目录
A. Make it White
B. Following the String
C. Choose the Different Ones!
D. Find the Different Ones!
A. Make it White
Problem - A - Codeforces
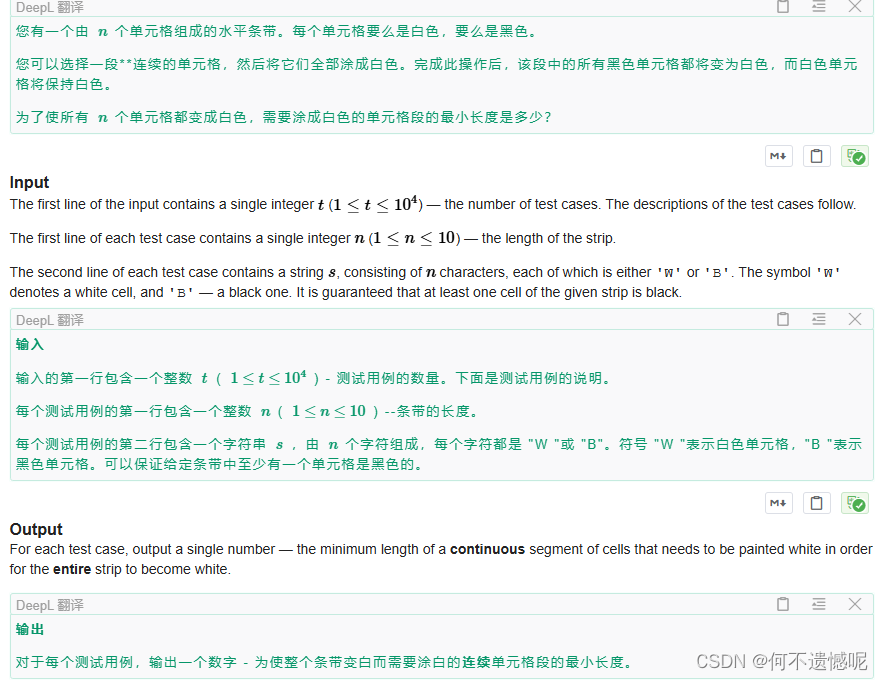

题意:问在一个只含有'W'和'B'元素的字符串中,选择一个L到R范围,将之间包含的B全部变成W,W则不变,找到(R-L+1)的最小值。
思路:因为每个B都需要染色,所以我们只需要找最左边的B和最右边的B,再加一些细节优化。
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
const int M = 100100;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
int pos1 = -1, pos2 = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (s[i] == 'B')
{
pos1 = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (s[i] == 'B')
{
pos2 = i;
break;
}
}
if (pos1 == -1 && pos2 == -1)
{
cout << "0\n";
return;
}
if (pos1 == pos2)
{
cout << "1\n";
return;
}
cout << abs(pos1 - pos2)+1 << "\n";
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. Following the String
Problem - B - Codeforces

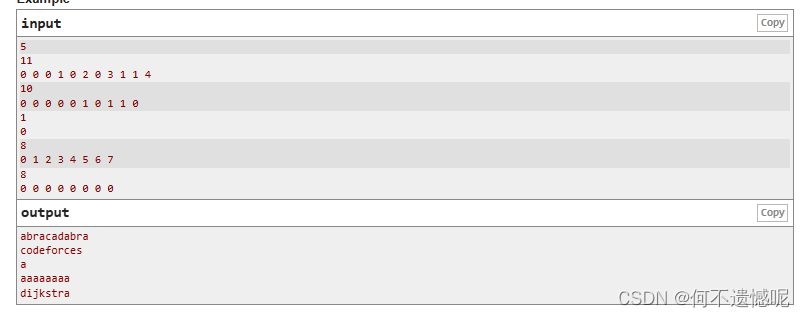
题意:给你一个数组,数组的大小代表,从0到这个这个,某个小写字母出现的次数,要求我们输出符合该数组对应的一个字符串。
思路:对于每个数组的元素,判断这个元素在之前出现了多少次,根据出现的次数n+‘a’为这个位置的小写字母,记录下来即可。
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
const int M = 100100;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
int pos[N];
void solve()
{
memset(pos, 0, sizeof(pos));
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
map<int, char>q;
char st = 'a';
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
q[i] = pos[a[i]] + 'a';
pos[a[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << q[i];
cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Choose the Different Ones!
Problem - C - Codeforces

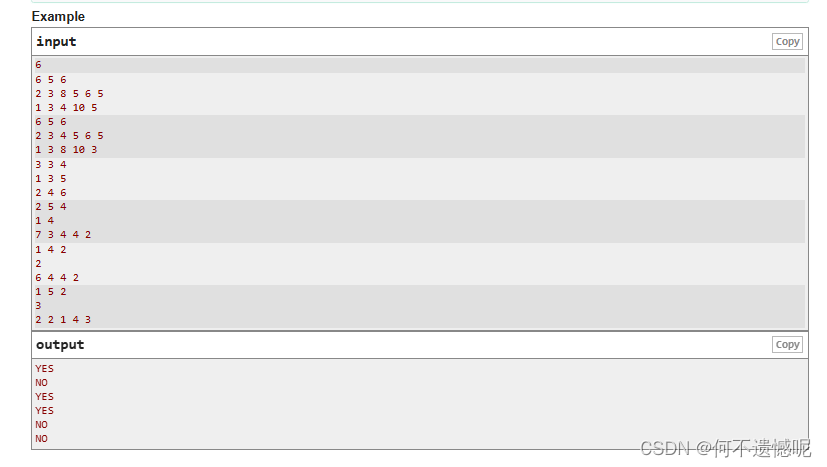
题意:在两个数组中,都只能拿k/2个元素,问是否可以找到1到k的所有元素。
思路:先对两个数组排序,我们只需要1到k之间的数,大于的就不需要了,用两个标记组数去计数两个数组中1到k之间元素的出现的情况,出现了标1,反之为0,当对于一个1到k之间的元素,这两个标记数组都是0,此时可以直接输出NO退出。
后面最关键的来了。
有时候会有元素只出现在某个数组中,如果不好好分配选择次数还是会找不全。
关键的就是计数两个数组你有我没有的数量。这两个的数量与k/2比较一下,若是有一个大于那么直接输出NO,反之输出YES。
下面是AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
const int M = 100100;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
void solve()
{
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector<int>a(n), b(m);
vector<int>f1(k + 1), f2(k + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) cin >> b[i];
sort(a.begin() , a.end());
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
ll t = 1,t1=0,t2=0,i=0,j=0;
if (n < k / 2 || m < k / 2)
{
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n && a[i] <= k; i++)
{
f1[a[i]] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m && b[i] <= k; i++)
{
f2[b[i]] = 1;
}
int c1 = 0, c2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
if (f1[i] == 0 && f2[i] == 0)
{
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
if (f1[i] && !f2[i]) c1++;
if (!f1[i] && f2[i]) c2++;
}
if (c1 > k / 2 || c2 > k / 2)
{
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
cout << "YES\n";
return;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. Find the Different Ones!
Problem - D - Codeforces


题意:给出一个长度为n的数组,再给出q次询问,问你L到R之间有没有一对不同的数,如果没有就输出两个-1,否则输出这两个数的下标。
思路:我们将这个问题分成两个问题;
1.我们如何判断L到R的范围有没有不同的数字。
2.我们如何快速得找到两个不同数子的下标。
(1)我们可以用一个标记数组来解决问题1。首先标记数组b的第一个元素为0,其他的元素判断。
从2开始,如果数组这个元素等于前一个元素,那么标记数组b当前的位置也是0,否则就是0+1=1。
循环到n就完成了。
我们此时发现L到R的范围,如果b[R]-b[L]==0,那么说明之间的元素都是相同的。
(2)现在我们解决第二个问题。
我们发现我们的标记数组b非常的巧妙,从b[L]到b[R]之间出现的第一个大于前一个元素的值就是我们要找的不同的下标。
但是线性搜索可能超时,我们直接用二分去缩短时间。
最后在0.999秒的时间复杂度下勉强拿下这道题。

下面是AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
const int M = 100100;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll q[N],a[N];
void solve()
{
ll n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
ll c = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (a[i] == a[i - 1]) q[i] = c;
else q[i] = ++c;
}
q[1] = 0;
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
ll l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
if (q[r] - q[l] == 0) cout << -1 << " " << -1 << "\n";
else
{
cout << l << " ";//二分
ll pos = upper_bound(q+l, q+r,q[l])-q;
cout << pos << "\n";
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}