简介
随着电子设备的广泛应用,PCB(印刷电路板)作为其核心部件,其质量和可靠性至关重要。然而,PCB生产过程中常常会出现各种缺陷,如鼠咬伤、开路、短路、杂散、伪铜等。这些缺陷可能导致设备故障,甚至引发严重的安全问题。为了提高PCB检测的效率和准确性,我们基于YOLOv5目标检测模型,开发了一套PCB电路板故障检测系统。本报告将详细介绍该系统的实际与实现,包括系统架构、功能实现、使用说明、检测示例、数据集获取与介绍、YOLOv5模型介绍及其训练过程。
系统架构
系统组成
- 用户界面(GUI):基于PyQt5实现,提供图像、视频及实时摄像头检测功能。
- 检测模型:基于YOLOv5的目标检测模型,用于识别PCB上的各种缺陷。
- 视频处理模块:处理视频流,实现逐帧检测。
- 数据管理模块:负责数据的加载、保存及标注。
工作流程
- 用户加载图像/视频或启动摄像头。
- 系统调用YOLOv5模型进行缺陷检测。
- 检测结果显示在GUI上,包括缺陷位置、种类及数量。
- 用户可以保存检测结果。
功能实现
import sys
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
import time
import os
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QFileDialog, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, \
QHBoxLayout, QSlider, QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap, QFont
from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer, QThread, pyqtSignal, Qt, QMutex, QWaitCondition
class YoloV5Detector:
def __init__(self):
self.model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path="./yolov5s_pcb.pt")
def detect_image(self, image_path):
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
results = self.model(image)
return results
def detect_frame(self, frame):
results = self.model(frame)
return results
class VideoProcessor(QThread):
frame_processed = pyqtSignal(np.ndarray)
fps_signal = pyqtSignal(float)
progress_signal = pyqtSignal(str)
object_count_signal = pyqtSignal(int)
category_count_signal = pyqtSignal(dict)
def __init__(self, video_path=None, use_camera=False, output_dir='output'):
super().__init__()
self.video_path = video_path
self.use_camera = use_camera
self.running = False
self.paused = False
self.mutex = QMutex()
self.condition = QWaitCondition()
self.detector = YoloV5Detector()
self.out = None
self.output_dir = output_dir
def run(self):
self.running = True
if self.use_camera:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.video_path)
if not cap.isOpened():
return
# Create unique filename based on current time
current_time = time.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
os.makedirs(self.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
output_file = os.path.join(self.output_dir, f'output_{current_time}.mp4')
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
if fps == 0: # If fps cannot be obtained, set a default value
fps = 30
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
self.out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_file, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
total_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
duration = total_frames / fps
last_time = time.time()
frame_count = 0
while self.running:
self.mutex.lock()
if self.paused:
self.condition.wait(self.mutex)
self.mutex.unlock()
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
#frame = cv2.resize(frame, (640, 640))
results = self.detector.detect_frame(frame)
annotated_frame = results.render()[0]
self.frame_processed.emit(annotated_frame)
object_count = len(results.xyxy[0]) # Number of detected objects
categories = results.names # Object category names
category_counts = {category: (results.pred[0][:, -1] == i).sum().item() for i, category in categories.items()}
non_zero_category_counts = {cat: count for cat, count in category_counts.items() if count > 0}
self.object_count_signal.emit(object_count)
self.category_count_signal.emit(non_zero_category_counts)
if self.out:
self.out.write(annotated_frame)
frame_count += 1
if frame_count % 10 == 0:
current_time = frame_count / fps
progress_text = f'{self.format_time(current_time)} / {self.format_time(duration)}'
self.progress_signal.emit(progress_text)
current_time = time.time()
show_fps = 1.0 / (current_time - last_time)
last_time = current_time
self.fps_signal.emit(show_fps)
cap.release()
if self.out:
self.out.release()
def format_time(self, seconds):
mins, secs = divmod(seconds, 60)
return f'{int(mins):02}:{int(secs):02}'
def pause(self):
self.paused = True
def resume(self):
self.paused = False
self.condition.wakeAll()
def stop(self):
self.running = False
self.resume()
self.wait()
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle('YOLOv5 PCB Defect Detection')
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 1000, 700)
self.layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.label = QLabel(self)
self.layout.addWidget(self.label)
self.fps_label = QLabel(self)
self.fps_label.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.layout.addWidget(self.fps_label)
self.object_count_label = QLabel(self)
self.object_count_label.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.layout.addWidget(self.object_count_label)
self.category_count_label = QLabel(self)
self.category_count_label.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.layout.addWidget(self.category_count_label)
self.progress_label = QLabel(self)
self.progress_label.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.layout.addWidget(self.progress_label)
self.slider = QSlider(Qt.Horizontal)
self.slider.setRange(0, 100)
self.slider.setValue(0)
self.slider.sliderPressed.connect(self.pause_video)
self.slider.sliderReleased.connect(self.resume_video)
self.layout.addWidget(self.slider)
button_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.btn_image = QPushButton('Open Image', self)
self.btn_image.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.btn_image.clicked.connect(self.open_image)
button_layout.addWidget(self.btn_image)
self.btn_video = QPushButton('Open Video', self)
self.btn_video.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.btn_video.clicked.connect(self.open_video)
button_layout.addWidget(self.btn_video)
self.btn_camera = QPushButton('Open Camera', self)
self.btn_camera.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.btn_camera.clicked.connect(self.open_camera)
button_layout.addWidget(self.btn_camera)
self.btn_save = QPushButton('Save Result', self)
self.btn_save.setFont(QFont('Arial', 14))
self.btn_save.clicked.connect(self.save_result)
button_layout.addWidget(self.btn_save)
self.layout.addLayout(button_layout)
self.container = QWidget()
self.container.setLayout(self.layout)
self.setCentralWidget(self.container)
self.cap = None
self.current_frame = None
self.video_processor = None
def open_image(self):
self.stop_video_processing()
file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Open Image', '', 'Images (*.png *.xpm *.jpg *.jpeg *.bmp)')
if file_name:
self.show_loading_message(True)
results = YoloV5Detector().detect_image(file_name)
self.current_frame = results.render()[0]
self.display_image(self.current_frame)
self.fps_label.setText('')
self.progress_label.setText('')
self.object_count_label.setText('')
self.category_count_label.setText('')
self.show_loading_message(False)
def open_video(self):
self.stop_video_processing()
file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, 'Open Video', '', 'Videos (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov *.mkv)')
if file_name:
self.show_loading_message(True)
self.start_video_processing(file_name)
def open_camera(self):
self.stop_video_processing()
self.show_loading_message(True)
self.start_video_processing(use_camera=True)
def show_loading_message(self, show):
self.btn_image.setEnabled(not show)
self.btn_video.setEnabled(not show)
self.btn_camera.setEnabled(not show)
self.btn_save.setEnabled(not show)
if show:
QApplication.setOverrideCursor(Qt.WaitCursor)
else:
QApplication.restoreOverrideCursor()
def start_video_processing(self, video_path=None, use_camera=False):
self.video_processor = VideoProcessor(video_path=video_path, use_camera=use_camera)
self.video_processor.frame_processed.connect(self.display_image)
self.video_processor.fps_signal.connect(self.update_fps)
self.video_processor.progress_signal.connect(self.update_progress)
self.video_processor.object_count_signal.connect(self.update_object_count)
self.video_processor.category_count_signal.connect(self.update_category_count)
self.video_processor.start()
self.show_loading_message(False)
def stop_video_processing(self):
if self.video_processor is not None:
self.video_processor.stop()
self.video_processor = None
def pause_video(self):
if self.video_processor is not None:
self.video_processor.pause()
def resume_video(self):
if self.video_processor is not None:
self.video_processor.resume()
def update_fps(self, fps):
self.fps_label.setText(f'FPS: {fps:.2f}')
def update_progress(self, progress):
self.progress_label.setText(progress)
def update_object_count(self, count):
self.object_count_label.setText(f'Object Count: {count}')
def update_category_count(self, category_counts):
category_count_text = 'Category Counts: ' + ', '.join([f'{cat}: {count}' for cat, count in category_counts.items()])
self.category_count_label.setText(category_count_text)
def display_image(self, frame):
self.current_frame = frame
rgb_frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
height, width, channel = frame.shape
bytes_per_line = 3 * width
convert_to_Qt_format = QImage(rgb_frame.data, width, height, bytes_per_line, QImage.Format_RGB888)
p = convert_to_Qt_format.scaled(1000, 600, aspectRatioMode=1)
self.label.setPixmap(QPixmap.fromImage(p))
def save_result(self):
if self.current_frame is not None:
file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getSaveFileName(self, 'Save Image', '', 'Images (*.png *.jpg *.jpeg *.bmp)')
if file_name:
cv2.imwrite(file_name, self.current_frame)
elif self.video_processor:
self.video_processor.stop()
self.video_processor.wait()
self.video_processor = None
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
使用说明
- 加载图像/视频:
- 点击“Open Image”按钮加载待检测的PCB图像。
- 点击“Open Video”按钮加载待检测的视频文件。
- 点击“Open Camera”按钮启动摄像头进行实时检测。
- 显示结果:
- 系统会在界面上显示检测到的缺陷位置和种类。
- 检测过程中,界面会显示实时帧率(FPS)、进度、缺陷数量及类别统计信息。
- 保存结果:
- 点击“Save Result”按钮可以保存当前检测结果。
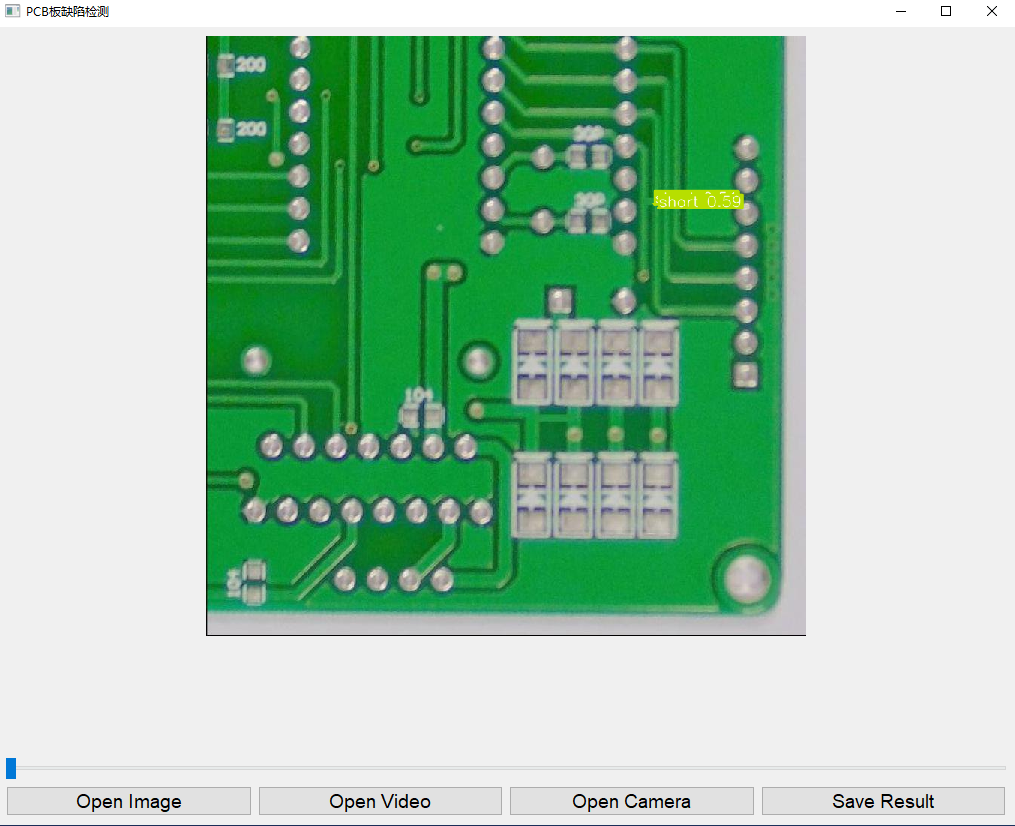
检测示例
系统在测试过程中,能够准确检测并标注出PCB上的各种缺陷,如鼠咬伤、开路、短路、杂散和伪铜等,检测效果如下图所示:




数据集获取与介绍
数据集介绍
为了训练和评估模型,我们使用了一个包含不同PCB缺陷的公开数据集。数据集包含以下内容:
- 图像数量:数据集中包含1386张标注好的PCB缺陷图像。
- 缺陷类型:鼠咬伤、开路、短路、杂散、伪铜等6种缺陷。
- 标注信息:每张图像都包含详细的标注信息,包括缺陷的位置和类别。
数据集获取
数据集可以通过以下链接获取:
- 公开数据集下载链接: https://robotics.pkusz.edu.cn/resources/dataset/
下载后,将数据集解压到指定目录,并根据YOLOv5格式进行组织。
YOLOv5介绍
YOLOv5简介
YOLOv5(You Only Look Once Version 5)是一个先进的目标检测模型,由Ultralytics团队开发。与其前身相比,YOLOv5在速度和精度上有了显著提升,能够在实时应用中表现出色。
官方模型
YOLOv5提供了多种预训练模型,分别适用于不同的检测任务和需求。我们选择了轻量级的YOLOv5s模型,并在此基础上进行了微调,以适应PCB缺陷检测的特定需求。
训练过程
数据准备
- 数据标注:使用LabelImg等工具对数据集进行标注,生成YOLOv5格式的标注文件。
- 数据划分:将数据集划分为训练集、验证集和测试集,比例为7:2:1。
模型训练
-
环境配置:在训练前,配置好所需的深度学习环境,包括安装PyTorch、YOLOv5等依赖项。
-
训练配置:设置训练参数,如学习率、批量大小、训练轮数等。
-
模型训练
:使用以下命令启动训练:
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 50 --data data.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache -
模型评估:在验证集上评估模型性能,记录精度、召回率、mAP等指标。
模型优化
- 超参数调整:根据评估结果调整学习率、批量大小、数据增强策略等超参数。
- 迁移学习:使用预训练模型进行迁移学习,提高模型在特定任务上的表现。
模型部署
- 模型保存:将训练好的模型保存为权重文件(如
yolov5s_pcb.pt)。 - 集成到系统:将模型集成到PCB缺陷检测系统中,实现实时检测功能。
结论
本报告详细介绍了基于YOLOv5的PCB电路板故障检测系统,包括系统架构、功能实现、使用说明、检测示例、数据集获取与介绍、YOLOv5模型介绍以及训练过程。该系统通过PyQt5提供了友好的用户界面,支持图像、视频和实时摄像头的缺陷检测,具有较高的检测精度和速度。未来可以进一步优化模型和系统,以提升PCB缺陷检测的准确性和实时性。
完整资料地址
- yolov5预训练模型地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
- 本文项目完整链接:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MpiPisKl4KeW_qu5rDa4LA?pwd=t3gu
- 包含: PyQT用户交互页面、训练好的PCB板瑕疵检测模型(yolov5s)、几张测试图片
- 提取码:t3gu
- 数据集:链接:https://robotics.pkusz.edu.cn/resources/dataset/