1. 问题背景
有一天给同事CR,看到一段这样的代码
try {
for (param : params) {
//并发处理,func无返回值
ThreadPool.submit(func(param));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("func抛异常啦,参数是:{}", param)
}我:你这段代码是利用并发降低RT对吧,如果func内部抛异常,你确定可以catch到吗
同事:可以啊, 为什么不可以(...
我:不如你run一把,在func mock一个异常出来试试
同事:我靠还真是
我:你可以用execute,改动比较小
同事:那么是为什么呢
2. 同事的例子
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 20, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
testExecute(executorService);
Thread.sleep(2000);
testSubmit1(executorService);
Thread.sleep(2000);
testSubmit2(executorService);
}
private static void testExecute(ExecutorService executorService) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
System.out.println("执行线程池execute方法");
throw new RuntimeException("execute方法抛出异常");
});
}
private static void testSubmit1(ExecutorService executorService) {
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("执行线程池submit方法1");
throw new RuntimeException("submit方法1抛出异常");
});
}
private static void testSubmit2(ExecutorService executorService) throws Exception {
Future<Object> feature = executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("执行线程池submit方法2");
throw new RuntimeException("submit方法2抛出异常");
});
feature.get();
}
}
执行结果:
执行线程池execute方法
Exception in thread "pool-1-thread-1" java.lang.RuntimeException: execute方法抛出异常
at ThreadPoolTest.lambda$testExecute$0(ThreadPoolTest.java:23)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
执行线程池submit方法1
执行线程池submit方法2
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: submit方法2抛出异常
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:122)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
at ThreadPoolTest.testSubmit2(ThreadPoolTest.java:39)
at ThreadPoolTest.main(ThreadPoolTest.java:17)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: submit方法2抛出异常
at ThreadPoolTest.lambda$testSubmit2$2(ThreadPoolTest.java:37)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run$$$capture(FutureTask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
3. 原理分析
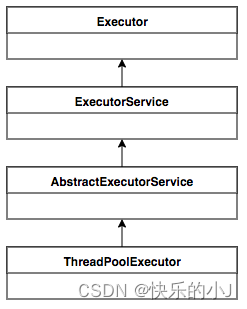
3.1 线程池包的继承结构
3.2 submit和execute方法的差异
3.2.1 execute
方法定义在最顶层的Executor接口,并且Executor接口有且仅有这一个方法
public interface Executor {
/**
* Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command
* may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling
* thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation.
*
* @param command the runnable task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be
* accepted for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
void execute(Runnable command);
}方法实现在ThreadPoolExecutor:
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}实际执行的过程,在worker(是runnable的实现类)的run方法,run方法实际执行的是runWorker方法
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// If pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. This
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownNow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}可以看到执行过程中,如果task.run();发生异常,没有catch处理,异常会层层向外抛出;最终进入finally块,执行processWorkerExit;
3.2.2 submit
submit方法定义在ExecutorService
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
/**
* Submits a value-returning task for execution and returns a
* Future representing the pending results of the task. The
* Future's {@code get} method will return the task's result upon
* successful completion.
*
* <p>
* If you would like to immediately block waiting
* for a task, you can use constructions of the form
* {@code result = exec.submit(aCallable).get();}
*
* <p>Note: The {@link Executors} class includes a set of methods
* that can convert some other common closure-like objects,
* for example, {@link java.security.PrivilegedAction} to
* {@link Callable} form so they can be submitted.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @param <T> the type of the task's result
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
/**
* Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future
* representing that task. The Future's {@code get} method will
* return the given result upon successful completion.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @param result the result to return
* @param <T> the type of the result
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
/**
* Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future
* representing that task. The Future's {@code get} method will
* return {@code null} upon <em>successful</em> completion.
*
* @param task the task to submit
* @return a Future representing pending completion of the task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if the task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if the task is null
*/
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
}
实现在AbstractExecutorService
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}可以看到这里创建了RunnableFuture(而不是基础的worker),顾名思义,RunnableFuture同时实现了Runnable和Future接口,也就意味着可以对该任务执行get操作,看看RunnableFuture的run方法:
public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}catch块对方法异常做了处理,与执行结果一同在Future中暂存起来;submit()执行完毕后返回Future对象,执行future.get()会触发异常的抛出;
当然了,如果你只是执行了submit,没有获取future,异常就会“神奇地”消失。
参考:
Java线程池实现原理及其在美团业务中的实践 - 美团技术团队
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/651997713