写 HTTP 客户端变得非常简单。通过注解来定义接口,Spring Cloud Feign 会自动生成实现该接口的 HTTP 客户端对象。
Netflix于2013年6月发布了Feign的第一个版本1.0.0,并于2016年7月发布了最后一个版本8.18.0。在2016年,Netflix将Feign捐献给社区,并于同年7月发布了OpenFeign的首个版本9.0.0,随后持续发布至今。因此,可以简单理解为Netflix Feign是OpenFeign的祖先,或者说OpenFeign是Netflix Feign的升级版。OpenFeign是Feign的一个更强大、更灵活的实现。(后续提到的Feign都是 OpenFeign)
Spring Cloud Feign 是 Spring 对 Feign 的封装,将 Feign 项目集成到 Spring Cloud 生态系统中。受 Feign 更名影响,Spring Cloud Feign 也有两个 starter:
spring-cloud-starter-feign
spring-cloud-starter-openfeign
由于 Feign 停更维护,因此我们使用的依赖是 spring-cloud-starter-openfeign。
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)
RPC(远程过程调用)是一种通过网络从远程计算机上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络通信细节的机制。RPC 可以使用多种网络协议进行通信,如 HTTP、TCP、UDP 等,并且在 TCP/IP 网络四层模型中跨越了传输层和应用层。简而言之,RPC 就是像调用本地方法一样调用远程方法。
常见的 RPC 框架有:
1. Dubbo:是一个高性能的 Java RPC 框架,提供透明化的远程方法调用,主要用于构建分布式服务架构。
2. Thrift:是一个由 Facebook 开发的跨语言的 RPC 框架,支持多种编程语言,适用于服务之间高效的通信。
3. gRPC: gRPC 是 Google 开发的高性能、开源的 RPC 框架,使用 Protocol Buffers 作为接口描述语言,支持多种编程语言,适用于不同平台的服务通信。
通过上述工具和框架,可以实现微服务之间的高效通信,无论是通过 HTTP 还是 RPC,选择何种方式取决于具体的业务需求和技术选型。
OpenFeign的使用
引入依赖
在order-service的pom中引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>添加注解
在启动类中添加注解,开启feign功能。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@EnableFeignClients # 开启openFeign功能
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}编写客户端
import com.demo.order.model.ProductInfo;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
// name:根据注册中心的服务名来调用
// path:调用product-service中的controller中的所有url都有path前缀
@FeignClient(name = "product-service", path = "/product")
// 根据product-service中的controller中的接口写方法
public interface ProductApi {
// 与product-service中的controller中的接口相对应
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId);
}远程调用
import com.demo.order.api.ProductApi;
import com.demo.order.mapper.OrderMapper;
import com.demo.order.model.OrderInfo;
import com.demo.order.model.ProductInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderMapper orderMapper;
@Autowired
private ProductApi productApi;
public OrderInfo selectOrderById(Integer orderId){
OrderInfo orderInfo = orderMapper.selectOrderById(orderId);
ProductInfo productInfo = productApi.getProductById(orderInfo.getProductId());
orderInfo.setProductInfo(productInfo);
return orderInfo;
}
}运行观察
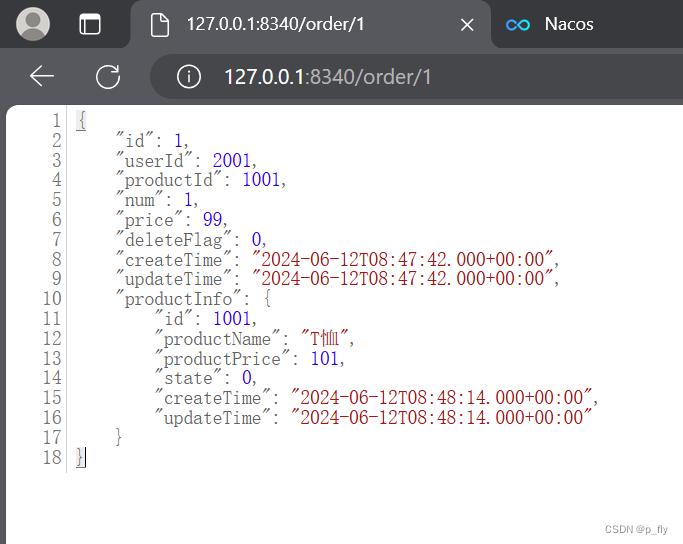
OpenFeign的参数传递
上面的代码只演示了从url中获取参数,接下来将演示使用单个/多个参数、对象、JSON的方式来接收参数。
调用过程:order-service中的一个controller 使用 feign的客户端,通过远程调用 调用 product-service中的controller方法。
对于product-service中的一个controller(服务方)
import com.demo.product.model.ProductInfo;
import com.demo.product.service.ProductService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/product")
@RestController
public class ProductController {
@Autowired
ProductService productService;
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
public ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId) {
log.info("接收到参数: productId" + productId);
return productService.selectProductById(productId);
}
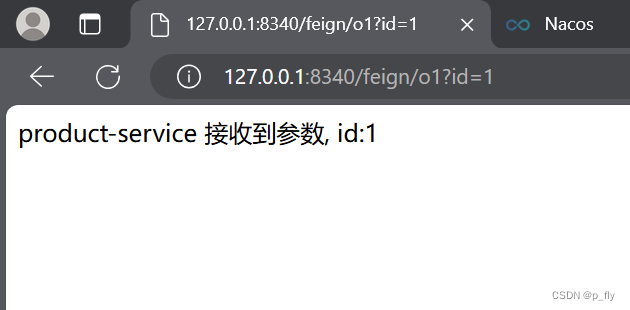
@RequestMapping("/p1")
public String p1(Integer id) {
return "product-service 接收到参数, id:" + id;
}
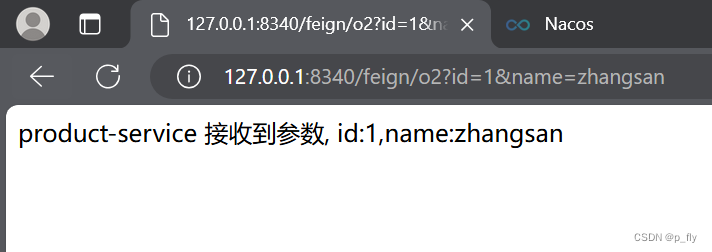
@RequestMapping("/p2")
public String p2(Integer id, String name) {
return "product-service 接收到参数, id:" + id + ",name:" + name;
}
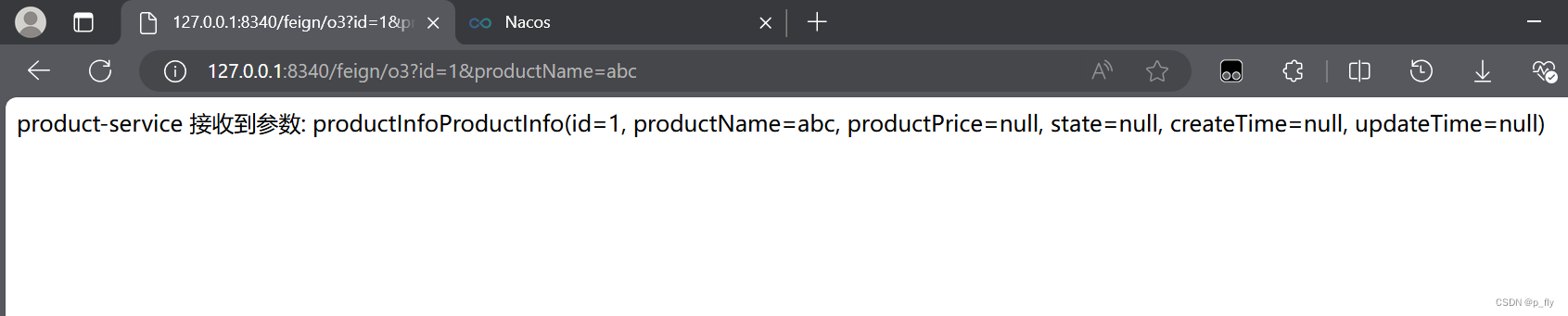
@RequestMapping("/p3")
public String p3(ProductInfo productInfo) {
return "product-service 接收到参数: productInfo" + productInfo.toString();
}
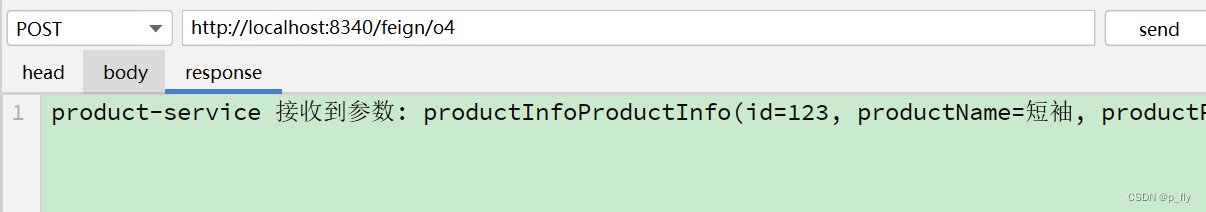
@RequestMapping("/p4")
public String p4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo) {
return "product-service 接收到参数: productInfo" + productInfo.toString();
}
}feign的客户端代码(远程调用桥梁)
import com.demo.order.model.ProductInfo;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.SpringQueryMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
// name:根据注册中心的服务名来调用
// path:调用product-service中的controller中的所有url都有path前缀
@FeignClient(name = "product-service", path = "/product")
// 根据product-service中的controller中的接口写方法
public interface ProductApi {
// 与product-service中的controller中的接口相对应
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId);
@RequestMapping("/p1")
String p1(@RequestParam("id") Integer id);
@RequestMapping("/p2")
String p2(@RequestParam("id") Integer id, @RequestParam("name") String name);
@RequestMapping("/p3")
// @SpringQueryMap:feign客户端接收对象的时候需要这个注解,springmvc的controller不需要
String p3(@SpringQueryMap ProductInfo productInfo);
@RequestMapping("/p4")
String p4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo);
}对于order-service中的一个controller(消费方)
import com.demo.order.api.ProductApi;
import com.demo.order.model.ProductInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* 测试feign的一个order-server的controller
* 通过feign的客户端,远程调用product-server接口
*/
@RequestMapping("/feign")
@RestController
public class TestFeignController {
@Autowired
private ProductApi productApi;
@RequestMapping("/o1")
public String o1(Integer id){
return productApi.p1(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/o2")
public String o2(Integer id, String name){
return productApi.p2(id,name);
}
@RequestMapping("/o3")
public String o3(ProductInfo productInfo){
return productApi.p3(productInfo);
}
@RequestMapping("/o4")
public String o4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo){
return productApi.p4(productInfo);
}
}此时来调用order-service中的controller方法。
OpenFeign最佳使用
上面使用feign的方式非常冗余,可以看到feign客户端代码和服务方提供的controller代码非常的相似。所以一般不使用上面的方式。一般有继承和抽取两种方式来使用feign。
继承
官方文档:Spring Cloud OpenFeign Features :: Spring Cloud Openfeign
下面将简单说明如何使用。
创建模块
这里是存放公共代码的模块。
引入依赖
把需要的依赖放到product-api的pom文件中
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>提取方法和实体类
把之前写到ProductApi接口中的方法放到ProductInterface中。
把ProductInfo也放到这里。product-service中的实体类可以删除了。
打jar包
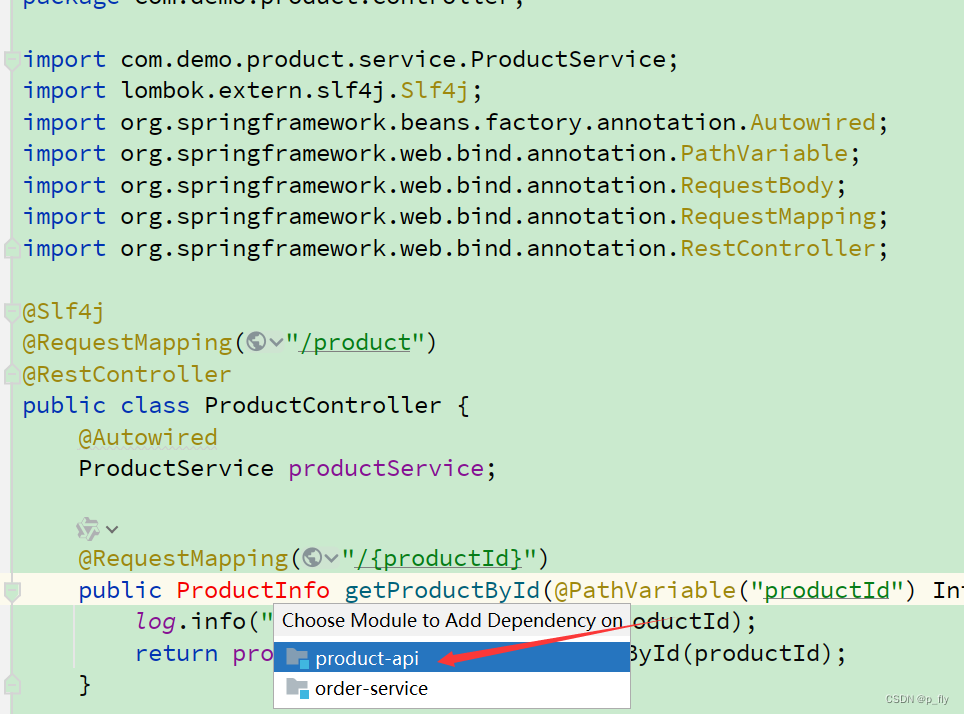
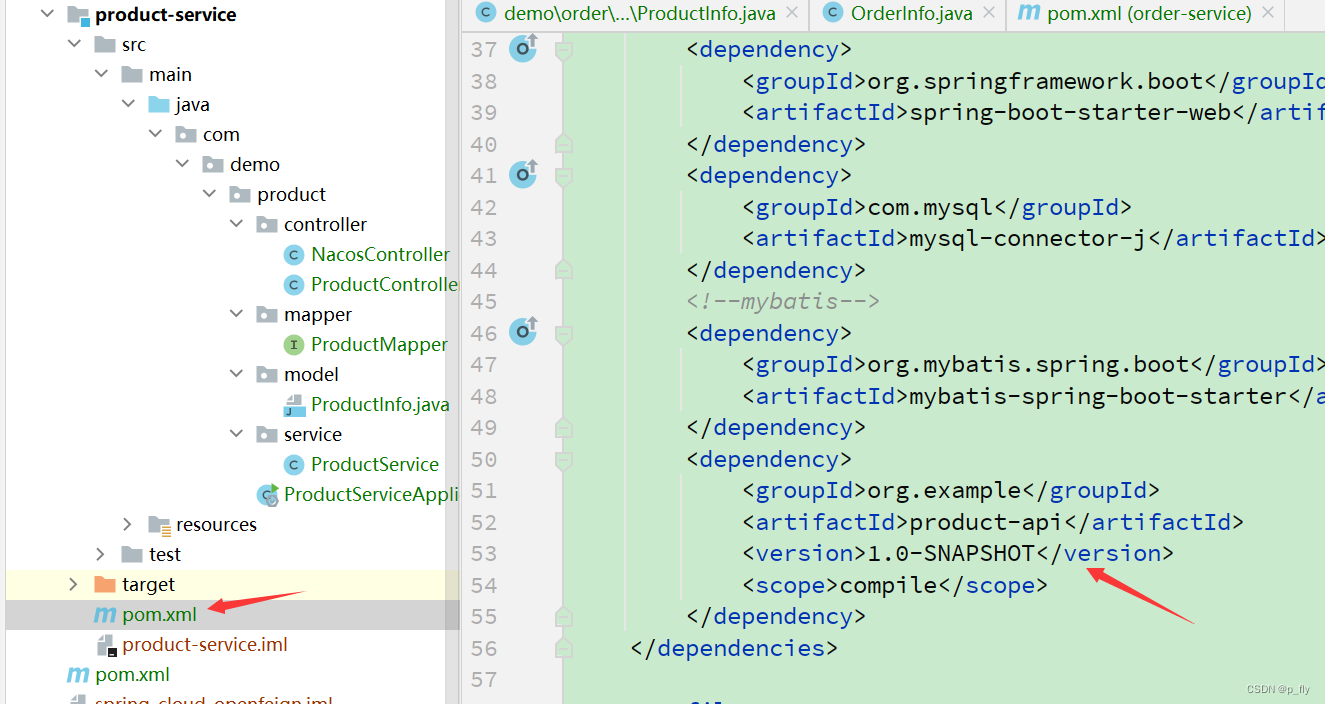
删除后,product-service中引用ProductInfo类的地方都会报错。解决方案:
暂时先把product-api这个jar包下载到本地,然后添加模块即可。
同理把order-service中的ProductInfo也删除,并进行上述操作,并重新导入ProductInfo。
服务方实现接口
import com.demo.product.api.ProductInterface;
import com.demo.product.model.ProductInfo;
import com.demo.product.service.ProductService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/product")
@RestController
public class ProductController implements ProductInterface {
@Autowired
ProductService productService;
@RequestMapping("/{productId}")
public ProductInfo getProductById(@PathVariable("productId") Integer productId) {
log.info("接收到参数: productId" + productId);
return productService.selectProductById(productId);
}
@RequestMapping("/p1")
public String p1(Integer id) {
return "product-service 接收到参数, id:" + id;
}
@RequestMapping("/p2")
public String p2(Integer id, String name) {
return "product-service 接收到参数, id:" + id + ",name:" + name;
}
@RequestMapping("/p3")
public String p3(ProductInfo productInfo) {
return "product-service 接收到参数: productInfo" + productInfo.toString();
}
@RequestMapping("/p4")
public String p4(@RequestBody ProductInfo productInfo) {
return "product-service 接收到参数: productInfo" + productInfo.toString();
}
}消费方继承接口
import com.demo.product.api.ProductInterface;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
// name:根据注册中心的服务名来调用
// path:调用product-service中的controller中的所有url都有path前缀
@FeignClient(name = "product-service", path = "/product")
// 根据product-service中的controller中的接口写方法
public interface ProductApi extends ProductInterface {
}
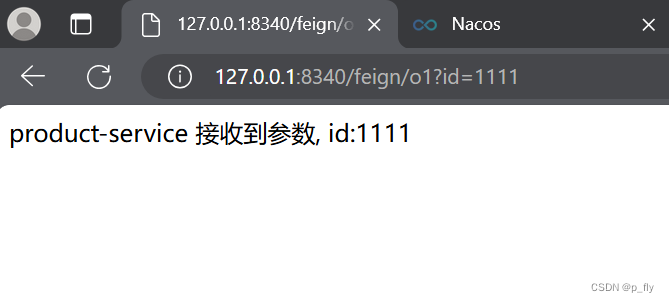
测试
可以正常使用。
抽取
官方推荐使用继承的方法来使用OpenFeign,但在企业开发中,更多的是把feign客户端接口抽取为一个独立的模块,并把涉及到的实体类等都放到这个模块,打成一个jar包。
创建模块
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>提取api接口等
把ProductApi复制粘贴到新模块中,并删除之前的。
把ProductInfo按照上面的操作同样的移动到新模块中。
服务端基本不用改,消费端需要从自身的拿取改到从公共模块拿取。
打jar包
对公共模块打jar包到本地。
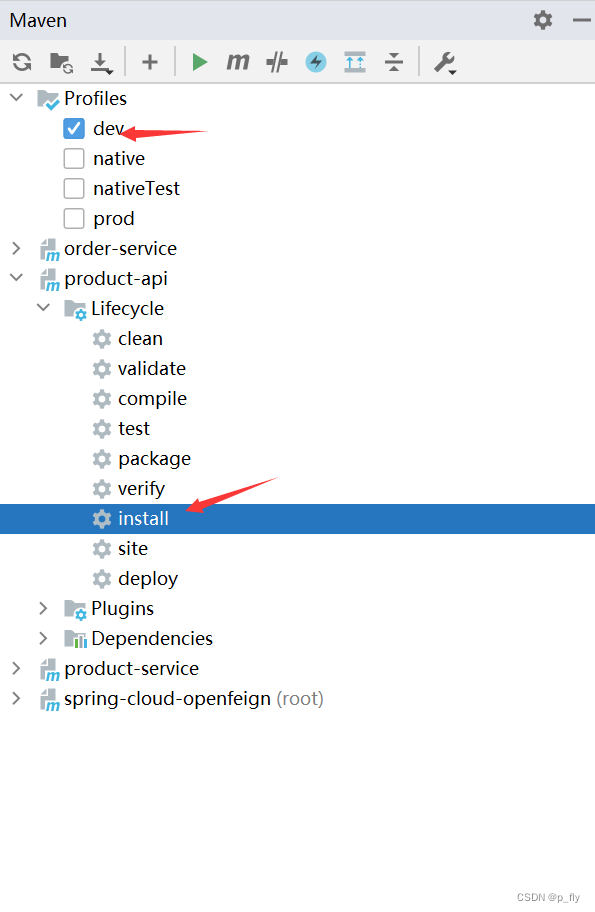
打完jar包后,在order-service中修改公共代码的使用路径。
添加扫描包
order-service启动的时候,只能扫描当前路径下的,无法扫描到公共模块的api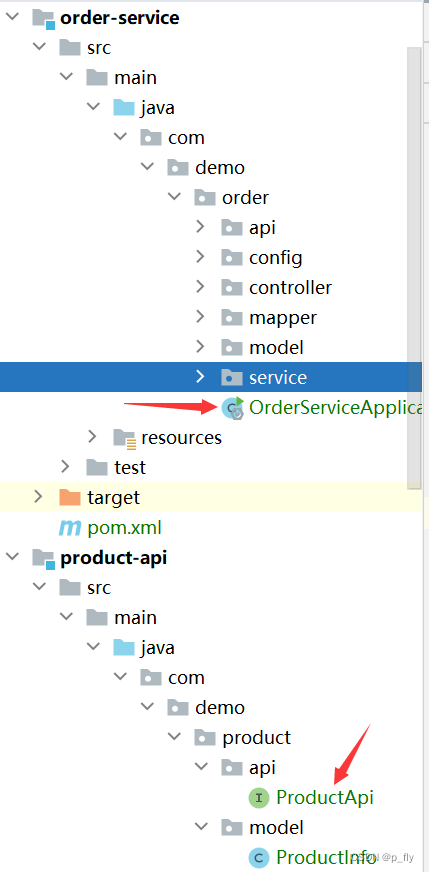
需要在启动类中添加扫描路径。
import com.demo.product.api.ProductApi;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
// clients 添加启动类无法扫描到的ProductApi
@EnableFeignClients(clients = {ProductApi.class})
@SpringBootApplication
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}测试
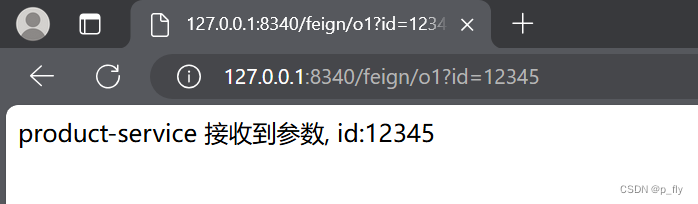
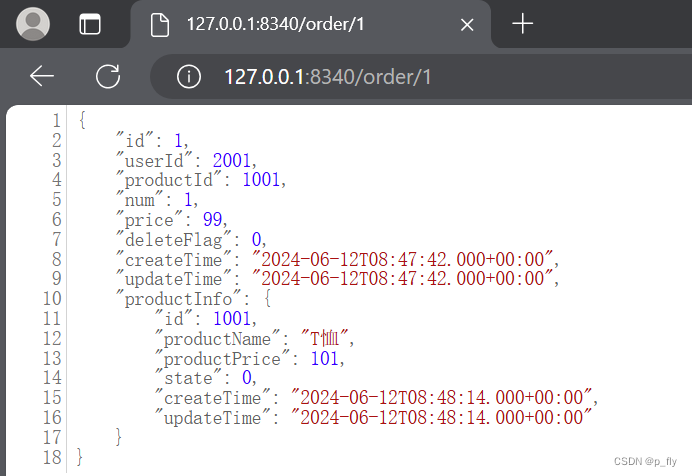
部署
这里部署的时候只有打包的地方和之前有区别。因为这里有个product-api的包是本地的,不是从maven仓库下载的。
解决方案:
- 把product-api上传到maven仓库(不推荐)如何发布Jar包到Maven中央仓库 – 过往记忆 (iteblog.com)
- 搭建maven私服,上传jar包到私服(企业做法)
- 从本地读取(个人使用)
这里使用从本地读取的方案。
把product-api打包
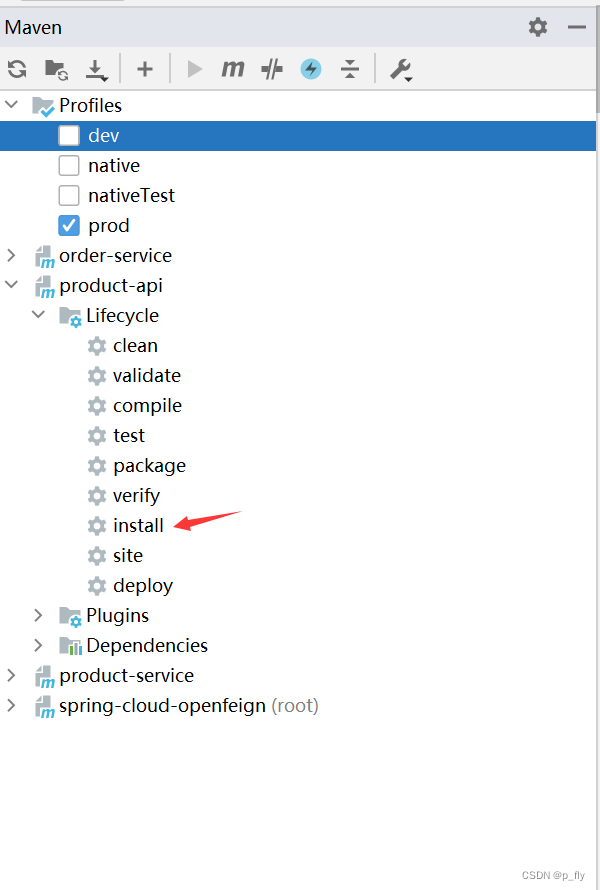
复制路径
修改pom
在order-service中修改一下pom,让它读本地的product-api的jar包。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>product-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- <scope>compile</scope>-->
<!-- 从本地仓库引入 -->
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>C:/Users/pxf/.m2/repository/org/example/product-api/1.0-SNAPSHOT/product-api-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar</systemPath>
</dependency> <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<!-- 让它可以引入本地jar包 -->
<configuration>
<includeSystemScope>true</includeSystemScope>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>后面的正常打包部署即可。



![[图解]建模相关的基础知识-16](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a913e98259a04f2cb2b1f1e96e7cfddd.png)