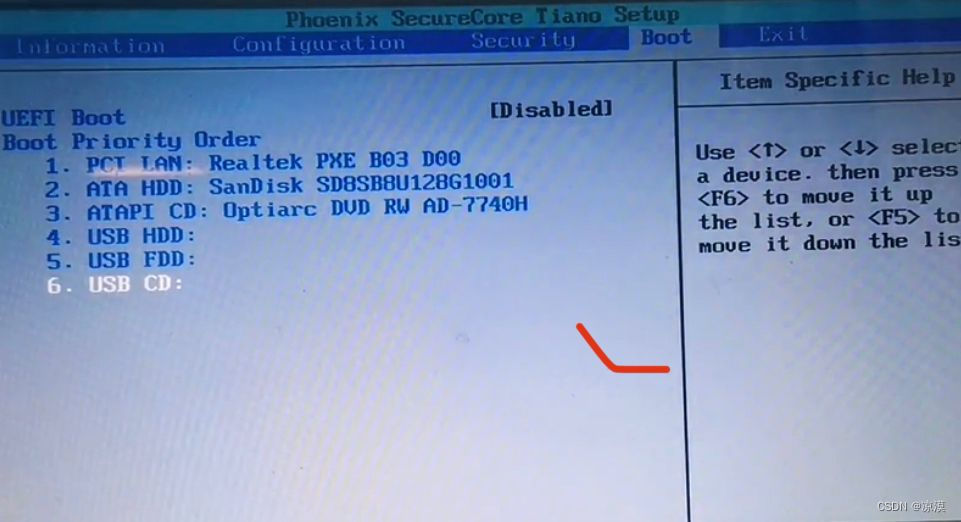
1.对list中的map进行分组
下面例子中,根据高度height属性进行分组
List<Map<String, Float>>originalList = new ArrayList<>();
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",10f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",11f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",20f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",21f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
Map<Object, List<Map>> groupedMap = originalList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(map -> {
return map.get("height");
}));
System.out.println(groupedMap);执行结果:
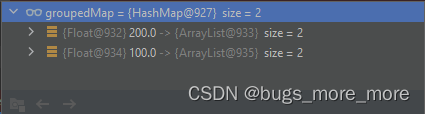
从结果可以看到,已经按照height进行分组成功了。
2.对list中的map进行分组,根据分组后的key进行排序
同样,还是先根据height进行分组,默认分组后生成的Map是不会根据高度进行排序的,因为Map没有这个功能,所以需要再多做一次才做。看代码:
List<Map<String, Float>>originalList = new ArrayList<>();
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",10f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",11f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",20f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",21f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
Map<Object, List<Map>> groupedMap = originalList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(map -> {
return map.get("height");
}));
// 使用TreeMap对键进行排序
TreeMap<Object, List<Map>> sortedGroupedMap = new TreeMap<Object, List<Map>>(groupedMap);
System.out.println(sortedGroupedMap);打印结果:
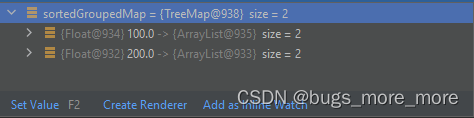
可以看到map第一个元素key是100,第二个key是200,说明排序成功
3.对list中的map进行分组,并求每个组中最大值对应的数据
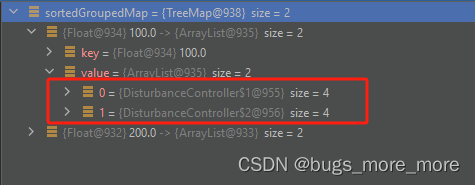
从图中可以看到heigh为100这组里面,有2条数据,这2个也是map,每个map中包含了lng,lat,height,val,现在要将val的值最大的那个map查出来。代码如下:
List<Map<String, Float>>originalList = new ArrayList<>();
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",10f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",11f);
put("height", 100.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",20f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
originalList.add(new HashMap<String,Float>() {{
put("lng", 180.0f);
put("lat",90f);
put("val",21f);
put("height", 200.0f);
}});
// 按照alti进行分组,并找出每个组中val的最大值
Map<Object, Optional<Map<String, Float>>> result = originalList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(map -> map.get("height"),Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(map -> Float.valueOf(map.get("val"))))
));
System.out.println(result);运行结果:
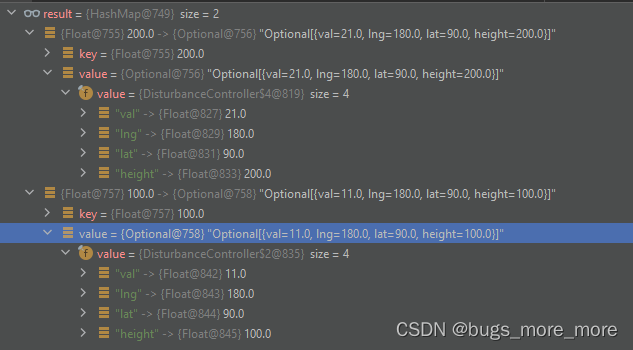
从结果可以看出通过height进行了分组,并将分组后,求出了每组中最大值的数据。